Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem Lec Prefinal Ass 2
Chem Lec Prefinal Ass 2
Uploaded by
joevic torrecampoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chem Lec Prefinal Ass 2
Chem Lec Prefinal Ass 2
Uploaded by
joevic torrecampoCopyright:
Available Formats
Punay, Christian Roanthony R.
CHEM 1
MWF 12:00PM-1:00PM
Define the following term:
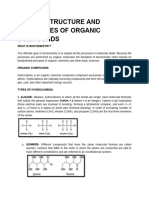
Organic Chemistry- is the study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and
preparation of carbon-containing compounds. Most organic compounds contain carbon and
hydrogen, but they may also include any number of other elements (e.g., nitrogen, oxygen,
halogens, phosphorus, silicon, sulfur).
Hydrocarbons- is the study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation
of carbon-containing compounds. Most organic compounds contain carbon and hydrogen, but
they may also include any number of other elements (e.g., nitrogen, oxygen, halogens,
phosphorus, silicon, sulfur).
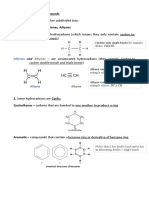
Alkanes- organic compounds that consist entirely of single-bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms
and lack any other functional groups. Alkanes have the general formula CnH2n+2 and can be
subdivided into the following three groups: the linear straight-chain alkanes, branched alkanes,
and cycloalkanes.
Alkenes- a class of hydrocarbons (e.g., containing only carbon and hydrogen) unsaturated
compounds with at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond. Another term used to describe
alkenes is olefins. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes due to the presence of the double
bond.
Alkynes- hydrocarbons which contain carbon-carbon triple bonds. Their general formula is
CnH2n-2 for molecules with one triple bond (and no rings). Alkynes undergo many of the same
reactions as alkenes, but can react twice because of the presence of the two p-bonds in the triple
bond.
Cycloalkanes- are cyclic hydrocarbons, meaning that the carbons of the molecule are arranged in
the form of a ring. Cycloalkanes are also saturated, meaning that all of the carbons atoms that
make up the ring are single bonded to other atoms (no double or triple bonds).
Hybridization- is the idea that atomic orbitals fuse to form newly hybridized orbitals, which in
turn, influences molecular geometry and bonding properties.
Sigma bonds- A stronger than that of Pi Bonds. Sigma bonds are formed first when atoms
interact.
Pi Bonds- Pi bonds are usually weaker compared to sigma bonds. Pi bonds between two atoms
are formed after sigma bonds are formed between them.
You might also like
- Chemistry ProjectDocument6 pagesChemistry ProjectAgnivo SahaNo ratings yet
- CHMDocument12 pagesCHMgabrf.pascualNo ratings yet
- Functional Group ThiolsDocument3 pagesFunctional Group ThiolsPat ChuaNo ratings yet
- Sci Chap 3rDocument6 pagesSci Chap 3rethan elizaldeNo ratings yet
- Organic CompoundsDocument22 pagesOrganic CompoundsMary Rose AguilaNo ratings yet
- Functional GroupsDocument33 pagesFunctional Groupsal.adrienneeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document9 pagesUnit 1Winrich Louise M. MontanoNo ratings yet
- Unit# 2: Basics of Organic Chemistry: by Doc Hira Younas (DPT, Isrs)Document28 pagesUnit# 2: Basics of Organic Chemistry: by Doc Hira Younas (DPT, Isrs)Muaaz Tahir Muaaz TahirNo ratings yet
- Organic Molecules Chemistry Grade 12: Everything Science WWW - Everythingscience.co - ZaDocument16 pagesOrganic Molecules Chemistry Grade 12: Everything Science WWW - Everythingscience.co - ZaAbhi SinghNo ratings yet
- Saturated Hydrocarbons ReviewerDocument15 pagesSaturated Hydrocarbons ReviewerViaBNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document35 pagesUnit 1RV Whatsapp statusNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry LecturesDocument32 pagesOrganic Chemistry LecturesAbdulHameedNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesReviewer For Organic ChemistryJona MaeNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry HandoutDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistry HandoutJason Dis-ag Alejandro IsangNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry-Good NotesDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistry-Good NotesOLIVIERNo ratings yet
- CHEM7-Organic ChemistryDocument30 pagesCHEM7-Organic ChemistryEmily SalibNo ratings yet
- Alkanes, Alkenes, AlkynesDocument7 pagesAlkanes, Alkenes, AlkynesMuhammad Hasnain AliNo ratings yet
- PART-1 - IUPAC Nomenclature of Saturated Hydrocarbons - AlkaneDocument17 pagesPART-1 - IUPAC Nomenclature of Saturated Hydrocarbons - AlkaneSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Organic Chemistry NotesDocument5 pagesGen Chem Organic Chemistry NotesVianneie Dominique BernadasNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument11 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsJulia NithdaleNo ratings yet
- Families of Organic CompoundsDocument8 pagesFamilies of Organic CompoundsJessa Mae LangcuyanNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Gr.1Document71 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes Gr.1HarijaNo ratings yet
- Functional G Chem 15th FebDocument64 pagesFunctional G Chem 15th FebAndrew GordonNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - FundamentalsDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry - FundamentalsMRUDULA HANNA REJINo ratings yet
- Natural Science PrelimDocument26 pagesNatural Science PrelimMew GulfNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Isomerism: It is known that a carbon-carbon double bond is made up of one σ bond and one π-bond. The π-bond presents free rotation about the double bond.ThisDocument3 pagesGeometrical Isomerism: It is known that a carbon-carbon double bond is made up of one σ bond and one π-bond. The π-bond presents free rotation about the double bond.ThisKisha KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Alkanes ChemistryDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Alkanes ChemistryChakalo HapalonNo ratings yet
- Unique Properties of Carbon: (Unbranched Chain)Document7 pagesUnique Properties of Carbon: (Unbranched Chain)mamta2111No ratings yet
- Functional GroupsDocument8 pagesFunctional GroupsMitch Jasdale Mentar QuimotNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compound PDFDocument5 pagesCarbon and Its Compound PDFAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- TopicDocument8 pagesTopicmanu cybercafeNo ratings yet
- V Aro HydrocarbonsDocument15 pagesV Aro HydrocarbonsSnehalata MishraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chem Module 1 NotesDocument144 pagesUnit 2 Chem Module 1 NotesBisham SiewNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument10 pagesHydrocarbonsjoeNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes Chapter 12Document16 pages11 Chemistry Notes Chapter 12avni AroraNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Chem Notes Anil CH 12. Organic Chemistry Some Basic ConceptsDocument19 pagesHsslive Xi Chem Notes Anil CH 12. Organic Chemistry Some Basic ConceptsKrishnendu NairNo ratings yet
- I CH 8 Chemistry Notes by AkDocument20 pagesI CH 8 Chemistry Notes by AkappugmenonNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: 1. Organic Chemistry Is The Study of Carbon CompoundsDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry: 1. Organic Chemistry Is The Study of Carbon Compoundsreadsalot2012No ratings yet
- Carbon PDFDocument46 pagesCarbon PDFRavi LathwalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemsitryDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemsitryRyanNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds Hand-Out For CHEM 2Document11 pagesOrganic Compounds Hand-Out For CHEM 2Rafael SumayaNo ratings yet
- chemistryDocument14 pageschemistrytvishatakkarNo ratings yet
- Goc 1641795035Document30 pagesGoc 1641795035joeNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistryespiritumikhailehayah28No ratings yet
- Topic 11: Organic Chemistry 11.1 Homologous SeriesDocument8 pagesTopic 11: Organic Chemistry 11.1 Homologous SeriesbnNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic CompoundsDocument43 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic CompoundsDarius Gan100% (1)
- Acquaintance With Covalent MoleculesDocument11 pagesAcquaintance With Covalent MoleculesAlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem 2010Document107 pagesOrganic Chem 2010张浩天No ratings yet
- 2.4 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument25 pages2.4 Introduction To Organic ChemistryMin YoonjiNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Docxnotes 1Document4 pagesINTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Docxnotes 1Diane Jane SalomonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry - Lecture 1Document59 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistry - Lecture 1Humayer MahmudNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Chapter 2 63-104Document42 pagesOrganic Chemistry Chapter 2 63-104mortemsondeathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Organi ChemistryDocument5 pagesChapter 12 Organi ChemistryMuhammad TayyabNo ratings yet
- Bonding of Hydrocarbons: Presented by Rina Mae Manceras Benjamin BagayanDocument33 pagesBonding of Hydrocarbons: Presented by Rina Mae Manceras Benjamin BagayanIce BearNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument62 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryytutwNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Functional GroupsDocument59 pagesUnit 2 - Functional GroupsNico MendezNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument3 pagesREVIEWEREmelly PadillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Organic ChemistryDocument43 pagesChapter 22 Organic Chemistryapi-703497157No ratings yet
- BSES26Document7 pagesBSES26jerico.lapurgaNo ratings yet
- AE120 - Unit 3&4Document19 pagesAE120 - Unit 3&4joevic torrecampoNo ratings yet
- 1.measures of Central TendencyDocument19 pages1.measures of Central Tendencyjoevic torrecampoNo ratings yet
- Final Copy Specific Heat Capacity ExperimentDocument3 pagesFinal Copy Specific Heat Capacity Experimentjoevic torrecampoNo ratings yet
- Soap Making (Cold Process)Document3 pagesSoap Making (Cold Process)joevic torrecampoNo ratings yet
- Plate6 Torrecampo-Layout1Document1 pagePlate6 Torrecampo-Layout1joevic torrecampoNo ratings yet
- Lab Apparatus and The Do and Donts (Torrecampo, Joevic)Document2 pagesLab Apparatus and The Do and Donts (Torrecampo, Joevic)joevic torrecampoNo ratings yet
- Ae NotesDocument6 pagesAe Notesjoevic torrecampoNo ratings yet
- Saint Augustine & Rene DescartesDocument13 pagesSaint Augustine & Rene Descartesjoevic torrecampo100% (1)
- HydrocarbonsDocument18 pagesHydrocarbonsjoevic torrecampoNo ratings yet