Professional Documents
Culture Documents
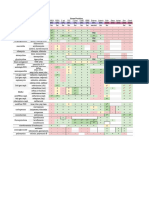
Table 9-6 - Antipsychotics and Side-Effect Profile
Table 9-6 - Antipsychotics and Side-Effect Profile
Uploaded by
Dragutin PetrićOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table 9-6 - Antipsychotics and Side-Effect Profile
Table 9-6 - Antipsychotics and Side-Effect Profile
Uploaded by
Dragutin PetrićCopyright:
Available Formats
Essentials of Psychiatry in Primary Care: Behavioral Health in the Medical Setting >Psychotic Disorders
Robert C. Smith, Gerald G. Osborn, Francesca C. Dwamena, Dale D'Mello, Laura Freilich, Heather S. Laird-Fick+
Table 9-6.Antipsychotics and Side-Effect Profile
Target Dose (mg/d) Metabolic Effecta EPS PRL Sedation Anticholinergic Hypotension
Quetiapine XR
300-800 ++ +/– – +++ + +++
Seroquel XR
Risperidoneb
4-6 ++ ++ +++ ++ – ++
Risperdal
Aripiprazole
10-30 + + – + – +
Abilify
Ziprasidonec
160 + + + ++ – +
Geodon
Olanzapine
10-20 +++ + + ++ ++ +/–
Zyprexa
Clozapined
300-450 +++ + + ++ ++ ++
Clozaril
EPS = extrapyramidal syndrome; PRL = prolactin.
aObtain fasting blood sugar at baseline, 12 weeks, and yearly.
bMay have marked prolactin increase; if clinical suspicion, obtain levels.
cMay prolong QTc (corrected QT interval on baseline ECG); if rises above >500 milliseconds, discontinue medication.
dSevere myeloid suppression and neutropenia potential: absolute neutrophil count weekly for first 6 months, biweekly for next 6 months, monthly thereafter (see text). Seizures are frequent at doses exceeding 600
mg/day.
Date of download: 12/26/22 from AccessMedicine: accessmedicine.mhmedical.com, Copyright © McGraw Hill. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Psychopharmacology (Fourth Edition) (Jerry Meyer) (Z-Library)Document841 pagesPsychopharmacology (Fourth Edition) (Jerry Meyer) (Z-Library)Dragutin Petrić100% (1)
- Clinical Handbook of Psychotropic Drugs, 25e (May 8, 2023) - (0889376328) - (Hogrefe Publishing) (Etc.) (Z-Library)Document555 pagesClinical Handbook of Psychotropic Drugs, 25e (May 8, 2023) - (0889376328) - (Hogrefe Publishing) (Etc.) (Z-Library)Dragutin Petrić100% (1)
- Table 25-5Document1 pageTable 25-5Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Table 25-5Document1 pageTable 25-5Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Default 2Document2 pagesDefault 2helixa42No ratings yet
- Page 62 TableDocument1 pagePage 62 Tablehelixa42No ratings yet
- Adverse Effects of Antipsychotic Meds - UpToDateDocument2 pagesAdverse Effects of Antipsychotic Meds - UpToDateJuan JoseNo ratings yet
- Stroke RSUD Dr. Adjidarmo: Clinical Pathway P KG CMDocument2 pagesStroke RSUD Dr. Adjidarmo: Clinical Pathway P KG CMBella Putria Gayuh RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- 1 - Klasifikasi, MOA, Resistensi ANTIBIOTIKDocument71 pages1 - Klasifikasi, MOA, Resistensi ANTIBIOTIKWiwiPutriDahlanNo ratings yet
- TANGGALDocument1 pageTANGGALvya14No ratings yet
- Daftar Obat High Alert Royal MaternityyDocument1 pageDaftar Obat High Alert Royal Maternityydiffa rahmaNo ratings yet
- Abx 2.0Document13 pagesAbx 2.0shaun.varghese7No ratings yet
- Terapi Psikofarmaka: DR - Deddy Soestiantoro SPKJDocument26 pagesTerapi Psikofarmaka: DR - Deddy Soestiantoro SPKJjojitrashNo ratings yet
- Ampi+Salbactum Amo+ Clavulanate Piper+Tazobactam: ST ST ND ND ND ND TH ST ND TH TH TH RD RD RD TH THDocument1 pageAmpi+Salbactum Amo+ Clavulanate Piper+Tazobactam: ST ST ND ND ND ND TH ST ND TH TH TH RD RD RD TH THAnnieNo ratings yet
- Covid - 19 Treatment Guidelines Gandhi Hospital and Medical College, TelanganaDocument9 pagesCovid - 19 Treatment Guidelines Gandhi Hospital and Medical College, TelanganaNikhilLokaNo ratings yet
- Psych Meds - Good Reference CardDocument2 pagesPsych Meds - Good Reference Cardwin100% (1)
- Clinical Pathway Saraf Meningitis TBDocument6 pagesClinical Pathway Saraf Meningitis TBklinik bgpNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway STEMI, Edit1Document5 pagesClinical Pathway STEMI, Edit1Sukar HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference BWDocument2 pagesQuick Reference BWmcbermudezNo ratings yet
- Studi Kasus Stroke: Nabiela Amaliya Haris 201110410311106 Farmasi BDocument23 pagesStudi Kasus Stroke: Nabiela Amaliya Haris 201110410311106 Farmasi BAyyRezki100% (1)
- Circ18 2000Document2 pagesCirc18 2000Mox LexNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathways Skizofrenia ResidualDocument3 pagesClinical Pathways Skizofrenia ResidualDian Jr BeyNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide April 2019 PDFDocument2 pagesQuick Reference Guide April 2019 PDFAaron ShokarNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide April 2019 PDFDocument2 pagesQuick Reference Guide April 2019 PDFAaron ShokarNo ratings yet
- Table 4-15 - Use of Atypical Antipsychotic Medications For BiDocument1 pageTable 4-15 - Use of Atypical Antipsychotic Medications For BiDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Pellets CombiniationDocument1 pagePellets CombiniationSharma TallaNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference To Psychotropic Medications: AntidepressantsDocument2 pagesQuick Reference To Psychotropic Medications: AntidepressantsNaiana PaulaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Drug Resistance and Genetic Properties of Salmonella Enterica Serotype Enteritidis Circulating in Chicken Farms in TunisiaDocument4 pagesAntimicrobial Drug Resistance and Genetic Properties of Salmonella Enterica Serotype Enteritidis Circulating in Chicken Farms in TunisiaPaula Manalo-SuliguinNo ratings yet
- Short BondpaperDocument3 pagesShort BondpaperjmbmandinNo ratings yet
- Danh Sach Hoat Chat Trong Che Pham Ytdp 08.39.35 28.10.2020Document1 pageDanh Sach Hoat Chat Trong Che Pham Ytdp 08.39.35 28.10.2020WIn NguYenNo ratings yet
- CladogramDocument1 pageCladogramjillianneramoranNo ratings yet
- Interference, Cross ReactivityDocument2 pagesInterference, Cross ReactivitycotonnilNo ratings yet
- Label Nama Kotak ObatDocument3 pagesLabel Nama Kotak Obatkimia farma 14No ratings yet
- Rsia Mutiara Bunda Salatiga, Jawa Tengah Pre Eklampsia Berat (Icd 10:)Document3 pagesRsia Mutiara Bunda Salatiga, Jawa Tengah Pre Eklampsia Berat (Icd 10:)Anonymous M81bZlK1No ratings yet
- Follow Up Dan DapusDocument5 pagesFollow Up Dan DapusMetyana CahyaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway NONSTEMI, Edit1Document5 pagesClinical Pathway NONSTEMI, Edit1Winda Rosita SeptantriNo ratings yet
- Intralabs PricelistDocument32 pagesIntralabs Pricelistfer nandoNo ratings yet
- Diabetic & Cardiac Care: An ISO 9001: 2008 Certified CoDocument2 pagesDiabetic & Cardiac Care: An ISO 9001: 2008 Certified CoManjir Sarma KatakiNo ratings yet
- GP Workshop-2Document115 pagesGP Workshop-2arafatreaganNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathways Diare HariDocument2 pagesClinical Pathways Diare HariDian Novi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathways Rsi Ibnu Sina Makassar SMF: Ilmu Penyakit SarafDocument2 pagesClinical Pathways Rsi Ibnu Sina Makassar SMF: Ilmu Penyakit SarafNajmawati AhmadNo ratings yet
- SOAP Sirosishematemesis MelenaDocument11 pagesSOAP Sirosishematemesis MelenaRaras Puspa WicitraNo ratings yet
- Follow Up Planning Diagnosis Treatment: Nocturnal Dyspneu)Document8 pagesFollow Up Planning Diagnosis Treatment: Nocturnal Dyspneu)husain abdul halimNo ratings yet
- Tabela Drogas Efeitos Colaterais PsiquiátricosDocument2 pagesTabela Drogas Efeitos Colaterais PsiquiátricosFelipe Hack de MouraNo ratings yet
- Wa0017.Document2 pagesWa0017.nicolegodoyn16No ratings yet
- Paket Medical Check UpDocument1 pagePaket Medical Check UpDwi EvanurvegaNo ratings yet
- Aristopharma Product ListDocument58 pagesAristopharma Product Listelectryfing asif100% (3)
- Product ListDocument48 pagesProduct ListRadisun LifesciencesNo ratings yet
- Best and Top PCD Pharma Franchise Company.Document48 pagesBest and Top PCD Pharma Franchise Company.PCDpharma FranchiseNo ratings yet
- Jenis ObatDocument5 pagesJenis ObatEva CitraNo ratings yet
- Reg Drug UVWXYZ May2011Document6 pagesReg Drug UVWXYZ May2011Robert LijaucoNo ratings yet
- Pest Tables Revised December 08Document2 pagesPest Tables Revised December 08Ali Asghar B. AfricawalaNo ratings yet
- Type2 Diabetes: Prasanna Babu 1St Pharm D - PBDocument15 pagesType2 Diabetes: Prasanna Babu 1St Pharm D - PBDhruthi SkmNo ratings yet
- Tarif Medical Check Up - Murni Teguh Memorial HospitalDocument4 pagesTarif Medical Check Up - Murni Teguh Memorial HospitalSR HasibuanNo ratings yet
- ReserachDocument142 pagesReserachBenjamin TantiansuNo ratings yet
- ANTIDEPRESAN RevisiDocument46 pagesANTIDEPRESAN RevisiRereNo ratings yet
- EMEA Ortho AssayMenu 2021 EMEADocument4 pagesEMEA Ortho AssayMenu 2021 EMEArose LiNo ratings yet
- Monitored Release Drugs - 2011Document18 pagesMonitored Release Drugs - 2011bgtbingoNo ratings yet
- FormularyDocument49 pagesFormularyvijay kumarNo ratings yet
- Emocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDocument153 pagesEmocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Psychiatry - A Case-Based Textbook, 2e (Mar 30, 2024) - (3031478010) - (Springer) (Ana Hategan, James A. Bourgeois Etc.) (Z-Library)Document939 pagesGeriatric Psychiatry - A Case-Based Textbook, 2e (Mar 30, 2024) - (3031478010) - (Springer) (Ana Hategan, James A. Bourgeois Etc.) (Z-Library)Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Emocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDocument153 pagesEmocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- ŠizofrenijaDocument216 pagesŠizofrenijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- PsihijatrijaDocument223 pagesPsihijatrijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Etika (Benedikt de Spinoza) (Z-Library)Document238 pagesEtika (Benedikt de Spinoza) (Z-Library)Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- EtikaDocument218 pagesEtikaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- ŠizofrenijaDocument3 pagesŠizofrenijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Agitacija Verbalna DeeskalacijaDocument2 pagesAgitacija Verbalna DeeskalacijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Kurs Pozitivne Filozofije Auguste ConteDocument152 pagesKurs Pozitivne Filozofije Auguste ConteDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Selected Root Causes of Moral DistressDocument1 pageSelected Root Causes of Moral DistressDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- 8Document1 page8Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- FDADocument2 pagesFDADragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- ŠizofrenijaDocument1 pageŠizofrenijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Gender PsychiatryDocument12 pagesGender PsychiatryDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- 7Document24 pages7Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Textbook of PsychiatryDocument3 pagesTextbook of PsychiatryDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy For Patients With Bipolar DisordersDocument1 pageDrug Therapy For Patients With Bipolar DisordersDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Stablo Odlučivanja Kako Odrediti Je Li Osoba Prikladna Za Liječenje Usmjereno Na PonašanjeDocument2 pagesStablo Odlučivanja Kako Odrediti Je Li Osoba Prikladna Za Liječenje Usmjereno Na PonašanjeDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Faze Liječenja Velikog Depresivnog PoremećajaDocument2 pagesFaze Liječenja Velikog Depresivnog PoremećajaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Stablo Odlučivanja StepDocument3 pagesStablo Odlučivanja StepDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Liječenje Depresije Naknadni PosjetiDocument3 pagesLiječenje Depresije Naknadni PosjetiDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- 6Document34 pages6Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet