Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - ANS
(11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - ANS
Uploaded by
sophia yeungCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 03 0580 42 2024 3RP Afp M24 20022024060643Document20 pages03 0580 42 2024 3RP Afp M24 20022024060643nflbubba468No ratings yet
- Cambridge Primary Mathematics Teacher's Resource 5 PDFDocument59 pagesCambridge Primary Mathematics Teacher's Resource 5 PDFykamran78% (36)
- Maths P2 April 2022Document16 pagesMaths P2 April 2022eddie zhou100% (3)
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.8-Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines - CQDocument6 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.8-Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- 3D Geometry & Triangles SolutionsDocument9 pages3D Geometry & Triangles SolutionsLinh (Viso) DoNo ratings yet
- 2022 CTSS EOY Exam - Sec 3 Express Mathematics - Paper 1 SolutionsDocument5 pages2022 CTSS EOY Exam - Sec 3 Express Mathematics - Paper 1 Solutionssuki080811No ratings yet
- (Mai 3.1-3.4) 3d Geometry - Triangles - SolutionsDocument8 pages(Mai 3.1-3.4) 3d Geometry - Triangles - SolutionsJuhi KastiyaNo ratings yet
- 2009 Maths MC SolutionDocument18 pages2009 Maths MC SolutionyshunmingNo ratings yet
- IX Mathematics MS (Annual Exam) 2022-23Document7 pagesIX Mathematics MS (Annual Exam) 2022-23DEBASHISH BHATTACHARYANo ratings yet
- SQP - 1 IX 23-24 MathsDocument6 pagesSQP - 1 IX 23-24 Mathsadhikarigautam696No ratings yet
- 13 August 2021 IIIrd ShiftDocument8 pages13 August 2021 IIIrd ShiftVivalta ModellingNo ratings yet
- HRT-3 For 9thDocument8 pagesHRT-3 For 9thsudhir_kumar_33No ratings yet
- Ss 3 Mathematics First Term ExamDocument7 pagesSs 3 Mathematics First Term ExamElena Salvatore100% (1)
- 2122 - G9 - MA - Term2 - Assessment - Paper - I - Revision Exercise - SolutionsDocument10 pages2122 - G9 - MA - Term2 - Assessment - Paper - I - Revision Exercise - Solutionshuang pok manNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Paper 3 - Solution: SECTION - A (40 Marks) Q. 1Document16 pagesICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Paper 3 - Solution: SECTION - A (40 Marks) Q. 1Niloy SahaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Paper 4 - Solution: SECTION - A (40 Marks) Q. 1Document15 pagesICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Paper 4 - Solution: SECTION - A (40 Marks) Q. 1Niloy SahaNo ratings yet
- 2021-2022 S4 Math Paper 2 SolutionDocument12 pages2021-2022 S4 Math Paper 2 SolutionPascal NgNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: For Pupils Currently in Year 7Document6 pagesMathematics: For Pupils Currently in Year 7Robert Neumark JonesNo ratings yet
- 18 Hkcee Math 2007 Paper 1 Solution OnlyDocument6 pages18 Hkcee Math 2007 Paper 1 Solution OnlyHerrscher of GamezNo ratings yet
- MiniDSE Paper 2 (Set5) - Full Sol - EngDocument8 pagesMiniDSE Paper 2 (Set5) - Full Sol - Engkawai wongNo ratings yet
- Extended Mathematics Exam JUNEDocument12 pagesExtended Mathematics Exam JUNECrystal LynnNo ratings yet
- S2 March Assessment Revision PDF VersionDocument15 pagesS2 March Assessment Revision PDF Versiongw22ahmedeshalNo ratings yet
- Maths BasicnotesDocument12 pagesMaths BasicnotesMoni SharmaNo ratings yet
- CE 412 - Lec 2B DDM Design ExampleDocument39 pagesCE 412 - Lec 2B DDM Design ExampleMuh UmaNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersDocument13 pagesMaths Class X Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersRishika AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper - 22Document7 pagesSample Question Paper - 2293519No ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper - 2 Class-IX Session - 2021-22Document14 pagesSample Question Paper - 2 Class-IX Session - 2021-22Vedang GuptaNo ratings yet
- Area Parallelogram McqsDocument10 pagesArea Parallelogram Mcqstahesin.a.mullaNo ratings yet
- Ace of Pace (Advanced) SolutionDocument10 pagesAce of Pace (Advanced) SolutionAyush ShindeNo ratings yet
- 2E Pasir Ris - P1 - AnswersDocument6 pages2E Pasir Ris - P1 - AnswerstyxgmcomNo ratings yet
- Math Work P2 2Document6 pagesMath Work P2 2yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class X Mathematics Basic 2023-24 Marking SchemeDocument12 pagesCBSE Class X Mathematics Basic 2023-24 Marking SchemeshailajamahadikNo ratings yet
- Math S Ans BasicDocument12 pagesMath S Ans BasicAyushman BeriaNo ratings yet
- DSE 2021 Paper 1 SolutionsDocument9 pagesDSE 2021 Paper 1 SolutionslokNo ratings yet
- Maths Annual ExamDocument6 pagesMaths Annual Examavirajrathi07No ratings yet
- f4 Maths National SchoolsDocument117 pagesf4 Maths National Schoolsalvinsivil63No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/02Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/02shcadministratorNo ratings yet
- D0679MA2 Ans 1Document10 pagesD0679MA2 Ans 1AnantNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper - 2 Class-IX Session - 2021-22Document14 pagesSample Question Paper - 2 Class-IX Session - 2021-22Sahana. S 21752No ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar Math Class 10 Chapter 07 Coordinate GeometryDocument36 pagesNcert Exemplar Math Class 10 Chapter 07 Coordinate Geometryyashagg2008No ratings yet
- MS Set 08Document10 pagesMS Set 08MUHAMMAD MOMINNo ratings yet
- (13-18) 2A-Ch.1-Rate - Ratio - ANSDocument10 pages(13-18) 2A-Ch.1-Rate - Ratio - ANSpatrickNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 3 KVDocument16 pagesSample Paper 3 KVlinux hack3No ratings yet
- Solution of TrianglesDocument10 pagesSolution of TrianglesMohd Harris100% (1)
- MAA SL 3.1-3.3 3D GEOMETRY - TRIANGLES - SolutionsDocument12 pagesMAA SL 3.1-3.3 3D GEOMETRY - TRIANGLES - Solutionseddy.etameNo ratings yet
- 13 Hkcee Math 2002 Paper 1 Solution OnlyDocument8 pages13 Hkcee Math 2002 Paper 1 Solution OnlyABCLOLNo ratings yet
- MS Set 11Document5 pagesMS Set 11MUHAMMAD MOMINNo ratings yet
- Test of MathDocument13 pagesTest of Mathdixitkavita02No ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar Math Class 09 Chapter 12 Herons FormulaDocument19 pagesNcert Exemplar Math Class 09 Chapter 12 Herons FormulaPRANAT JAIN VII DNo ratings yet
- SetA - 10 - Maths Basic Marking SchemeDocument10 pagesSetA - 10 - Maths Basic Marking SchemesamarthbadoniyaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics PQMSDocument22 pagesMathematics PQMSHans rajNo ratings yet
- Quiz (1-11) WA PQRSDocument7 pagesQuiz (1-11) WA PQRSRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-05 at 2.50.12 PMDocument4 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-05 at 2.50.12 PMronghui009No ratings yet
- Nsejs Geometry Sa1Document6 pagesNsejs Geometry Sa1Daksh Bhardwaj VIII-A Roll No 2No ratings yet
- f4 Solution of TrianglesDocument0 pagesf4 Solution of TrianglesvioletgohNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Sep 08, 2021Document5 pagesAdobe Scan Sep 08, 2021madhavgovind9cNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry II Solution / Answer of Conventional Questions: 1. (08-09 Final Exam) Method IDocument5 pagesTrigonometry II Solution / Answer of Conventional Questions: 1. (08-09 Final Exam) Method IEvanna ChungNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Nov 2000 Paper 5Document3 pagesEdexcel Nov 2000 Paper 5Varun PanickerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSEDocument8 pagesCambridge IGCSEZacarias LaricohuallpaNo ratings yet
- TERM END ASSESSMENT II Answer KeyDocument6 pagesTERM END ASSESSMENT II Answer KeyShipra AroraNo ratings yet
- 04 Dse Math 2014 Paper 1 Solution OnlyDocument7 pages04 Dse Math 2014 Paper 1 Solution OnlyHerrscher of GamezNo ratings yet
- MiniDSE Paper 2 (Set 4) - Full Sol - EngDocument9 pagesMiniDSE Paper 2 (Set 4) - Full Sol - Engkawai wongNo ratings yet
- 9 Matematika UzbDocument2 pages9 Matematika UzbNancy Nancy111No ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - MCDocument7 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (14-19) 3B-Ch.11-Measures of Central Tendency - MCDocument4 pages(14-19) 3B-Ch.11-Measures of Central Tendency - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - CQDocument10 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.9-Trigonometric Relations - CQDocument3 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.9-Trigonometric Relations - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.8-Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines - MCDocument8 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.8-Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.8-Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines - ANSDocument12 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.8-Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines - ANSsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.9-Trigonometric Relations - MCDocument4 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.9-Trigonometric Relations - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.9-Trigonometric Relations - AnsDocument8 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.9-Trigonometric Relations - Anssophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.10-Applications of Trigonometry - CQDocument2 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.10-Applications of Trigonometry - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.11-Introduction To Probability - CQDocument3 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.11-Introduction To Probability - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.10-Applications of Trigonometry - MCDocument3 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.10-Applications of Trigonometry - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.10-Applications of Trigonometry - ANSDocument4 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.10-Applications of Trigonometry - ANSsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 1A-Ch.1-Directed Numbers - The Number Line - MCDocument4 pages(11-16) 1A-Ch.1-Directed Numbers - The Number Line - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.11-Introduction To Probability - AnsDocument3 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.11-Introduction To Probability - Anssophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (12-17) 1A-Ch.2-Introduction To Algebra - MCDocument7 pages(12-17) 1A-Ch.2-Introduction To Algebra - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.11-Introduction To Probability - MCDocument3 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.11-Introduction To Probability - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 1A-Ch.3-Algebraic Equations in 1 Unknown - CQDocument2 pages(11-16) 1A-Ch.3-Algebraic Equations in 1 Unknown - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (12-17) 1A-Ch.2-Introduction To Algebra - CQDocument4 pages(12-17) 1A-Ch.2-Introduction To Algebra - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 1A-Ch.3-Algebraic Equations in 1 Unknown - MCDocument4 pages(11-16) 1A-Ch.3-Algebraic Equations in 1 Unknown - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 1A-Ch.1-Directed Numbers - The Number Line - CQDocument4 pages(11-16) 1A-Ch.1-Directed Numbers - The Number Line - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (12-17) 1A-Ch.2-Introduction To Algebra - ANSDocument5 pages(12-17) 1A-Ch.2-Introduction To Algebra - ANSsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 1A-Ch.1-Directed Numbers - The Number Line - ANSDocument6 pages(11-16) 1A-Ch.1-Directed Numbers - The Number Line - ANSsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 1A-Ch.3-Algebraic Equations in 1 Unknown - ANSDocument6 pages(11-16) 1A-Ch.3-Algebraic Equations in 1 Unknown - ANSsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 1A-Ch.0-Basic Mathematics - MCDocument5 pages(11-16) 1A-Ch.0-Basic Mathematics - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- EXAMHJA123Document18 pagesEXAMHJA123Fady MagedNo ratings yet
- Math - 7th Grade Teaching NotesDocument16 pagesMath - 7th Grade Teaching NotesPara ParadiseNo ratings yet
- The Dynamic Response of Tyres To Brake Torque Variations and Road Unevennesses PDFDocument316 pagesThe Dynamic Response of Tyres To Brake Torque Variations and Road Unevennesses PDFgpdwp100% (1)
- Year 10 Baseline Test Maths Higher CalculatorDocument8 pagesYear 10 Baseline Test Maths Higher CalculatorJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Paper 0580/11 Paper 11 (Core)Document70 pagesMathematics: Paper 0580/11 Paper 11 (Core)Laiba HassanNo ratings yet
- Solved CAT 2008 Paper With SolutionsDocument52 pagesSolved CAT 2008 Paper With SolutionsRohit GargNo ratings yet
- 3001 AssessmentsDocument52 pages3001 Assessmentsadnanarif929No ratings yet
- CAT Sample Paper 2Document35 pagesCAT Sample Paper 2Rudra DesaiNo ratings yet
- 9th Question PaperDocument5 pages9th Question Paperhi byeNo ratings yet
- LP Circumference of A CircleDocument3 pagesLP Circumference of A CirclePeter O. Goyena100% (1)
- Ilearn - 1A - AERIAL PHOTODocument24 pagesIlearn - 1A - AERIAL PHOTOflwrxoxoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument24 pagesCambridge Ordinary LevelGamerUltimate GamingNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument18 pagesGeometryicynitrogen9087No ratings yet
- JC Mathematics 2018-2020 PDFDocument28 pagesJC Mathematics 2018-2020 PDFLindela M Buz-BèéNo ratings yet
- Volume of Irregular Shaped SolidsDocument18 pagesVolume of Irregular Shaped SolidsmalarNo ratings yet
- Plane Geometry Quiz S2023Document14 pagesPlane Geometry Quiz S2023Angelo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Mathematics Grade 12Document20 pagesDokumen - Tips Mathematics Grade 12justinchilunsaNo ratings yet
- Surface and Volume Integrals: Study GuideDocument35 pagesSurface and Volume Integrals: Study GuideAkshay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Math5 - Q4 - Module6 - Finding The Volume of A Given Cube and Rectangular Prism Using Cu. CM and Cu. MDocument20 pagesMath5 - Q4 - Module6 - Finding The Volume of A Given Cube and Rectangular Prism Using Cu. CM and Cu. MEric D. ValleNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Irregular Structures Under Earthquake Loads Analysis of Irregular Structures Under Earthquake LoadsDocument14 pagesAnalysis of Irregular Structures Under Earthquake Loads Analysis of Irregular Structures Under Earthquake LoadsAnis ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- IMC GeometryDocument8 pagesIMC GeometryV HNo ratings yet
- SPM Mock ExamDocument10 pagesSPM Mock ExamNarendrn KanaesonNo ratings yet
- Matematik Latihan Masa Cuti Tingkatan Lima Set 1: BC Ad A C B DDocument23 pagesMatematik Latihan Masa Cuti Tingkatan Lima Set 1: BC Ad A C B DEmylia LiyanaNo ratings yet
- Math1 2017Document121 pagesMath1 2017Cathy AngNo ratings yet
- AltitudeDocument18 pagesAltitudeMichael AlvarezNo ratings yet
- My Project On CONSTRUCTION OF SHAPES USING CURVESDocument56 pagesMy Project On CONSTRUCTION OF SHAPES USING CURVESIram KhanNo ratings yet
(11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - ANS
(11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - ANS
Uploaded by
sophia yeungOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - ANS
(11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - ANS
Uploaded by
sophia yeungCopyright:
Available Formats
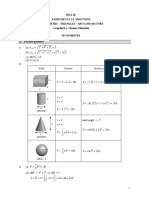
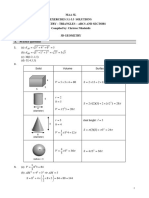
Ch.
07 Areas & Volumes GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions Page 1 of 13
Areas & Volumes
Solutions / Answers of Conventional Questions
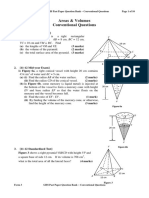
1. [11-12 Mid-year Exam]
(a) MC = 12 ÷ 2 = 6 (cm)
In VCM,
VM 10 2 6 2
= 8 (cm)
ME = 8 ÷ 2 = 4 (cm)
In VEM,
VE 8 2 4 2
48 or ≈ 6.9282
4 3 (cm) or 6.93 (cm), cor. to 3 sig. fig.
(b) Vol. of the pyramid
1
3
(12)(8) 48
≈ 222 (cm3) or 128 3 (cm 3 )
(c) Draw VP AB at P OR “Refer to the fig.”
AP = 8 ÷ 2 = 4 (cm)
In VAP,
VP VA2 AP 2
102 42
84 (cm) or 2 21 (cm) or 9.1652 (cm)
Area of VAB
1
2
8 84 4 84 (cm 2 )
or 8 21 (cm 2 ) or 36.661 (cm2)
Area of VBC
1
128 48 (cm 2 )
2
Total surface area of the pyramid
8(12) 2 4 84 2(48)
(16 21 192) (cm 2 )
or 265 (cm2), cor. to 3 sig. fig.
Form 3 GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions [鍵入文字]
Ch. 07 Areas & Volumes GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions Page 2 of 13
2. [11-12 Mid-year Exam]
1
(a) (i) ( AB ) 2 (20 5) 45
3
AB2 = 9
AB = 3 cm
(ii) ∵ ABV ~ CDV
AB AV
∴
CD CV
3 20 5
CD 20
CD = 4 cm
(b) (i) EF : EV = CD : CV
= 4 : 20
=1:5
(ii) Vol. of the mercury cone
1
(4) 2 (20) 45
3
2
106 45
3
2
61
3
185
(cm ) OR 193.73 (cm )
3 3
3
Let EV = h cm.
h
EF
5
2
1 h 185
h
3 5 3
h3
185
25
h = 16.7, cor. to 3 sig. fig.
∴ The height of the mercury cone is 16.7 cm.
Form 3 GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions [鍵入文字]
Ch. 07 Areas & Volumes GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions Page 3 of 13
3. [11-12 Standardized Test]
1
(12) 2 (VP ) 768
3
VP = 16 (cm)
Draw PQ BC (or VQ BC) at Q and join VQ.
VPQ = 90o
VQ VP 2 PQ 2
2
12
162
2
292 (cm) or 2 73 (cm)
∴ The total area of all lateral faces
1
2
12 292 4
= 410 (cm2), cor. to 3 sig. fig.
OR 48 73 (cm 2 )
4. [10-11 Standardized Test]
(a) x : y : z = h : (h + 2h) : (h + 2h + 3h)
=1:3:6
(b) Curved surface area of A : (A + B) : (A + B + C)
= 12 : 32 : 62
= 1 : 9 : 36
= 10 cm2 : (A + B) cm2 : (A + B + C) cm2
∴ Curved surface area of A + B
= 10 × 9 = 90 (cm2)
Curved surface area of A + B + C
= 10 × 36
= 360 (cm2)
Curved surface area of part C
= 360 – 90 = 270 (cm2)
y 3h 1
(c)
z 6h 2
z = 2y
2 3 1 2 1
y z (6h) y 2 (3h)
3 3 3
2 y 3 (2 y) 2 (6h) y 2 (3h)
2 y 3 24 y 2 h 3 y 2 h
2 y 3 21y 2 h
2y
h
21
Form 3 GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions [鍵入文字]
Ch. 07 Areas & Volumes GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions Page 4 of 13
5. [12-13 Standardized Test2 #2]
(a) Method 1:
2 9 2 3
360
θ 120
Method 2:
92 39
360
θ 120
(b) The volume
3 9 2 32
1 2
3 6 2
80.0 cm 3 (cor. to 3 sig. fig.)
6. [12-13 Standardized Test2 #6]
(a) AB 9
20 16 9
3
AB 20
5
12 cm
(b) AB : EF
=3:5
≠3:4
The two pyramids are not similar.
7. [12-13 Final Exam #13]
5 h
(a)
15 12
h=4
(b) Vol. of the container
1 1
(15 2 )(12) (5 2 )(4) (15 2 )(9)
3 3
1
900 33 2025
3
2
2891 (cm 3 )
3
2800 cm 3
It will not overflow.
Form 3 GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions [鍵入文字]
Ch. 07 Areas & Volumes GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions Page 5 of 13
(c) Let V cm3 be the vol. of the smaller container.
2
2891 3
3 12 4 9
V 16
3
2 17
V 2891
3 16
7573.8 (cm3 )
The volume of oil left is
2800 7573.8
= 1220 (cm3), cor. to 3 sig. fig.
8. [12-13 S6 Mock Exam #5]
(a) Area of the sector VBB’
= (6) 12 2 6 2 = 36 5 cm2
or
253 cm2 (252.8933303 cm2)
(b) BVB'
(12 2 6 2 ) 36 5
360
BVB' 161 (160.9968944)
9. [12-13 S6 Mock Exam #13]
Height of the whole pyramid = 9 cm
Top length of jelly
cm
Vol of space
cm3
Vol of ice-cream
cm3
Since , it will overflow. I
agree
Form 3 GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions [鍵入文字]
Ch. 07 Areas & Volumes GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions Page 6 of 13
10. [12-13 Mid-year exam, 6]
1
(a) AB 2 15 1280
3
AB2 = 256
AB = 16 (cm)
(b) EF = 16 cm ÷ 2 = 8 cm
In VEF,
VF 2 = 152 + 82 = 289
VF = 17 (cm)
Total surface area
= 544 + 256
= 800 (cm2)
11. [13-14 Standardized Test2 #2]
(a) Method 1:
The diameter of each smaller sphere
1
12 3
8
= 6 (cm)
Method 2:
Let V1 cm3 , V2 cm3, d1 cm and d2 cm be the volumes and diameters of the larger and smaller spheres resp.
3
V1 d1
V2 d 2
3
8 12
1 d 2
12 3
82
d2
d2 6
The diameter of each smaller sphere is 6 cm.
Method 3:
Let r cm be the radius of each smaller sphere.
3
4 12 4
8 r3
3 2 3
216 8 r 3
r 3
The diameter of each smaller sphere is
3 cm × 2 = 6 cm.
(b) The volume of the metal sphere
3
4 12
3 2
= 288
905 (cm3)
The volume of the largest pyramid
1
122 12
3
576 (cm3 )
905 cm3
I do not agree with Rachel.
Form 3 GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions [鍵入文字]
Ch. 07 Areas & Volumes GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions Page 7 of 13
12. [13-14 Final Exam, #13]
(a) Let the height of the cone be h cm.
1 5 4 1 4
4 2 h 43 23
3 6 3 2 3
1 40 1
h 128 32
3 3 3
OR 4 4 h 42 2 10 2
9 3 3
40
h 160
3
h = 12
The height of the cone is 12 cm.
(b) Method 1:
Let the radius of the other cone be r cm.
4 1
23 r 2 6
3 3
32 = 6r2
16
r2
3
4
r 2.309
3
12 2 4
But
6 1 2.309
The two cones are not similar
I don’t agree with Mary.
Method 2:
Vol. of the1st cone
Vol. of the 2nd cone
1
(4 2 ) (12)
3
4
(2 3 )
3
6
1
3
But Height of the1st cone 12 8 6
3
Height of the 2nd cone
6 1 1
The two cones are not similar
I don’t agree with Mary.
13. [13-14 S.6 Mock Exam #11]
11(a) Let r cm be the radius of the hemisphere.
Therefore, the radius is cm
Form 3 GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions [鍵入文字]
Ch. 07 Areas & Volumes GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions Page 8 of 13
(b)
Enough
14. [14-15 S.6 Mock Exam #14]
(a) Let r cm and h cm be the base radius and the height of
cone B respectively.
r h 3 8
4 6 1
r 8, h 12
Let k cm be the height of the small cone cut off.
k 1
12 8
k = 1.5
Volume of the required frustum
=
1
3
1
8 2 12 12 1.5
3
= 255.5 cm3
(b) Volume of the smaller frustum
=
1
3
1
4 2 6 12 1.5
3
= 31.5 cm3
Refer to the figure,
Form 3 GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions [鍵入文字]
Ch. 07 Areas & Volumes GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions Page 9 of 13
t cm
s cm
1 cm
4 cm
1 2
3 s 12 t 3 1 1.5 255.5 31.5
1 2
s 12 t
8 12
s 2 12 t 673.5
12 t 1.5s
1.5s 3 673.5
s 3 449
s 3 449
t 12 1.5 3 449
0.514 0.5
Therefore the claim is disagreed.
vol. of sand remaining in the bigger frustum
255.5 31.5
224
224.5 12 t
3
256 12
t 0.514 0.5
Therefore the claim is disagreed.
Form 3 GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions [鍵入文字]
Ch. 07 Areas & Volumes GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions Page 10 of 13
15. [14-15 Standardized Test #8]
(a) Refer to the figure,
VD 12
VD 11.6 20
20VD 12VD 139.2
VD 17.4 (cm)
VA 29 cm
Height of cone VAB = 292 202
= 21(cm)
Height of cone VCD = 17.42 122
= 12.6(cm)
Volume of frustum ABCD
=
1
3
1
3
202 21 122 12.6
= 2195.2 (cm3)
3
Volume of frustum ABCD 11.6 8
(b)
Volume of frustum X 5.8 1
Volume of frustum X = 2195.2 8
= 274.4 (cm3)
(c) Let h cm be the height of two conical covers.
base radius of large cone 20 2
base radius of small cone 10 1
height of large cone h 1
height of small cone h 1
base radius of large cone height of large cone
base radius of small cone height of small cone
The two covers are not similar.
Therefore, P and Q no longer similar.
The claim is disagreed.
Form 3 GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions [鍵入文字]
Ch. 07 Areas & Volumes GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions Page 11 of 13
16. [14-15 Final Exam #13]
13. (a) Volume of red layer = 1 2 2 6
3
8 (cm )
3
--- 1A
1
(b) Let the upper base radius of the blue layer be r1 cm.
r1 15
2 6
r1 5
Volume of blue layer = 1 52 15 8
3
117 (cm3)
3
new volume of jelly 1 1
(c)
125 2 8
either one
125
(cm )
3
New vol. of jelly = correct use
8
of vol. ratio
3
new volume of red jelly 1 1
----1M
8 2 8
New vol. of red jelly = (cm3)
New vol. of blue jelly = 125
8
= 117 (cm )
3
117
Vol. of blue mixture has to prepare = 40
8
585 (cm3)
2
Capacity of the bowl = x3
3
2
x 3 585
3
x 9.57 >9.5
Therefore, the bowl with internal radius 9.5 cm is not enough to prepare the mixture.
Form 3 GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions [鍵入文字]
Ch. 07 Areas & Volumes GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions Page 12 of 13
Method 2:
Vol. of blue mixture has to prepare
= 1 2.52 7.5 1 12 3 40 ---1M (either one)+ 1M
3
3
1838 (cm3)
Capacity of the bowl
= 2 (9.5)3
3
1795 (cm3)
< Volume of blue mixture
Therefore, the bowl with internal radius 9.5
cm is not enough to prepare the
mixture. –1A f.t.
17. [15-16 Mid-year Exam #7]
1
(a) AB 2 VO 512
3
AB 3 512
AB 8 (cm)
(b) Total surface area
= 42 242 8 2 4 82
453 (cm )
2
18. [15-16 Standardized Test #4]
(a)
1 2
3
1 4 1
r 8 r 3 r 2 20
2 3 3
r 6
3
(b) Slant height of the cone 6 2 82
= 10 (cm)
Total surface area of the solid
2 6 20 6 10 2 62
372 (cm 2 )
3
19. [15-16 Final Exam #15]
2 128
(a) Volume of the hemisphere = (4) 3 = (cm3)
3 3
(b) Let the height be h cm and slant height be l cm,
(4)l 6656
6656
(4) 4 2 h 2 6656 42 h2
4
h 2 16 416
h 20
The height is 20 cm.
Form 3 GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions [鍵入文字]
Ch. 07 Areas & Volumes GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions Page 13 of 13
(c) Let the new height be h’ cm,
2
h'
1.04
h
h' 1.04h
Percentage change of height
1.04h h
= 100%
h
1.98%
20. [15-16 Final Exam #20]
Radius of cylinder = r
Radius of the cone = 4r
Height of the cone be 4h
Height of the cylinder = 4h – h = 3h
Original Volume
4r 2 4h
1
3
64r 2 h
3
New volume
64r 2 h
r 2 (3h)
3
55r 2 h
3
Percentage change
55r 2 h 64r 2 h
3 3 100%
64r 2 h
3
= –14.0625%
Areas & Volumes
Answers of Multiple Choice Questions
1 C 2 A 3 B 4 C 5 B
6 C 7 B 8 B 9 C 10 A
11 B 12 D 13 B 14 D 15 C
16 D 17 C 18 D 19 D 20 A
21 C 22 B 23 B 24 C 25 B
26 C 27 C 28 D 29 C 30 B
Form 3 GHS Past Paper Question Bank – Solutions [鍵入文字]
You might also like
- 03 0580 42 2024 3RP Afp M24 20022024060643Document20 pages03 0580 42 2024 3RP Afp M24 20022024060643nflbubba468No ratings yet
- Cambridge Primary Mathematics Teacher's Resource 5 PDFDocument59 pagesCambridge Primary Mathematics Teacher's Resource 5 PDFykamran78% (36)
- Maths P2 April 2022Document16 pagesMaths P2 April 2022eddie zhou100% (3)
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.8-Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines - CQDocument6 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.8-Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- 3D Geometry & Triangles SolutionsDocument9 pages3D Geometry & Triangles SolutionsLinh (Viso) DoNo ratings yet
- 2022 CTSS EOY Exam - Sec 3 Express Mathematics - Paper 1 SolutionsDocument5 pages2022 CTSS EOY Exam - Sec 3 Express Mathematics - Paper 1 Solutionssuki080811No ratings yet
- (Mai 3.1-3.4) 3d Geometry - Triangles - SolutionsDocument8 pages(Mai 3.1-3.4) 3d Geometry - Triangles - SolutionsJuhi KastiyaNo ratings yet
- 2009 Maths MC SolutionDocument18 pages2009 Maths MC SolutionyshunmingNo ratings yet
- IX Mathematics MS (Annual Exam) 2022-23Document7 pagesIX Mathematics MS (Annual Exam) 2022-23DEBASHISH BHATTACHARYANo ratings yet
- SQP - 1 IX 23-24 MathsDocument6 pagesSQP - 1 IX 23-24 Mathsadhikarigautam696No ratings yet
- 13 August 2021 IIIrd ShiftDocument8 pages13 August 2021 IIIrd ShiftVivalta ModellingNo ratings yet
- HRT-3 For 9thDocument8 pagesHRT-3 For 9thsudhir_kumar_33No ratings yet
- Ss 3 Mathematics First Term ExamDocument7 pagesSs 3 Mathematics First Term ExamElena Salvatore100% (1)
- 2122 - G9 - MA - Term2 - Assessment - Paper - I - Revision Exercise - SolutionsDocument10 pages2122 - G9 - MA - Term2 - Assessment - Paper - I - Revision Exercise - Solutionshuang pok manNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Paper 3 - Solution: SECTION - A (40 Marks) Q. 1Document16 pagesICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Paper 3 - Solution: SECTION - A (40 Marks) Q. 1Niloy SahaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Paper 4 - Solution: SECTION - A (40 Marks) Q. 1Document15 pagesICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Paper 4 - Solution: SECTION - A (40 Marks) Q. 1Niloy SahaNo ratings yet
- 2021-2022 S4 Math Paper 2 SolutionDocument12 pages2021-2022 S4 Math Paper 2 SolutionPascal NgNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: For Pupils Currently in Year 7Document6 pagesMathematics: For Pupils Currently in Year 7Robert Neumark JonesNo ratings yet
- 18 Hkcee Math 2007 Paper 1 Solution OnlyDocument6 pages18 Hkcee Math 2007 Paper 1 Solution OnlyHerrscher of GamezNo ratings yet
- MiniDSE Paper 2 (Set5) - Full Sol - EngDocument8 pagesMiniDSE Paper 2 (Set5) - Full Sol - Engkawai wongNo ratings yet
- Extended Mathematics Exam JUNEDocument12 pagesExtended Mathematics Exam JUNECrystal LynnNo ratings yet
- S2 March Assessment Revision PDF VersionDocument15 pagesS2 March Assessment Revision PDF Versiongw22ahmedeshalNo ratings yet
- Maths BasicnotesDocument12 pagesMaths BasicnotesMoni SharmaNo ratings yet
- CE 412 - Lec 2B DDM Design ExampleDocument39 pagesCE 412 - Lec 2B DDM Design ExampleMuh UmaNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersDocument13 pagesMaths Class X Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersRishika AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper - 22Document7 pagesSample Question Paper - 2293519No ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper - 2 Class-IX Session - 2021-22Document14 pagesSample Question Paper - 2 Class-IX Session - 2021-22Vedang GuptaNo ratings yet
- Area Parallelogram McqsDocument10 pagesArea Parallelogram Mcqstahesin.a.mullaNo ratings yet
- Ace of Pace (Advanced) SolutionDocument10 pagesAce of Pace (Advanced) SolutionAyush ShindeNo ratings yet
- 2E Pasir Ris - P1 - AnswersDocument6 pages2E Pasir Ris - P1 - AnswerstyxgmcomNo ratings yet
- Math Work P2 2Document6 pagesMath Work P2 2yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class X Mathematics Basic 2023-24 Marking SchemeDocument12 pagesCBSE Class X Mathematics Basic 2023-24 Marking SchemeshailajamahadikNo ratings yet
- Math S Ans BasicDocument12 pagesMath S Ans BasicAyushman BeriaNo ratings yet
- DSE 2021 Paper 1 SolutionsDocument9 pagesDSE 2021 Paper 1 SolutionslokNo ratings yet
- Maths Annual ExamDocument6 pagesMaths Annual Examavirajrathi07No ratings yet
- f4 Maths National SchoolsDocument117 pagesf4 Maths National Schoolsalvinsivil63No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/02Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/02shcadministratorNo ratings yet
- D0679MA2 Ans 1Document10 pagesD0679MA2 Ans 1AnantNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper - 2 Class-IX Session - 2021-22Document14 pagesSample Question Paper - 2 Class-IX Session - 2021-22Sahana. S 21752No ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar Math Class 10 Chapter 07 Coordinate GeometryDocument36 pagesNcert Exemplar Math Class 10 Chapter 07 Coordinate Geometryyashagg2008No ratings yet
- MS Set 08Document10 pagesMS Set 08MUHAMMAD MOMINNo ratings yet
- (13-18) 2A-Ch.1-Rate - Ratio - ANSDocument10 pages(13-18) 2A-Ch.1-Rate - Ratio - ANSpatrickNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 3 KVDocument16 pagesSample Paper 3 KVlinux hack3No ratings yet
- Solution of TrianglesDocument10 pagesSolution of TrianglesMohd Harris100% (1)
- MAA SL 3.1-3.3 3D GEOMETRY - TRIANGLES - SolutionsDocument12 pagesMAA SL 3.1-3.3 3D GEOMETRY - TRIANGLES - Solutionseddy.etameNo ratings yet
- 13 Hkcee Math 2002 Paper 1 Solution OnlyDocument8 pages13 Hkcee Math 2002 Paper 1 Solution OnlyABCLOLNo ratings yet
- MS Set 11Document5 pagesMS Set 11MUHAMMAD MOMINNo ratings yet
- Test of MathDocument13 pagesTest of Mathdixitkavita02No ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar Math Class 09 Chapter 12 Herons FormulaDocument19 pagesNcert Exemplar Math Class 09 Chapter 12 Herons FormulaPRANAT JAIN VII DNo ratings yet
- SetA - 10 - Maths Basic Marking SchemeDocument10 pagesSetA - 10 - Maths Basic Marking SchemesamarthbadoniyaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics PQMSDocument22 pagesMathematics PQMSHans rajNo ratings yet
- Quiz (1-11) WA PQRSDocument7 pagesQuiz (1-11) WA PQRSRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-05 at 2.50.12 PMDocument4 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-05 at 2.50.12 PMronghui009No ratings yet
- Nsejs Geometry Sa1Document6 pagesNsejs Geometry Sa1Daksh Bhardwaj VIII-A Roll No 2No ratings yet
- f4 Solution of TrianglesDocument0 pagesf4 Solution of TrianglesvioletgohNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Sep 08, 2021Document5 pagesAdobe Scan Sep 08, 2021madhavgovind9cNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry II Solution / Answer of Conventional Questions: 1. (08-09 Final Exam) Method IDocument5 pagesTrigonometry II Solution / Answer of Conventional Questions: 1. (08-09 Final Exam) Method IEvanna ChungNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Nov 2000 Paper 5Document3 pagesEdexcel Nov 2000 Paper 5Varun PanickerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSEDocument8 pagesCambridge IGCSEZacarias LaricohuallpaNo ratings yet
- TERM END ASSESSMENT II Answer KeyDocument6 pagesTERM END ASSESSMENT II Answer KeyShipra AroraNo ratings yet
- 04 Dse Math 2014 Paper 1 Solution OnlyDocument7 pages04 Dse Math 2014 Paper 1 Solution OnlyHerrscher of GamezNo ratings yet
- MiniDSE Paper 2 (Set 4) - Full Sol - EngDocument9 pagesMiniDSE Paper 2 (Set 4) - Full Sol - Engkawai wongNo ratings yet
- 9 Matematika UzbDocument2 pages9 Matematika UzbNancy Nancy111No ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - MCDocument7 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (14-19) 3B-Ch.11-Measures of Central Tendency - MCDocument4 pages(14-19) 3B-Ch.11-Measures of Central Tendency - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - CQDocument10 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.7-Areas - Volumes (III) - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.9-Trigonometric Relations - CQDocument3 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.9-Trigonometric Relations - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.8-Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines - MCDocument8 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.8-Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.8-Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines - ANSDocument12 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.8-Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines - ANSsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.9-Trigonometric Relations - MCDocument4 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.9-Trigonometric Relations - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.9-Trigonometric Relations - AnsDocument8 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.9-Trigonometric Relations - Anssophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.10-Applications of Trigonometry - CQDocument2 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.10-Applications of Trigonometry - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.11-Introduction To Probability - CQDocument3 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.11-Introduction To Probability - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.10-Applications of Trigonometry - MCDocument3 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.10-Applications of Trigonometry - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.10-Applications of Trigonometry - ANSDocument4 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.10-Applications of Trigonometry - ANSsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 1A-Ch.1-Directed Numbers - The Number Line - MCDocument4 pages(11-16) 1A-Ch.1-Directed Numbers - The Number Line - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.11-Introduction To Probability - AnsDocument3 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.11-Introduction To Probability - Anssophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (12-17) 1A-Ch.2-Introduction To Algebra - MCDocument7 pages(12-17) 1A-Ch.2-Introduction To Algebra - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3B-Ch.11-Introduction To Probability - MCDocument3 pages(11-16) 3B-Ch.11-Introduction To Probability - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 1A-Ch.3-Algebraic Equations in 1 Unknown - CQDocument2 pages(11-16) 1A-Ch.3-Algebraic Equations in 1 Unknown - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (12-17) 1A-Ch.2-Introduction To Algebra - CQDocument4 pages(12-17) 1A-Ch.2-Introduction To Algebra - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 1A-Ch.3-Algebraic Equations in 1 Unknown - MCDocument4 pages(11-16) 1A-Ch.3-Algebraic Equations in 1 Unknown - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 1A-Ch.1-Directed Numbers - The Number Line - CQDocument4 pages(11-16) 1A-Ch.1-Directed Numbers - The Number Line - CQsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (12-17) 1A-Ch.2-Introduction To Algebra - ANSDocument5 pages(12-17) 1A-Ch.2-Introduction To Algebra - ANSsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 1A-Ch.1-Directed Numbers - The Number Line - ANSDocument6 pages(11-16) 1A-Ch.1-Directed Numbers - The Number Line - ANSsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 1A-Ch.3-Algebraic Equations in 1 Unknown - ANSDocument6 pages(11-16) 1A-Ch.3-Algebraic Equations in 1 Unknown - ANSsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 1A-Ch.0-Basic Mathematics - MCDocument5 pages(11-16) 1A-Ch.0-Basic Mathematics - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- EXAMHJA123Document18 pagesEXAMHJA123Fady MagedNo ratings yet
- Math - 7th Grade Teaching NotesDocument16 pagesMath - 7th Grade Teaching NotesPara ParadiseNo ratings yet
- The Dynamic Response of Tyres To Brake Torque Variations and Road Unevennesses PDFDocument316 pagesThe Dynamic Response of Tyres To Brake Torque Variations and Road Unevennesses PDFgpdwp100% (1)
- Year 10 Baseline Test Maths Higher CalculatorDocument8 pagesYear 10 Baseline Test Maths Higher CalculatorJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Paper 0580/11 Paper 11 (Core)Document70 pagesMathematics: Paper 0580/11 Paper 11 (Core)Laiba HassanNo ratings yet
- Solved CAT 2008 Paper With SolutionsDocument52 pagesSolved CAT 2008 Paper With SolutionsRohit GargNo ratings yet
- 3001 AssessmentsDocument52 pages3001 Assessmentsadnanarif929No ratings yet
- CAT Sample Paper 2Document35 pagesCAT Sample Paper 2Rudra DesaiNo ratings yet
- 9th Question PaperDocument5 pages9th Question Paperhi byeNo ratings yet
- LP Circumference of A CircleDocument3 pagesLP Circumference of A CirclePeter O. Goyena100% (1)
- Ilearn - 1A - AERIAL PHOTODocument24 pagesIlearn - 1A - AERIAL PHOTOflwrxoxoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument24 pagesCambridge Ordinary LevelGamerUltimate GamingNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument18 pagesGeometryicynitrogen9087No ratings yet
- JC Mathematics 2018-2020 PDFDocument28 pagesJC Mathematics 2018-2020 PDFLindela M Buz-BèéNo ratings yet
- Volume of Irregular Shaped SolidsDocument18 pagesVolume of Irregular Shaped SolidsmalarNo ratings yet
- Plane Geometry Quiz S2023Document14 pagesPlane Geometry Quiz S2023Angelo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Mathematics Grade 12Document20 pagesDokumen - Tips Mathematics Grade 12justinchilunsaNo ratings yet
- Surface and Volume Integrals: Study GuideDocument35 pagesSurface and Volume Integrals: Study GuideAkshay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Math5 - Q4 - Module6 - Finding The Volume of A Given Cube and Rectangular Prism Using Cu. CM and Cu. MDocument20 pagesMath5 - Q4 - Module6 - Finding The Volume of A Given Cube and Rectangular Prism Using Cu. CM and Cu. MEric D. ValleNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Irregular Structures Under Earthquake Loads Analysis of Irregular Structures Under Earthquake LoadsDocument14 pagesAnalysis of Irregular Structures Under Earthquake Loads Analysis of Irregular Structures Under Earthquake LoadsAnis ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- IMC GeometryDocument8 pagesIMC GeometryV HNo ratings yet
- SPM Mock ExamDocument10 pagesSPM Mock ExamNarendrn KanaesonNo ratings yet
- Matematik Latihan Masa Cuti Tingkatan Lima Set 1: BC Ad A C B DDocument23 pagesMatematik Latihan Masa Cuti Tingkatan Lima Set 1: BC Ad A C B DEmylia LiyanaNo ratings yet
- Math1 2017Document121 pagesMath1 2017Cathy AngNo ratings yet
- AltitudeDocument18 pagesAltitudeMichael AlvarezNo ratings yet
- My Project On CONSTRUCTION OF SHAPES USING CURVESDocument56 pagesMy Project On CONSTRUCTION OF SHAPES USING CURVESIram KhanNo ratings yet