Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Harolds Taylor Series Cheat Sheet 2022
Harolds Taylor Series Cheat Sheet 2022
Uploaded by
MagedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Harolds Taylor Series Cheat Sheet 2022
Harolds Taylor Series Cheat Sheet 2022
Uploaded by
MagedCopyright:
Available Formats
Harold’s Taylor Series
Cheat Sheet
22 October 2022
Power Series
+∞
Power Series About Zero
∑ 𝑎𝑛 𝑥 𝑛 = 𝑎0 + 𝑎1 𝑥 + 𝑎2 𝑥 2 + 𝑎3 𝑥 3 + 𝑎4 𝑥 4 + ⋯
Geometric Series if 𝑎𝑛 = 𝑎
𝑛=0
+∞
Power Series ∑ 𝑎𝑛 (𝑥 − 𝑐)𝑛 = 𝑎0 + 𝑎1 (𝑥 − 𝑐) + 𝑎2 (𝑥 − 𝑐)2 + ⋯
𝑛=0
Approximation Polynomial
𝒇(𝒙) = 𝑷𝒏 (𝒙) + 𝑹𝒏 (𝒙)
𝑃𝑛 (𝑥) = 𝑛𝑡ℎ 𝑑𝑒𝑔𝑟𝑒𝑒 𝑝𝑜𝑙𝑦𝑛𝑜𝑚𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑎𝑝𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑥𝑖𝑚𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
𝑅𝑛 (𝑥) = ± 𝐸𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟
𝑁𝑂𝑇𝐸: 𝑃𝑛 (𝑥) 𝑖𝑠 𝑒𝑎𝑠𝑦 𝑡𝑜 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑑𝑖𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑡𝑒
Maclaurin Series
+∞
Maclaurin Series 𝒇(𝒏) (𝟎) 𝒏
𝒇(𝒙) ≈ 𝑷𝒏 (𝒙) = ∑ 𝒙
Taylor Series centered about 𝑥 = 0 𝒏!
𝒏=𝟎
(𝑛+1)
𝑓 (𝑥 ∗ ) 𝑛+1
𝑅𝑛 (𝑥) = 𝑥
Maclaurin Series Remainder (𝑛 + 1)!
where 𝑥 ≤ 𝑥 ∗ ≤ 𝑚𝑎𝑥 and lim 𝑅𝑛 (𝑥) = 0
𝑥→+∞
Taylor Series
+∞
Taylor Series 𝑓 (𝑛) (𝑐)
𝑓(𝑥) ≈ 𝑃𝑛 (𝑥) = ∑ (𝑥 − 𝑐)𝑛
Maclaurin Series if 𝑐 = 0 𝑛!
𝑛=0
Copyright © 2015-2022 by Harold Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor 1
𝑓 (𝑛+1) (𝑥 ∗ )
𝑅𝑛 (𝑥) = (𝑥 − 𝑐)𝑛+1
Taylor Series Remainder (𝑛 + 1)!
where 𝑥 ≤ 𝑥 ∗ ≤ 𝑐 and lim 𝑅𝑛 (𝑥) = 0
𝑥→+∞
Summation Form Expanded Form
Exponential Functions
∞
𝒙
𝒙𝒏 𝑥2 𝑥3 𝑥4 𝑥5 𝑥6 𝑥7 𝑥8
𝒆 =∑ 𝒇𝒐𝒓 𝒂𝒍𝒍 𝒙 1+𝑥+ + + + + + + +⋯
𝒏! 2! 3! 4! 5! 6! 7! 8!
𝒏=𝟎
∞
(𝑥 ln(𝑎))𝑛 [𝑥 ln(𝑎)]2 [𝑥 ln(𝑎)]3
𝑎 𝑥 = 𝑒 𝑥 ln (𝑎) = ∑ 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑎𝑙𝑙 𝑥 1 + 𝑥 ln(𝑎) + + +⋯
𝑛! 2! 3!
𝑛=0
Natural Logarithms
∞
𝑥𝑛 𝑥2 𝑥3 𝑥4 𝑥5 𝑥6 𝑥7 𝑥8
ln (1 − 𝑥) = ∑ 𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < 1 𝑥+ + + + + + + +⋯
𝑛 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
𝑛=1
∞
(−1)𝑛−1 (𝑥 − 1)𝑛 (𝑥 − 1)2 (𝑥 − 1)3 (𝑥 − 1)4
ln (𝑥) = ∑ 𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < 1 (𝑥 − 1) − + − +⋯
𝑛 2 3 4
𝑛=1
∞
(−𝟏)𝒏−𝟏 𝒏 𝑥2 𝑥3 𝑥4 𝑥5 𝑥6 𝑥7 𝑥8
𝐥𝐧 (𝟏 + 𝒙) = ∑ 𝒙 𝒇𝒐𝒓 |𝒙| < 𝟏 𝑥− + − + − + − +⋯
𝒏 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
𝒏=𝟏
∞
1+𝑥 2 2𝑥 2 2𝑥 3 2𝑥 4 2𝑥 5 2𝑥 6 2𝑥 7
ln ( )=∑ 𝑥 2𝑛−1 𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < 1 2𝑥 − + − + − + −⋯
1−𝑥 2𝑛 − 1 3 5 7 9 11 13
𝑛=1
Geometric Series
∞
1
= ∑(−1)𝑛 (𝑥 − 1)𝑛 𝑓𝑜𝑟 0 < 𝑥 < 2 1 − (𝑥 − 1) + (𝑥 − 1)2 − (𝑥 − 1)3 + (𝑥 − 1)4 + ⋯
𝑥
𝑛=0
∞
1
= ∑(−1)𝑛 𝑥 𝑛 𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < 1 1 − 𝑥 + 𝑥2 − 𝑥3 + 𝑥4 − 𝑥5 + 𝑥6 − 𝑥7 + 𝑥8 − ⋯
1+𝑥
𝑛=0
∞
𝟏
= ∑ 𝒙𝒏 𝒇𝒐𝒓 |𝒙| < 𝟏 1 + 𝑥 + 𝑥2 + 𝑥3 + 𝑥4 + 𝑥5 + 𝑥6 + 𝑥7 + 𝑥8 + ⋯
𝟏−𝒙
𝒏=𝟎
∞
1
= ∑(−1)𝑛 𝑥 2𝑛 𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < 1 1 − 𝑥 2 + 𝑥 4 − 𝑥 6 + 𝑥 8 − 𝑥 10 + 𝑥 12 − 𝑥 14 + ⋯
1 + 𝑥2
𝑛=0
∞
1
= ∑ 𝑥 2𝑛 𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < 1 1 + 𝑥 2 + 𝑥 4 + 𝑥 6 + 𝑥 8 + 𝑥 10 + 𝑥 12 + 𝑥 14 + ⋯
1 − 𝑥2
𝑛=0
∞
1
= ∑(−1)𝑛−1 𝑛𝑥 𝑛−1 𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < 1 1 − 2𝑥 + 3𝑥 2 − 4𝑥 3 + 5𝑥 4 − 6𝑥 5 + 7𝑥 6 − ⋯
(1 + 𝑥)2
𝑛=1
∞
1
= ∑ 𝑛𝑥 𝑛−1 𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < 1 1 + 2𝑥 + 3𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 3 + 5𝑥 4 + 6𝑥 5 + 7𝑥 6 + ⋯
(1 − 𝑥)2
𝑛=1
Copyright © 2015-2022 by Harold Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor 2
∞
1 (−1)𝑛−1 (𝑛 − 1)𝑛 𝑛−2
= ∑ 𝑥
(1 + 𝑥)3 2 1 − 3𝑥 + 6𝑥 2 − 10𝑥 3 + 15𝑥 4 − 21𝑥 5 + 28𝑥 6 − ⋯
𝑛=2
𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < 1
∞
1 (𝑛 − 1)𝑛 𝑛−2
3
=∑ 𝑥 𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < 1 1 + 3𝑥 + 6𝑥 2 + 10𝑥 3 + 15𝑥 4 + 21𝑥 5 + 28𝑥 6 + ⋯
(1 − 𝑥) 2
𝑛=2
∞
(−1)𝑛 (2𝑛)! 1 1 1 5 4 7 5 21 5
√1 + 𝑥 = ∑ 𝑥𝑛 1 + 𝑥 − 𝑥2 + 𝑥3 − 𝑥 + 𝑥 − 𝑥
4𝑛 (𝑛!)2 (1 − 2𝑛) 2 8 16 128 256 1,024
𝑛=0
𝑓𝑜𝑟 − 1 < 𝑥 ≤ 1 +⋯
∞
(2𝑛)! 1 1 1 5 4 7 5 21 5
√1 − 𝑥 = ∑ 𝑛 𝑥𝑛 1 − 𝑥 − 𝑥2 − 𝑥3 − 𝑥 − 𝑥 − 𝑥
4 (𝑛!)2 (1 − 2𝑛) 2 8 16 128 256 1,024
𝑛=0
𝑓𝑜𝑟 − 1 < 𝑥 ≤ 1 −⋯
∞
(−1)𝑛 (2𝑛)!
2
√1 + 𝑥 = ∑ 𝑛 𝑥 2𝑛 1 1 1 5 8 7 10
4 (𝑛!)2 (1 − 2𝑛) 1 + 𝑥2 − 𝑥4 + 𝑥6 − 𝑥 + 𝑥 −⋯
𝑛=0 2 8 16 128 256
𝑓𝑜𝑟 − 1 < 𝑥 ≤ 1
∞
(2𝑛)!
√1 − 𝑥 2 = ∑ 𝑛 𝑥 2𝑛 1 1 1 5 8 7 10
4 (𝑛!)2 (1 − 2𝑛) 1 − 𝑥2 − 𝑥4 − 𝑥6 − 𝑥 − 𝑥 −⋯
𝑛=0 2 8 16 128 256
𝑓𝑜𝑟 − 1 < 𝑥 ≤ 1
(𝑛)‼ = 𝑛(𝑛 − 2)(𝑛 − 4) … 6 ∙ 4 ∙ 2 𝑖𝑓 𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑛
Double Factorial (!!) (𝑛)‼ = 𝑛(𝑛 − 2)(𝑛 − 4) … 5 ∙ 3 ∙ 1 𝑖𝑓 𝑜𝑑𝑑
𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 0‼ = 1 𝑎𝑛𝑑 ─1‼ = 1
∞
1 (−1)𝑛 (2𝑛 − 1)‼ 𝑛
=∑ 𝑥 1 1∙3 2 1∙3∙5 3 1∙3∙5∙7 4
√1 + 𝑥 (2𝑛)‼ 1− 𝑥+ 𝑥 − 𝑥 + 𝑥 −⋯
𝑛=0 2 2∙4 2∙4∙6 2∙4∙6∙8
𝑓𝑜𝑟 − 1 < 𝑥 ≤ 1
∞
1 (2𝑛 − 1)‼ 𝑛
=∑ 𝑥 1 1∙3 2 1∙3∙5 3 1∙3∙5∙7 4
√1 − 𝑥 (2𝑛)‼ 1+ 𝑥+ 𝑥 + 𝑥 + 𝑥 +⋯
𝑛=0 2 2∙4 2∙4∙6 2∙4∙6∙8
𝑓𝑜𝑟 − 1 < 𝑥 ≤ 1
∞
1 (−1)𝑛 (2𝑛 − 1)‼ 2𝑛
=∑ 𝑥 1 1∙3 4 1∙3∙5 6 1∙3∙5∙7 8
√1 + 𝑥 2 𝑛=0 (2𝑛)‼ 1 − 𝑥2 + 𝑥 − 𝑥 + 𝑥 −⋯
2 2∙4 2∙4∙6 2∙4∙6∙8
𝑓𝑜𝑟 − 1 < 𝑥 ≤ 1
∞
1 (2𝑛 − 1)‼ 2𝑛
=∑ 𝑥 1 1∙3 4 1∙3∙5 6 1∙3∙5∙7 8
√1 − 𝑥 2 (2𝑛)‼ 1 + 𝑥2 + 𝑥 + 𝑥 + 𝑥 +⋯
𝑛=0 2 2∙4 2∙4∙6 2∙4∙6∙8
𝑓𝑜𝑟 − 1 < 𝑥 ≤ 1
Copyright © 2015-2022 by Harold Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor 3
Binomial Series
+∞
𝑟
(1 + 𝑥) = ∑ ( ) 𝑥 𝑛
𝑟
𝑛
𝑛=0
𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < 1 and all complex r where
𝑛 𝑟(𝑟 − 1) 2 𝑟(𝑟 − 1)(𝑟 − 2) 3
𝑟 𝑟−𝑘+1 1 + 𝑟𝑥 + 𝑥 + 𝑥 +⋯
( )=∏ 2! 3!
𝑛 𝑘
𝑘=1
𝑟(𝑟 − 1)(𝑟 − 2) … (𝑟 − 𝑛 + 1)
=
𝑛!
Trigonometric Functions
∞
(−𝟏)𝒏 𝑥 3 𝑥 5 𝑥 7 𝑥 9 𝑥 11 𝑥 13 𝑥 15
𝐬𝐢𝐧 (𝒙) = ∑ 𝒙𝟐𝒏+𝟏 𝒇𝒐𝒓 𝒂𝒍𝒍 𝒙 𝑥− + − + − + − +⋯
(𝟐𝒏 + 𝟏)! 3! 5! 7! 9! 11! 13! 15!
𝒏=𝟎
∞
(−𝟏)𝒏 𝟐𝒏 𝑥 2 𝑥 4 𝑥 6 𝑥 8 𝑥 10 𝑥 12 𝑥 14
𝐜𝐨𝐬 (𝒙) = ∑ 𝒙 𝒇𝒐𝒓 𝒂𝒍𝒍 𝒙 1− + − + − + − +⋯
(𝟐𝒏)! 2! 4! 6! 8! 10! 12! 14!
𝒏=𝟎
∞ 𝑛−1
(−1) 22𝑛 (22𝑛 − 1) 𝐵2𝑛 2𝑛−1 1 2 17 7 62 9
tan (𝑥) = ∑ 𝑥 𝑥 + 𝑥3 + 𝑥5 + 𝑥 + 𝑥
(2𝑛)! 3 15 315 2,835
𝑛=1
𝜋 1,382 11 21,844 13
𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < + 𝑥 + 𝑥 +⋯
2 155,925 608,1075
∞
(−1)𝑛 𝐸2𝑛 2𝑛
sec (𝑥) = ∑ 𝑥 𝑥2 𝑥4 𝑥6 𝑥8 𝑥 10
(2𝑛)!
𝑛=0 1+ + 5 + 61 + 1,385 + 50,521 +⋯
𝜋 2! 4! 6! 8! 10!
𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| <
2
∞
(−1)𝑛−1 2 (22𝑛−1 − 1) 𝐵2𝑛 2𝑛−1
csc (𝑥) = ∑ 𝑥 1 1 7 3 31 127
(2𝑛)! + 𝑥+ 𝑥 + 𝑥5 + 𝑥7 + ⋯
𝑛=0 𝑥 6 360 15,120 604,800
𝑓𝑜𝑟 0 < 𝑥 < 𝜋
∞
(−1)𝑛 22𝑛 𝐵2𝑛 2𝑛−1
cot (𝑥) =∑ 𝑥 1 1 1 2 5 1 4
(2𝑛)! − 𝑥 − 𝑥3 − 𝑥 − 𝑥7 − 𝑥9 − ⋯
𝑛=0 𝑥 3 45 189 4,725 2,835
𝑓𝑜𝑟 0 < 𝑥 < 𝜋
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
∞
−1
(2𝑛)!
sin (𝑥) = ∑ 𝑛 2 𝑥 2𝑛+1
(2 𝑛!) (2𝑛 + 1)
𝑛=0
𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| ≤ 1 𝑥3 1 ∙ 3𝑥 5 1 ∙ 3 ∙ 5𝑥 7 1 ∙ 3 ∙ 5 ∙ 7𝑥 9
𝑥+ + + + +⋯
∞ 1 2∙3 2∙4∙5 2∙4∙6∙7 2∙4∙6∙8∙9
𝛤 (𝑛 + 2)
−1
sin (𝑥) = ∑ 𝑥 2𝑛+1
𝑛=0
√𝜋 (2𝑛 + 1) 𝑛!
𝜋
cos−1 (𝑥) = − sin−1(𝑥) 𝜋 𝑥3 1 ∙ 3𝑥 5 1 ∙ 3 ∙ 5𝑥 7
2 −𝑥− − − −⋯
𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| ≤ 1 2 2∙3 2∙4∙5 2∙4∙6∙7
Copyright © 2015-2022 by Harold Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor 4
𝑥3 𝑥5 𝑥7 𝑥9
∞ 𝑥 −
+ − + − ⋯ 𝑓𝑜𝑟 − 1 < 𝑥 < 1
(−𝟏)𝒏 𝟐𝒏+𝟏 3 5 7 9
−𝟏
𝐭𝐚𝐧 (𝒙) = ∑ 𝒙 𝜋 1 1 1 1 1
(𝟐𝒏 + 𝟏) − + 3 − 5 + 7 − 9 + ⋯ 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑥 ≥ 1
𝒏=𝟎 2 𝑥 3𝑥 5𝑥 7𝑥 9𝑥
𝒇𝒐𝒓 |𝒙| < 𝟏 𝜋 1 1 1 1 1
− − + 3 − 5 + 7 − 9 + ⋯ 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑥 < 1
2 𝑥 3𝑥 5𝑥 7𝑥 9𝑥
sec −1(𝑥) = −𝑖 ln(𝑥) + 𝑖 ln(2)
∞ 𝑖 3𝑖 5𝑖
𝑖 (2𝑛 + 1)! 𝑥 2𝑛+2 −𝑖 ln(𝑥) + 𝑖 ln(2) − 𝑥 2 − 𝑥 4 − 𝑥 6 − ⋯
− ∑ 𝑛 4 32 96
4 4 [(𝑛 + 1)!]2
𝑛=0
𝜋
csc −1(𝑥) = 𝑖 ln(𝑥) − 𝑖 ln(2) +
∞
2 𝜋 𝑖 2 3𝑖 4 5𝑖 6
𝑖 (2𝑛 + 1)! 𝑥 2𝑛+2 𝑖 ln(𝑥) − 𝑖 ln(2) + + 𝑥 + 𝑥 + 𝑥 +⋯
+ ∑ 𝑛 2 4 32 96
4 4 [(𝑛 + 1)!]2
𝑛=0
𝜋 𝑥3 𝑥5 𝑥7 𝑥9
− 𝑥 + − + − + ⋯ 𝑓𝑜𝑟 − 1 < 𝑥 < 1
𝜋 2 3 5 7 9
cot −1(𝑥) = − tan−1 (𝑥) 1 1 1 1 1
2 − 3 + 5 − 7 + 9 − ⋯ 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑥 ≥ 1
𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < 1 𝑥 3𝑥 5𝑥 7𝑥 9𝑥
1 1 1 1 1
𝜋 + − 3 + 5 − 7 + 9 − ⋯ 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑥 < 1
𝑥 3𝑥 5𝑥 7𝑥 9𝑥
Hyperbolic Functions
∞
𝑒 𝑥 − 𝑒 −𝑥 𝑥 2𝑛+1 𝑥 3 𝑥 5 𝑥 7 𝑥 9 𝑥 11 𝑥 13 𝑥 15
sinh (𝑥) = =∑ 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑎𝑙𝑙 𝑥 𝑥+ + + + + + + +⋯
2 (2𝑛 + 1)! 3! 5! 7! 9! 11! 13! 15!
𝑛=0
∞
𝑒 𝑥 + 𝑒 −𝑥 𝑥 2𝑛 𝑥 2 𝑥 4 𝑥 6 𝑥 8 𝑥 10 𝑥 12 𝑥 14
cosh (𝑥) = =∑ 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑎𝑙𝑙 𝑥 1+ + + + + + + +⋯
2 (2𝑛)! 2! 4! 6! 8! 10! 12! 14!
𝑛=0
𝑒 𝑥 − 𝑒 −𝑥 𝑥3 𝑥5 𝑥7 𝑥9 𝑥 11
tanh (𝑥) = 𝑥 𝑥−2 + 16 − 272 + 7,936 − 353,792
𝑒 + 𝑒 −𝑥 3! 5! 7! 9! 11!
∞ 2𝑛 2𝑛
2 (2 − 1) 𝐵2𝑛 2𝑛−1 +⋯
tanh (𝑥) = ∑ 𝑥 1 2 17 7 62 9 1,382 11
(2𝑛)! 𝑥 − 𝑥3 + 𝑥5 − 𝑥 + 𝑥 − 𝑥
𝑛=1
𝜋 3 15 315 2,835 155,925
𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < +⋯
2
∞
𝐸2𝑛 2𝑛
sech (𝑥) = ∑ 𝑥 𝑥2 𝑥4 𝑥6 𝑥8 𝑥 10
(2𝑛)!
𝑛=0 1− + 5 − 61 + 1,385 − 50,521 +⋯
𝜋 2! 4! 6! 8! 10!
𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| <
2
∞
1 (2 − 22𝑛 ) 𝐵2𝑛 2𝑛−1
csch (𝑥) = + ∑ 𝑥 1 1 7 3 31 127
𝑥 (2𝑛)! − 𝑥+ 𝑥 − 𝑥5 + 𝑥7 − ⋯
𝑛=1 𝑥 6 360 15,120 604,800
𝑓𝑜𝑟 0 < |𝑥| < 𝜋
∞
1 (−1)𝑛−1 22𝑛 𝐵2𝑛 2𝑛−1
coth (𝑥) = + ∑ 𝑥 1 1 1 2 5 1 4
𝑥 (2𝑛)! + 𝑥 − 𝑥3 + 𝑥 − 𝑥7 + 𝑥9 − ⋯
𝑛=1 𝑥 3 45 945 4,725 2,835
𝑓𝑜𝑟 0 < |𝑥| < 𝜋
Copyright © 2015-2022 by Harold Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor 5
Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
∞
−1
(−1)𝑛 (2𝑛)!
sinh (𝑥) = ∑ 𝑥 2𝑛+1
(2𝑛 𝑛!)2 (2𝑛 + 1)
𝑛=0 𝑥3 1 ∙ 3𝑥 5 1 ∙ 3 ∙ 5𝑥 7 1 ∙ 3 ∙ 5 ∙ 7𝑥 9
𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| ≤ 1 𝑥− + − + −⋯
∞ 2∙3 2∙4∙5 2∙4∙6∙7 2∙4∙6∙8∙9
(−1)𝑛 (2𝑛 − 1)‼ 2𝑛+1
sinh−1 (𝑥) = ∑ 𝑥
(2𝑛 + 1)(2𝑛)‼
𝑛=0
∞
−1
𝜋 2−𝑛
cosh (𝑥) = 𝑖 − 𝑖 ∑ 𝑥 2𝑛+1 𝜋𝑖 𝑖 𝑥 3 𝑖 ∙ 1 ∙ 3𝑥 5 𝑖 ∙ 1 ∙ 3 ∙ 5𝑥 7
2 𝑛! (2𝑛 + 1) −𝑖𝑥− − − −⋯
𝑛=0 2 2∙3 2∙4∙5 2∙4∙6∙7
𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| ≤ 1
∞
−1
𝑥 2𝑛+1
tanh (𝑥) = ∑ 𝑥 3 𝑥 5 𝑥 7 𝑥 9 𝑥 11 𝑥 13 𝑥 15
2𝑛 + 1 𝑥+ + + + + + + +⋯
𝑛=0 3 5 7 9 11 13 15
𝑓𝑜𝑟 |𝑥| < 1, 𝑥 ≠ ±1
−1
sech (𝑥) = − ln(𝑥) + ln(2)
∞ 1 3𝑖 5𝑖
1 (2𝑛 + 1)! 𝑥 2𝑛+2 − ln(𝑥) + ln(2) + 𝑥 2 + 𝑥 4 + 𝑥 6 + ⋯
+ ∑ 𝑛 4 32 96
4 4 [(𝑛 + 1)!]2
𝑛=0
csch−1(𝑥) = − ln(𝑥) + ln(2)
∞ 1 3𝑖 5𝑖
1 (−1)𝑛 (2𝑛 + 1)! 𝑥 2𝑛+2 − ln(𝑥) + ln(2) + 𝑥 2 − 𝑥 4 + 𝑥 6 − ⋯
+ ∑ 4 32 96
4 4𝑛 [(𝑛 + 1)!]2
𝑛=0
∞
−1
𝑖𝜋 𝑥 2𝑛+1 𝑖𝜋 𝑥 3 𝑥 5 𝑥 7 𝑥 9 𝑥 11 𝑥 13
coth (𝑥) = − + ∑ =− +𝑥+ + + + + + +⋯
2 2𝑛 + 1 2 3 5 7 9 11 13
𝑛=0
Copyright © 2015-2022 by Harold Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor 6
Bernoulli Numbers Euler Numbers Gamma Function
𝐵0 = 1 1
𝛤0 = 𝛤 ( ) = √𝜋
1 2
𝐵1 = −
2 3 √𝜋
1 𝐸0 = 1 𝛤1 = 𝛤 ( ) =
𝐵2 = 2 2
6 𝐸1 = 0 5 3√𝜋
1 𝐸2 = −1 𝛤2 = 𝛤 ( ) =
𝐵4 = − 2 4
30 𝐸3 = 0 7 15√𝜋
1 𝛤3 = 𝛤 ( ) =
𝐵6 = 𝐸4 = 5 2 8
42
𝐸5 = 0 9 105√𝜋
1 𝛤4 = 𝛤 ( ) = ,
𝐵8 = − 𝐸6 = −61 2 16
30
5 𝐸8 = 1,385 11 945√𝜋
𝐵10 = 𝛤5 = 𝛤 ( ) =
66 𝐸10 = −50,521 2 32
691 𝐸12 = 2,702,765 13 10,395√𝜋
𝐵12 = − 𝛤6 = 𝛤 ( ) =
2,730 𝐸14 = −199,360,981 2 64
7 𝐸16 = 19,391,512,145 15 135,135√𝜋
𝐵14 = 𝛤7 = 𝛤 ( ) =
6 𝐸18 = −2,404,879,675,441 2 128
3,617
𝐵16 = − 𝐸20 = 370,371,188,237,525 17 2,027,025√𝜋
510 𝛤8 = 𝛤 ( ) =
𝐸22 = −69,348,874,393,137,901 2 256
438,675
𝐵18 = 19 34,459,425√𝜋
798 𝛤9 = 𝛤 ( ) =
174,611 𝐸2𝑛+1 = 0 2 512
𝐵20 = − 21 654,729,075√𝜋
330 𝛤10 = 𝛤 ( ) =
854,513 2 1,024
𝐵22 =
138
Generating Function
∞
𝛤(𝑡) = ∫ 𝑥 𝑡−1 𝑒 −𝑥 𝑑𝑥
∞ 0
𝑡 𝐵𝑛 𝑛
𝑡
=∑ 𝑡 ∞ 1 (2𝑛)!
𝑒 −1 𝑛! 1 2 𝐸𝑛 𝑛 𝛤 ( + 𝑛) = 𝑛 √𝜋
𝑛=0 = 𝑡 −𝑡
=∑ 𝑡 2 4 𝑛!
cosh (𝑡) 𝑒 + 𝑒 𝑛! 𝑛 (𝑛 − 2)‼
𝑛=0
𝛤( ) = 𝑛−1 √𝜋
2
2 2
Recursive Definition Iterated Sum Recursive Definition
𝐵𝑚 (𝑛) 𝛤(𝑛 + 1) = 𝑛 ∙ 𝛤(𝑛)
𝑚−1 𝐸2𝑛
𝑚 𝐵𝑘 (𝑛) 2𝑛+1 𝑘 𝑛 𝑛−2 𝑛−2
= 𝑛𝑚 − ∑ ( ) 𝑘 (−1)𝑗 (𝑘 − 2𝑗)2𝑛+1 𝛤( ) = ( )∙𝛤( )
𝑘 𝑚−𝑘+1 = 𝑖 ∑ ∑( ) 2 2 2
𝑘=0 𝑗 2𝑘 𝑖 𝑘 𝑘 1
𝐵0 (𝑛) = 1
𝑘=1 𝑗=0 𝛤 ( ) = √𝜋
2
Sources:
• https://www.wolframalpha.com
Copyright © 2015-2022 by Harold Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor 7
• https://en.wikipedia.org
• http://ddmf.msr-inria.inria.fr/1.9.1/ddmf
• http://web.mit.edu/kenta/www/three/taylor.html
Copyright © 2015-2022 by Harold Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor 8
You might also like
- Powers of Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument3 pagesPowers of Hyperbolic FunctionsKenneth TanNo ratings yet
- Power Series and TheoremsDocument4 pagesPower Series and TheoremsYen, Charles Enzeih CasimiroNo ratings yet
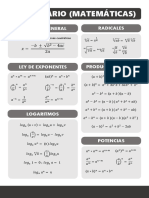
- By: Jhon Añez: Aritmética Desigualdades Radicales PotenciaciónDocument3 pagesBy: Jhon Añez: Aritmética Desigualdades Radicales PotenciaciónJhon D'LozxoNo ratings yet
- Distribucion de Poisson e Introduccion A Las Distribuciones ContinuasDocument8 pagesDistribucion de Poisson e Introduccion A Las Distribuciones ContinuasAlejandro Hernandez PinedaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Bsam65Document4 pagesFinal Exam Bsam65Carl DevinNo ratings yet
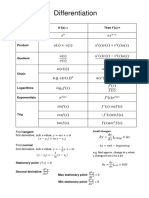
- Differentiation: Rule If F (X) Then F' (X) BasicDocument2 pagesDifferentiation: Rule If F (X) Then F' (X) BasicJo-LieAngNo ratings yet
- Formulario Calculo Integral-DiferencialDocument9 pagesFormulario Calculo Integral-DiferencialLuis SalomNo ratings yet
- Formulario Calculo Integral-DiferencialDocument5 pagesFormulario Calculo Integral-DiferencialLuis SalomNo ratings yet
- 5 Maks Qs - Ans II PU MathematicsDocument27 pages5 Maks Qs - Ans II PU MathematicsMirza SabeelNo ratings yet
- Formula Maths T SEM 2Document2 pagesFormula Maths T SEM 2Huang TangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SolutionsDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Solutionshappy062733No ratings yet
- Formulario Pre..Document7 pagesFormulario Pre..MILTON ANABI SAIWANo ratings yet
- Statistics Formulae BookletDocument36 pagesStatistics Formulae BookletKarl LewisNo ratings yet
- Super HojaDocument3 pagesSuper HojaWilfriSegundoIzquierdoNo ratings yet
- Theory of Approximation and Splines-I Lecture 02 Error Bound For Lagrange Interpolation PolynomialDocument4 pagesTheory of Approximation and Splines-I Lecture 02 Error Bound For Lagrange Interpolation PolynomialMusavarah SarwarNo ratings yet
- Math FormulasDocument25 pagesMath FormulasEduard Joseph Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- A2 Pure Math NotesDocument7 pagesA2 Pure Math NotesSHREYA NARANGNo ratings yet
- Formulario+de+Matemática+Básica+ +Profe+IsmarDocument1 pageFormulario+de+Matemática+Básica+ +Profe+IsmarmjaNo ratings yet
- Fourier TC Vs 4Document33 pagesFourier TC Vs 4Daniel MedauraNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument1 pageFormulasYenifer GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Formulario LaPlaceDocument1 pageFormulario LaPlaceandres.castellonNo ratings yet
- Clave de Primer Parcial de Matemática IV. 2022Document9 pagesClave de Primer Parcial de Matemática IV. 2022César Augusto GuidoNo ratings yet
- Methods ConnectEd TI-NspireDocument38 pagesMethods ConnectEd TI-Nspiremvz61484No ratings yet
- Super HojaDocument2 pagesSuper HojaKyara MolinaNo ratings yet
- Super Hoja PDFDocument2 pagesSuper Hoja PDFYUNIOR ESTRADANo ratings yet
- Super Hoja 1Document2 pagesSuper Hoja 1Daniel Diaz CastilloNo ratings yet
- Super HojaDocument2 pagesSuper HojaasdsdadNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument4 pagesFormula SheetSyasya AziziNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Quick ReviewDocument7 pagesMathematics Quick ReviewRC Rech CimafrancaNo ratings yet
- Equations: Right Angled Triangles: Soh Sin ( °) - Cah Cos ( °) - Toa Tan ( °)Document1 pageEquations: Right Angled Triangles: Soh Sin ( °) - Cah Cos ( °) - Toa Tan ( °)Jay AmbadkarNo ratings yet
- Nucleo - Imagen - Nulidad y RangoDocument4 pagesNucleo - Imagen - Nulidad y RangoἉρῆδ ΠολέμουNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 (Fourier Series)Document24 pagesUnit 5 (Fourier Series)krushil tejaniNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Quick ReviewDocument9 pagesMathematics Quick ReviewRC Rech CimafrancaNo ratings yet
- BMATE201 - Module 3Document35 pagesBMATE201 - Module 3Aditya VernekarNo ratings yet
- Curve Sketching: Example 1Document22 pagesCurve Sketching: Example 1Hin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- Hermite Differential EquationDocument10 pagesHermite Differential EquationNirmal KumarNo ratings yet
- Mata 33Document37 pagesMata 33Aissatou FallNo ratings yet
- 597 - Correction TD Fonction CirculaireDocument4 pages597 - Correction TD Fonction CirculaireToxic DEVNo ratings yet
- Universidad José Carlos MariáteguiDocument4 pagesUniversidad José Carlos MariáteguitreisythaisRNo ratings yet
- MAK202E Numerical Methods Formula-Sheet-V3-20230606 (ATÇ)Document2 pagesMAK202E Numerical Methods Formula-Sheet-V3-20230606 (ATÇ)Ege ÖztaşNo ratings yet
- Taylor Series in Finite FormDocument8 pagesTaylor Series in Finite FormLOLNo ratings yet
- 03 - HW Function Limits A SolutionsDocument13 pages03 - HW Function Limits A SolutionsMaxNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Integrales InmediatasDocument2 pagesTabla de Integrales Inmediatasjose robertoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 &6 Differentiation &its Applications: Quotient RuleDocument2 pagesChapter 5 &6 Differentiation &its Applications: Quotient RuleRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis: Lecture - 14Document8 pagesNumerical Analysis: Lecture - 14Muhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Tabelul PrimitevelorDocument2 pagesTabelul PrimitevelorIoana EnachiNo ratings yet
- Lineal PracticaDocument5 pagesLineal PracticaYherik Daner Acho VaquiataNo ratings yet
- FORMULA SHEET Test 2Document1 pageFORMULA SHEET Test 2singhjobanjit99No ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet晓春王No ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics Formula SpecDocument33 pagesPure Mathematics Formula SpecSubaproNo ratings yet
- Mat Discreta IIDocument6 pagesMat Discreta IIBruno GarateNo ratings yet
- 2nd Module - Numerical Solutions To CE Problems - Taylor Series Expansion - Part 1Document7 pages2nd Module - Numerical Solutions To CE Problems - Taylor Series Expansion - Part 1ELSA M. ARCIBAL100% (1)
- DerivadaDocument1 pageDerivadaDaniel Estrada RochabrunNo ratings yet
- Answers to selected exercises from 06 - HW: We can use the approximation at 𝑥 = 𝑎 + Δ𝑥 near aDocument4 pagesAnswers to selected exercises from 06 - HW: We can use the approximation at 𝑥 = 𝑎 + Δ𝑥 near aSuman BhurtelNo ratings yet
- Notes - Fourier Series in (0,2π)Document39 pagesNotes - Fourier Series in (0,2π)vu1f2122093No ratings yet
- BS Caculus2Document4 pagesBS Caculus2Ayesha NasirNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - EM1 - EM2Document12 pagesFormula Sheet - EM1 - EM2Ziyang XieNo ratings yet
- Tabela Transformadas LaplaceDocument2 pagesTabela Transformadas LaplacePedro OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Reglas de DerivaciónDocument1 pageReglas de Derivaciónaxelmontenegro007No ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Chain Rule ProofDocument2 pagesChain Rule ProofOmar TalaatNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 PDFDocument27 pagesProblem Set 2 PDFjacob quizonNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument5 pagesHyperbolic FunctionsNelsonMoseMNo ratings yet
- Power SeriesDocument80 pagesPower SeriesKaran PeshwaniNo ratings yet
- Functional Series. Pointwise and Uniform ConvergenceDocument17 pagesFunctional Series. Pointwise and Uniform ConvergenceProbenEksNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument21 pagesMathssalmaNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 Trigonometric EquationsDocument17 pagesRD Sharma Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 Trigonometric EquationsBhushan kumarNo ratings yet
- D'Alembert's Ratio Test of Convergence of SeriesDocument4 pagesD'Alembert's Ratio Test of Convergence of Seriessmoking llamaNo ratings yet
- Tarea 8. Empuje. Douglas VargasDocument672 pagesTarea 8. Empuje. Douglas VargasJOhan VArgas''No ratings yet
- Lesson 3c Power Series Radius and Interval of ConvergenceDocument12 pagesLesson 3c Power Series Radius and Interval of ConvergenceSheena Marie DuardasNo ratings yet
- List of FormulaDocument3 pagesList of FormulaAnggun AureolaNo ratings yet
- Math 163 Wa 1 F23Document2 pagesMath 163 Wa 1 F23li871668578No ratings yet
- Math 4130 Fall 20214 SeriesDocument57 pagesMath 4130 Fall 20214 SeriesVansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 Convergence Tests For SeriesDocument2 pagesLecture 14 Convergence Tests For SeriesShresth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.4-Derivatives of Some Transcendental FunctionsDocument9 pagesTopic 2.4-Derivatives of Some Transcendental FunctionsArfred NatividadNo ratings yet
- LHR and Improper IntegralsDocument22 pagesLHR and Improper IntegralsLoraine Ruth LumenNo ratings yet
- Murali Rao, Henrik Stetkaer - Complex Analysis - An Invitation - A Concise Introduction To Complex Function Theory-World Scientific Publishing Company (1991) PDFDocument252 pagesMurali Rao, Henrik Stetkaer - Complex Analysis - An Invitation - A Concise Introduction To Complex Function Theory-World Scientific Publishing Company (1991) PDFSiswadi JalyieNo ratings yet
- BSC Bed Math Syllabus 2 YearDocument3 pagesBSC Bed Math Syllabus 2 Yearlelico724No ratings yet
- Do Now Learning Target: - 1.4: Rational vs. Irrational NumbersDocument15 pagesDo Now Learning Target: - 1.4: Rational vs. Irrational NumbersCaty LiesekeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Infinite Series: U U U UDocument4 pagesChapter 4 Infinite Series: U U U UAbhijeet DadheechNo ratings yet
- Power Series, Taylor Series: Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 10/e by Edwin KreyszigDocument69 pagesPower Series, Taylor Series: Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 10/e by Edwin Kreyszighf100% (1)
- I.T. de Arco TripleDocument4 pagesI.T. de Arco TripleJoel Gilber Capcha GarcilazoNo ratings yet
- 10th Intro To TrigoDocument11 pages10th Intro To TrigoDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- ps11 9Document11 pagesps11 9frak ksaNo ratings yet
- XI - Maths - Chapter 3 - TRIGONOMETRY UPTO TRANSFORMATIONS (73-109)Document37 pagesXI - Maths - Chapter 3 - TRIGONOMETRY UPTO TRANSFORMATIONS (73-109)SANTHOSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Monotonicity GB Sir ModuleDocument10 pagesMonotonicity GB Sir ModuleDevesh TripathiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2: Analytic FunctionsDocument36 pagesCHAPTER 2: Analytic Functionsjudy.pierce330100% (11)
- MAT-101 Engineering Mathematics 1 Differential Calculus Lecture-1 Differentiation: Basic Concepts To RememberDocument4 pagesMAT-101 Engineering Mathematics 1 Differential Calculus Lecture-1 Differentiation: Basic Concepts To RememberTorcoxk NamgayNo ratings yet
- Proofs You Need Not Be Able To Reproduce.: 3.1 Convergent SequencesDocument4 pagesProofs You Need Not Be Able To Reproduce.: 3.1 Convergent Sequenceslessinah mbeleNo ratings yet