Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Climate Activity Worksheet
Climate Activity Worksheet
Uploaded by
Teddy jeremyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- LEED GA V4 Practise Exam (40 Q)Document10 pagesLEED GA V4 Practise Exam (40 Q)Aneesha MuthurajNo ratings yet
- Raft FoundationsDocument26 pagesRaft FoundationsSanjana Bhandiwad100% (3)
- Effects of Climate Change What Does It Mean? How Is This Caused by Climate Change? What Are The Consequences?Document3 pagesEffects of Climate Change What Does It Mean? How Is This Caused by Climate Change? What Are The Consequences?Reymark Alciso EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Cibse Swimming PoolpdfDocument13 pagesCibse Swimming PoolpdfBao Loc DuongNo ratings yet
- Ocean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Part OneDocument4 pagesOcean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Part OneSiyeon CrewsNo ratings yet
- Bella Marine Biology 205 PDF FreeDocument3 pagesBella Marine Biology 205 PDF FreeduhhhNo ratings yet
- Ocean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Part OneDocument3 pagesOcean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Part OneAaron CoxNo ratings yet
- Climate Activity WorksheetDocument3 pagesClimate Activity Worksheetseanj1756No ratings yet
- Ocean's Impact On Climate Activity WorksheetDocument5 pagesOcean's Impact On Climate Activity WorksheetTrinity GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Climate Activity Worksheet (Pumiphat)Document5 pagesClimate Activity Worksheet (Pumiphat)Pumiphat SukkhoNo ratings yet
- Ocean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Part OneDocument6 pagesOcean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Part OneColtonTvNo ratings yet
- Blue Lined Climate Change Environment InfographicDocument1 pageBlue Lined Climate Change Environment InfographicGem CarmelNo ratings yet
- Climate Change EcosystemsDocument2 pagesClimate Change EcosystemsvizzeNo ratings yet
- CC 10Document3 pagesCC 10api-323888481No ratings yet
- Roes Sig 2004Document25 pagesRoes Sig 2004Mohammad LakNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Climate Change On Aquaculture: DR - Soheila Khoshnevis Yazdi and DR - Bahram ShakouriDocument5 pagesThe Effects of Climate Change On Aquaculture: DR - Soheila Khoshnevis Yazdi and DR - Bahram ShakouriHASSAN AKHTARNo ratings yet
- Triptico Global WarmingDocument2 pagesTriptico Global WarmingAna Silvia Garza100% (1)
- Before and After The Deluge: Rain-On-Snow Flooding Effects On Aquatic Invertebrate Communities of Small Streams in The Sierra Nevada, CaliforniaDocument14 pagesBefore and After The Deluge: Rain-On-Snow Flooding Effects On Aquatic Invertebrate Communities of Small Streams in The Sierra Nevada, CaliforniavalentinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 19Document8 pagesLesson 19maureensolano63No ratings yet
- Performance Check 1 - Earth ScienceDocument2 pagesPerformance Check 1 - Earth Scienceyuuna yuunaNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument1 pageGlobal WarmingDayu Btarismari 12No ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument1 pageGlobal WarmingDayu Btarismari 12No ratings yet
- The Day After Tomorrow: Konrad F 43 Florczak@Document4 pagesThe Day After Tomorrow: Konrad F 43 Florczak@Jaija J JayanNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Module 4Document2 pagesClimate Change Module 4Belle MendozaNo ratings yet
- To Be Sustained by The Sea, We Must Sustain The Sea : BstractDocument26 pagesTo Be Sustained by The Sea, We Must Sustain The Sea : BstractguptaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Animal Ecology - 2021 - Osgood - Effects of Climate Change Driven Gradual and Acute Temperature Changes On SharkDocument13 pagesJournal of Animal Ecology - 2021 - Osgood - Effects of Climate Change Driven Gradual and Acute Temperature Changes On Sharktonkadujmovic4No ratings yet
- Efeitos Alteracao Climatica em Algas MarinhasDocument28 pagesEfeitos Alteracao Climatica em Algas MarinhasGuilherme MedeirosNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Adaptations of Sandy Beach Macrofauna in Face of Climate Change Impacts A Conceptual FrameworkDocument11 pagesBehavioral Adaptations of Sandy Beach Macrofauna in Face of Climate Change Impacts A Conceptual FrameworkNM100% (1)
- Impact Oa To CetaceansDocument8 pagesImpact Oa To CetaceansRahma ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Yajnik Bookreview 2013Document2 pagesYajnik Bookreview 2013kisuyaNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Transforms Coral Reef Assemblages: Nature April 2018Document17 pagesGlobal Warming Transforms Coral Reef Assemblages: Nature April 2018Roberto Hernandez-landaNo ratings yet
- DRRR Unit 3 L1-L3Document4 pagesDRRR Unit 3 L1-L3Mary Rose TuburanNo ratings yet
- Rhoko Quilban 9 - St. AlbertDocument4 pagesRhoko Quilban 9 - St. AlbertJohn Eridog Xcx-World MatelaNo ratings yet
- The Flood ReviewingDocument3 pagesThe Flood ReviewingJangbu SherpaNo ratings yet
- Doubling of Surface Oceanic Meridional Heat TranspDocument11 pagesDoubling of Surface Oceanic Meridional Heat Transpdhruba.climateNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument14 pagesGlobal WarmingSachin KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Formal Final With Track ChangesDocument8 pagesFormal Final With Track Changesapi-620232040No ratings yet
- FactSheets EN PDFDocument12 pagesFactSheets EN PDFJom VillNo ratings yet
- EAS 4300: Introduction To Oceanography, FALL 2009: InstructorsDocument23 pagesEAS 4300: Introduction To Oceanography, FALL 2009: InstructorsPankaj MunjalNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument21 pagesClimate ChangeBishal SarkarNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Marine Heatwaves On Top Predator Distributions Are Variable But PredictableDocument10 pagesImpacts of Marine Heatwaves On Top Predator Distributions Are Variable But PredictableIlfa FinandaNo ratings yet
- USABO Climates, Biomes, EcosystemsDocument11 pagesUSABO Climates, Biomes, EcosystemsEmelyn PagsanjanNo ratings yet
- Gadus MorhuaDocument11 pagesGadus MorhuaThomas LanssensNo ratings yet
- The Global Crisis of Our TimeDocument11 pagesThe Global Crisis of Our TimeJuan Arevalo LetradoNo ratings yet
- The Uncertain Future of The Coasts: Chapter 03Document21 pagesThe Uncertain Future of The Coasts: Chapter 03amandaNo ratings yet
- Causes & Effects of Climate ChangeDocument8 pagesCauses & Effects of Climate ChangeJade DyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Anthropogenic Effects On The OceansDocument31 pagesLecture 11 Anthropogenic Effects On The OceansHarry DouglasNo ratings yet
- Cooling WatersDocument11 pagesCooling WatersmohtashimahmNo ratings yet
- General Climate Change Brochure Print VersionDocument2 pagesGeneral Climate Change Brochure Print VersionsanjuktNo ratings yet
- What's Harming Our OceansDocument5 pagesWhat's Harming Our OceansLia KristermanNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 EcosystemDocument18 pagesUnit 13 EcosystemDevang ParekhNo ratings yet
- Manners FloodplainDevelopmentEl 2007Document22 pagesManners FloodplainDevelopmentEl 2007Luis Fernando Bejar LuksicNo ratings yet
- FormalfinalDocument8 pagesFormalfinalapi-620232040No ratings yet
- The Resilience of Life To Astrophysical Events: David Sloan, Rafael Alves Batista & Abraham LoebDocument5 pagesThe Resilience of Life To Astrophysical Events: David Sloan, Rafael Alves Batista & Abraham Loebদিব্যোদয় ভৌমিকNo ratings yet
- Subsystem InterconnectionDocument1 pageSubsystem Interconnectionkaito kazeNo ratings yet
- DeforestationDocument8 pagesDeforestationgabrieleyannNo ratings yet
- 1985-The Greenhouse Effect and Nature ReservesDocument12 pages1985-The Greenhouse Effect and Nature ReservesMaría Andérez FernándezNo ratings yet
- Li 2014Document15 pagesLi 2014kiansanei14No ratings yet
- WHAT WILL HAPPEN IF THE EARTH MELTS FEW YEARS FROM Now GABRIENTEDocument1 pageWHAT WILL HAPPEN IF THE EARTH MELTS FEW YEARS FROM Now GABRIENTEraprapanianoNo ratings yet
- The Overarching Impacts of Climate Change On Islands With Track ChangesDocument10 pagesThe Overarching Impacts of Climate Change On Islands With Track Changesapi-711083315No ratings yet
- Tectonic Eustasy: Shoreline Changes Submerged Coasts Submergent ShorelineDocument61 pagesTectonic Eustasy: Shoreline Changes Submerged Coasts Submergent ShorelineivanNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Its Effects On Ecosystems, Habitats and BiotaDocument29 pagesClimate Change and Its Effects On Ecosystems, Habitats and BiotaCaptain ChemicalNo ratings yet
- Sudden Spring: Stories of Adaptation in a Climate-Changed SouthFrom EverandSudden Spring: Stories of Adaptation in a Climate-Changed SouthRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Social Media - Affecting For Better or Worse - EditedDocument8 pagesSocial Media - Affecting For Better or Worse - EditedTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- INT 220 Business Brief Course ProjectDocument5 pagesINT 220 Business Brief Course ProjectTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Time To Stop Hooking Up (You Know What You Want) Synthesis Essay - EditedDocument5 pagesTime To Stop Hooking Up (You Know What You Want) Synthesis Essay - EditedTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Seasons of Change Activity WorksheetDocument2 pagesSeasons of Change Activity WorksheetTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Literature Analysis Essay .EditedDocument5 pagesLiterature Analysis Essay .EditedTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Touchstone 3.1.editedDocument5 pagesTouchstone 3.1.editedTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Intervention MappingDocument14 pagesIntervention MappingTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- PPM EN 2005 03 JanczakDocument14 pagesPPM EN 2005 03 JanczakTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- CHSC 5200 - Chapter 8Document13 pagesCHSC 5200 - Chapter 8Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document34 pagesWeek 2Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document33 pagesWeek 5Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- EAE 313 AEC 307 PUBLIC FINANCE fINAL (2) - 1-1-2Document150 pagesEAE 313 AEC 307 PUBLIC FINANCE fINAL (2) - 1-1-2Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Week 3.1Document32 pagesWeek 3.1Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- The Rise and Fall of Oedipus The KingDocument4 pagesThe Rise and Fall of Oedipus The KingTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document30 pagesWeek 1Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document25 pagesWeek 3Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Week 3.2Document21 pagesWeek 3.2Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Checklist of Requirements For Manufacturing Economic Zone ApplicationDocument1 pageChecklist of Requirements For Manufacturing Economic Zone ApplicationRenz Albert TejadillaNo ratings yet
- Environment PDFDocument121 pagesEnvironment PDFas1510No ratings yet
- Mini-Reader: © Gilbert Barrera 2019Document20 pagesMini-Reader: © Gilbert Barrera 2019ghadeer alkhayat100% (1)
- Civil Engineering and Urban Planning: An International Journal (CiVEJ)Document1 pageCivil Engineering and Urban Planning: An International Journal (CiVEJ)Matthew JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Geoarchaeology of The Louisiana Coastal PlainDocument126 pagesGeoarchaeology of The Louisiana Coastal Plainetchplain100% (1)
- Higien and SanitationDocument31 pagesHigien and SanitationyeliNo ratings yet
- FertilizerDocument2 pagesFertilizerRyan DeMayNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Reservoir Water Tightness TestsDocument14 pagesMethod Statement For Reservoir Water Tightness TestsbruNo ratings yet
- Moisture Vapor Transfer Theory: Fabric Objective Measurement Assignment - 3Document19 pagesMoisture Vapor Transfer Theory: Fabric Objective Measurement Assignment - 3NiveditaKumariNo ratings yet
- Eh Risk Assessment Draft 1Document9 pagesEh Risk Assessment Draft 1api-547026973No ratings yet
- Trickling Filter 175Document13 pagesTrickling Filter 175suman subedi100% (1)
- Term Paper 9G 2Document4 pagesTerm Paper 9G 2EnamariNo ratings yet
- p1 r1 ReportDocument11 pagesp1 r1 ReportPravinAlbdusMathewNo ratings yet
- Site AnalysisDocument3 pagesSite AnalysisRohit Sharma0% (1)
- 9 - SOP - Daikin's Solution For Wound Cleaning v2.0Document2 pages9 - SOP - Daikin's Solution For Wound Cleaning v2.0Adji KhurniawanNo ratings yet
- Planning Building Rule Amendments NKDA 2021Document4 pagesPlanning Building Rule Amendments NKDA 2021Ankita JainNo ratings yet
- WreDocument12 pagesWrepratik maneNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris Sma BrosurDocument3 pagesBahasa Inggris Sma BrosurSupri HandokoNo ratings yet
- Module V: Stability Analysis of Gravity DamsDocument4 pagesModule V: Stability Analysis of Gravity DamsabshawNo ratings yet
- Conventional and Non-Conventional Energy Sources - Short Essay For Students PDFDocument9 pagesConventional and Non-Conventional Energy Sources - Short Essay For Students PDFsomesh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Property: Duct Bank 600X600Document1 pageProperty: Duct Bank 600X600Byambasuren batbayarNo ratings yet
- VFA FittingsCatalogueDocument164 pagesVFA FittingsCatalogueDimitar KondinskiNo ratings yet
- Hempadur Mastic 45880 (9588000000)Document10 pagesHempadur Mastic 45880 (9588000000)mukeshayoorNo ratings yet
- Oral ProceedingsDocument575 pagesOral ProceedingssubcenterNo ratings yet
- Barton On Sea Case StudyDocument2 pagesBarton On Sea Case StudyBluecephalasNo ratings yet
- Panga SSB Camp QuotationDocument3 pagesPanga SSB Camp QuotationSaptarishi BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Engineering and Environment DrawingDocument95 pagesIrrigation Engineering and Environment DrawingSE3094- Soundarya.SNo ratings yet
Climate Activity Worksheet
Climate Activity Worksheet
Uploaded by
Teddy jeremyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Climate Activity Worksheet
Climate Activity Worksheet
Uploaded by
Teddy jeremyCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|20687926
Climate activity worksheet
Marine Biology (Nova Southeastern University)
Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by teddy jeremy (teddyjeremy8@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|20687926
Name:t_______________________________Date:_____________
Ocean’s Impact on Climate Activity Worksheet
Instructions: While exploring the effects of climate change on glaciers in the Ocean's Impact on Climate
Activity, record your findings below. You will submit your completed activity worksheet.
(30 points possible)
Part One
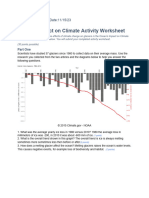
Scientists have studied 37 glaciers since 1980 to collect data on their average mass. Use the
research you collected from the two articles and the diagrams below to help you answer the
following questions.
© 2015 Climate.gov - NOAA
1. What was the average yearly ice loss in 1980 versus 2010? (1 point)
In 1980 the average loss in mm of month was -200, in 2010 it was about -600 mm of
water
2. What is the overall trend shown in this graph? (2 points)
The overall trend is that ice is continuously melting, some years more than others.
3. How does a melting glacier affect the ocean? (2 points)
Melting glaciers can raise the ocean’s water levels and disrupt currents. This can cause
a whole series of negative events, such as loss of biodiversity and habitat.
© 2015 NASA.gov
4. Looking at the heat circulation in the ocean, what might happen to it if large amounts of cold
water are added in the Polar Regions as glaciers melt? (3 points)
If large amounts of cold water are added into the Polar regions as glaciers, it could
disrupt and slow down the ocean’s circulation . This could lead to abrupt climate change
and disruptions in the marine food web.
5. Based on your response above, what effect could this have on the climate in your area? (2
points)
This could cause the climate around me to suffer, it would most likely cause an increase in the
green house effect and global warming. Meaning the temperatures around me, and globally
would increase. There would be more intense storms and disruption in weather patterns.
Part Two
Complete the inquiry chart below by exploring each question in the top row. First, fill in what you
think about each question. Then use the lesson and reliable sources to research more about
each question. Next, fill in each box with evidence from your sources, and be sure to list the
source you used. Finally, pull the ideas together in a short summary on the bottom row. (20
points)
Downloaded by teddy jeremy (teddyjeremy8@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|20687926
Inquiry How does solar How do the How does How does
Chart radiation affect ocean climate climate
climate? currents change affect change affect
affect the ocean? the
climate? biodiversity of
marine
ecosystems?
What I think Solar radiation Ocean Can cause Can cause an
is responsible currents can fresh water imbalance in
for the Earth affect the glaciers to the marine
warming up, weather melt, food web,
and increased patterns, increased sea changes in
overall intensity of levels, and the
temperatures storms, decreed environment
on Earth. temperature marine will cause
s, and biodiversity. species to
heavier die, and
winds. maladaptation
will cause
species to
die.
Source 1 Imbalance Without Climate Rapidly
between currents change can warming
incoming solar global cause coral ocean
radiation and temperature bleaching, temperatures
outgoing s would be fish migration, would cause
thermal more loss of many species
radiation will extreme, species, to relocate,
likely cause being very ocean while those
Earth to heat hot at the acidification, that cannot
up, and melt equator and higher sea would face
polar ice caps. cold toward levels, extinction,
https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/F
eatures/SORCE/sorce_04.php the poles. increased disrupting the
Much of temperatures. entire food
https://www.epa.gov/climate-in
Earth would dicators/oceans chain.
https://phys.org/news/2015-08-
be climate-impacts-marine-biodive
rsity.html
inhabitable.
https://oceanexplorer.noaa.g
ov/facts/climate.html
Source 2 Earth’s climate The ocean’s Temperature Higher acidity
depends on the global increase in levels in the
balance circulation the ocean are ocean will,
between system plays leading to fish cause species
incoming a key role in stocks moving to die off and
radiation and distributing north to relocate, coral
out coming heat energy, cooler waters, bleaching will
thermal regulating the acidity of happen,
radiation. The weather and the ocean has leaving
imbalance will climate, and increased, species
cause Earth to cycling vital without
and fishes are
heat up, melting nutrients and shelter.
affected by https://www.science.org.au/curi
ice caps, rising gasses, ous/earth-environment/climate-
Downloaded by teddy jeremy (teddyjeremy8@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|20687926
https://www.nationalgeograp change-and-biodiversity
sea levels, hic.org/media/ocean-current the increase
violent climate s-and-climate/ in
patterns. acidity.http://climefish.e
https://www.nasa.gov/centers/godd u/how-climate-change-affect-th
ard/news/topstory/2008/solar_varia e-ocean/
bility.html
Source 3 Ice exposed at The The ocean There is an
the Earth’s displaced absorbs CO2 increased risk
surface absorb warm water from the of species
more incoming raises the atmosphere extinction.
solar radiation temperature and the CO2 Warmer
and release the of the air reacts with seawater,
heat into the while the seawater, rising sea
atmosphere, cold water increasing the levels, and
causing more cools the air, ocean’s increased
global warming. and the land acidity. Higher acidity will
https://scied.ucar.edu/longco
ntent/climate-and-ice where the acidity is cause species
wind blows. harmful to to die.
https://www.worldatlas. https://sanctuaries.noaa.gov/ne
com/articles/how-do-oc coral and ws/features/0609_changingclim
ate.html
ean-currents-affect-clim
ate.html
other
marinehttps://www.nati
onalgeographic.org/media/ocea
n-impacts-climate-change/life
Summary Solar radiation Ocean Oceans are Marine
causes polar currents can becoming species will
ice caps to cause the more acidic die, leave, or
melt, increased climate to and warmer, become
global face very this is causing extinct as sea
temperatures, extreme species to levels rise,
raised sea temperature die, marine water
levels, and s. It also life to leave, temperature
more global makes the and coral become
warming. temperature dying. warmer, and
of the ocean acidity levels
in areas increase.
unstable.
Downloaded by teddy jeremy (teddyjeremy8@gmail.com)
You might also like
- LEED GA V4 Practise Exam (40 Q)Document10 pagesLEED GA V4 Practise Exam (40 Q)Aneesha MuthurajNo ratings yet
- Raft FoundationsDocument26 pagesRaft FoundationsSanjana Bhandiwad100% (3)
- Effects of Climate Change What Does It Mean? How Is This Caused by Climate Change? What Are The Consequences?Document3 pagesEffects of Climate Change What Does It Mean? How Is This Caused by Climate Change? What Are The Consequences?Reymark Alciso EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Cibse Swimming PoolpdfDocument13 pagesCibse Swimming PoolpdfBao Loc DuongNo ratings yet
- Ocean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Part OneDocument4 pagesOcean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Part OneSiyeon CrewsNo ratings yet
- Bella Marine Biology 205 PDF FreeDocument3 pagesBella Marine Biology 205 PDF FreeduhhhNo ratings yet
- Ocean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Part OneDocument3 pagesOcean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Part OneAaron CoxNo ratings yet
- Climate Activity WorksheetDocument3 pagesClimate Activity Worksheetseanj1756No ratings yet
- Ocean's Impact On Climate Activity WorksheetDocument5 pagesOcean's Impact On Climate Activity WorksheetTrinity GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Climate Activity Worksheet (Pumiphat)Document5 pagesClimate Activity Worksheet (Pumiphat)Pumiphat SukkhoNo ratings yet
- Ocean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Part OneDocument6 pagesOcean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Part OneColtonTvNo ratings yet
- Blue Lined Climate Change Environment InfographicDocument1 pageBlue Lined Climate Change Environment InfographicGem CarmelNo ratings yet
- Climate Change EcosystemsDocument2 pagesClimate Change EcosystemsvizzeNo ratings yet
- CC 10Document3 pagesCC 10api-323888481No ratings yet
- Roes Sig 2004Document25 pagesRoes Sig 2004Mohammad LakNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Climate Change On Aquaculture: DR - Soheila Khoshnevis Yazdi and DR - Bahram ShakouriDocument5 pagesThe Effects of Climate Change On Aquaculture: DR - Soheila Khoshnevis Yazdi and DR - Bahram ShakouriHASSAN AKHTARNo ratings yet
- Triptico Global WarmingDocument2 pagesTriptico Global WarmingAna Silvia Garza100% (1)
- Before and After The Deluge: Rain-On-Snow Flooding Effects On Aquatic Invertebrate Communities of Small Streams in The Sierra Nevada, CaliforniaDocument14 pagesBefore and After The Deluge: Rain-On-Snow Flooding Effects On Aquatic Invertebrate Communities of Small Streams in The Sierra Nevada, CaliforniavalentinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 19Document8 pagesLesson 19maureensolano63No ratings yet
- Performance Check 1 - Earth ScienceDocument2 pagesPerformance Check 1 - Earth Scienceyuuna yuunaNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument1 pageGlobal WarmingDayu Btarismari 12No ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument1 pageGlobal WarmingDayu Btarismari 12No ratings yet
- The Day After Tomorrow: Konrad F 43 Florczak@Document4 pagesThe Day After Tomorrow: Konrad F 43 Florczak@Jaija J JayanNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Module 4Document2 pagesClimate Change Module 4Belle MendozaNo ratings yet
- To Be Sustained by The Sea, We Must Sustain The Sea : BstractDocument26 pagesTo Be Sustained by The Sea, We Must Sustain The Sea : BstractguptaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Animal Ecology - 2021 - Osgood - Effects of Climate Change Driven Gradual and Acute Temperature Changes On SharkDocument13 pagesJournal of Animal Ecology - 2021 - Osgood - Effects of Climate Change Driven Gradual and Acute Temperature Changes On Sharktonkadujmovic4No ratings yet
- Efeitos Alteracao Climatica em Algas MarinhasDocument28 pagesEfeitos Alteracao Climatica em Algas MarinhasGuilherme MedeirosNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Adaptations of Sandy Beach Macrofauna in Face of Climate Change Impacts A Conceptual FrameworkDocument11 pagesBehavioral Adaptations of Sandy Beach Macrofauna in Face of Climate Change Impacts A Conceptual FrameworkNM100% (1)
- Impact Oa To CetaceansDocument8 pagesImpact Oa To CetaceansRahma ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Yajnik Bookreview 2013Document2 pagesYajnik Bookreview 2013kisuyaNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Transforms Coral Reef Assemblages: Nature April 2018Document17 pagesGlobal Warming Transforms Coral Reef Assemblages: Nature April 2018Roberto Hernandez-landaNo ratings yet
- DRRR Unit 3 L1-L3Document4 pagesDRRR Unit 3 L1-L3Mary Rose TuburanNo ratings yet
- Rhoko Quilban 9 - St. AlbertDocument4 pagesRhoko Quilban 9 - St. AlbertJohn Eridog Xcx-World MatelaNo ratings yet
- The Flood ReviewingDocument3 pagesThe Flood ReviewingJangbu SherpaNo ratings yet
- Doubling of Surface Oceanic Meridional Heat TranspDocument11 pagesDoubling of Surface Oceanic Meridional Heat Transpdhruba.climateNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument14 pagesGlobal WarmingSachin KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Formal Final With Track ChangesDocument8 pagesFormal Final With Track Changesapi-620232040No ratings yet
- FactSheets EN PDFDocument12 pagesFactSheets EN PDFJom VillNo ratings yet
- EAS 4300: Introduction To Oceanography, FALL 2009: InstructorsDocument23 pagesEAS 4300: Introduction To Oceanography, FALL 2009: InstructorsPankaj MunjalNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument21 pagesClimate ChangeBishal SarkarNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Marine Heatwaves On Top Predator Distributions Are Variable But PredictableDocument10 pagesImpacts of Marine Heatwaves On Top Predator Distributions Are Variable But PredictableIlfa FinandaNo ratings yet
- USABO Climates, Biomes, EcosystemsDocument11 pagesUSABO Climates, Biomes, EcosystemsEmelyn PagsanjanNo ratings yet
- Gadus MorhuaDocument11 pagesGadus MorhuaThomas LanssensNo ratings yet
- The Global Crisis of Our TimeDocument11 pagesThe Global Crisis of Our TimeJuan Arevalo LetradoNo ratings yet
- The Uncertain Future of The Coasts: Chapter 03Document21 pagesThe Uncertain Future of The Coasts: Chapter 03amandaNo ratings yet
- Causes & Effects of Climate ChangeDocument8 pagesCauses & Effects of Climate ChangeJade DyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Anthropogenic Effects On The OceansDocument31 pagesLecture 11 Anthropogenic Effects On The OceansHarry DouglasNo ratings yet
- Cooling WatersDocument11 pagesCooling WatersmohtashimahmNo ratings yet
- General Climate Change Brochure Print VersionDocument2 pagesGeneral Climate Change Brochure Print VersionsanjuktNo ratings yet
- What's Harming Our OceansDocument5 pagesWhat's Harming Our OceansLia KristermanNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 EcosystemDocument18 pagesUnit 13 EcosystemDevang ParekhNo ratings yet
- Manners FloodplainDevelopmentEl 2007Document22 pagesManners FloodplainDevelopmentEl 2007Luis Fernando Bejar LuksicNo ratings yet
- FormalfinalDocument8 pagesFormalfinalapi-620232040No ratings yet
- The Resilience of Life To Astrophysical Events: David Sloan, Rafael Alves Batista & Abraham LoebDocument5 pagesThe Resilience of Life To Astrophysical Events: David Sloan, Rafael Alves Batista & Abraham Loebদিব্যোদয় ভৌমিকNo ratings yet
- Subsystem InterconnectionDocument1 pageSubsystem Interconnectionkaito kazeNo ratings yet
- DeforestationDocument8 pagesDeforestationgabrieleyannNo ratings yet
- 1985-The Greenhouse Effect and Nature ReservesDocument12 pages1985-The Greenhouse Effect and Nature ReservesMaría Andérez FernándezNo ratings yet
- Li 2014Document15 pagesLi 2014kiansanei14No ratings yet
- WHAT WILL HAPPEN IF THE EARTH MELTS FEW YEARS FROM Now GABRIENTEDocument1 pageWHAT WILL HAPPEN IF THE EARTH MELTS FEW YEARS FROM Now GABRIENTEraprapanianoNo ratings yet
- The Overarching Impacts of Climate Change On Islands With Track ChangesDocument10 pagesThe Overarching Impacts of Climate Change On Islands With Track Changesapi-711083315No ratings yet
- Tectonic Eustasy: Shoreline Changes Submerged Coasts Submergent ShorelineDocument61 pagesTectonic Eustasy: Shoreline Changes Submerged Coasts Submergent ShorelineivanNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Its Effects On Ecosystems, Habitats and BiotaDocument29 pagesClimate Change and Its Effects On Ecosystems, Habitats and BiotaCaptain ChemicalNo ratings yet
- Sudden Spring: Stories of Adaptation in a Climate-Changed SouthFrom EverandSudden Spring: Stories of Adaptation in a Climate-Changed SouthRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Social Media - Affecting For Better or Worse - EditedDocument8 pagesSocial Media - Affecting For Better or Worse - EditedTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- INT 220 Business Brief Course ProjectDocument5 pagesINT 220 Business Brief Course ProjectTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Time To Stop Hooking Up (You Know What You Want) Synthesis Essay - EditedDocument5 pagesTime To Stop Hooking Up (You Know What You Want) Synthesis Essay - EditedTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Seasons of Change Activity WorksheetDocument2 pagesSeasons of Change Activity WorksheetTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Literature Analysis Essay .EditedDocument5 pagesLiterature Analysis Essay .EditedTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Touchstone 3.1.editedDocument5 pagesTouchstone 3.1.editedTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Intervention MappingDocument14 pagesIntervention MappingTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- PPM EN 2005 03 JanczakDocument14 pagesPPM EN 2005 03 JanczakTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- CHSC 5200 - Chapter 8Document13 pagesCHSC 5200 - Chapter 8Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document34 pagesWeek 2Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document33 pagesWeek 5Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- EAE 313 AEC 307 PUBLIC FINANCE fINAL (2) - 1-1-2Document150 pagesEAE 313 AEC 307 PUBLIC FINANCE fINAL (2) - 1-1-2Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Week 3.1Document32 pagesWeek 3.1Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- The Rise and Fall of Oedipus The KingDocument4 pagesThe Rise and Fall of Oedipus The KingTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document30 pagesWeek 1Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document25 pagesWeek 3Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Week 3.2Document21 pagesWeek 3.2Teddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- Checklist of Requirements For Manufacturing Economic Zone ApplicationDocument1 pageChecklist of Requirements For Manufacturing Economic Zone ApplicationRenz Albert TejadillaNo ratings yet
- Environment PDFDocument121 pagesEnvironment PDFas1510No ratings yet
- Mini-Reader: © Gilbert Barrera 2019Document20 pagesMini-Reader: © Gilbert Barrera 2019ghadeer alkhayat100% (1)
- Civil Engineering and Urban Planning: An International Journal (CiVEJ)Document1 pageCivil Engineering and Urban Planning: An International Journal (CiVEJ)Matthew JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Geoarchaeology of The Louisiana Coastal PlainDocument126 pagesGeoarchaeology of The Louisiana Coastal Plainetchplain100% (1)
- Higien and SanitationDocument31 pagesHigien and SanitationyeliNo ratings yet
- FertilizerDocument2 pagesFertilizerRyan DeMayNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Reservoir Water Tightness TestsDocument14 pagesMethod Statement For Reservoir Water Tightness TestsbruNo ratings yet
- Moisture Vapor Transfer Theory: Fabric Objective Measurement Assignment - 3Document19 pagesMoisture Vapor Transfer Theory: Fabric Objective Measurement Assignment - 3NiveditaKumariNo ratings yet
- Eh Risk Assessment Draft 1Document9 pagesEh Risk Assessment Draft 1api-547026973No ratings yet
- Trickling Filter 175Document13 pagesTrickling Filter 175suman subedi100% (1)
- Term Paper 9G 2Document4 pagesTerm Paper 9G 2EnamariNo ratings yet
- p1 r1 ReportDocument11 pagesp1 r1 ReportPravinAlbdusMathewNo ratings yet
- Site AnalysisDocument3 pagesSite AnalysisRohit Sharma0% (1)
- 9 - SOP - Daikin's Solution For Wound Cleaning v2.0Document2 pages9 - SOP - Daikin's Solution For Wound Cleaning v2.0Adji KhurniawanNo ratings yet
- Planning Building Rule Amendments NKDA 2021Document4 pagesPlanning Building Rule Amendments NKDA 2021Ankita JainNo ratings yet
- WreDocument12 pagesWrepratik maneNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris Sma BrosurDocument3 pagesBahasa Inggris Sma BrosurSupri HandokoNo ratings yet
- Module V: Stability Analysis of Gravity DamsDocument4 pagesModule V: Stability Analysis of Gravity DamsabshawNo ratings yet
- Conventional and Non-Conventional Energy Sources - Short Essay For Students PDFDocument9 pagesConventional and Non-Conventional Energy Sources - Short Essay For Students PDFsomesh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Property: Duct Bank 600X600Document1 pageProperty: Duct Bank 600X600Byambasuren batbayarNo ratings yet
- VFA FittingsCatalogueDocument164 pagesVFA FittingsCatalogueDimitar KondinskiNo ratings yet
- Hempadur Mastic 45880 (9588000000)Document10 pagesHempadur Mastic 45880 (9588000000)mukeshayoorNo ratings yet
- Oral ProceedingsDocument575 pagesOral ProceedingssubcenterNo ratings yet
- Barton On Sea Case StudyDocument2 pagesBarton On Sea Case StudyBluecephalasNo ratings yet
- Panga SSB Camp QuotationDocument3 pagesPanga SSB Camp QuotationSaptarishi BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Engineering and Environment DrawingDocument95 pagesIrrigation Engineering and Environment DrawingSE3094- Soundarya.SNo ratings yet