Professional Documents
Culture Documents
14 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 Install
14 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 Install
Uploaded by
hjmclddgbolrlsxbknCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Splunk Forwarders Tech BriefDocument2 pagesSplunk Forwarders Tech BriefAhmed ElmasryNo ratings yet
- f5 Agility Labs Waf PDFDocument344 pagesf5 Agility Labs Waf PDFCoolrRaju100% (1)
- Zimbra Os Multi-Server InstallDocument60 pagesZimbra Os Multi-Server Installneoman552No ratings yet
- Splunk PCI 2.0 DataSourceDocument64 pagesSplunk PCI 2.0 DataSourceyoungwarrior888No ratings yet
- Different Stages in Data PipelineDocument7 pagesDifferent Stages in Data PipelineSantoshNo ratings yet
- Data Onboarding From ScratchDocument51 pagesData Onboarding From ScratchAbhinavNo ratings yet
- Backing Up and Restoring Configuration Files - NIOS Admin Guide - Infoblox Documentation PortalDocument6 pagesBacking Up and Restoring Configuration Files - NIOS Admin Guide - Infoblox Documentation Portalroot403rsNo ratings yet
- Splunk Cloud Platform Splunk Cloud Platform Admin Manual 8.2.2203Document7 pagesSplunk Cloud Platform Splunk Cloud Platform Admin Manual 8.2.2203EDu JoseNo ratings yet
- Splunk BasicsDocument13 pagesSplunk Basicsakshat jainNo ratings yet
- f5 Arcsight F5BIG-IPsyslogConfigDocument12 pagesf5 Arcsight F5BIG-IPsyslogConfigsachinkoenigNo ratings yet
- Working With The Data Synchronization ToolDocument40 pagesWorking With The Data Synchronization ToolNaga Pradeep VeerisettyNo ratings yet
- Splunk ForwardersDocument5 pagesSplunk Forwardersq_riusNo ratings yet
- Splunk Course NotesDocument70 pagesSplunk Course NotesKaniNo ratings yet
- Splunk-5 0 3-TutorialDocument88 pagesSplunk-5 0 3-TutorialcarlgrahamNo ratings yet
- OPSEC - How To InstallDocument44 pagesOPSEC - How To InstallanitaNo ratings yet
- 8 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page8 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- BackupDocument5 pagesBackupSanjay PawarNo ratings yet
- SOC Prime SSL Framework v.1.5.2 GuideDocument17 pagesSOC Prime SSL Framework v.1.5.2 GuidenawabkabirNo ratings yet
- Cloud Object Storage Cos Splunk Architecture Configuration Integration Guide 1 - 63028763USENDocument50 pagesCloud Object Storage Cos Splunk Architecture Configuration Integration Guide 1 - 63028763USENZoumana DiomandeNo ratings yet
- Splunk Interview QuestionsDocument14 pagesSplunk Interview QuestionsGani RKNo ratings yet
- Lab Book Checkpoint 2Document14 pagesLab Book Checkpoint 2Ace Writer1No ratings yet
- Splunk 5.0.2 TutorialDocument88 pagesSplunk 5.0.2 Tutorialprosarath100% (1)
- OverviewDocument5 pagesOverviewMelatNo ratings yet
- eCIR LabsDocument258 pageseCIR Labsexams6055No ratings yet
- E - NetworkAttachedStorage PDFDocument65 pagesE - NetworkAttachedStorage PDFNorisham Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- BP-How To Install A SmartPlant Materials Service PackDocument13 pagesBP-How To Install A SmartPlant Materials Service PackDucVikingNo ratings yet
- Splunk Best Practices: Table of ContentsDocument10 pagesSplunk Best Practices: Table of ContentsljdwhizNo ratings yet
- Splunk MaterialDocument170 pagesSplunk Materialvenkatasai100% (3)
- Splunk PPT Satinder Singh SandhuDocument146 pagesSplunk PPT Satinder Singh SandhuSatinder Singh SandhuNo ratings yet
- Security Data Lake PDFDocument37 pagesSecurity Data Lake PDFmahendra_kutare100% (1)
- Unit - 1 Module 2Document62 pagesUnit - 1 Module 2Kashish VermaNo ratings yet
- Deploying Splunk Enterprise On Microsoft AzureDocument4 pagesDeploying Splunk Enterprise On Microsoft AzurefatouNo ratings yet
- Splunk 20230910-Wa0000Document28 pagesSplunk 20230910-Wa0000suraj patilNo ratings yet
- 3 Security: 3.1 Data Protection and PrivacyDocument16 pages3 Security: 3.1 Data Protection and Privacyramanarekha7206No ratings yet
- Employees Sample Database: 1 Preface and Legal NoticesDocument8 pagesEmployees Sample Database: 1 Preface and Legal NoticesHiren P HirenNo ratings yet
- Employee en PDFDocument8 pagesEmployee en PDFAngelNo ratings yet
- © 2019 Caendra Inc. - Hera For IHRP - Effectively Using Splunk (Scenario 1)Document37 pages© 2019 Caendra Inc. - Hera For IHRP - Effectively Using Splunk (Scenario 1)Saw Gyi100% (1)
- Oracle Golden Gate PresentationDocument20 pagesOracle Golden Gate Presentationsuganya88No ratings yet
- Micro Focus Security Arcsight Connectors: Smartconnector For Arbor Networks Peakflow Syslog Configuration GuideDocument11 pagesMicro Focus Security Arcsight Connectors: Smartconnector For Arbor Networks Peakflow Syslog Configuration Guideajay kumarNo ratings yet
- Forwarder 9.2.1 ForwarderDocument62 pagesForwarder 9.2.1 ForwarderLeonardio perezNo ratings yet
- 02 Connect Student Guide v6.1.2Document15 pages02 Connect Student Guide v6.1.2nino ponceNo ratings yet
- Whats NewDocument9 pagesWhats NewFirmansyah AlfaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction - Data Structures and AlgorithmsDocument10 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction - Data Structures and Algorithmsnordvtech2023No ratings yet
- Data Structures and Algorithms Quick GuideDocument73 pagesData Structures and Algorithms Quick GuideKishan KoyaniNo ratings yet
- Creating A Response Toolkit: Gathering The ToolsDocument26 pagesCreating A Response Toolkit: Gathering The ToolsSitha Pranitha BasavarajuNo ratings yet
- Migrating and Converting Non Cdbs PDB Different Endian Operating SystemDocument31 pagesMigrating and Converting Non Cdbs PDB Different Endian Operating SystemNikolya SmirnoffNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Splunk Interview Questions 1671145278Document15 pagesTop 100 Splunk Interview Questions 1671145278rrrNo ratings yet
- Data StructuresDocument12 pagesData StructuresJoshNo ratings yet
- Data Deduplication Data DomainDocument24 pagesData Deduplication Data DomainwailimNo ratings yet
- CC04 Chapter 1Document7 pagesCC04 Chapter 1reymarrodriguez403No ratings yet
- Ehdf QB Iat 2Document17 pagesEhdf QB Iat 2Prashik GamreNo ratings yet
- Splunk Forwarders Tech BriefDocument3 pagesSplunk Forwarders Tech BriefZoumana DiomandeNo ratings yet
- DSP Workflow - Retrieving Data For A Well From Multiple Data Sources and Editing That DataDocument12 pagesDSP Workflow - Retrieving Data For A Well From Multiple Data Sources and Editing That DataTripoli ManoNo ratings yet
- Guide For Interface Developers: Everything You Need To Know About Energyplus Input and OutputDocument34 pagesGuide For Interface Developers: Everything You Need To Know About Energyplus Input and OutputBasil OguakaNo ratings yet
- C01. Linux OperationDocument11 pagesC01. Linux OperationZhang JuNo ratings yet
- Notes TerraformDocument138 pagesNotes TerraformJuan PintoNo ratings yet
- Informatica - 3 - Knowledge Is MoneyDocument39 pagesInformatica - 3 - Knowledge Is Moneyamulya.1rn15ec016No ratings yet
- SecurityDocument19 pagesSecurityMina W. SayedNo ratings yet
- Enable DIF For EquipmentDocument20 pagesEnable DIF For EquipmentMahesh PidshettiNo ratings yet
- Splunk 1Document4 pagesSplunk 1Kartheek sNo ratings yet
- Sending Additional Files From SAP Netweaver PI To Third Party FTP Location PDFDocument9 pagesSending Additional Files From SAP Netweaver PI To Third Party FTP Location PDFsadakolikoNo ratings yet
- Managing PeopleSoft on the Oracle Cloud: Best Practices with PeopleSoft Cloud ManagerFrom EverandManaging PeopleSoft on the Oracle Cloud: Best Practices with PeopleSoft Cloud ManagerNo ratings yet
- 34 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page34 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 36 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page36 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 38 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page38 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 26 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page26 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 30 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page30 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 18 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page18 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 22 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page22 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 8 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page8 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 32 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page32 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 20 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page20 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 16 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page16 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- Splunk Enterprise Security Part1Document1 pageSplunk Enterprise Security Part1hjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 6 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page6 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 24 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page24 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 12 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page12 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 10 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page10 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- Protocol Gateway: SYNC 2000Document2 pagesProtocol Gateway: SYNC 2000tran TXPNo ratings yet
- LGConnectedCare Operations ManualDocument67 pagesLGConnectedCare Operations Manualaalarroque852No ratings yet
- DSLS PDFDocument153 pagesDSLS PDFBruno CarboniNo ratings yet
- Nse4 FGT-6Document51 pagesNse4 FGT-6rizkyNo ratings yet
- PAN-EDU-101 - Lab Manual PAN-OS 6.0 - Rev A PDFDocument48 pagesPAN-EDU-101 - Lab Manual PAN-OS 6.0 - Rev A PDFRuben De Sis Temas0% (2)
- MCBSC O&MDocument116 pagesMCBSC O&MMatias Ayllon100% (2)
- Fortinac: Juniper Ex Switch 802.1X-Mac-Authentication Device IntegrationDocument14 pagesFortinac: Juniper Ex Switch 802.1X-Mac-Authentication Device IntegrationSaid bel haj letaiefNo ratings yet
- Uthernet II Manual 17 Nov 18Document52 pagesUthernet II Manual 17 Nov 18nealNo ratings yet
- VM210ENDocument94 pagesVM210ENChhoan NhunNo ratings yet
- LogDocument23 pagesLogPrincess Dianne BalsaNo ratings yet
- Libra Shutdown Menu Libra Client Libra Shutdown Menu: Name Description and UsageDocument4 pagesLibra Shutdown Menu Libra Client Libra Shutdown Menu: Name Description and UsageMehdi RahmatiNo ratings yet
- Stulz Wib 67c 0514 enDocument50 pagesStulz Wib 67c 0514 enPabloNo ratings yet
- CCNA Pass4sure 200-120 BraindumpsDocument16 pagesCCNA Pass4sure 200-120 Braindumpspass4surebraindumpsNo ratings yet
- RB750r2 PDFDocument3 pagesRB750r2 PDFRahmat HidayatNo ratings yet
- Ats-Ip-Kit A 1Document2 pagesAts-Ip-Kit A 1ranajithdkNo ratings yet
- Check Point Sandblast PoC Guide v91Document102 pagesCheck Point Sandblast PoC Guide v91Fabio SouzaNo ratings yet
- 6293a Enu CompanionDocument107 pages6293a Enu CompanionStephanie DominguezNo ratings yet
- Networking NotesDocument25 pagesNetworking NotesRichelieu Pippen MoyonNo ratings yet
- Cisco Security Architectures BookDocument286 pagesCisco Security Architectures Bookboxman636100% (1)
- ZTE MF283 Manual EN PDFDocument28 pagesZTE MF283 Manual EN PDFNereo ReoliquioNo ratings yet
- DViewCam Manual 311Document170 pagesDViewCam Manual 311THE LISTNo ratings yet
- Network Layer Samia'Document10 pagesNetwork Layer Samia'Dark GardianNo ratings yet
- A Research On The Vulnerability in Popular P2P ProtocolsDocument5 pagesA Research On The Vulnerability in Popular P2P ProtocolsSyndu PramandaNo ratings yet
- How To Setup Mobility Extension On 2n OfficerouteDocument14 pagesHow To Setup Mobility Extension On 2n Officeroutegnatagbi8696No ratings yet
- NetBrain System Setup Guide Distributed DeploymentDocument108 pagesNetBrain System Setup Guide Distributed Deploymentajrob69_187428023No ratings yet
- AttendHRM User ManualDocument131 pagesAttendHRM User ManualSeshukumar Mathampalli100% (1)
- IT Careers & Networking: Paul Patti, PH.DDocument25 pagesIT Careers & Networking: Paul Patti, PH.DBeyNo ratings yet
- Tcp/Ip Vulnerabilities and WeaknessesDocument25 pagesTcp/Ip Vulnerabilities and Weaknessesomjaijagdish.raiNo ratings yet
14 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 Install
14 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 Install
Uploaded by
hjmclddgbolrlsxbknOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
14 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 Install
14 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 Install
Uploaded by
hjmclddgbolrlsxbknCopyright:
Available Formats
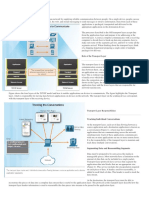
Data source planning for Splunk Enterprise Security
The volume, type, and number of data sources influences the overall Splunk platform architecture, the number and
placement of forwarders, estimated load, and impact on network resources.
Splunk Enterprise Security requires that all data sources comply with the Splunk Common Information Model (CIM).
Enterprise Security is designed to leverage the CIM standardized data models both when searching data to populate
dashboard panels and views, and when providing data for correlation searches.
Map add-ons to data sources
The add-ons included with Splunk Enterprise Security are designed to parse and categorize known data sources and
other technologies for CIM compliance.
For each data source:
1. Identify the add-on: Identify the technology and determine the corresponding add-on. The primary sources for
add-ons are the Technology-specific add-ons provided with Enterprise Security and the CIM-compatible content
available on Splunkbase. If the add-on you want to use is not already compatible with the CIM, modify it to
support CIM data schemas. For an example, see Use the CIM to normalize data at search time in the Common
Information Model Add-on Manual.
2. Install the add-on: Install the add-on on the Enterprise Security search head. Install add-ons that perform
index-time processing on each indexer. If the forwarder architecture includes sending data through a parsing or
heavy forwarder, the add-on might be needed on the heavy forwarder. Splunk Cloud Platform customers must
work with Splunk Support to install add-ons on search heads and indexers, but are responsible for on-premises
forwarders.
3. Configure the server, device, or technology where necessary: Enable logging or data collection for the device or
application and/or configure the output for collection by a Splunk instance. Consult the vendor documentation for
implementation steps.
4. Customize the add-on where necessary: An add-on might require customization, such as setting the location or
source of the data, choosing whether the data is located in a file or in a database, or other unique settings.
5. Set up a Splunk data input and confirm the source type settings: The README file of the add-on includes
information about the source type setting associated with the data, and might include customization notes about
configuring the input.
Considerations for data inputs
Splunk platform instances provide several types of input configurations to ingest data. Depending on the technology or
source being collected, choose the input method that matches the infrastructure requirements based on the performance
impact, ease of data access, stability, minimizing source latency, and maintainability.
• Monitoring files: Deploy a Splunk forwarder on each system hosting the files, and set the source type on the
forwarder using an input configuration. If you have a large number of systems with identical files, use the Splunk
Enterprise deployment server to set up standardized file inputs across large groups of forwarders.
• Monitoring network ports: Use standard tools such as a syslog server, or create listener ports on a forwarder.
Sending multiple network sources to the same port or file complicates source typing. For more information, see
the Splunk platform documentation.
• For Splunk Enterprise, see Get data from TCP and UDP ports in Splunk Enterprise Getting Data
In.
12
You might also like
- Splunk Forwarders Tech BriefDocument2 pagesSplunk Forwarders Tech BriefAhmed ElmasryNo ratings yet
- f5 Agility Labs Waf PDFDocument344 pagesf5 Agility Labs Waf PDFCoolrRaju100% (1)
- Zimbra Os Multi-Server InstallDocument60 pagesZimbra Os Multi-Server Installneoman552No ratings yet
- Splunk PCI 2.0 DataSourceDocument64 pagesSplunk PCI 2.0 DataSourceyoungwarrior888No ratings yet
- Different Stages in Data PipelineDocument7 pagesDifferent Stages in Data PipelineSantoshNo ratings yet
- Data Onboarding From ScratchDocument51 pagesData Onboarding From ScratchAbhinavNo ratings yet
- Backing Up and Restoring Configuration Files - NIOS Admin Guide - Infoblox Documentation PortalDocument6 pagesBacking Up and Restoring Configuration Files - NIOS Admin Guide - Infoblox Documentation Portalroot403rsNo ratings yet
- Splunk Cloud Platform Splunk Cloud Platform Admin Manual 8.2.2203Document7 pagesSplunk Cloud Platform Splunk Cloud Platform Admin Manual 8.2.2203EDu JoseNo ratings yet
- Splunk BasicsDocument13 pagesSplunk Basicsakshat jainNo ratings yet
- f5 Arcsight F5BIG-IPsyslogConfigDocument12 pagesf5 Arcsight F5BIG-IPsyslogConfigsachinkoenigNo ratings yet
- Working With The Data Synchronization ToolDocument40 pagesWorking With The Data Synchronization ToolNaga Pradeep VeerisettyNo ratings yet
- Splunk ForwardersDocument5 pagesSplunk Forwardersq_riusNo ratings yet
- Splunk Course NotesDocument70 pagesSplunk Course NotesKaniNo ratings yet
- Splunk-5 0 3-TutorialDocument88 pagesSplunk-5 0 3-TutorialcarlgrahamNo ratings yet
- OPSEC - How To InstallDocument44 pagesOPSEC - How To InstallanitaNo ratings yet
- 8 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page8 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- BackupDocument5 pagesBackupSanjay PawarNo ratings yet
- SOC Prime SSL Framework v.1.5.2 GuideDocument17 pagesSOC Prime SSL Framework v.1.5.2 GuidenawabkabirNo ratings yet
- Cloud Object Storage Cos Splunk Architecture Configuration Integration Guide 1 - 63028763USENDocument50 pagesCloud Object Storage Cos Splunk Architecture Configuration Integration Guide 1 - 63028763USENZoumana DiomandeNo ratings yet
- Splunk Interview QuestionsDocument14 pagesSplunk Interview QuestionsGani RKNo ratings yet
- Lab Book Checkpoint 2Document14 pagesLab Book Checkpoint 2Ace Writer1No ratings yet
- Splunk 5.0.2 TutorialDocument88 pagesSplunk 5.0.2 Tutorialprosarath100% (1)
- OverviewDocument5 pagesOverviewMelatNo ratings yet
- eCIR LabsDocument258 pageseCIR Labsexams6055No ratings yet
- E - NetworkAttachedStorage PDFDocument65 pagesE - NetworkAttachedStorage PDFNorisham Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- BP-How To Install A SmartPlant Materials Service PackDocument13 pagesBP-How To Install A SmartPlant Materials Service PackDucVikingNo ratings yet
- Splunk Best Practices: Table of ContentsDocument10 pagesSplunk Best Practices: Table of ContentsljdwhizNo ratings yet
- Splunk MaterialDocument170 pagesSplunk Materialvenkatasai100% (3)
- Splunk PPT Satinder Singh SandhuDocument146 pagesSplunk PPT Satinder Singh SandhuSatinder Singh SandhuNo ratings yet
- Security Data Lake PDFDocument37 pagesSecurity Data Lake PDFmahendra_kutare100% (1)
- Unit - 1 Module 2Document62 pagesUnit - 1 Module 2Kashish VermaNo ratings yet
- Deploying Splunk Enterprise On Microsoft AzureDocument4 pagesDeploying Splunk Enterprise On Microsoft AzurefatouNo ratings yet
- Splunk 20230910-Wa0000Document28 pagesSplunk 20230910-Wa0000suraj patilNo ratings yet
- 3 Security: 3.1 Data Protection and PrivacyDocument16 pages3 Security: 3.1 Data Protection and Privacyramanarekha7206No ratings yet
- Employees Sample Database: 1 Preface and Legal NoticesDocument8 pagesEmployees Sample Database: 1 Preface and Legal NoticesHiren P HirenNo ratings yet
- Employee en PDFDocument8 pagesEmployee en PDFAngelNo ratings yet
- © 2019 Caendra Inc. - Hera For IHRP - Effectively Using Splunk (Scenario 1)Document37 pages© 2019 Caendra Inc. - Hera For IHRP - Effectively Using Splunk (Scenario 1)Saw Gyi100% (1)
- Oracle Golden Gate PresentationDocument20 pagesOracle Golden Gate Presentationsuganya88No ratings yet
- Micro Focus Security Arcsight Connectors: Smartconnector For Arbor Networks Peakflow Syslog Configuration GuideDocument11 pagesMicro Focus Security Arcsight Connectors: Smartconnector For Arbor Networks Peakflow Syslog Configuration Guideajay kumarNo ratings yet
- Forwarder 9.2.1 ForwarderDocument62 pagesForwarder 9.2.1 ForwarderLeonardio perezNo ratings yet
- 02 Connect Student Guide v6.1.2Document15 pages02 Connect Student Guide v6.1.2nino ponceNo ratings yet
- Whats NewDocument9 pagesWhats NewFirmansyah AlfaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction - Data Structures and AlgorithmsDocument10 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction - Data Structures and Algorithmsnordvtech2023No ratings yet
- Data Structures and Algorithms Quick GuideDocument73 pagesData Structures and Algorithms Quick GuideKishan KoyaniNo ratings yet
- Creating A Response Toolkit: Gathering The ToolsDocument26 pagesCreating A Response Toolkit: Gathering The ToolsSitha Pranitha BasavarajuNo ratings yet
- Migrating and Converting Non Cdbs PDB Different Endian Operating SystemDocument31 pagesMigrating and Converting Non Cdbs PDB Different Endian Operating SystemNikolya SmirnoffNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Splunk Interview Questions 1671145278Document15 pagesTop 100 Splunk Interview Questions 1671145278rrrNo ratings yet
- Data StructuresDocument12 pagesData StructuresJoshNo ratings yet
- Data Deduplication Data DomainDocument24 pagesData Deduplication Data DomainwailimNo ratings yet
- CC04 Chapter 1Document7 pagesCC04 Chapter 1reymarrodriguez403No ratings yet
- Ehdf QB Iat 2Document17 pagesEhdf QB Iat 2Prashik GamreNo ratings yet
- Splunk Forwarders Tech BriefDocument3 pagesSplunk Forwarders Tech BriefZoumana DiomandeNo ratings yet
- DSP Workflow - Retrieving Data For A Well From Multiple Data Sources and Editing That DataDocument12 pagesDSP Workflow - Retrieving Data For A Well From Multiple Data Sources and Editing That DataTripoli ManoNo ratings yet
- Guide For Interface Developers: Everything You Need To Know About Energyplus Input and OutputDocument34 pagesGuide For Interface Developers: Everything You Need To Know About Energyplus Input and OutputBasil OguakaNo ratings yet
- C01. Linux OperationDocument11 pagesC01. Linux OperationZhang JuNo ratings yet
- Notes TerraformDocument138 pagesNotes TerraformJuan PintoNo ratings yet
- Informatica - 3 - Knowledge Is MoneyDocument39 pagesInformatica - 3 - Knowledge Is Moneyamulya.1rn15ec016No ratings yet
- SecurityDocument19 pagesSecurityMina W. SayedNo ratings yet
- Enable DIF For EquipmentDocument20 pagesEnable DIF For EquipmentMahesh PidshettiNo ratings yet
- Splunk 1Document4 pagesSplunk 1Kartheek sNo ratings yet
- Sending Additional Files From SAP Netweaver PI To Third Party FTP Location PDFDocument9 pagesSending Additional Files From SAP Netweaver PI To Third Party FTP Location PDFsadakolikoNo ratings yet
- Managing PeopleSoft on the Oracle Cloud: Best Practices with PeopleSoft Cloud ManagerFrom EverandManaging PeopleSoft on the Oracle Cloud: Best Practices with PeopleSoft Cloud ManagerNo ratings yet
- 34 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page34 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 36 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page36 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 38 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page38 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 26 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page26 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 30 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page30 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 18 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page18 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 22 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page22 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 8 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page8 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 32 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page32 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 20 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page20 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 16 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page16 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- Splunk Enterprise Security Part1Document1 pageSplunk Enterprise Security Part1hjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 6 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page6 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 24 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page24 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 12 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page12 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- 10 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallDocument1 page10 - 7 PDF - ES 7.0.2 InstallhjmclddgbolrlsxbknNo ratings yet
- Protocol Gateway: SYNC 2000Document2 pagesProtocol Gateway: SYNC 2000tran TXPNo ratings yet
- LGConnectedCare Operations ManualDocument67 pagesLGConnectedCare Operations Manualaalarroque852No ratings yet
- DSLS PDFDocument153 pagesDSLS PDFBruno CarboniNo ratings yet
- Nse4 FGT-6Document51 pagesNse4 FGT-6rizkyNo ratings yet
- PAN-EDU-101 - Lab Manual PAN-OS 6.0 - Rev A PDFDocument48 pagesPAN-EDU-101 - Lab Manual PAN-OS 6.0 - Rev A PDFRuben De Sis Temas0% (2)
- MCBSC O&MDocument116 pagesMCBSC O&MMatias Ayllon100% (2)
- Fortinac: Juniper Ex Switch 802.1X-Mac-Authentication Device IntegrationDocument14 pagesFortinac: Juniper Ex Switch 802.1X-Mac-Authentication Device IntegrationSaid bel haj letaiefNo ratings yet
- Uthernet II Manual 17 Nov 18Document52 pagesUthernet II Manual 17 Nov 18nealNo ratings yet
- VM210ENDocument94 pagesVM210ENChhoan NhunNo ratings yet
- LogDocument23 pagesLogPrincess Dianne BalsaNo ratings yet
- Libra Shutdown Menu Libra Client Libra Shutdown Menu: Name Description and UsageDocument4 pagesLibra Shutdown Menu Libra Client Libra Shutdown Menu: Name Description and UsageMehdi RahmatiNo ratings yet
- Stulz Wib 67c 0514 enDocument50 pagesStulz Wib 67c 0514 enPabloNo ratings yet
- CCNA Pass4sure 200-120 BraindumpsDocument16 pagesCCNA Pass4sure 200-120 Braindumpspass4surebraindumpsNo ratings yet
- RB750r2 PDFDocument3 pagesRB750r2 PDFRahmat HidayatNo ratings yet
- Ats-Ip-Kit A 1Document2 pagesAts-Ip-Kit A 1ranajithdkNo ratings yet
- Check Point Sandblast PoC Guide v91Document102 pagesCheck Point Sandblast PoC Guide v91Fabio SouzaNo ratings yet
- 6293a Enu CompanionDocument107 pages6293a Enu CompanionStephanie DominguezNo ratings yet
- Networking NotesDocument25 pagesNetworking NotesRichelieu Pippen MoyonNo ratings yet
- Cisco Security Architectures BookDocument286 pagesCisco Security Architectures Bookboxman636100% (1)
- ZTE MF283 Manual EN PDFDocument28 pagesZTE MF283 Manual EN PDFNereo ReoliquioNo ratings yet
- DViewCam Manual 311Document170 pagesDViewCam Manual 311THE LISTNo ratings yet
- Network Layer Samia'Document10 pagesNetwork Layer Samia'Dark GardianNo ratings yet
- A Research On The Vulnerability in Popular P2P ProtocolsDocument5 pagesA Research On The Vulnerability in Popular P2P ProtocolsSyndu PramandaNo ratings yet
- How To Setup Mobility Extension On 2n OfficerouteDocument14 pagesHow To Setup Mobility Extension On 2n Officeroutegnatagbi8696No ratings yet
- NetBrain System Setup Guide Distributed DeploymentDocument108 pagesNetBrain System Setup Guide Distributed Deploymentajrob69_187428023No ratings yet
- AttendHRM User ManualDocument131 pagesAttendHRM User ManualSeshukumar Mathampalli100% (1)
- IT Careers & Networking: Paul Patti, PH.DDocument25 pagesIT Careers & Networking: Paul Patti, PH.DBeyNo ratings yet
- Tcp/Ip Vulnerabilities and WeaknessesDocument25 pagesTcp/Ip Vulnerabilities and Weaknessesomjaijagdish.raiNo ratings yet