Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hall Technique: Definition
Hall Technique: Definition
Uploaded by
Mohamed KilaniCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Diagnosing Early Interceptive Orthodontic Problems - Part 1: 2 CE CreditsDocument11 pagesDiagnosing Early Interceptive Orthodontic Problems - Part 1: 2 CE CreditsVijay Prabu GNo ratings yet
- CG A013 04 Stainless Steel Crowns in Deciduous MolarsDocument5 pagesCG A013 04 Stainless Steel Crowns in Deciduous MolarsmahmoudNo ratings yet
- Serial ExtractionDocument38 pagesSerial ExtractionRamy HanyNo ratings yet
- Lab 08 Oracle Access Management - Access Manager 11G R2 Ps3 2 Legged Mobile OauthDocument39 pagesLab 08 Oracle Access Management - Access Manager 11G R2 Ps3 2 Legged Mobile OauthAshutosh NichatNo ratings yet
- Statics and Mechnics of StructuresDocument511 pagesStatics and Mechnics of StructuresPrabu RengarajanNo ratings yet
- Thierry Bardini. Junkware. The Essential Junkiness of Our Culture and BiologyDocument298 pagesThierry Bardini. Junkware. The Essential Junkiness of Our Culture and BiologyJulieta Yelin100% (1)
- Clamps Specification GeneralDocument20 pagesClamps Specification Generalpiyush_123456789No ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Dentition and OcclusionDocument3 pagesGrowth and Development of Dentition and OcclusionFidz Lianko100% (2)
- Development of OcclusionDocument50 pagesDevelopment of OcclusionSaid Said100% (1)
- Dental CariesDocument120 pagesDental CariesSomya Jain100% (5)
- Oral Surgery in Children Lect 4Document39 pagesOral Surgery in Children Lect 4Jessica AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Development of Occlusion (Seminar 1)Document47 pagesDevelopment of Occlusion (Seminar 1)Isha GargNo ratings yet
- Pulpo, Pulpec, Apex, Injuries 1Document6 pagesPulpo, Pulpec, Apex, Injuries 1Cyril Almario Cunanan100% (1)
- NQVH The Hall Technique ManualDocument19 pagesNQVH The Hall Technique Manualpriti adsulNo ratings yet
- Development of Dentition WordDocument21 pagesDevelopment of Dentition Wordshubhangi_jain_10100% (1)
- Trauma To Primary DentitionDocument107 pagesTrauma To Primary DentitionShameena KnNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 P 4Document5 pagesLec 5 P 4brshlwnytwaftkhr956No ratings yet
- Childhood Caries & Dental Trauma On Primary Teeth: Henri Hartman, Drg. SP - KGADocument52 pagesChildhood Caries & Dental Trauma On Primary Teeth: Henri Hartman, Drg. SP - KGALila VininingtyasNo ratings yet
- 12-Restorative Dentistry For ChildrenDocument59 pages12-Restorative Dentistry For Childrenحمزہ محبNo ratings yet
- Interceptive FinalDocument60 pagesInterceptive FinalRaj SinghNo ratings yet
- Classifications of Caries LesionsDocument2 pagesClassifications of Caries LesionsDeniaAlyaTsaryNo ratings yet
- Bell 2 PDFDocument31 pagesBell 2 PDFMirza GlusacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Pediatric Dentoalveolar Surgery.50015-6Document21 pagesChapter 10 Pediatric Dentoalveolar Surgery.50015-6Zelallem AnileyNo ratings yet
- Hall TechniqueDocument19 pagesHall TechniqueanatomimanusiaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Space Management in Pediatric DentistryDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Space Management in Pediatric DentistryHussain HNo ratings yet
- Smile Makeover in ChildrenDocument7 pagesSmile Makeover in Childrendavidiaz1989No ratings yet
- On ImpactionDocument44 pagesOn Impactionmesssi269No ratings yet
- CHP 11 Moderate Nonskeletal Problems in Preadolescent ChildrenDocument6 pagesCHP 11 Moderate Nonskeletal Problems in Preadolescent ChildrenJack Pai33% (3)
- TUTORIAL IN ENGLISH Blok 12Document7 pagesTUTORIAL IN ENGLISH Blok 12Ifata RDNo ratings yet
- Pitandfissuresealant Dharmendraandaditigupta 160112155722Document29 pagesPitandfissuresealant Dharmendraandaditigupta 160112155722AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Ortho (Lec)Document2 pagesOrtho (Lec)Leigh BelmonteNo ratings yet
- Age Appropriate Orthodontics Overview HO 2013Document31 pagesAge Appropriate Orthodontics Overview HO 2013javi222222No ratings yet
- Short Cases NovDocument64 pagesShort Cases NovSoha Jan KhuhawarNo ratings yet
- Ped. Dent, Pub. Health (2) - 6 - Management of Traumatic Dental InjuriesDocument30 pagesPed. Dent, Pub. Health (2) - 6 - Management of Traumatic Dental InjuriesEslam HafezNo ratings yet
- Space MaintenanceDocument10 pagesSpace Maintenanceتوباك شاكورNo ratings yet
- Canine ImpactionDocument10 pagesCanine ImpactionPZ100% (1)
- Fixed Removable ProstheTicsDocument9 pagesFixed Removable ProstheTicsSumi AliNo ratings yet
- Orthodontics: Development of Occlusion Dr. Ayam A. TahaDocument18 pagesOrthodontics: Development of Occlusion Dr. Ayam A. TahaMastoCoranNo ratings yet
- Carious Cavities Classification by Black. Features of Carious Cavities Preparation of The 1-st and 5-th Black's ClassesDocument24 pagesCarious Cavities Classification by Black. Features of Carious Cavities Preparation of The 1-st and 5-th Black's ClassesmanarchikNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Classification of Dental CariesDocument4 pagesLecture 2-Classification of Dental CariesAli Al-Qudsi100% (3)
- DEvelopment of Normal OcclusionDocument7 pagesDEvelopment of Normal OcclusionMohammed HassanNo ratings yet
- Cavitypreparation 130320103634 Phpapp01Document60 pagesCavitypreparation 130320103634 Phpapp01Sumit BediNo ratings yet
- Preventive & Interceptive OrthodonticsDocument50 pagesPreventive & Interceptive OrthodonticsDeebah ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Primary TeethDocument6 pagesExtraction of Primary TeethmirfanulhaqNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesLiterature ReviewPuteri NazirahNo ratings yet
- Dental Crowding AbdullahDocument15 pagesDental Crowding AbdullahAbdullah Muhammed khaleel HassanNo ratings yet
- Methods of Space Gaining in OrthodonticsDocument41 pagesMethods of Space Gaining in OrthodonticsAwas AwasNo ratings yet
- Primary Teeth ThesisDocument4 pagesPrimary Teeth Thesisgbvc57fd100% (2)
- 12 ChapterDocument51 pages12 ChapterNaresh TeresNo ratings yet
- Pulp Therapy For The Young Permanent Dentition: ApexogenesisDocument15 pagesPulp Therapy For The Young Permanent Dentition: Apexogenesisapi-3855312No ratings yet
- Dental Caries Pathology, Diagnosis and PreventionDocument75 pagesDental Caries Pathology, Diagnosis and PreventionInky DarkNo ratings yet
- Crowding 180601115625 PDFDocument109 pagesCrowding 180601115625 PDFVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Prolonged Retention, Ankylosis and Infraocclusion of Deciduous Teeth Ok OkDocument5 pagesProlonged Retention, Ankylosis and Infraocclusion of Deciduous Teeth Ok OkRahulLife'sNo ratings yet
- Enamel Defects in Permanent First Molars and Incisors in Individuals With Cleft Lip And/or PalateDocument5 pagesEnamel Defects in Permanent First Molars and Incisors in Individuals With Cleft Lip And/or PalatefatimahNo ratings yet
- A Labially Positioned Mesiodens: Case Report: Robert J. Henry, DDS, MS A. Charles Post, DDSDocument5 pagesA Labially Positioned Mesiodens: Case Report: Robert J. Henry, DDS, MS A. Charles Post, DDSDr. Naji ArandiNo ratings yet
- Regional Early Development and Eruption of Permanent Teeth Case ReportDocument5 pagesRegional Early Development and Eruption of Permanent Teeth Case ReportAngelia PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document4 pagesLec 4Pakistan Dental SocietyNo ratings yet
- 25-Space Maintenance For Areas of Multiple Loss of TeethDocument10 pages25-Space Maintenance For Areas of Multiple Loss of TeethAhmed aljumailiNo ratings yet
- 2015 Pattern of Maxillary and Mandibular Proximal Enamel Thickness at The Contact Area of The Permanent Dentition From First Molar To First MolarDocument10 pages2015 Pattern of Maxillary and Mandibular Proximal Enamel Thickness at The Contact Area of The Permanent Dentition From First Molar To First MolarElías Enrique MartínezNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment Planning For Crowding, SpacingDocument66 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment Planning For Crowding, SpacingMadhumithaNo ratings yet
- Inlays & Onlays Clinical Experiences and Literature Review: Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & TherapyDocument7 pagesInlays & Onlays Clinical Experiences and Literature Review: Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & TherapycindyannisamelatiNo ratings yet
- Restoring Esthetics With Ceramic Laminate in ToothDocument4 pagesRestoring Esthetics With Ceramic Laminate in Toothikeuchi_ogawaNo ratings yet
- Osmf 521Document131 pagesOsmf 521Mohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Imp 521Document149 pagesImp 521Mohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Pedo 521Document160 pagesPedo 521Mohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Rprosd 521Document130 pagesRprosd 521Mohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Perio 521Document181 pagesPerio 521Mohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Management of Non-Carious LesionsDocument22 pagesManagement of Non-Carious LesionsMohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- جدول الفرقة الخامسة خريف 2022Document2 pagesجدول الفرقة الخامسة خريف 2022Mohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Suturing TechniquesDocument2 pagesSuturing TechniquesMohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- INDEX of CLINICAL PARTIAL DENTURE BOOKDocument1 pageINDEX of CLINICAL PARTIAL DENTURE BOOKMohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Clinical RPD Book CoverDocument1 pageClinical RPD Book CoverMohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Mouth PreparationDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Mouth PreparationMohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Metal TRY IN OF RPDDocument10 pagesChapter 5 Metal TRY IN OF RPDMohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Primary ImpressionDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Primary ImpressionMohamed Kilani100% (1)
- Chapter 1 DiagnosisDocument32 pagesChapter 1 DiagnosisMohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- 9966.10 The Double Life of Alfred BloggsDocument2 pages9966.10 The Double Life of Alfred BloggsAbdelkrim BenyahiaNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Worksheet and Management PlanDocument12 pagesRisk Assessment Worksheet and Management PlanpearlramarNo ratings yet
- Calculation ReportDocument126 pagesCalculation Reportisaacjoe77No ratings yet
- Heston Blumenthal Dinner 2011Document5 pagesHeston Blumenthal Dinner 2011SeymourpowellNo ratings yet
- Long-Lasting Effects of Distrust in Government and Science On Mental Health Eight Years After The Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant DisasterDocument6 pagesLong-Lasting Effects of Distrust in Government and Science On Mental Health Eight Years After The Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant DisasterIkhtiarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Moral Agent: Camarines Norte State CollegeDocument4 pagesLesson 1 The Moral Agent: Camarines Norte State CollegeJeanNo ratings yet
- How To Build A Wordpress Site in 30 MinutesDocument24 pagesHow To Build A Wordpress Site in 30 Minutesnestor martourezNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: English As A Second Language 0510/22 October/November 2020Document10 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: English As A Second Language 0510/22 October/November 2020HaithamNo ratings yet
- Sherlock Holmes SPECKLED BAND COMPLETE.Document12 pagesSherlock Holmes SPECKLED BAND COMPLETE.Fernanda SerralNo ratings yet
- Assessment Two Description Term 1 2019 Ver1Document3 pagesAssessment Two Description Term 1 2019 Ver1Smit PatelNo ratings yet
- 2 UMTS Radio Interface Physical LayerDocument56 pages2 UMTS Radio Interface Physical LayerKuldeep KashyapNo ratings yet
- The Revelation of Righteous Judgment SeriesDocument12 pagesThe Revelation of Righteous Judgment SeriesEnrique RamosNo ratings yet
- Feelings Needs CNVCDocument4 pagesFeelings Needs CNVCPopescu M.No ratings yet
- Putting The Balanced ScorecardDocument12 pagesPutting The Balanced ScorecardArnabNo ratings yet
- Position PaperDocument10 pagesPosition PaperJude Vincent DayawonNo ratings yet
- Research Design MBA MK02 UNIT IIDocument15 pagesResearch Design MBA MK02 UNIT IIAmit Kumar100% (3)
- Advance c7065 Consumibles.Document9 pagesAdvance c7065 Consumibles.gabyNo ratings yet
- TOAD Getting Started GuideDocument50 pagesTOAD Getting Started Guidesmruti_2012No ratings yet
- Ma History Dissertation StructureDocument7 pagesMa History Dissertation StructureCheapCustomPapersSingapore100% (1)
- Silk - Putative Persian Perversities Published PDFDocument32 pagesSilk - Putative Persian Perversities Published PDFEhsan DarwishmoqaddamNo ratings yet
- Assignment On InflationDocument7 pagesAssignment On InflationKhalid Mahmood100% (4)
- English 8 DLPDocument21 pagesEnglish 8 DLPRichelle Cayubit Dela Peña-LosdoNo ratings yet
- Double Effect Evaporator OperationDocument6 pagesDouble Effect Evaporator Operationpaulhill222No ratings yet
- Katarungang Pambarangay Law PDFDocument8 pagesKatarungang Pambarangay Law PDFChristine Nartea100% (1)
- "Analysis of Marketing Strategies of Nestle Maggi: Winter ReportDocument51 pages"Analysis of Marketing Strategies of Nestle Maggi: Winter ReportAnonymous PbMgeIvKNo ratings yet
Hall Technique: Definition
Hall Technique: Definition
Uploaded by
Mohamed KilaniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hall Technique: Definition
Hall Technique: Definition
Uploaded by
Mohamed KilaniCopyright:
Available Formats
Hall Technique
Definition: non-invasive Treatment of baby back Teeth (For molars only)
delay sealed under stainless steel' crown without Cavity. Prep, anesthesia,
Cavies removal or even Tooth reduction
it's a biologically oriented strategy (biological Control of dental Cavies)
Early childhood Caries: according to pediatric dentistry it's one Tooth or more
which are
(missed filled or decayed)
child must be equal or less Than 71 months old about 5,899 = 6 years old
or less
Sever early Childhood Caries: 1- Move Than 3 years & there is any sign of
smooth surface Caries (anteriors)
2- At the age of 3-5 years & DMF recorded more Than his age ex: 3 years old &
DMF 4 or more ، 4 years old & DMF 5 or 6 or More
Challenges of Treatment of Pedantic Teeth
1) Thickness of primary Teeth (enamel & dentin) less than in permanent (1
ml, 1 ml) So, danger of pulp exposure is more.
2) high pulp horns rate of decay reached to pulp faster.
3) management of Pediatrics is difficult.
4) parent satisfaction ((The Most Challenging one)).
- We have shift from Conventional approach (Canes removal & restoration) To
non / less invasive biological approach (Control of the biofilm biologically) by
disruption of the decay environment & preserve the Tooth Structure.
- After one year of using Hall Technique success rate 98%
- After 2 years - 4 years of using Hall Technique success rate
95%
ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
By Doctor Norna Hall (2006)
She uses ST.ST Crown & sealed a delayed Tooth with glass ionomer by Finger
pressure or asking the Child to bite.
ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
When We Can use hall Technique. ()الشروط
a) When no signs or symptoms. or any Complain by the child from The tooth.
b) No any sign of pulp involvement & Caries is present in dentin.
ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
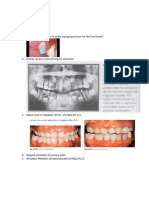
Indication ()امتحان
1) Proximal lesions (Two or more surfaces) Radiographically, a clear band of
dentin should be seen between Carious lesion & pulp, the Carious lesion
doesn't extend beyond the middle third of dentine
(no indicated لو أكتر من كده يبقى٣/٢ ل٣/١ معدى منهcares )يعنى
2) Restoration of Fractured Primary molars or badly delayed.
3) Developmental problems (Localized or generalized), i.e. enamel
hypoplasia, dentinogenesis imperfecta + amelogenesis imperfecta, MAI
4) High risk patients of developing Caries.
5) To protect & restore extensive Tooth loss due to erosion, Attrition.
6) As a support for some dental appliances ex, space Maintainers.
7) Special needs patients or Abrasion or where regular oral hygiene is
impaired lending to break down of regular direct restoration.
8) Partially submerged primary molars to maintain mesiodistal space &
occlusal vertical height.
Hall Technique not indicted When
In Case of incipient Caries (spot prep or Conservative Tooth preparation) is
done.
In Case of pulp involvement.
Badly broken down Tooth & We Cannot Cover it by Crown.
When parents not accept or approve the metal display of ST.ST Crown.
Mechanism of hall Technique
Prober seal of The Tooth (we may use smaller ST.ST Crown size or open the
Contact by elastic band).
This will separate the Caries enlivenment from the substrate & nutrition.
Changes will occur in bacterial profile of dental Caries.
Lesion will not progress.
اول زيادة ونسيبه أسبوعelastic band ﺑنﺤﻂ ال
embrasure الثانيﺔ فﻲ الedge والocclusal area ﺑتبقﻲ فوق الband ﺑتاﻋﺔ الupper edge
Modified Hall technique contact area ﺑتﺨتﻠﻒ ﺑس اننا ﺑنﻔتﺢ
1- Predental Period
Gum pads – grooves dental – gingival – lateral - transverse
Self-limited pseudo C.II
Bite
2- deciduous dentition period (6M-6y)
Generalized spaces
Primate spaces
Normal over bite
Terminal plane Flush اﻷفﻀﻞ فﻲ المرحﻠﺔ دى انه يكون
لو سأل ﻋنNormal characteristic features of (3 years old) اﻻجاﺑﺔ هتكون نﻔس اﻷرﺑع نقﻂ
3- Mixed dentition (6 – 9) early ، (9 – 12) late
Early & late mesial shift
Mesial step Terminal plane
Leeway space
Occlusion at 6 years.
Characteristics.
a) Edge to edge relation of anterior (self-limity)
occur due to
- Attrition
- Mandibular growth
b) Spacing Persists between Primary anteriors
c) Mesial step Terminal plane
occur due to
- Bodily movement growth of mandible
- Closure of primate spaces (at early mesial shift)
d) First permanent molar eruption
At (8 – 9) years
A. Deep over bite due to: eruption of upper& lower permanent incisors with
great height different between them & Primary molars
B. Ugly duckling Stage due to: Diastema between Two Permeant Centrals &
Flared letoval permanent incisors (self-limiting Condition)
C. Incisal liability due to: difference in size between large permeant Teeth
with smaller size primary teeth (self-limiting Condition)
Incisal liability is corrected by:
1- Generalized spaces 2- Inter Canine width
3- Primate spaces 4- Labial inclination
at (10 – 12) years
a) Central Diastema Closure (by eruption of Permanent Canines)
b) Correction of deep bite (by the emption of premolars)
c) Closure of leeway space (late mesial shift)
You might also like
- Diagnosing Early Interceptive Orthodontic Problems - Part 1: 2 CE CreditsDocument11 pagesDiagnosing Early Interceptive Orthodontic Problems - Part 1: 2 CE CreditsVijay Prabu GNo ratings yet
- CG A013 04 Stainless Steel Crowns in Deciduous MolarsDocument5 pagesCG A013 04 Stainless Steel Crowns in Deciduous MolarsmahmoudNo ratings yet
- Serial ExtractionDocument38 pagesSerial ExtractionRamy HanyNo ratings yet
- Lab 08 Oracle Access Management - Access Manager 11G R2 Ps3 2 Legged Mobile OauthDocument39 pagesLab 08 Oracle Access Management - Access Manager 11G R2 Ps3 2 Legged Mobile OauthAshutosh NichatNo ratings yet
- Statics and Mechnics of StructuresDocument511 pagesStatics and Mechnics of StructuresPrabu RengarajanNo ratings yet
- Thierry Bardini. Junkware. The Essential Junkiness of Our Culture and BiologyDocument298 pagesThierry Bardini. Junkware. The Essential Junkiness of Our Culture and BiologyJulieta Yelin100% (1)
- Clamps Specification GeneralDocument20 pagesClamps Specification Generalpiyush_123456789No ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Dentition and OcclusionDocument3 pagesGrowth and Development of Dentition and OcclusionFidz Lianko100% (2)
- Development of OcclusionDocument50 pagesDevelopment of OcclusionSaid Said100% (1)
- Dental CariesDocument120 pagesDental CariesSomya Jain100% (5)
- Oral Surgery in Children Lect 4Document39 pagesOral Surgery in Children Lect 4Jessica AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Development of Occlusion (Seminar 1)Document47 pagesDevelopment of Occlusion (Seminar 1)Isha GargNo ratings yet
- Pulpo, Pulpec, Apex, Injuries 1Document6 pagesPulpo, Pulpec, Apex, Injuries 1Cyril Almario Cunanan100% (1)
- NQVH The Hall Technique ManualDocument19 pagesNQVH The Hall Technique Manualpriti adsulNo ratings yet
- Development of Dentition WordDocument21 pagesDevelopment of Dentition Wordshubhangi_jain_10100% (1)
- Trauma To Primary DentitionDocument107 pagesTrauma To Primary DentitionShameena KnNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 P 4Document5 pagesLec 5 P 4brshlwnytwaftkhr956No ratings yet
- Childhood Caries & Dental Trauma On Primary Teeth: Henri Hartman, Drg. SP - KGADocument52 pagesChildhood Caries & Dental Trauma On Primary Teeth: Henri Hartman, Drg. SP - KGALila VininingtyasNo ratings yet
- 12-Restorative Dentistry For ChildrenDocument59 pages12-Restorative Dentistry For Childrenحمزہ محبNo ratings yet
- Interceptive FinalDocument60 pagesInterceptive FinalRaj SinghNo ratings yet
- Classifications of Caries LesionsDocument2 pagesClassifications of Caries LesionsDeniaAlyaTsaryNo ratings yet
- Bell 2 PDFDocument31 pagesBell 2 PDFMirza GlusacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Pediatric Dentoalveolar Surgery.50015-6Document21 pagesChapter 10 Pediatric Dentoalveolar Surgery.50015-6Zelallem AnileyNo ratings yet
- Hall TechniqueDocument19 pagesHall TechniqueanatomimanusiaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Space Management in Pediatric DentistryDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Space Management in Pediatric DentistryHussain HNo ratings yet
- Smile Makeover in ChildrenDocument7 pagesSmile Makeover in Childrendavidiaz1989No ratings yet
- On ImpactionDocument44 pagesOn Impactionmesssi269No ratings yet
- CHP 11 Moderate Nonskeletal Problems in Preadolescent ChildrenDocument6 pagesCHP 11 Moderate Nonskeletal Problems in Preadolescent ChildrenJack Pai33% (3)
- TUTORIAL IN ENGLISH Blok 12Document7 pagesTUTORIAL IN ENGLISH Blok 12Ifata RDNo ratings yet
- Pitandfissuresealant Dharmendraandaditigupta 160112155722Document29 pagesPitandfissuresealant Dharmendraandaditigupta 160112155722AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Ortho (Lec)Document2 pagesOrtho (Lec)Leigh BelmonteNo ratings yet
- Age Appropriate Orthodontics Overview HO 2013Document31 pagesAge Appropriate Orthodontics Overview HO 2013javi222222No ratings yet
- Short Cases NovDocument64 pagesShort Cases NovSoha Jan KhuhawarNo ratings yet
- Ped. Dent, Pub. Health (2) - 6 - Management of Traumatic Dental InjuriesDocument30 pagesPed. Dent, Pub. Health (2) - 6 - Management of Traumatic Dental InjuriesEslam HafezNo ratings yet
- Space MaintenanceDocument10 pagesSpace Maintenanceتوباك شاكورNo ratings yet
- Canine ImpactionDocument10 pagesCanine ImpactionPZ100% (1)
- Fixed Removable ProstheTicsDocument9 pagesFixed Removable ProstheTicsSumi AliNo ratings yet
- Orthodontics: Development of Occlusion Dr. Ayam A. TahaDocument18 pagesOrthodontics: Development of Occlusion Dr. Ayam A. TahaMastoCoranNo ratings yet
- Carious Cavities Classification by Black. Features of Carious Cavities Preparation of The 1-st and 5-th Black's ClassesDocument24 pagesCarious Cavities Classification by Black. Features of Carious Cavities Preparation of The 1-st and 5-th Black's ClassesmanarchikNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Classification of Dental CariesDocument4 pagesLecture 2-Classification of Dental CariesAli Al-Qudsi100% (3)
- DEvelopment of Normal OcclusionDocument7 pagesDEvelopment of Normal OcclusionMohammed HassanNo ratings yet
- Cavitypreparation 130320103634 Phpapp01Document60 pagesCavitypreparation 130320103634 Phpapp01Sumit BediNo ratings yet
- Preventive & Interceptive OrthodonticsDocument50 pagesPreventive & Interceptive OrthodonticsDeebah ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Primary TeethDocument6 pagesExtraction of Primary TeethmirfanulhaqNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesLiterature ReviewPuteri NazirahNo ratings yet
- Dental Crowding AbdullahDocument15 pagesDental Crowding AbdullahAbdullah Muhammed khaleel HassanNo ratings yet
- Methods of Space Gaining in OrthodonticsDocument41 pagesMethods of Space Gaining in OrthodonticsAwas AwasNo ratings yet
- Primary Teeth ThesisDocument4 pagesPrimary Teeth Thesisgbvc57fd100% (2)
- 12 ChapterDocument51 pages12 ChapterNaresh TeresNo ratings yet
- Pulp Therapy For The Young Permanent Dentition: ApexogenesisDocument15 pagesPulp Therapy For The Young Permanent Dentition: Apexogenesisapi-3855312No ratings yet
- Dental Caries Pathology, Diagnosis and PreventionDocument75 pagesDental Caries Pathology, Diagnosis and PreventionInky DarkNo ratings yet
- Crowding 180601115625 PDFDocument109 pagesCrowding 180601115625 PDFVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Prolonged Retention, Ankylosis and Infraocclusion of Deciduous Teeth Ok OkDocument5 pagesProlonged Retention, Ankylosis and Infraocclusion of Deciduous Teeth Ok OkRahulLife'sNo ratings yet
- Enamel Defects in Permanent First Molars and Incisors in Individuals With Cleft Lip And/or PalateDocument5 pagesEnamel Defects in Permanent First Molars and Incisors in Individuals With Cleft Lip And/or PalatefatimahNo ratings yet
- A Labially Positioned Mesiodens: Case Report: Robert J. Henry, DDS, MS A. Charles Post, DDSDocument5 pagesA Labially Positioned Mesiodens: Case Report: Robert J. Henry, DDS, MS A. Charles Post, DDSDr. Naji ArandiNo ratings yet
- Regional Early Development and Eruption of Permanent Teeth Case ReportDocument5 pagesRegional Early Development and Eruption of Permanent Teeth Case ReportAngelia PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document4 pagesLec 4Pakistan Dental SocietyNo ratings yet
- 25-Space Maintenance For Areas of Multiple Loss of TeethDocument10 pages25-Space Maintenance For Areas of Multiple Loss of TeethAhmed aljumailiNo ratings yet
- 2015 Pattern of Maxillary and Mandibular Proximal Enamel Thickness at The Contact Area of The Permanent Dentition From First Molar To First MolarDocument10 pages2015 Pattern of Maxillary and Mandibular Proximal Enamel Thickness at The Contact Area of The Permanent Dentition From First Molar To First MolarElías Enrique MartínezNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment Planning For Crowding, SpacingDocument66 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment Planning For Crowding, SpacingMadhumithaNo ratings yet
- Inlays & Onlays Clinical Experiences and Literature Review: Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & TherapyDocument7 pagesInlays & Onlays Clinical Experiences and Literature Review: Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & TherapycindyannisamelatiNo ratings yet
- Restoring Esthetics With Ceramic Laminate in ToothDocument4 pagesRestoring Esthetics With Ceramic Laminate in Toothikeuchi_ogawaNo ratings yet
- Osmf 521Document131 pagesOsmf 521Mohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Imp 521Document149 pagesImp 521Mohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Pedo 521Document160 pagesPedo 521Mohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Rprosd 521Document130 pagesRprosd 521Mohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Perio 521Document181 pagesPerio 521Mohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Management of Non-Carious LesionsDocument22 pagesManagement of Non-Carious LesionsMohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- جدول الفرقة الخامسة خريف 2022Document2 pagesجدول الفرقة الخامسة خريف 2022Mohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Suturing TechniquesDocument2 pagesSuturing TechniquesMohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- INDEX of CLINICAL PARTIAL DENTURE BOOKDocument1 pageINDEX of CLINICAL PARTIAL DENTURE BOOKMohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Clinical RPD Book CoverDocument1 pageClinical RPD Book CoverMohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Mouth PreparationDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Mouth PreparationMohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Metal TRY IN OF RPDDocument10 pagesChapter 5 Metal TRY IN OF RPDMohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Primary ImpressionDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Primary ImpressionMohamed Kilani100% (1)
- Chapter 1 DiagnosisDocument32 pagesChapter 1 DiagnosisMohamed KilaniNo ratings yet
- 9966.10 The Double Life of Alfred BloggsDocument2 pages9966.10 The Double Life of Alfred BloggsAbdelkrim BenyahiaNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Worksheet and Management PlanDocument12 pagesRisk Assessment Worksheet and Management PlanpearlramarNo ratings yet
- Calculation ReportDocument126 pagesCalculation Reportisaacjoe77No ratings yet
- Heston Blumenthal Dinner 2011Document5 pagesHeston Blumenthal Dinner 2011SeymourpowellNo ratings yet
- Long-Lasting Effects of Distrust in Government and Science On Mental Health Eight Years After The Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant DisasterDocument6 pagesLong-Lasting Effects of Distrust in Government and Science On Mental Health Eight Years After The Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant DisasterIkhtiarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Moral Agent: Camarines Norte State CollegeDocument4 pagesLesson 1 The Moral Agent: Camarines Norte State CollegeJeanNo ratings yet
- How To Build A Wordpress Site in 30 MinutesDocument24 pagesHow To Build A Wordpress Site in 30 Minutesnestor martourezNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: English As A Second Language 0510/22 October/November 2020Document10 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: English As A Second Language 0510/22 October/November 2020HaithamNo ratings yet
- Sherlock Holmes SPECKLED BAND COMPLETE.Document12 pagesSherlock Holmes SPECKLED BAND COMPLETE.Fernanda SerralNo ratings yet
- Assessment Two Description Term 1 2019 Ver1Document3 pagesAssessment Two Description Term 1 2019 Ver1Smit PatelNo ratings yet
- 2 UMTS Radio Interface Physical LayerDocument56 pages2 UMTS Radio Interface Physical LayerKuldeep KashyapNo ratings yet
- The Revelation of Righteous Judgment SeriesDocument12 pagesThe Revelation of Righteous Judgment SeriesEnrique RamosNo ratings yet
- Feelings Needs CNVCDocument4 pagesFeelings Needs CNVCPopescu M.No ratings yet
- Putting The Balanced ScorecardDocument12 pagesPutting The Balanced ScorecardArnabNo ratings yet
- Position PaperDocument10 pagesPosition PaperJude Vincent DayawonNo ratings yet
- Research Design MBA MK02 UNIT IIDocument15 pagesResearch Design MBA MK02 UNIT IIAmit Kumar100% (3)
- Advance c7065 Consumibles.Document9 pagesAdvance c7065 Consumibles.gabyNo ratings yet
- TOAD Getting Started GuideDocument50 pagesTOAD Getting Started Guidesmruti_2012No ratings yet
- Ma History Dissertation StructureDocument7 pagesMa History Dissertation StructureCheapCustomPapersSingapore100% (1)
- Silk - Putative Persian Perversities Published PDFDocument32 pagesSilk - Putative Persian Perversities Published PDFEhsan DarwishmoqaddamNo ratings yet
- Assignment On InflationDocument7 pagesAssignment On InflationKhalid Mahmood100% (4)
- English 8 DLPDocument21 pagesEnglish 8 DLPRichelle Cayubit Dela Peña-LosdoNo ratings yet
- Double Effect Evaporator OperationDocument6 pagesDouble Effect Evaporator Operationpaulhill222No ratings yet
- Katarungang Pambarangay Law PDFDocument8 pagesKatarungang Pambarangay Law PDFChristine Nartea100% (1)
- "Analysis of Marketing Strategies of Nestle Maggi: Winter ReportDocument51 pages"Analysis of Marketing Strategies of Nestle Maggi: Winter ReportAnonymous PbMgeIvKNo ratings yet