Professional Documents
Culture Documents
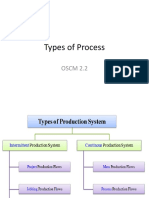
Types of Production Systems
Types of Production Systems
Uploaded by
md saif0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views5 pagesThere are two main types of production systems: intermittent and continuous. Intermittent systems produce goods in small batches based on customer orders and use flexible general purpose machines. Continuous systems constantly produce standardized goods on a large scale based on demand forecasts using specialized equipment. Within these two types are sub-categories like mass production, process production, project production, jobbing production, and batch production which differ in their production flows, scales, flexibility, and other characteristics.
Original Description:
production management unit 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere are two main types of production systems: intermittent and continuous. Intermittent systems produce goods in small batches based on customer orders and use flexible general purpose machines. Continuous systems constantly produce standardized goods on a large scale based on demand forecasts using specialized equipment. Within these two types are sub-categories like mass production, process production, project production, jobbing production, and batch production which differ in their production flows, scales, flexibility, and other characteristics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views5 pagesTypes of Production Systems
Types of Production Systems
Uploaded by
md saifThere are two main types of production systems: intermittent and continuous. Intermittent systems produce goods in small batches based on customer orders and use flexible general purpose machines. Continuous systems constantly produce standardized goods on a large scale based on demand forecasts using specialized equipment. Within these two types are sub-categories like mass production, process production, project production, jobbing production, and batch production which differ in their production flows, scales, flexibility, and other characteristics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
Types of production/manufacturing systems
The types of production system are grouped under two categories
Intermittent production system
Continuous production system.
Intermittent production system
Intermittent means something that starts (initiates) and stops (halts) at
irregular (unfixed) intervals (time gaps).
In the intermittent production system, goods are produced based on
customer's orders. These goods are produced on a small scale. The
flow of production is intermittent (irregular). In other words, the flow
of production is not continuous. In this system, large varieties of
products are produced. These products are of different sizes. The
design of these products goes on changing. It keeps changing
according to the design and size of the product. Therefore, this system
is very flexible.
Examples of Intermittent production system- Goldsmith and
tailor
The characteristics of an intermittent production system are listed
as follows:
The flow of production is not continuous. It is intermittent.
Wide varieties of products are produced.
The volume of production is small.
General purpose machines are used. These machines can be used to
produce different types of products.
The sequence of operation goes on changing as per the design of
the product.
The quantity, size, shape, design, etc. of the product depends on the
customer's orders.
Continuous production system
Continuous means something that operates constantly without any
irregularities or frequent halts.
In the continuous production system, goods are produced constantly
as per demand forecast. Goods are produced on a large scale for
stocking and selling. They are not produced on customer's orders.
Here, the inputs and outputs are standardized along with the
production process and sequence.
Examples of Continuous production system-Food Industry and
Fuel Industry
Characteristics of a continuous production system are listed as
follows:
The flow of production is continuous. It is not intermittent.
The products are standardized.
The products are produced on predetermined quality standards.
The products are produced in anticipation(An expectation) of
demand.
Standardized routing sheets and schedules are prepared
Continuous production can be
1. Mass production flows
2. Process production flows
Mass production flows
Here, company produces different types of products on a
large-scale and stock them in warehouses until they are
demanded in the market.
The goods are produced either with the help of a single
operation or uses a series of operations.
E.g. of mass production is the production of toothpastes,
soaps, pens, etc.
Characteristics mass production flows
There is a continuous flow of production. However, this depends
on the demand in the market.
Here, there is limited work-in-progress.
Supervision is easy because only few instructions are necessary.
The material handling is done mostly by machines, i.e. conveyors
and automatic transfer machines.
The flow of materials is continuous. There is little or no queuing at
any stage of production.
Process production flows
Here, a single product is produced and stocked in warehouses until it
is demanded in the market. The flexibility of these plants is almost
zero because only one product can be produced.
Examples of these plants include, steel, cement, paper, sugar,
etc.
Characteristics process production flows
There is a highly mechanized system for handling materials.
Conveyors and automatic transfer machines are used to move the
materials from one stage to another.
Low-skilled labour and skilled technicians are required.
There is very less work-in-progress because material flow is
continuous.
The production planning and scheduling can be decided well in
advance.
The full production system is designed to produce only one specific
type of item.
Types of an intermittent production system include:
Project production flows
Jobbing production flows
Batch production flows.
Project production flows
Here, in project production flows, company accepts a single,
complex order or contract. The order must be completed within a
given period of time and at an estimated cost.
Examples of project production flows mainly include,
construction of airports, dams, roads, buildings, shipbuilding, etc.
Characteristics project production
The requirement of resources is not same (it varies). Generally, the
resource requirement at the beginning is low. Then in mid of
production, the requirement increases. Finally, it slows down when
the project is near its completion phase.
Many agencies are involved in the project. Each agency performs
specialized jobs. Here, coordination between agencies is important
because all jobs are interrelated.
Delays take place in completion of projects due to its complexity
and massiveness.
As routing and scheduling changes with fresh orders, proper
inspection is required at each stage of production.
Job production
Here, in jobbing production flows, company accepts a contract to
produce either one or few units of a product strictly as per
specifications given by the customer. The product is produced within
a given period and at a fixed cost. This cost is fixed at the time of
signing the contract.
Examples of such jobbing production flows include, services
given by repair shops, tailoring shops, manufacturer of special
machine tools, etc.
Characteristics job production
The production of items takes place in small lots. Sometimes only
one product is produced at one time.
The items are manufactured strictly as per customer's
specifications.
Highly skilled labour is required to perform specialized jobs.
There is disproportionate manufacturing cycle time. For e.g. the
time needed to design the product may be more than the
manufacturing time.
Batch production
In batch production flows, the production schedule is decided
according to specific orders or are based on the demand forecasts.
Here, the production of items takes place in lots or batches. A product
is divided into different jobs. All jobs of one batch of production must
be completed before starting the next batch of production.
Examples of batch production flows include, manufacturing of
drugs and pharmaceuticals, medium and heavy machineries, etc.
Characteristics batch production
The products are made and kept in stock until their demand arises
in the market.
General purpose machines and handling equipments, which can do
many different jobs quickly are installed. This is because large
varieties of items are to be produced.
There is a possibility of large work-in-progress due to many
reasons.
There is a need for detailed production planning and control.
You might also like
- Types of Production SystemsDocument5 pagesTypes of Production Systemsjgkonnully92% (13)
- Bar Business PlanDocument22 pagesBar Business Plansmelissah1100% (2)
- Kedir Accounting ProposalDocument22 pagesKedir Accounting ProposalAhmed92% (13)
- Types of Production SystemDocument6 pagesTypes of Production SystemJyoti NawlaniNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Manufacturing ProcessDocument23 pagesDifferent Types of Manufacturing Processshrutiagarwal9229No ratings yet
- Employee Non Disclosure, Non Solicitation and Non Compete AgreementDocument4 pagesEmployee Non Disclosure, Non Solicitation and Non Compete AgreementkratiNo ratings yet
- Types of Production SystemDocument8 pagesTypes of Production SystemFaisal khanNo ratings yet
- 2.2 OscmTypes of ProcessDocument26 pages2.2 OscmTypes of ProcessSandeep LondheNo ratings yet
- Types of Production SystemsDocument39 pagesTypes of Production Systemsshushantsonwani416No ratings yet
- DT.03.02.2022 Ananta Prasad Nanda Asst - Prof. (Om) Outline: Production System and TypesDocument17 pagesDT.03.02.2022 Ananta Prasad Nanda Asst - Prof. (Om) Outline: Production System and TypesSubham .MNo ratings yet
- Types of Production SystemsDocument15 pagesTypes of Production SystemsAnimesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Types of Production SystemsDocument5 pagesTypes of Production Systemsburhan shahNo ratings yet
- Types of Manufacturing SystemsDocument25 pagesTypes of Manufacturing SystemsAnonymous ZId2RKNo ratings yet
- Types of Production SystemDocument4 pagesTypes of Production SystemDemi DelizoNo ratings yet
- Types of Production SystemDocument6 pagesTypes of Production SystemkshitijNo ratings yet
- Production System in Operations ManagementDocument18 pagesProduction System in Operations ManagementMark Angelo NioscoNo ratings yet
- Production and Operation ManagementDocument41 pagesProduction and Operation ManagementJessamine Romano AplodNo ratings yet
- Types of Production Systems A Production Manager Will Have To Choose TheDocument10 pagesTypes of Production Systems A Production Manager Will Have To Choose TheAfad KhanNo ratings yet
- TQM YoutubeDocument5 pagesTQM YoutubeJacob ManaloNo ratings yet
- Continuous Production SystemDocument7 pagesContinuous Production SystemPooja NagNo ratings yet
- Production Systems BBA 6th Sem 7 12 r93OLsHZSkDocument21 pagesProduction Systems BBA 6th Sem 7 12 r93OLsHZSkVISHAL MISHRANo ratings yet
- The Nature of Production: InputDocument9 pagesThe Nature of Production: InputDacia HigginsNo ratings yet
- Types of Production SystemDocument4 pagesTypes of Production SystemHIMANSHU DARGANNo ratings yet
- Continuous Process Project: Types of ProcessesDocument6 pagesContinuous Process Project: Types of ProcessesppiyaaNo ratings yet
- Production ManagementDocument21 pagesProduction ManagementRahul PuriNo ratings yet
- 2nd Chapter OMDocument48 pages2nd Chapter OMmanoj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Om2 TPSDocument21 pagesOm2 TPSharischarmNo ratings yet
- Continuous ProductionDocument4 pagesContinuous ProductionAkanksha Kumari100% (1)
- Unit Ii OmDocument10 pagesUnit Ii OmAtish ArakkaNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument58 pages1 PDFMK ReddyNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT3Document3 pagesASSIGNMENT3Nitheesh vinodNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operation ManagementDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Operation ManagementSwati KatariaNo ratings yet
- Explain Intermittent and Continuous Operations. Under What Type of Situation It Would Be Used in Automobile IndustryDocument25 pagesExplain Intermittent and Continuous Operations. Under What Type of Situation It Would Be Used in Automobile IndustryfrancisNo ratings yet
- Business Functions: Unit 5: Production and Operations Management FunctionDocument25 pagesBusiness Functions: Unit 5: Production and Operations Management Functiongatete samNo ratings yet
- Unit II PMGTDocument15 pagesUnit II PMGTAshish UikeyNo ratings yet
- Form Through Chemical or Mechanical Process To Create or Enhance The Utility of The Product To The User."Document16 pagesForm Through Chemical or Mechanical Process To Create or Enhance The Utility of The Product To The User."Binit Kumar ChhantyalNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Systems - Lesson 2Document27 pagesManufacturing Systems - Lesson 2Atanu MandalNo ratings yet
- Classification of Production SystemDocument7 pagesClassification of Production SystemRahul BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- PoM Unit - 1Document21 pagesPoM Unit - 1Dharani C KNo ratings yet
- PM-Solved Paper 2006Document27 pagesPM-Solved Paper 2006anuragmamgainNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Production SystemsDocument39 pagesLec 1 Production SystemslympazzkarimiNo ratings yet
- Materials and Manufacturing Processes (191001)Document5 pagesMaterials and Manufacturing Processes (191001)Atta ur rehman ManiNo ratings yet
- CH I - Introduction To Opeartion ManagementDocument38 pagesCH I - Introduction To Opeartion ManagementSanjay ThakurNo ratings yet
- Design of Manufacturing ProcessDocument51 pagesDesign of Manufacturing Process2slice.workNo ratings yet
- PPPC Assignment Unit 1Document7 pagesPPPC Assignment Unit 1Rutuja MahindrakarNo ratings yet
- MS I-VDocument41 pagesMS I-VAlisNo ratings yet
- Kritika (21421096)Document9 pagesKritika (21421096)Mohit sharmaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Flow Process ExampleDocument4 pagesContinuous Flow Process ExampleSheena Mae PalaspasNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - POM NewDocument26 pagesUnit 3 - POM NewYogitha GowdaNo ratings yet
- Production Control N Capacity CalDocument23 pagesProduction Control N Capacity CalSHIKHA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Entrepreneurship - Management - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument22 pagesUnit 4 - Entrepreneurship - Management - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRhode MarshallNo ratings yet
- Production Capacity 62584Document16 pagesProduction Capacity 62584temesgen bimrawNo ratings yet
- Plant LayoutDocument6 pagesPlant LayoutMehwish ButtNo ratings yet
- Unit3 PPCDocument7 pagesUnit3 PPCanishvancha0% (1)
- Types of Production ProcessDocument24 pagesTypes of Production ProcessPRIYANK89% (18)
- Questionnaire: GS1 WebsiteDocument6 pagesQuestionnaire: GS1 WebsiteSOHEL BANGINo ratings yet
- Sybba Sem III SCM CHP 2Document62 pagesSybba Sem III SCM CHP 2Snehal BhorkhadeNo ratings yet
- Types of Production SystemsDocument26 pagesTypes of Production Systemsjsofv5533No ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument75 pagesUnit 2 NotesrajeeevaNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 MEE2013 ETH VL2023240101818 2023-07-26 Reference-Material-IDocument21 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 MEE2013 ETH VL2023240101818 2023-07-26 Reference-Material-Ijayfulewar23No ratings yet
- Material Planning and BudgetingDocument17 pagesMaterial Planning and Budgetingedupurpose486375% (4)
- Creating a One-Piece Flow and Production Cell: Just-in-time Production with Toyota’s Single Piece FlowFrom EverandCreating a One-Piece Flow and Production Cell: Just-in-time Production with Toyota’s Single Piece FlowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- How to Create Continuous Production Flow?: Toyota Production System ConceptsFrom EverandHow to Create Continuous Production Flow?: Toyota Production System ConceptsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Product DesignDocument2 pagesProduct Designmd saifNo ratings yet
- Mobile App Based OperationDocument7 pagesMobile App Based Operationmd saifNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Articles SolDocument1 pageAssignment 2 Articles Solmd saifNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Prepostion SolDocument1 pageAssignment 1 Prepostion Solmd saifNo ratings yet
- Dividend Decisions Unit 5Document8 pagesDividend Decisions Unit 5md saifNo ratings yet
- Vedant SDocument1 pageVedant Smd saifNo ratings yet
- Mobile App Based Operation 4Document22 pagesMobile App Based Operation 4md saifNo ratings yet
- Accounting EquationDocument55 pagesAccounting EquationRahul VermaNo ratings yet
- Gross IncomeDocument54 pagesGross IncomeErneylou RanayNo ratings yet
- Policy Surrender / Variable Life Transaction Form: POL - ADMIN-054-0721-1 Page 1 ofDocument2 pagesPolicy Surrender / Variable Life Transaction Form: POL - ADMIN-054-0721-1 Page 1 ofEllalaineJoy AllierNo ratings yet
- Indian Pump IndustryDocument4 pagesIndian Pump IndustryGaurav Bagaria100% (1)
- Economics, and Economic Terminology: BITS PilaniDocument408 pagesEconomics, and Economic Terminology: BITS PilaniModh MahatoNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Dissertation IdeasDocument8 pagesOperations Management Dissertation IdeasCustomPapersUK100% (1)
- Philo John MINOR PROJECTDocument31 pagesPhilo John MINOR PROJECTPhilo JohnNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument18 pagesFinal ExamHarryNo ratings yet
- ABNR-Guide To Doing Business in Indonesia 9Document58 pagesABNR-Guide To Doing Business in Indonesia 9Marisah Ulfah100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Cost Accounting 4th Edition Lanen Solutions Manual DownloadDocument51 pagesFundamentals of Cost Accounting 4th Edition Lanen Solutions Manual DownloadVerna English100% (23)
- Asha Insurance CompanyDocument38 pagesAsha Insurance CompanyKamrul Hasan ShaonNo ratings yet
- Accounting - Is - The - Language - Thread - by - Brianferoldi - May 2, 23 - From - Rattibha PDFDocument18 pagesAccounting - Is - The - Language - Thread - by - Brianferoldi - May 2, 23 - From - Rattibha PDFSantoshNo ratings yet
- Procurement Policy Fair International Trading CorpDocument6 pagesProcurement Policy Fair International Trading CorpinfoNo ratings yet
- Purpose / Reasons of Preparing Departmental Accounts:: Less: Sales Returns/ Returns InwardsDocument1 pagePurpose / Reasons of Preparing Departmental Accounts:: Less: Sales Returns/ Returns InwardsTan Shu YuinNo ratings yet
- Customer Receipt: Being Amount Paid For On Just DialDocument2 pagesCustomer Receipt: Being Amount Paid For On Just DialSurinder GhattauraNo ratings yet
- World Economic Forum - Annual Report 2002/2003Document40 pagesWorld Economic Forum - Annual Report 2002/2003World Economic Forum100% (12)
- Buying Your First Home in Jacksonville, FL A Comprehensive Guide For Homebuyers For The First TimeDocument5 pagesBuying Your First Home in Jacksonville, FL A Comprehensive Guide For Homebuyers For The First Timekumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Executive Summry of AmwayDocument45 pagesExecutive Summry of AmwaySwapnil Sonawane0% (1)
- Behavioral FinanceDocument5 pagesBehavioral FinancemanojeethNo ratings yet
- Treasury Accountant - Job PostDocument1 pageTreasury Accountant - Job PostKhaled HelmyNo ratings yet
- Lüdeke-Freund Et Al - 2018 - Circular Economy Business Model PatternsDocument27 pagesLüdeke-Freund Et Al - 2018 - Circular Economy Business Model PatternsSWAPNIL BHOYENo ratings yet
- ABM MCQ Test Sept 2021Document7 pagesABM MCQ Test Sept 2021Shyam PatelNo ratings yet
- Resume 1677970930438Document1 pageResume 1677970930438sesan jonasNo ratings yet
- Singapore Airlines-Case Discussion: Kharthik Narayanan, Somyadeep Mandal, Monica, Sheryn Samson, Parul, LakshmipriyaDocument9 pagesSingapore Airlines-Case Discussion: Kharthik Narayanan, Somyadeep Mandal, Monica, Sheryn Samson, Parul, LakshmipriyaKharthik NarayananNo ratings yet
- Fractional Reserve Banking - Nov29 PDFDocument19 pagesFractional Reserve Banking - Nov29 PDFArrow &Co.No ratings yet
- Illustrative Examples 9Document3 pagesIllustrative Examples 9Banjo A. ReyesNo ratings yet
- Strategic Change ManagementDocument20 pagesStrategic Change ManagementAkhtar Ali100% (5)