Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resource and Development Pyq
Resource and Development Pyq
Uploaded by
opop0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views13 pages1. The document discusses various questions related to resources in India, including classification of resources, land degradation, soil types, and sustainable development.
2. Key points include classification of resources by origin (biotic and abiotic), ownership (individual, community, national, international), and status (potential, developed, reserve, stock).
3. Soil types discussed include black soil found in Maharashtra and regur soil found in the Deccan trap region.
Original Description:
Original Title
resource and development pyq
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document discusses various questions related to resources in India, including classification of resources, land degradation, soil types, and sustainable development.
2. Key points include classification of resources by origin (biotic and abiotic), ownership (individual, community, national, international), and status (potential, developed, reserve, stock).
3. Soil types discussed include black soil found in Maharashtra and regur soil found in the Deccan trap region.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views13 pagesResource and Development Pyq
Resource and Development Pyq
Uploaded by
opop1. The document discusses various questions related to resources in India, including classification of resources, land degradation, soil types, and sustainable development.
2. Key points include classification of resources by origin (biotic and abiotic), ownership (individual, community, national, international), and status (potential, developed, reserve, stock).
3. Soil types discussed include black soil found in Maharashtra and regur soil found in the Deccan trap region.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 13
1 Mark Questions
1. Being a tropical country, India has enormous possibilities of
tapping solar energy. Suggest any one way to popularize its
maximum use.
[1M, 2021 Sample Paper]
A1. Making people aware about renewable energy .
. resources/use of rooftop solar panels/solar street lighting
. system/any other relevant point.
2. A concerted effort has to be made for sustainable development.
Suggest any one step in conserving our mineral resources for
the future.
[1M, 2021 Sample Paper]
A2. Improved technologies/ Recycling of metals/ Using scrap
. metals and other substitutes / Any other relevant point
3. Define Sustainable development.
[1M, 2020]
A3. Present generation fulfils its needs while considering the
. needs of the future generation as well.
4. Classify resources on the basis of origin
[1M, 2018]
A4. Resources classification on the basis of origin:
(i) Biotic resources: All living organisms in our environment
are known as biotic resources.
Example: Tree, animal, insects etc.
(ii) Abiotic resources: All non-living things present in our
environment are known as abiotic resources.
Example: earth, air, water, metals, rocks etc.
5. What do you understand by a ‘Resource’? Give examples
[1M, 2015]
A5. Everything available in our environment which can be used to
. satisfy our needs, is called a resource. It should be
. technologically accessible, economically feasible and
. culturally acceptable. Only then, it can be termed as a
. ‘Resource’. Examples are: minerals, forests, fossil fuels etc
6. Give any two examples of non-renewable resources.
[1M, 2015]
A6. Non-renewable resources are resources which once get
. exhausted, cannot be remade. They take a long geological
. period of time, i.e., millions of years, in their formation, e.g.,
. minerals, fossil fuels, etc.
7. Which factor is mainly responsible for maximum land
degradation in India?
[1M, 2015]
A7. Over-grazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation.
. States where over-grazing has resulted in land degradation are
. Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra.
8. In what broad category do the soils of Maharashtra fall?
[1M, 2014]
A8. Black soil region also known as regur soils.
3 Mark Questions
9. Suggest and explain any three ways to protect land from
degradation in various states of India.
[3M, 2021 Sample Paper]
A9. The ways are :
(i) Afforestation.
(ii) Proper management of grazing.
(iii) Planting of shelter belts of plants.
(iv) Stabilization of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes.
(v) Control of mining activities. (Any 3)
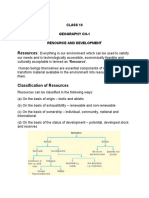
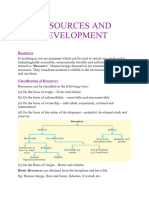
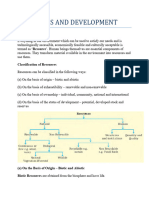
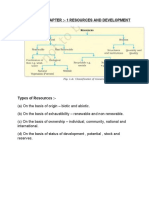
10. Write the classification of resources on four different bases.
[3M, 2015]
A10. Resources can be classified in the following four ways:
(a) On the basis of Origin:
• Biotic
• Abiotic
(b) On the basis of exhaustibility:
• Renewable
• Non-renewable
(c) On the basis of ownership:
• Individual (Personal)
• Community
• National
• International
(d) On the basis of status and development:
• Potential
• Developed
• Reserve
• Stock
11. Explain three stages of ‘resource planning.’
[3M, 2015]
A11. Three stages of resource planning:
1. Identification and inventory of resources across the
regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping
and the qualitative and quantitative estimation and
measurement of the resources.
2. Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate
technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing
resource development plans.
3. Matching the resource development plans with overall
national development plans.
12. Give the distribution of black/regur Soil.
[3M, 2015]
A14. This soil is typical of the Deccan Trap region.
• It is spread over north west Deccan plateau and is made up of
lava flows.
• This soil covers the plateaus of Maharashtra, Saurashtra,
Malwa, Madhya Pradesh and Chattisgarh and extends along
the Godavari and Krishna Valleys.
13. “Planning is the widely accepted strategy for judicious use of
. resources in a country like India”. Justify this statement with
. two relevant points and an example.
[3M, 2013]
A13.
1. There are regions which are rich in certain types of
resources but are deficient in some other resources.
For example: Arunachal has abundance of water but
lacks in infrastructural development.
2. There are some regions which can be considered self
sufficient in terms of availability of resources. For
example: The states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and
Madhya Pradesh are rich in minerals and coal deposits.
3. There are some regions which have acute shortage of
some vital resources.
For example: The state of Rajasthan is well endowed with
solar and wind energy but lacks in water resources.
14. Explain the concept of resource conservation as voiced by
Gandhiji.
[3M, 2014]
A14. Gandhiji voiced his concern about resource conservation in
. these Words: “There is enough far everybody’s need and not
. for anybody’s greed.” He placed the greedy and selfish
, individuals as the root cause for resource depletion at the
. global level. He was against ‘mass production’ and wanted to
. replace it with ‘production by the masses’.
1. Indiscriminate use of resources by human beings has led
to the depletion of resources for satisfying the greed of few
individuals.
2. Irrational consumption and over-utilization of resources
leads to socio-economic and environmental problems.
15. Explain three types of soil erosion mostly observed in India.
Mention human activities that are responsible for soil erosion.
[3M, 2013]
A15.
1. Gully erosion
The running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes
deep channels,
called gullies. They make the land unfit for cultivation. Such
lands are called ‘Badlands’.
2. Sheet erosion
Sometimes water flows as a sheet over large areas down a
slope. In this case top layer of the soil is washed away.
3. Wind erosion
Wind blows off loose and dry soil from flat and sloping land
causing erosion.
5 Mark Questions
16. ‘The challenge of sustainable development requires control
over industrial pollution.’ Substantiate the statement with
examples.
[5M, 2020]
A16.
i. On one hand Industries lead to extensive industrial growth
and expansion, other hand these are also the cause of
environmental degeneration which prompt to the different
type of air, water pollution.
ii. There is an increasing requirement to use a further
sustainable model.
iii. Industries must produce eco-friendly products and dump
wastes responsibly.
iv. Use of latest technology can help industries to control
pollution and lead towards sustainable mode of operation.
v. Industries use- Reuse-Recycle-Refuse approach.
17. Write six characteristics of regur soils (black soils)
[5M, 2015]
A17.
1. They are made up of extremely fine, i.e. clayey material.
2. They have capacity to hold moisture that makes them ideal for
growing cotton.
3. They are rich in soil nutrients such as calcium carbonate,
magnesium, potash and lime.
4. These soils are generally poor in phosphoric contents.
5. They develop deep cracks during dry hot weather, which helps
in the proper aeration of soil.
6. These soils are sticky when wet and difficult to work unless
tilled immediately after the first shower.
18. Explain four types of resources based on ownership and give
one example of each type.
[5M, 2014]
A18. On the basis of ownership, there are four types of resources:
1. Individual Resources :- Resources, which are owned privately
by individuals, e.g., farmers own
pieces of land or houses. Plantation, pasture lands, water in
wells are some resources owned by individuals.
2. Community Owned Resources :- These resources are
accessible to all the members of the community, e.g., village
ponds, public parks, playgrounds in urban areas are
accessible to all the residents of that area.
3. National Resources :- All the resources within the political
boundary of a nation including the territorial water (oceanic
area upto 12 nautical miles from the coast) extending into the
ocean and resources therein belong to the nation, e.g., all
minerals, forests, wildlife, water resources, land etc.
4. International Resources :- There are international institutions
which own and regulate some resources, e.g., The oceanic
resources beyond 200 km of the Exclusive Economic Zone
belong to the open ocean and no individual country can utilise
these without the concurrence of international institutions.
19. Write some measures/ways to solve problems of land
degradation.
[5M, 2014]
A19. Measures to conserve land:
1. Afforestation.
2. Proper management of grazing to control over-grazing.
3. Planting of shelter belts of plants.
4. Stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes.
5. Control of mining activities.
20. Write the main characteristics of arid soils.
[5M, 2014]
A20.
1. Arid soils range from red to brown in colour.
2. They have a sandy texture.
3. They are saline in nature. In areas where salt content in high,
common salt is obtained by evaporation.
4. Arid soil lacks humus and is moisture deficient.
5. The lower horizons of the soil have kankars because of high
calcium content which restrict infiltration of water.
6. Proper irrigation helps make these soils cultivable, e.g.,
Western Rajasthan
21. “The future generation may not have sufficient resources as
compared to the present generation”. Justify the statement by
giving suitable examples.
[5M, 2012]
A21.
Present sources of energy in India are coal, petroleum, natural
gas, solar energy, wind energy, hydel power, electricity, wood
for fire, cow dung etc. Most of these are non-renewable
sources of energy which may get exhausted after some time.
These are available in limited quantities. The present rate of
consumption is higher than the rate at which these resources
are being replenished and should be preserved for our future
generations.
In fifty years’ time, India may depend largely on non-
conventional sources of energy which are available in
abundance such as solar energy, hydel energy, wind energy
etc. The total hydel power potential in India is estimated at
1,50,000 MW of which only one-sixth has been developed so
far.
1. Development of a country needs to be continuous.
Every country would like to have the level of
development go up further.
2. Many scientists have warned that the present levels of
development cannot be sustained for the future as the
present rate of consumption of both renewable and
non-renewable resources is very high. Rapid
industrialisation has led to environment degradation.
3. Sustainability development aims at development
without damaging the environment and at the same
time conserving for the future.
4. Sustainability of development is essential not only for
the present generation but also for future generations
to ensure a good life.
You might also like
- Ecl Kidolgozott TételekDocument34 pagesEcl Kidolgozott TételekKesjár Mária100% (3)
- Principles of Brownfield Regeneration: Cleanup, Design, and Reuse of Derelict LandFrom EverandPrinciples of Brownfield Regeneration: Cleanup, Design, and Reuse of Derelict LandNo ratings yet
- Intro To Philosophy of Human Person 1st Quarter Module 4Document33 pagesIntro To Philosophy of Human Person 1st Quarter Module 4Gold Aziphil Galiza91% (22)
- Resources and Development Shobhit NirwanDocument13 pagesResources and Development Shobhit NirwanRadhika RameshNo ratings yet
- QuestionBankGeographyCass 10CH1Document3 pagesQuestionBankGeographyCass 10CH1Viveha Priya Jayamani 66No ratings yet
- GeoDocument28 pagesGeoSakshi GoelNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Geo. CH 1 - Resource and Development NotesDocument13 pagesClass 10 Geo. CH 1 - Resource and Development Notessadhna yadav100% (2)
- Grade 10 Ch. 1 Geo.Document9 pagesGrade 10 Ch. 1 Geo.punian344No ratings yet
- Resources and Development AssignmentDocument6 pagesResources and Development AssignmentBhavya AhujaNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument30 pagesGeographyA:-Piyush ShirsekarNo ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument11 pagesResources and Developmentpujal dabasNo ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument32 pagesResources and DevelopmentSwastiNo ratings yet
- Geo-Qns. Ans - Resource and DevelopmentDocument7 pagesGeo-Qns. Ans - Resource and Developmentvmahale339No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentRBSNo ratings yet
- Notes Class X Geography Resources Question AnswerDocument9 pagesNotes Class X Geography Resources Question AnswerAarush BindalNo ratings yet
- Original 1587566839 Resource and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesOriginal 1587566839 Resource and DevelopmentS KannanNo ratings yet
- Geography Class 10Document56 pagesGeography Class 10niwanshi1No ratings yet
- Classification of ResourcesDocument11 pagesClassification of ResourcesbasilNo ratings yet
- LVCRbrDxIrwSgaijfkS6Document6 pagesLVCRbrDxIrwSgaijfkS6Shivangi sundaramNo ratings yet
- Ch-1Resources and DevelopmentDocument13 pagesCh-1Resources and Developmentys432805No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Resources and Development Part B Question and AnswersDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Resources and Development Part B Question and Answersaloma.alvaresNo ratings yet
- Resource and DevelopmentDocument26 pagesResource and DevelopmentthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Classification of Resources: Notes Class 10 Chapter 1 - Resources and Development GeographyDocument18 pagesClassification of Resources: Notes Class 10 Chapter 1 - Resources and Development GeographyMANISH JOSHINo ratings yet
- Geography Les 1 With AnsDocument10 pagesGeography Les 1 With AnsMokshita JainNo ratings yet
- Geography-Resources and Development Q - ADocument7 pagesGeography-Resources and Development Q - ANaman GamingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 GeographyDocument6 pagesChapter 1 GeographyTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Resource and Devepmt Notes 2024Document9 pagesResource and Devepmt Notes 2024yashwantbb28No ratings yet
- CH 1 Geo X NotesDocument15 pagesCH 1 Geo X NoteskniFe VisualzNo ratings yet
- Grade X Geography Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesGrade X Geography Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentMohammed OwaisNo ratings yet
- Geo Chap 1 NotesDocument12 pagesGeo Chap 1 NotesCranston VideoNo ratings yet
- Resources and Development: by Adarsh - NJDocument27 pagesResources and Development: by Adarsh - NJAnkur ChopraNo ratings yet
- PZXtHSVFprt8PiZkEfaiDocument4 pagesPZXtHSVFprt8PiZkEfaiShivangi sundaramNo ratings yet
- CLASS 10 CH-1 GEOGRAPHY Question-AnswersDocument4 pagesCLASS 10 CH-1 GEOGRAPHY Question-AnswersDoonites DelhiNo ratings yet
- Geography Notes by S.KDocument8 pagesGeography Notes by S.KTech GURUNo ratings yet
- __studentinfo_Homework_cd15db89c0aa4d31bf7065b2851472acDocument3 pages__studentinfo_Homework_cd15db89c0aa4d31bf7065b2851472acxtremeib13No ratings yet
- Resource and Development: Questions of 3/4 MarksDocument9 pagesResource and Development: Questions of 3/4 MarksLATHEKA SKNo ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument8 pagesResources and Developmentsayedsaifullah.knbossNo ratings yet
- Gidb5856658 - Resource and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesGidb5856658 - Resource and DevelopmentSprihi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Resources and Development: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument17 pagesChapter 1 - Resources and Development: Multiple Choice QuestionsreemNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 8 Geography Book-1Document15 pagesNCERT Class 8 Geography Book-1vkgNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document 1 3Document7 pagesUntitled Document 1 3Himesh kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Resource and DevelopmentDocument6 pagesResource and DevelopmentvrajNo ratings yet
- Resources and Development NotesDocument10 pagesResources and Development NotesKushan MittalNo ratings yet
- Geography 1 Class X Assignment (2020-21)Document6 pagesGeography 1 Class X Assignment (2020-21)Binode SarkarNo ratings yet
- Geography Notes For Class: X (Social Science) : Chapter 1: Resources and Development Remember These PointsDocument4 pagesGeography Notes For Class: X (Social Science) : Chapter 1: Resources and Development Remember These PointsAkshit SethiNo ratings yet
- Resources and Development (Geo)Document5 pagesResources and Development (Geo)kumarshivam58156No ratings yet
- Geo ch-1 Class 10Document9 pagesGeo ch-1 Class 10nayshajain63No ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument13 pagesResources and DevelopmentRiyansh WarikooNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Resources and Development BoardPrep SolutionDocument10 pagesClass 10th Resources and Development BoardPrep SolutionABISHUA HANOK LALNo ratings yet
- Geo-10 2Document107 pagesGeo-10 2SonalikaNo ratings yet
- Geography CHDocument9 pagesGeography CHsendpradip3No ratings yet
- Practice Questions Chap Geography 1Document2 pagesPractice Questions Chap Geography 1ajabgajab.edNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentDocument26 pagesChapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentvedanimefanNo ratings yet
- Resources and Devolopment NotesDocument20 pagesResources and Devolopment NotesDanyaNo ratings yet
- 10geo-Chap1-Resources and DevelopmentDocument7 pages10geo-Chap1-Resources and DevelopmentYukti KoliNo ratings yet
- 01-Resource and Development (Part-01)Document5 pages01-Resource and Development (Part-01)Archit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Resource and DevelopmentDocument7 pagesResource and DevelopmentedumatracNo ratings yet
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentDocument11 pagesCBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentEKLABAY SONINo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Resources and Development: CBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science GeographyDocument38 pagesChapter 1 - Resources and Development: CBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science GeographyscedhuNo ratings yet
- Resources and Development NotesDocument27 pagesResources and Development NotesbhaviknsrNo ratings yet
- Social Science Class 10 Important Questions Geography Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentDocument17 pagesSocial Science Class 10 Important Questions Geography Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentRITESH KUMAR SAHUNo ratings yet
- Notes on Resource and Development STD-10 (2024)Document11 pagesNotes on Resource and Development STD-10 (2024)chaitanyabharate1No ratings yet
- Impact of Tourism Industry On Economic Growth in Thailand 2Document2 pagesImpact of Tourism Industry On Economic Growth in Thailand 2thapaganesh942No ratings yet
- NIFT GAT 2020 Sample Paper MFMDocument24 pagesNIFT GAT 2020 Sample Paper MFMSHIVAM BHANDARINo ratings yet
- Unit 10: Ethics: Listening 2 Lecturer: NG Thao TrangDocument37 pagesUnit 10: Ethics: Listening 2 Lecturer: NG Thao TrangANH LA KIEUNo ratings yet
- CWP18911 Space 1889 - Thunders of Venus (2017)Document28 pagesCWP18911 Space 1889 - Thunders of Venus (2017)Leo Knøsgaard Heby100% (1)
- De Young, R. (2013) Environmental Psychology Overview, in Huffman & Klein (Eds) Green Organizations (Pp. 17-33)Document10 pagesDe Young, R. (2013) Environmental Psychology Overview, in Huffman & Klein (Eds) Green Organizations (Pp. 17-33)MemoonaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change ContentDocument12 pagesClimate Change Contentjasson babaNo ratings yet
- PL3 - San Jose - Mindoro - AnthonyDocument15 pagesPL3 - San Jose - Mindoro - AnthonyJherick SandovalNo ratings yet
- A Solid Waste Management Survey in Davao Del Sur (School and Household Waste Management Survey)Document6 pagesA Solid Waste Management Survey in Davao Del Sur (School and Household Waste Management Survey)sishu21No ratings yet
- Results and Discussions On Compaction CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesResults and Discussions On Compaction CharacteristicsAll in one TECHYNo ratings yet
- Effect of Ground Water TableDocument3 pagesEffect of Ground Water TableahmedNo ratings yet
- Pertacorta Quiz 2Document3 pagesPertacorta Quiz 2Isamarch Caday PertacortaNo ratings yet
- Lgaip Provincial Validation: LGU Grant Assistance For Innovative PracticesDocument22 pagesLgaip Provincial Validation: LGU Grant Assistance For Innovative PracticesJohn UndaNo ratings yet
- HIRAC (Commissioning Operations)Document2 pagesHIRAC (Commissioning Operations)hendraNo ratings yet
- COP26 Climate Our Future Powerpoint Ages 11 PlusDocument27 pagesCOP26 Climate Our Future Powerpoint Ages 11 PlusMark Jay BaclaanNo ratings yet
- CCUS Standardisation Developments - CO2MPRISE WorkshopDocument36 pagesCCUS Standardisation Developments - CO2MPRISE WorkshopJarno DakhorstNo ratings yet
- Review Questionnaire 9TH Third TermDocument7 pagesReview Questionnaire 9TH Third TermAna Sofia Guzman FernandezNo ratings yet
- Annex 7 2022 March 14 RLA Introduction DocumentDocument14 pagesAnnex 7 2022 March 14 RLA Introduction DocumentKunto Anjono PriyambodoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Economic Accounting in The Netherlands: Organisation, Output and DissiminationDocument21 pagesEnvironmental Economic Accounting in The Netherlands: Organisation, Output and DissiminationMadhavi SoelemanNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument8 pagesAnnotated BibliographyANGELICA MAE HOFILEÑANo ratings yet
- Course Description For ITU Env EngDocument4 pagesCourse Description For ITU Env EngDilay AğaoğluNo ratings yet
- Environmental History - Latin American Studies - Oxford BibliographiesDocument32 pagesEnvironmental History - Latin American Studies - Oxford BibliographiesSebastian Diaz AngelNo ratings yet
- AddRes - OD5 - Mock Test - T2Document14 pagesAddRes - OD5 - Mock Test - T2Emily Anabel quezada roseroNo ratings yet
- Proposed Methodology: Project NameDocument10 pagesProposed Methodology: Project NameVIKASH PEERTHYNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management in HouseholdDocument5 pagesSolid Waste Management in HouseholdHOPLOPZ GAMINGNo ratings yet
- (개정) 2022년 - 영어I - YBM (한상호) - Special Lesson - 적중예상문제 1회 실전 - OK (20220801수정)Document15 pages(개정) 2022년 - 영어I - YBM (한상호) - Special Lesson - 적중예상문제 1회 실전 - OK (20220801수정)Danny HongNo ratings yet
- Angeles Ol85 Activitym2.6Document2 pagesAngeles Ol85 Activitym2.6wegNo ratings yet
- BODIAN Simple in Means, Rich in Ends A Conversation With Arne NaessDocument8 pagesBODIAN Simple in Means, Rich in Ends A Conversation With Arne NaessptqkNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet Ironite SpongeDocument4 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet Ironite Spongefs1640No ratings yet