Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enviscipracticequestions
Enviscipracticequestions
Uploaded by
Blexx Lagrimas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageThe document contains practice questions for an environmental science exam covering topics like biodiversity, global warming, pollution, population ecology, habitat loss, sustainability, and the ozone layer. It asks questions about definitions, examples, causes, and key terms related to these environmental topics.
Original Description:
Original Title
enviscipracticequestions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document contains practice questions for an environmental science exam covering topics like biodiversity, global warming, pollution, population ecology, habitat loss, sustainability, and the ozone layer. It asks questions about definitions, examples, causes, and key terms related to these environmental topics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageEnviscipracticequestions
Enviscipracticequestions
Uploaded by
Blexx LagrimasThe document contains practice questions for an environmental science exam covering topics like biodiversity, global warming, pollution, population ecology, habitat loss, sustainability, and the ozone layer. It asks questions about definitions, examples, causes, and key terms related to these environmental topics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Practice questions for envi sci
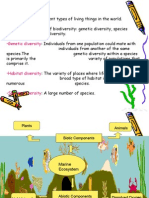
• What does “bio-” in biodiversity means?
• It is where all the different kinds of life are found in one area.
• It is the sum of all various life forms such as fungi, protozoa, bacteria and multicellular
organisms such as mammals and flowering plants.
• A condition where grasslands turn into desert-like conditions because of poor water management
and soil quality.
• The condition when the global climate becomes warmer.
• The cause of global warming is the increasing amount of ______ in the atmosphere.
• The ozone layer protects the earth from harmful radiation from the sun called ______.
• Poor water quality, heavy metal contamination in the rivers and plastics in the ocean are
examples of _______.
• An acid rain is an example of what type of pollution?
• Sounds from vehicles that affects behavior of species such as lowered mating rates and increase
of avoidance in that area is an example of _________.
• This pollution disrupts the natural patterns of wildlife due to excessive use of light.
• Burning of fossil fuels can cause nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide to react that leads to
rain that can slowly destroy buildings and affect the pH of water supplies in the environment.
What phenomena is this?
• Large patches of forests that are lost because they are not replaced as fast as they are
harvested.
• It is the responsible use of natural resources to protect the environment.
• Biodiversity has three key components except ________.
• It is important for food, drugs, maintaining ecological stability, aesthetic and cultural
benefits.
• A change in water quality caused by human activities that impacts living organisms.
• Species that are not native in the area and have no natural predators.
• It is a serious burden in our ecosystems and finances worldwide.
• The process when habitats become smaller pockets due to human activity.
• Any garbage or refuse, sludge or other discarded material resulting from industrial, commercial,
mining and agricultural operations.
• Long-term changes in the global climate.
• CFCs is the acronym for ______________.
• What year was it that evidence of a large “ozone hole” was discovered?
• From the previous question, where was it located?
• It describes a group of individual species.
• It describes a collection of different species in an area.
• A population that shows a J-shaped graph is said to be _________.
• A population that has reached an S-shaped graph is said to be ______.
• Age structure where majority of the population is not mature enough to reproduce.
• Age structure where majority of the population is capable of reproduction.
• Age structure where majority of the population are those too old to reproduce.
• The number of individuals in a population found in a particular area or volume
• Species that tend to be opportunists and reproduce quickly.
• Species that tend to be competitive and have longer gestation period
• It occurs when natural environments are transformed or modified to serve human needs.
• A process where biodiversity is removed faster than it can be replenished.
• Species that have spread outside of their natural habitat and threaten biodiversity in their
new area.
• It creates deadzones in the water. Deadzones are areas of no oxygen in aquatic bodies.
• An air pollution phenomena where there is an accumulation of smoke and fumes in urban cities.
• It is anything that degrades water quality.
• It is the final driver of biodiversity loss.
• It is the responsible use of natural resources.
• It is caused by a build-up of greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere and alters climate
patterns.
• A loss of a nearly all population of a species or its entirety.
• Species where its population is threatened to extinction.
• Species whose area is restricted to a particular area; often endangered.
• Local parts of the habitat become separated because of habitat loss.
• It is the layer in the atmosphere which blocks or lessens the amount of UV radiation.
• These chemicals were the cause of the “ozone hole”.
You might also like
- Environmental ScienceDocument10 pagesEnvironmental Sciencemattblack71471% (7)
- L2-Environmental Engineering - Main ConsiderationDocument29 pagesL2-Environmental Engineering - Main ConsiderationYusf ari jerjisNo ratings yet
- Environment ManagementDocument150 pagesEnvironment Managementcotade5392No ratings yet
- Human Influences On EcosystemDocument34 pagesHuman Influences On Ecosystembella annariNo ratings yet
- PollutionDocument23 pagesPollutionkaiya mollenthielNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Components of EcosystemDocument24 pagesChapter2 Components of EcosystemvenjosagadbuhayNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Distribution of BiodiversityDocument21 pagesWeek 11 Distribution of BiodiversityGhulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- CNR Module1Document40 pagesCNR Module1Harshith Kumar hvNo ratings yet
- Ecology Important Env. IssuesDocument47 pagesEcology Important Env. Issuesajaya4kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies: Compensatory AssignmentDocument13 pagesEnvironmental Studies: Compensatory AssignmentPrachiChauhanNo ratings yet
- Est CH 1Document54 pagesEst CH 1Dhanshree GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Effects of Humans On EcosystemsDocument20 pagesEffects of Humans On Ecosystemsr. mnzimaNo ratings yet
- By: - Shefali - Nikyta - Garima - Aashish - Rahul - Nikhil - TanmayDocument42 pagesBy: - Shefali - Nikyta - Garima - Aashish - Rahul - Nikhil - TanmayNIKNISHNo ratings yet
- GROUP-2: Presentation On Enviornmental StudiesDocument20 pagesGROUP-2: Presentation On Enviornmental Studieschirag mataiNo ratings yet
- S Material 1695985482 Environment 5 C e Batch 29 09 2023Document42 pagesS Material 1695985482 Environment 5 C e Batch 29 09 2023thangasachithananthan.rvsNo ratings yet
- Effect of Humans On EcosystemDocument14 pagesEffect of Humans On EcosystemmalaikaNo ratings yet
- Environment Seminar 1Document11 pagesEnvironment Seminar 1cyrusNo ratings yet
- L1Document60 pagesL1Kawinharsun DNo ratings yet
- UNITIMergedDocument111 pagesUNITIMergedmalikanuj0151No ratings yet
- Introduction To Environment and Environmental Studies: Mahmoud I. Mahmoud Assistant Professor Cihan University - EbilDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Environment and Environmental Studies: Mahmoud I. Mahmoud Assistant Professor Cihan University - EbilMahmoud I. MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Consequences of BiodiversityDocument16 pagesConsequences of BiodiversityNeeru RedhuNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Environmental StudiesDocument40 pagesUnit 5: Environmental StudiesRakshana NairNo ratings yet
- UploadDocument34 pagesUploadKimi DeolNo ratings yet
- 2017 Question Paper: Submitted By: Priyanka Roy B.SC Interior Design Guwahati College of Architecture and PlanningDocument30 pages2017 Question Paper: Submitted By: Priyanka Roy B.SC Interior Design Guwahati College of Architecture and PlanningSaurabh DeyNo ratings yet
- Environmental Issues PDFDocument36 pagesEnvironmental Issues PDFसमीर कुमार आतिशNo ratings yet
- Intervensi BiodiversityDocument6 pagesIntervensi BiodiversityhanifNo ratings yet
- Global Environmental Issues and ProblemsDocument28 pagesGlobal Environmental Issues and ProblemsHarshita MunotNo ratings yet
- Human Environment InteractionsDocument27 pagesHuman Environment Interactionsjyjkmhz97gNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument2 pagesNatural ResourceshomamunfatNo ratings yet
- G3 - Sustainable Development NotesDocument6 pagesG3 - Sustainable Development Noteskshreyaas80No ratings yet
- Computer PresentationDocument19 pagesComputer PresentationSANGEEN KHANNo ratings yet
- On EVS-UNIT-1Document17 pagesOn EVS-UNIT-1dipra mitra100% (2)
- Lec 1Document29 pagesLec 1aminabutt4524No ratings yet
- Enviornmnet Components and RelationshipDocument23 pagesEnviornmnet Components and Relationshipsehrish iqbalNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Environment Management and Human Rights Module OneDocument36 pagesQuestion Bank Environment Management and Human Rights Module Oneѕαlυ ѕαвυNo ratings yet
- Environmental System: Done By: Lana Shabsough Sameera OwedahDocument25 pagesEnvironmental System: Done By: Lana Shabsough Sameera OwedahLana ShabsoughNo ratings yet
- BiologyIIforNonMajorsII 14Document64 pagesBiologyIIforNonMajorsII 14Mmoh87No ratings yet
- Environmental Science Semester Question Bank Class 9: Our Environmental Problems Lesson No 1Document22 pagesEnvironmental Science Semester Question Bank Class 9: Our Environmental Problems Lesson No 1PrashantNo ratings yet
- Ssac 2104Document100 pagesSsac 2104Amrutha amrNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (EMHR)Document36 pagesQuestion Bank (EMHR)Neeraj KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ingles Manuela QDocument15 pagesIngles Manuela Qbeatrizvillasalo2006No ratings yet
- Human Environment Chap 13Document23 pagesHuman Environment Chap 13Sophea Mercer AnaisNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document38 pagesUnit 2N.S Achyuth AnandNo ratings yet
- Human Activities That Affect Natural EcosystemsDocument15 pagesHuman Activities That Affect Natural EcosystemsDiego SandovalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-2Document27 pagesUnit 1-2Vishika jainNo ratings yet
- Types, Features, Structure, and Function of Ecosystem (Terrestrial/aquatic)Document24 pagesTypes, Features, Structure, and Function of Ecosystem (Terrestrial/aquatic)Bhavvyam BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Environmental PollutionDocument49 pagesEnvironmental PollutionAria PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Biodiversity - Threats To BiodiversityDocument20 pagesLecture 3 - Biodiversity - Threats To BiodiversitySimphiweNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science: Air Pollution Biodiversity DepletionDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Science: Air Pollution Biodiversity DepletionSneha MehtaNo ratings yet
- Humans and Nature: An OverviewDocument55 pagesHumans and Nature: An OverviewJeffreyNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 NotesDocument12 pagesTopic 3 NotesRaviNo ratings yet
- 3 - EcosystemsDocument43 pages3 - EcosystemsMisaki ShirabeNo ratings yet
- Human Activity Impact On EnvironmentDocument29 pagesHuman Activity Impact On EnvironmentHemant KushwahNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument63 pagesBiodiversitybhuvanashreemsNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 (Full) - Significance of BiodiversityDocument12 pagesUnit 3 (Full) - Significance of BiodiversityEsai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Ecosystem: 1.climate ChangeDocument8 pagesFactors Affecting Ecosystem: 1.climate ChangeprasannashivanandmalagundNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Environmental Issues and ConcernsDocument85 pagesChapter 5 - Environmental Issues and ConcernsbtstjaNo ratings yet
- ENVIRONMENTDocument62 pagesENVIRONMENTTanya AroraNo ratings yet
- 14 EcologyDocument93 pages14 EcologyGuru temp id-04 for Sekolah-8252 MoeNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem NotesDocument50 pagesEcosystem NotesMahendra DevikarNo ratings yet
- Core Energy: The Cry of the Earth: Climate Change and the Loss of BiodiversityFrom EverandCore Energy: The Cry of the Earth: Climate Change and the Loss of BiodiversityNo ratings yet
- AutopsyDocument8 pagesAutopsyBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Chlamydiaceae Mycoplasma Ureaplasma SpirochaetesDocument65 pagesChlamydiaceae Mycoplasma Ureaplasma SpirochaetesBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Rickettsiaceae and Other Related OrganismsDocument14 pagesRickettsiaceae and Other Related OrganismsBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument47 pagesTuberculosisBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet No. 8Document5 pagesActivity Sheet No. 8Blexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Oc13med Vmo, History, Administration Transes FinalDocument5 pagesOc13med Vmo, History, Administration Transes FinalBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Automated Machines MedtekDocument7 pagesAutomated Machines MedtekBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Human Population Dynamics NotesDocument120 pagesHuman Population Dynamics NotesBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Gel101sw Environmental Science, Energy, Biogeochem Transes FinalDocument6 pagesGel101sw Environmental Science, Energy, Biogeochem Transes FinalBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Soc Econ Transes Module 1 - 4 FinalDocument15 pagesSoc Econ Transes Module 1 - 4 FinalBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Species ConceptsDocument33 pagesSpecies ConceptsBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Habitat and Niche-1Document5 pagesHabitat and Niche-1Blexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- General Electives I Sample QuestionsDocument2 pagesGeneral Electives I Sample QuestionsBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Proteins: Sheila Mai S. Rocabo, RMT, MSMTDocument37 pagesProteins: Sheila Mai S. Rocabo, RMT, MSMTBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- LabMan Midterm NotesDocument12 pagesLabMan Midterm NotesBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- DYNAMICSDocument6 pagesDYNAMICSBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Raiders of SuluDocument1 pageRaiders of SuluBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Ethics Midterm Week 1-3 Lecture NotesDocument14 pagesEthics Midterm Week 1-3 Lecture NotesBlexx LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Alum BrochureDocument2 pagesAlum Brochurepramod DudhaneNo ratings yet
- Ambar Indraswari - 952023105 - Portofolio UTS Bahasa InggrisDocument5 pagesAmbar Indraswari - 952023105 - Portofolio UTS Bahasa InggrisAmbar IndraswariNo ratings yet
- 913-916 (4553)Document4 pages913-916 (4553)Sandy Wahyu DNo ratings yet
- Ecology - BSC (H) Botany - IV SemesterDocument6 pagesEcology - BSC (H) Botany - IV Semestervishnu tyagiNo ratings yet
- 5 Unconfined AquifersDocument10 pages5 Unconfined Aquiferstom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1 Product and Company IdentificationDocument3 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1 Product and Company IdentificationDita NursaiidahNo ratings yet
- Multi Dimensional Approaches To Scaling Up Coral Reef Restoration - T LamontDocument11 pagesMulti Dimensional Approaches To Scaling Up Coral Reef Restoration - T LamontCarm TesoroNo ratings yet
- A Study of LCA On Tofu IndustryDocument7 pagesA Study of LCA On Tofu IndustryNuyul FaizahNo ratings yet
- 10. LUYỆN VIẾT ĐOẠN VĂN TIẾNG ANH - ON DEFORESTATIONDocument3 pages10. LUYỆN VIẾT ĐOẠN VĂN TIẾNG ANH - ON DEFORESTATIONVũ TuấnNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Stanbio TrigliseridaDocument4 pagesMSDS - Stanbio TrigliseridaDoni Eka Prasetiyo100% (1)
- Indicator and Methods For The Ecological Status Assessment Under The WFD Linkages Between Chemical and Biological Quality of Surface WatersDocument262 pagesIndicator and Methods For The Ecological Status Assessment Under The WFD Linkages Between Chemical and Biological Quality of Surface WatersAstrit E. Salihu100% (1)
- WWF Org. SAIDocument18 pagesWWF Org. SAIRares-Ioan ManescuNo ratings yet
- JX-4B Full Auto Wash Recycling System-Liv-2021.9.22Document4 pagesJX-4B Full Auto Wash Recycling System-Liv-2021.9.22romdreNo ratings yet
- Bioindicators - Using Organisms To Measure Environmental Impacts - Learn Science at ScitableDocument10 pagesBioindicators - Using Organisms To Measure Environmental Impacts - Learn Science at ScitableP KalaiselviNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Sustainable Engineering-Module-1Document57 pagesIntroduction To Sustainable Engineering-Module-1freeguba100% (7)
- Water Reuse in Developing Countries: The Golden Rule of Wastewater ReuseDocument12 pagesWater Reuse in Developing Countries: The Golden Rule of Wastewater ReuseHanna SilverioNo ratings yet
- ClihydDocument4 pagesClihydPooja PandeyNo ratings yet
- Global Warming in CaribbeanDocument1 pageGlobal Warming in CaribbeanShamir RagoonananNo ratings yet
- Somalia - Improving Access To Water and Sanitation in Rural Somalia - ESMPDocument21 pagesSomalia - Improving Access To Water and Sanitation in Rural Somalia - ESMPAhmedNo ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument11 pagesAgricultureElisa FriggieriNo ratings yet
- Environmental Work Program: Mines and Geosciences BureauDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Work Program: Mines and Geosciences BureauKristy Edgie AlburoNo ratings yet
- Waste WaterDocument36 pagesWaste WaterAyush VoraNo ratings yet
- Seaweeds and Their Role in Globally Changing EnvirDocument465 pagesSeaweeds and Their Role in Globally Changing EnvirTamara DíazNo ratings yet
- Soil Degradation: A Challenge To Sustainable AgricultureDocument6 pagesSoil Degradation: A Challenge To Sustainable AgricultureAmin MojiriNo ratings yet
- Check Dams (CD) EC-12: DescriptionDocument6 pagesCheck Dams (CD) EC-12: DescriptionmarthantyNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Quiz in Special TopicsDocument10 pagesCompilation of Quiz in Special TopicsIme MisaNo ratings yet
- Hydrographic Surveying: - Uses of Hydrographic SurveyDocument7 pagesHydrographic Surveying: - Uses of Hydrographic SurveyShahid AliNo ratings yet
- Climate Museum ShowcaseDocument5 pagesClimate Museum Showcaseapi-403105736No ratings yet
- What Is ForestDocument3 pagesWhat Is Forestshush10No ratings yet