Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Salt 4 - Zinc Sulphate
Salt 4 - Zinc Sulphate
Uploaded by
aaravOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Salt 4 - Zinc Sulphate
Salt 4 - Zinc Sulphate
Uploaded by
aaravCopyright:
Available Formats
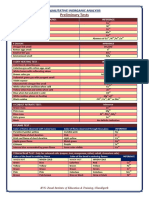
Salt Analysis
Aim: To detect the acidic and basic radicals present in the given salt.
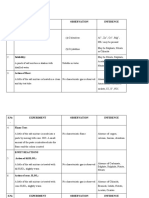
Test Observation Inference
1) Colour White Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Ni2+, Mn2+,
Co2+ absent.
2) Smell No specific odour NH4+, CH3COO-, S2- absent.
3) Density Heavy Salts of Pb2+, Ba2+ may be
present.
4) Deliquescence Salt does not absorb Chlorides of Zn2+, Mg2+
moisture absent.
5) Dry heating test a) Salt decrepitates Pb(NO3)2, KBr, NaCl may be
Heat a pinch of salt in a dry present.
test tube. b) Yellow residue when
hot; white residue Zn2+ may be present.
when cold.
6) Charcoal cavity test
Mix a pinch of salt with Yellow residue Zn2+ may be present.
double the quantity of
Na2CO3 & heat the mixture on
charcoal cavity in reducing
flame.
7) Flame test
Prepare a paste of salt with No specific colour Nothing definite.
conc. HCl & introduce it into
the flame using a platinum
wire loop.
IDENTIFICATION OF ACIDIC RADICALS
8) Dilute H2SO4 test
Salt + dil. H2SO4 No gas evolved. CO32-, SO32-,NO2-, S2- absent.
9) KMnO4 test
Salt + dil. H2SO4 + boil + dil. Pink colour of KMnO4 is not Cl-, Br-, I-, C2O42-, absent.
H2SO4 + 1 drop KMnO4 decolourised.
10) Conc. H2SO4 test
Salt + conc. H2SO4 , heat No gas evolved. Cl-, Br -, I-, C2O42-, CH3COO-
absent.
11) Test for SO42-
Salt + dil.HCl, boil + BaCl2 White ppt insoluble in conc SO42- present.
solution HCl.
Confirmatory Test for sulphate (SO42-)
12) Lead acetate test
Aqueous salt solution + lead White ppt soluble in excess of SO42- confirmed.
acetate solution. hot ammonium acetate
solution.
IDENTIFICATION OF BASIC RADICALS
13) Test for NH4+
Salt + conc.NaOH, boil and No brown ppt Group 0 (NH4+) absent.
add this solution into
Nessler’s reagent
Preparation of Original Solution (OS)
14) Salt + water, shake well. Salt is soluble in water. Label it as OS.
15) OS + dil HCl No white ppt Group I absent.
16) OS + dil HCl + H2S gas No black/yellow ppt Group II absent.
17) OS + conc. HNO3 + No reddish brown/ white ppt Group III absent.
NH4Cl, Boil, cool and add
NH4OH
18) OS + conc. HNO3 + White ppt formed Group IV (Zn2+) present.
NH4Cl, Boil, cool and add
NH4OH + H2S gas
Confirmatory Test for Zn2+
White ppt + dil HCl, boil + Bluish white ppt formed. Zn2+ confirmed.
potassium ferrocyanide
OR
White ppt + dil HCl, boil + White ppt soluble in excess of Zn2+ confirmed.
NaOH NaOH
CHEMICAL EQUATIONS:
CT for sulphate (SO42-)
Na2SO4 + Pb(CH3COO)2 → PbSO4 + 2CH3COONa
White ppt
CT for aluminium (Zn2+)
ZnS + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2S ↑
Potassium ferrocyanide test
2ZnCl2 + K4[Fe(CN)6] → Zn2[Fe(CN)6] ↓ + 4 KCl
Bluish white ppt
OR
Sodium Hydroxide test
ZnCl2 + 2NaOH → Zn(OH)2 ↓+ 2NaCl
White ppt
Zn(OH)2 + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + 2H2O
soluble
RESULT TABLE:
Basic Radical Zinc (Zn2+)
Acidic Radical Sulphate (SO42-)
Salt Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4)
You might also like
- QA Notes - Test For Cations and AnionsDocument9 pagesQA Notes - Test For Cations and Anionschong5683% (24)
- Cobalt Amine Complexes Uv Vis SpectraDocument7 pagesCobalt Amine Complexes Uv Vis SpectraHyga ForcarNo ratings yet
- HSE-Plustwo-Chemistry-SYSTEMATIC ANALYSIS OF SIMPLE SALTS-Anil-Hsslive PDFDocument2 pagesHSE-Plustwo-Chemistry-SYSTEMATIC ANALYSIS OF SIMPLE SALTS-Anil-Hsslive PDFMallu Tech33% (3)
- 3 25 10citypaperwebDocument20 pages3 25 10citypaperwebPaul BlakeNo ratings yet
- Salt 2 - Lead NitrateDocument2 pagesSalt 2 - Lead NitrateaaravNo ratings yet
- Salt No 2 - Systematic Qualitative Analysis of Inorganic SaltDocument3 pagesSalt No 2 - Systematic Qualitative Analysis of Inorganic SaltChris DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis General ProcedureDocument7 pagesSalt Analysis General Procedurefranklin mahizhaNo ratings yet
- Systematic Qualitative Analysis of Simple SaltDocument9 pagesSystematic Qualitative Analysis of Simple SaltNisha VethigaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Inorganic Analysis)Document4 pagesQualitative Inorganic Analysis)himanshumallikaNo ratings yet
- RDSO Specification No. WD06-TPV-93 (Rev.01)Document15 pagesRDSO Specification No. WD06-TPV-93 (Rev.01)Ashlin AugustyNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis ChartDocument4 pagesSalt Analysis ChartHENo ratings yet
- Salts FormationDocument19 pagesSalts FormationUrwa Abdul MannanNo ratings yet
- 1 Salt Analysis - 1Document8 pages1 Salt Analysis - 1HER OICNo ratings yet
- Copper SulphateDocument4 pagesCopper SulphateSanNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis Notes 12Document42 pagesSalt Analysis Notes 12allancholan200609No ratings yet
- Chemical Test Orgnic Chemistry 2020Document4 pagesChemical Test Orgnic Chemistry 2020Mukesh GanjawalaNo ratings yet
- Salts and Salt PreparationDocument36 pagesSalts and Salt PreparationGABRIELLE FOSTER100% (1)
- Copper SulphateDocument4 pagesCopper SulphatesachinswamykvNo ratings yet
- Hse Plustwo Chemistry Systematic Analysis of Simple Salts Anil HssliveDocument2 pagesHse Plustwo Chemistry Systematic Analysis of Simple Salts Anil HssliveGopakumar KNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical: Experiment No. - 09Document6 pagesChemistry Practical: Experiment No. - 09chetan sharmaNo ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Full One Mark Questions With Answer Key English MediumDocument67 pages11th Chemistry Full One Mark Questions With Answer Key English Medium19 Vasanth PurushothamanNo ratings yet
- Acid Base and Salts - Part 6-Qualitative AnalysisDocument30 pagesAcid Base and Salts - Part 6-Qualitative AnalysisKronix GamingNo ratings yet
- Aluminium SulphateDocument4 pagesAluminium SulphateSanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Colour Compound (Mega) 215Document2 pagesAssignment Colour Compound (Mega) 215Anant JainNo ratings yet
- INUKA Product Catalogue 2023 Effective April 2023 PDFDocument48 pagesINUKA Product Catalogue 2023 Effective April 2023 PDFAnathiNo ratings yet
- Systematic Qualitative Analysis of Simple Inorganic Salt PDFDocument11 pagesSystematic Qualitative Analysis of Simple Inorganic Salt PDFThriambakeshwar ShramaNo ratings yet
- Aluminium NitrateDocument3 pagesAluminium NitrategumtammNo ratings yet
- LT - Batch A - Unit Test - 6 - CHE & BOT - 23.03.2023 - A Type PDFDocument16 pagesLT - Batch A - Unit Test - 6 - CHE & BOT - 23.03.2023 - A Type PDFVENUGOPALARAONo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument26 pagesSalt AnalysisNikhil MishraNo ratings yet
- EXP 3 CHM213 UiTMDocument5 pagesEXP 3 CHM213 UiTMnureenNo ratings yet
- Ch-1-Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument7 pagesCh-1-Chemical Reactions and EquationsIcravus GoldNo ratings yet
- Systematic Semi-Micro Qualitative Analysis of An Inorganic SaltDocument11 pagesSystematic Semi-Micro Qualitative Analysis of An Inorganic SaltNidhi PrasadNo ratings yet
- S.No - Experiment Observation InferenceDocument7 pagesS.No - Experiment Observation InferenceArchana ArchuNo ratings yet
- 12th Class Chapter Amines Wise QP 2022-23Document6 pages12th Class Chapter Amines Wise QP 2022-23Gunjan BisenNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Study List - Grade 10Document2 pagesFinal Exam Study List - Grade 10AhmedNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis ProcedureDocument8 pagesSalt Analysis ProcedureIzuku MidoriaNo ratings yet
- Ammonium ChlorideDocument4 pagesAmmonium ChlorideSanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of 15 Simple Salts Xi STD-1 PDFDocument38 pagesAnalysis of 15 Simple Salts Xi STD-1 PDFAnisha Fathima Begum100% (1)
- Towards A Business Model For Second-Life Batteries-Barriers, Opportunities, Uncertainties, and TechnologiesDocument19 pagesTowards A Business Model For Second-Life Batteries-Barriers, Opportunities, Uncertainties, and TechnologiesCarlosNo ratings yet
- HSE-Plustwo-Chemistry-SYSTEMATIC ANALYSIS OF SIMPLE SALTS-Anil-Hsslive PDFDocument2 pagesHSE-Plustwo-Chemistry-SYSTEMATIC ANALYSIS OF SIMPLE SALTS-Anil-Hsslive PDFMallu Tech100% (1)
- Redox Note ADocument29 pagesRedox Note AuniverseNo ratings yet
- Inbound 7714832539582663562Document17 pagesInbound 7714832539582663562Julesbon ParsaliganNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument8 pagesSalt AnalysisSyed Mohdammad AliNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument8 pagesSalt AnalysisRaziaNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Salt Analysis 1 PDFDocument13 pagesScheme of Salt Analysis 1 PDFFreyaNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis of PB (NO3) 2Document7 pagesSalt Analysis of PB (NO3) 2piyush rajputNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis of PB (NO3) 2Document7 pagesSalt Analysis of PB (NO3) 2piyush rajput100% (3)
- 18.salt Zinc Carbonate 4Document3 pages18.salt Zinc Carbonate 4Sarthika Gaulkar0% (1)
- Salt Analysis - PracticalDocument10 pagesSalt Analysis - PracticalClassXII CSNo ratings yet
- Suryadatta National School: A.Y. 2022-23 Standard Xii Chemistry Journal IndexDocument8 pagesSuryadatta National School: A.Y. 2022-23 Standard Xii Chemistry Journal IndexKairav Bharat PathakNo ratings yet
- Null 27Document5 pagesNull 27BTS ArmyNo ratings yet
- Salt 1 - Systematic Qualitative Analysis of Inorganic SaltDocument3 pagesSalt 1 - Systematic Qualitative Analysis of Inorganic SaltChris DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 2024Document7 pagesSalt Analysis 2024mullappillilismailNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 3Document4 pagesSalt Analysis 3snehanp2005No ratings yet
- 17.salt Aluminium Sulphate 3Document3 pages17.salt Aluminium Sulphate 3Sarthika GaulkarNo ratings yet
- Salt 7 Barium ChlorideDocument2 pagesSalt 7 Barium ChlorideKumaranRamuNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Sulphate (Al2 (SO4) 3)Document3 pagesAluminium Sulphate (Al2 (SO4) 3)Rajesh Mishra100% (2)
- Salt AnalysisDocument5 pagesSalt AnalysisbriefcinemablitzNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis - Barium NitrateDocument2 pagesSalt Analysis - Barium NitrateSwarnabha Bhattacharyya100% (2)
- Salt Analysis: Test For AnionsDocument5 pagesSalt Analysis: Test For AnionsMamata RNo ratings yet
- ( Zinc Acetate) SYSTEMATIC ANALYSIS OF SIMPLE SALT No 8Document5 pages( Zinc Acetate) SYSTEMATIC ANALYSIS OF SIMPLE SALT No 8sharang1234567890No ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory AaravDocument11 pagesChemistry Investigatory AaravaaravNo ratings yet
- XII Food Sample 1 & 2Document3 pagesXII Food Sample 1 & 2aaravNo ratings yet
- Salt 5 - Calcium ChlorideDocument3 pagesSalt 5 - Calcium ChlorideaaravNo ratings yet
- Salt 2 - Lead NitrateDocument2 pagesSalt 2 - Lead NitrateaaravNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument2 pagesChromatographyaaravNo ratings yet
- Activity 06Document2 pagesActivity 06aaravNo ratings yet
- Activity 05Document2 pagesActivity 05aaravNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectaaravNo ratings yet
- Pricelist 2020 Bahan Farmasi - 1Document7 pagesPricelist 2020 Bahan Farmasi - 1ningsih rezekiNo ratings yet
- Sulit 4541/1: 4541/1 Hak Cipta Parwah Intelek SPM PPD Subis SulitDocument9 pagesSulit 4541/1: 4541/1 Hak Cipta Parwah Intelek SPM PPD Subis SulitNurain Babu OsmanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument23 pagesChemistry Projectkavishree sNo ratings yet
- Soal BingDocument29 pagesSoal BingEka Puspa Krisna MurtiNo ratings yet
- Identification Test PDFDocument3 pagesIdentification Test PDFayaMhaeNo ratings yet
- Booklet 7 FinalDocument36 pagesBooklet 7 FinalpavijayaNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument25 pagesAcid BasethipanduNo ratings yet
- Anion Exchange Membranes Derived From Main Group and Metal Based - 2022 - PolymeDocument13 pagesAnion Exchange Membranes Derived From Main Group and Metal Based - 2022 - PolymeLeyla UNo ratings yet
- 4500 NitrogenoDocument6 pages4500 NitrogenoErick Michael GarciaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz 5.3 Transition ElementsDocument13 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz 5.3 Transition Elementsrabab elkomyNo ratings yet
- Past Product Sourced AmendedDocument11 pagesPast Product Sourced AmendedCharlesNo ratings yet
- Steam Generation in Power - DOC043.53.30251.Mar17Document9 pagesSteam Generation in Power - DOC043.53.30251.Mar17NO BOTHERNo ratings yet
- OxalateDocument5 pagesOxalateNitin HansaliaNo ratings yet
- Chem f4 (SALTS)Document26 pagesChem f4 (SALTS)nur asyiqinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Analysis of Cuprous Oxide and Copper Pigments: Standard Test Methods ForDocument5 pagesChemical Analysis of Cuprous Oxide and Copper Pigments: Standard Test Methods ForLito EstimosNo ratings yet
- Lista de Kit MerckDocument37 pagesLista de Kit MerckjosianearaujomartinsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Product List - Smart Lab-MSIDocument4 pagesChemical Product List - Smart Lab-MSIGandi Sogandi100% (1)
- CilDocument18 pagesCilRobby Setiabudi TjangNo ratings yet
- UN - DG Alphabetical Chemical List PDFDocument68 pagesUN - DG Alphabetical Chemical List PDFmrmenellisNo ratings yet
- Fertigation - of - Vegetable PDFDocument48 pagesFertigation - of - Vegetable PDFYowan SolomunNo ratings yet
- Ammonium Sulfate by Direct Route PDFDocument4 pagesAmmonium Sulfate by Direct Route PDFsandipkumardshahNo ratings yet
- Padasalai Net 12th Chemistry Study Material Sal Analysis emDocument24 pagesPadasalai Net 12th Chemistry Study Material Sal Analysis emSenthil NatarajanNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2017Document22 pagesICSE Class 10 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2017lokesh bhagatNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge Ordinary Levelman swaggerNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Vapor Test For Determining Susceptibility To Stress Corrosion Cracking in Copper AlloysDocument4 pagesAmmonia Vapor Test For Determining Susceptibility To Stress Corrosion Cracking in Copper AlloysDanZel DanNo ratings yet
- Caking Processes in Granular NPK FertilizerDocument4 pagesCaking Processes in Granular NPK Fertilizerboukari.lamiaNo ratings yet
- PH SolutionDocument5 pagesPH SolutionHmingsangliana HauhnarNo ratings yet
- 3.1.13. Plastic AdditivesDocument3 pages3.1.13. Plastic AdditivesPamela FioravantiNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Analysis MethodDocument10 pagesAmmonia Analysis MethodMp 's PrettyNo ratings yet