Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skoolbeep Saltanalysis 1667820136384
Skoolbeep Saltanalysis 1667820136384
Uploaded by
Thiru EditsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Skoolbeep Saltanalysis 1667820136384
Skoolbeep Saltanalysis 1667820136384
Uploaded by
Thiru EditsCopyright:
Available Formats
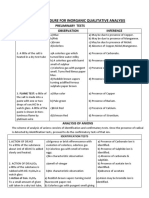
I.
PRELIMINARY TESTS
S. No. EXPERIMENT OBSERVATION INFERENCE
1 SOLUBILITY 1) Soluble 1) May be Sulphate,
Nitrate, Chloride or
A little of the salt is Ammonium
shaken with water. Carbonate.
2) Insoluble 2) May be Carbonate
or Sulphide.
2 ACTION OF HEAT: 1) Colourless, odourless 1) May be Carbonate.
gas turning limewater
A small amount of milky.
the salt is heated
gently in a dry test 2) Decripitation occurs 2) May be Nitrate.
tube. with evolution of
reddish brown gas.
3) Salt sublimes with 3) May be
evolution of pungent Ammonium.
smelling gas giving
dense white fumes with
a glass rod dipped in
conc
HCl.
4) The white salt turns 4) May be Zinc.
yellow on heating.
5) No characteristic 5) Absence of
change. Carbonate, Nitrate,
Ammonium and Zinc.
3 FLAME TEST: 1) Bluish colour flame. 1) Presence of
Copper.
A small amount of 2) Brick red flame. 2) Presence of
the salt is made into Calcium.
a paste with conc.
HCl in a watch glass 3) Grassy green flame. 3) Presence of Barium.
and introduced into
the non-luminous 4) No characteristic 4) Absence of Copper,
part of the Bunsen coloured flame. Calcium and Barium.
flame.
4 ASH TEST: 1) Green ash. 1) Presence of Zinc.
A filter paper is
soaked into a paste of
2) Blue ash. 2) Presence of
the salt with conc.
Aluminium.
HCl and Cobalt
Nitrate solution in a 3) Pink ash. 3) Presence of
watch glass and Magnesium.
burnt. 4) No characteristic 4) Absence of Zinc,
coloured ash. Aluminium and
Magnesium.
II. TESTS FOR ACID RADICALS
5 ACTION OF DIL HCl 1) Brisk effervescence 1) Carbonate is
of colourless, confirmed.
To a small amount of the odourless gas turning
salt dilute HCl is added. lime water milky.
2) Rotten egg smelling 2) Sulphide is
gas turning lead confirmed.
acetate paper black.
3) No characteristic 3) Absence of
change. Sulphide /
Carbonate.
6 COPPER TURNINGS 1) Reddish brown gas 1) Presence of
TEST: is evolved. Nitrate.
A small amount of the salt
is heated with Copper
Turnings and a few drops
of conc. Sulphuric acid.
2) No reddish brown 2) Absence of
gas is evolved. Nitrate.
7 CHROMYL CHLORIDE 1) Red orange vapours 1) Chloride is
TEST: evolved are passed confirmed.
through water to get a
To a small amount of the yellow solution, which
substance a pinch of on adding lead acetate
Potassium Dichromate is forms a yellow
added and heated with few precipitate.
drops of conc. Sulphuric
acid.
2) No Red orange 2) Absence of
vapours. chloride.
1) Pungent smelling 1) Presence of
gas forming dense Ammonium.
white fumes with a
glass rod dipped in
conc. HCl and also
turns litmus paper
blue.
2) No pungent 2) Absence of
smelling gas. Ammonium.
8 ACTION OF NaOH: 1) Pungent smelling 1) Presence of
gas forming dense Ammonium.
A small amount of the white fumes with a
substance is heated with glass rod dipped in
Sodium Hydroxide. conc. HCl and also
turns litmus paper
blue.
2) No pungent 2) Absence of
smelling gas. Ammonium.
III. TESTS WITH SODIUM CARBONATE EXTRACT
9. PREPARATION OF SODIUM CARBONATE EXTRACT:
A small amount of salt is mixed with twice the amount of sodium carbonate and 20ml of
distilled water is added, boiled for 10 minutes, cooled and filtered. The filtrate is called
“SODIUM CARBONATE EXTRACT”.
S. EXPERIMENT OBSERVATION INFERENCE
No
10 BARIUM CHLORIDE 1) A white precipitate, 1) Sulphate is
TEST: insoluble in conc. HCl. confirmed.
To a few drops of the
extract, dilute 2) No white 2) Absence of
Hydrochloric Acid is precipitate. Sulphate
added until the
effervescence ceases and
2ml of Barium chloride
solution is added.
11 SILVER NITRATE 1) A curdy white 1) Presence of
TEST: precipitate, soluble in Chloride.
excess of ammonium
To a few drops of the hydroxide.
extract dilute Nitric Acid
is added until the
effervescence ceases and
2ml of Silver Nitrate 2) A black precipitate. 2) Presence of
solution is added. Sulphide.
3) No precipitate. 3) Absence of
chloride/ sulphide.
12 BROWN RING TEST: 1) Brown ring is 1) Nitrate is
formed at the junction confirmed.
To a few drops of extract of the two layers.
dilute Sulphuric acid is
added until the
effervescence ceases, then
freshly prepared.
2) No brown ring. 2) Absence of
Nitrate.
IV .IDENTIFICATION OF THE BASIC RADICALS
13. PREPARATION OF ORIGINAL SOLUTION:
The original solution is prepared by dissolving the salt in
# Water (When the salt is water soluble)
# Dil. HCl (When the salt is water insoluble)
# Hot mixture of dil. HCl + dil. HNO3 (When the salt is sulphide)
14. GROUP IDENTIFICATION
S. EXPERIMENT OBSERVATION INFERENCE
No
1 To a few drops of the 1) White precipitate. 1) Presence of First
original solution 2ml of Group. (Pb).
dilute HCl acid is added.
2) No characteristic 2) Absence of First
precipitate. Group (Pb).
2 To a few drops of the 1) Black precipitate. 1) Presence of Second
original solution 2ml of Group (Cu).
dilute HCl acid and H2S
gas is passed. 2) No characteristic 2) Absence of Second
precipitate. Group (Cu).
3 To a few drops of the 1) Gelatinous white 1) Presence of Third
original solution 1ml precipitate. Group (Al / Fe).
NH4Cl and 2ml NH4OH
solutions are added. 2) No characteristic 2) Absence of Third
precipitate. Group (Al / Fe).
4 To a few drops of the 1) Dirty white 1) Presence of Fourth
original solution 1ml precipitate. Group Zn,Mn.
NH4Cl and 2ml NH4OH
solutions are added and 2) No characteristic 2) Absence of Fourth
H2S gas is passed. precipitate. Group Zn,Mn.
5 To a few drops of the 1) White precipitate. 1) Presence of Fifth
original solution 1ml Group (Ca / Ba).
NH4Cl, 2ml NH4OH and
2ml (NH4)2CO3 solutions
are added. 2) No characteristic 2) Absence of Fifth
precipitate. Group (Ca / Ba).
6 To a few drops of the 1) White precipitate. 1) Presence of Sixth
original solution 1ml Group (Mg).
NH4Cl, 2ml NH4OH and
2ml Di Sodium
Hydrogen Phosphate are 2) No characteristic 2) Absence of Sixth
added. precipitate. Group (Mg).
V .CONFIRMATORY TESTS FOR BASIC RADICALS
S. EXPERIMENT OBSERVATION INFERENCE
No
AMMONIUM
1 Original solution + Sodium Reddish brown Ammonium is
Hydroxide + Nessler’s precipitate. confirmed.
reagent.
First group - LEAD
1 Original solution + Yellow precipitate. Lead is confirmed.
Potassium Chromate.
2 Original solution + Yellow precipitate Lead is confirmed.
Potassium Iodide. soluble in hot water
which reappears as
golden yellow spangles
on cooling.
Third group - ALUMINIUM
1 Original solution + Sodium White precipitate Aluminium is
Hydroxide in drops to soluble in excess of confirmed.
excess. sodium hydroxide.
2 Original solution + A bright red lake. Aluminium is
Ammonium Hydroxide + confirmed.
Aluminon reagent.
Fourth group - ZINC
1 Original solution + Sodium White precipitate Zinc is confirmed.
Hydroxide soluble in excess of
sodium hydroxide.
2 Original solution + White precipitate Zinc is
Potassium Ferro cyanide. soluble in excess of confirmed.
sodium hydroxide &
insoluble in dilute acid.
3 Added lead dioxide to Pink Colouration Mn (II) Confirmed.
above solution, then added formed.
concentrated nitric acid.
Boiled it.
Fifth group - CALCIUM
1 Original solution + No precipitate. Calcium is
Potassium Chromate. confirmed.
2 Original solution + White precipitate Calcium is
Ammonium Hydroxide + insoluble in acetic acid. confirmed.
Ammonium Oxalate.
Fifth group - BARIUM
1 Original solution + Yellow precipitate, Barium is
Potassium Chromate. soluble in acid. confirmed.
2 Original solution + Dilute White precipitate Barium is
Sulphuric Acid. insoluble in acetic acid. confirmed.
Sixth group - MAGNESIUM
1 Original solution + Sodium White precipitate, Magnesium is
Hydroxide. insoluble in excess of confirmed.
sodium hydroxide.
2 Original solution + Blue precipitate. Magnesium is
Magneson reagent. confirmed.
RESULT
The given simple salt contains
1. Basic Radical : __________________
2. Acid Radical : __________________
You might also like
- Ammonium Chloride Salt Analysis TestDocument2 pagesAmmonium Chloride Salt Analysis TestSantosh Kumar Sahu100% (1)
- General Procedure For The Systematic Analysis of A Simple SaltDocument6 pagesGeneral Procedure For The Systematic Analysis of A Simple SaltDrGaurav Rajput50% (10)
- Flowmeter DemonstrationDocument24 pagesFlowmeter DemonstrationNajwa Ghazali100% (16)
- General Procedure For The Systematic Analysis of A Simple SaltDocument13 pagesGeneral Procedure For The Systematic Analysis of A Simple SaltArulNo ratings yet
- General ProcedureDocument8 pagesGeneral ProcedureArjun .kNo ratings yet
- Final Salt AnalysisDocument8 pagesFinal Salt AnalysisAnonymous SomeoneNo ratings yet
- General Procedure For Salt AnalysisDocument11 pagesGeneral Procedure For Salt Analysiskarthikeya devarajNo ratings yet
- Wa0016.Document6 pagesWa0016.Kalaivani PrabaharanNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis ProcedureDocument8 pagesSalt Analysis ProcedureIzuku MidoriaNo ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Salt Study Material emDocument2 pages11th Chemistry Salt Study Material emNewbeeNo ratings yet
- CHS - Salt Analysis SchemeDocument9 pagesCHS - Salt Analysis Schemeaarya15100651No ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument6 pagesSalt AnalysisManikandan sNo ratings yet
- Systematic Procedure For Inorganic Qualitative Analysis: I. Preliminary Tests Experiment Observation InferenceDocument7 pagesSystematic Procedure For Inorganic Qualitative Analysis: I. Preliminary Tests Experiment Observation InferenceAbhijithNo ratings yet
- General Salt ProcedureDocument7 pagesGeneral Salt ProcedureArchanaa PadmavathiNo ratings yet
- Practicals-Grade XIDocument5 pagesPracticals-Grade XIboobalaaNo ratings yet
- Salt ProcedureDocument28 pagesSalt Procedurevijayalakshmi.9597888177No ratings yet
- Scheme of Analysis of Inorganic SaltDocument11 pagesScheme of Analysis of Inorganic SaltHemsuta S.BNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Organic Compound Analysis em 217324Document4 pagesNamma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Organic Compound Analysis em 217324plakshmirsmNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis ProcedureDocument7 pagesSalt Analysis ProcedureNivetha Shree ANo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument14 pagesSalt Analysistamilarasi.shanmugamNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis Iis 2022Document9 pagesQualitative Analysis Iis 2022kskskNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Scheme of Analysis Experiment Observation InferenceDocument15 pagesChemistry Scheme of Analysis Experiment Observation InferenceMuhsina FathimaNo ratings yet
- Xi Salt Analysis emDocument4 pagesXi Salt Analysis emᏚᴇʟᴠᴀ Ꮐᴀɴᴀʙᴀᴛʜʏ ཞPNo ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry ResearchDocument35 pages11th Chemistry Researchktmloversan95No ratings yet
- Scheme of Salt AnalysisDocument8 pagesScheme of Salt AnalysisAz Ahmed100% (1)
- Scheme of Qualitative Analysis of Simple salt-NPS WDocument8 pagesScheme of Qualitative Analysis of Simple salt-NPS Wpoojaluv25No ratings yet
- INORGANIC SALT ANALYSIS - Ammonium Carbonate S.No Experiment Observation InferenceDocument24 pagesINORGANIC SALT ANALYSIS - Ammonium Carbonate S.No Experiment Observation InferenceRyoshiNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis - 1 NH4ClDocument2 pagesSalt Analysis - 1 NH4Clmystical moonbeamNo ratings yet
- Scheme For Salt AnalysisDocument11 pagesScheme For Salt AnalysisJaefar ShameemNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument9 pagesSalt AnalysismohtashimahmNo ratings yet
- Salt Full Procedure English-Converted - 2Document6 pagesSalt Full Procedure English-Converted - 2Rekha LalNo ratings yet
- SaltDocument5 pagesSaltJhaswanth PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Salt Analysis Record WritingDocument20 pagesInorganic Salt Analysis Record WritingDineshNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis SchemeDocument6 pagesSalt Analysis SchemeAMBRIN ABDULNo ratings yet
- Xi Salt Analysis em PDFDocument3 pagesXi Salt Analysis em PDFvvn natrajNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument8 pagesSalt AnalysisB.K.Sivaraj raj0% (1)
- Lead AcetateDocument3 pagesLead AcetatePushpa KaladeviNo ratings yet
- General Salt Analysis ProcedureDocument10 pagesGeneral Salt Analysis ProcedureAkshat KashyapNo ratings yet
- Salt 6 Lead NitrateDocument3 pagesSalt 6 Lead NitrateKumaranRamuNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis (1) - 1658383575Document8 pagesSalt Analysis (1) - 1658383575NIGHNA BHARWANI 9266No ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry em Practical 2018 To 2019 - T. MuruganDocument6 pagesClass 11 Chemistry em Practical 2018 To 2019 - T. Murugansathish150398No ratings yet
- Systematic Qualitative Analysis of Simple SaltDocument9 pagesSystematic Qualitative Analysis of Simple SaltNisha VethigaNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis Procedure .Document13 pagesSalt Analysis Procedure .Tharangini AkkinsNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis ProcedureDocument40 pagesSalt Analysis ProcedureChris BijuNo ratings yet
- Salt 5 Aluminium NitrateDocument2 pagesSalt 5 Aluminium NitrateKumaranRamuNo ratings yet
- Che Lab Procedures (Xi 0 Xii) - 1Document5 pagesChe Lab Procedures (Xi 0 Xii) - 1Aswath G KNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis SchemeDocument10 pagesSalt Analysis SchemeNISHAL NIYASNo ratings yet
- Salt-3 Aluminium SulphateDocument4 pagesSalt-3 Aluminium Sulphatebapna.aaradhya2007No ratings yet
- Scheme of Salt Analysis: Experiment Observation Inference Chemical Reactions Preliminary ExperimentsDocument8 pagesScheme of Salt Analysis: Experiment Observation Inference Chemical Reactions Preliminary ExperimentsLitmus GodNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Inorganic Analysis: I. Physical Examination of The Salt Experiment Observation InferenceDocument9 pagesQualitative Inorganic Analysis: I. Physical Examination of The Salt Experiment Observation InferenceAarohiNo ratings yet
- Experiment Observation Inference Action of Dil. HC1:: Hydrochloric AcidDocument4 pagesExperiment Observation Inference Action of Dil. HC1:: Hydrochloric AcidVarun Ignatius JauhariNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument10 pagesSalt Analysisamrita girishNo ratings yet
- Practicals-Class Xi Salt AnalysisDocument12 pagesPracticals-Class Xi Salt AnalysisMariappan NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 1Document2 pagesSalt Analysis 1sowndharya.abigailNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis - 1Document4 pagesSalt Analysis - 1snehanp2005No ratings yet
- Scheme of Analysis of Salt.Document4 pagesScheme of Analysis of Salt.noorNo ratings yet
- Lead Nitrate Salt AnalysisDocument3 pagesLead Nitrate Salt AnalysisJo RajNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis I: Experiment Observations Inference Preliminary TestsDocument19 pagesSalt Analysis I: Experiment Observations Inference Preliminary TestsPreetam Kalyaan100% (1)
- Salt Analysis Chemistry Lab PDFDocument9 pagesSalt Analysis Chemistry Lab PDFkushal aggarwalNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Formulation and Manufacturing ProcessDocument14 pagesFormulation and Manufacturing ProcessStalson FernandesNo ratings yet
- Science 14 Entrance 2018Document19 pagesScience 14 Entrance 2018Shanila KhanNo ratings yet
- N. Kannan, D. Vakeesan / Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 62 (2016) 1092 - 1105 1100Document2 pagesN. Kannan, D. Vakeesan / Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 62 (2016) 1092 - 1105 1100dean sgsitsNo ratings yet
- Yin PingDocument6 pagesYin PingleilabellaNo ratings yet
- Particle Like Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation: Yudhiakto PramudyaDocument53 pagesParticle Like Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation: Yudhiakto PramudyaMengharu BiruNo ratings yet
- 2018 Book IndustrialApplicationsOfPolyLa PDFDocument233 pages2018 Book IndustrialApplicationsOfPolyLa PDFNick AmayaNo ratings yet
- Frt11 BetzDocument25 pagesFrt11 BetzArindam DasNo ratings yet
- ASTM D4362 - 19 Standard Specification For Propane Thermophysical Property TablesDocument12 pagesASTM D4362 - 19 Standard Specification For Propane Thermophysical Property TablesSusana Nicole Arellano HernandezNo ratings yet
- SDS Xaerus XR 534 SeriesDocument8 pagesSDS Xaerus XR 534 SeriesYosef SetiawanNo ratings yet
- LS-PH90 - Tabla de Errores de LavasecarropasDocument19 pagesLS-PH90 - Tabla de Errores de LavasecarropasFotoediciones MaelNo ratings yet
- High Speed Cutting MachineDocument2 pagesHigh Speed Cutting Machinefog900No ratings yet
- Basf - I&i LaundryDocument21 pagesBasf - I&i Laundrysrushti100% (2)
- Earth Science Reviewer The Layers of The Earth and Its CompositionDocument4 pagesEarth Science Reviewer The Layers of The Earth and Its Compositionkenshin copradaNo ratings yet
- Microwave Synthesis SolutionsDocument12 pagesMicrowave Synthesis SolutionsbekkuNo ratings yet
- Binary 6Document6 pagesBinary 6حسين كاظم ياسينNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document18 pagesChapter 3eileenNo ratings yet
- JEST2011 Question PaperDocument4 pagesJEST2011 Question PaperVidya Sagar100% (6)
- Dyeing of Turquiose PDFDocument31 pagesDyeing of Turquiose PDFrahul trivedi100% (1)
- 4A'S Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Document7 pages4A'S Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Dina ReclaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Stoichiometry PDFDocument41 pagesChapter 3 Stoichiometry PDFAbou WalidNo ratings yet
- Clin1 Kinetic: Ggt-Gisan - GGTDocument1 pageClin1 Kinetic: Ggt-Gisan - GGTHussein N. FarhatNo ratings yet
- JA SOLAR 440watt Solar Panel DatasheetDocument2 pagesJA SOLAR 440watt Solar Panel DatasheetAntonio CanalesNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Tartaric Acid During Hydration of Portland CementDocument7 pagesInteraction of Tartaric Acid During Hydration of Portland CementWahid KarolNo ratings yet
- Science: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument24 pagesScience: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsRoxanne Manaloto100% (1)
- Die Design and Dough Expansion in Low Moisture Extrusion-Cooking ProcessDocument14 pagesDie Design and Dough Expansion in Low Moisture Extrusion-Cooking ProcessMuhammad HammadNo ratings yet
- Safi Mock Exams 1Document3 pagesSafi Mock Exams 1ABDUL RAUFNo ratings yet
- Physics GRD 12 Wonderland Sky RiderDocument5 pagesPhysics GRD 12 Wonderland Sky RiderHell Razer100% (7)
- Cane Juice ClarificationDocument77 pagesCane Juice Clarificationsena100% (2)
- Safety Standard: FOR Hydrogen and HydrogenDocument390 pagesSafety Standard: FOR Hydrogen and Hydrogenmeshekhar700No ratings yet