Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Immuno Sero Lec Week 2 Transes
Immuno Sero Lec Week 2 Transes
Uploaded by
Koarie Frae ZuleCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Immunology MCQ DrNaeem PDFDocument163 pagesImmunology MCQ DrNaeem PDFA-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOLOGY - 2 - Lymphoid SystemDocument2 pagesIMMUNOLOGY - 2 - Lymphoid SystemFelix NepumocenoNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Immune System NotesDocument7 pagesAdaptive Immune System Notesolmilloanne02No ratings yet
- Tissue and Organs of The Immune System: Learning GoalsDocument113 pagesTissue and Organs of The Immune System: Learning Goalsbright nvachirawit100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Basic ImmunologyDocument64 pagesChapter 2 Basic ImmunologykelifamohammadsaniabdulfatahNo ratings yet
- DermatitisDocument31 pagesDermatitisJoanne LagusadNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Immune SystemDocument19 pagesOrgans of The Immune SystemprabuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010Document85 pagesChapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010TofikNo ratings yet
- By The End of This Chapter You Should Be Able ToDocument13 pagesBy The End of This Chapter You Should Be Able ToMac Kevin MandapNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument10 pagesLymphatic SystemPasipanodya MuzendaNo ratings yet
- 3 Organs of The Immune SystemDocument30 pages3 Organs of The Immune SystemRayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Function of Lymphoid Tissues: Wesam Mohammed EmharibDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Function of Lymphoid Tissues: Wesam Mohammed Emharibنسيم حامدNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System ReviewerDocument5 pagesLymphatic System ReviewerCHRISTIAN JUSTINE NARVAZANo ratings yet
- 1 - Hema Lec FinalsDocument8 pages1 - Hema Lec FinalsFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Immunology - Nursing HandoutsDocument22 pagesImmunology - Nursing HandoutsRayePrudente100% (1)
- Powerlecture: ImmunityDocument107 pagesPowerlecture: Immunitymr. nicartNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument21 pagesImmune SystemAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Antigen Presentation and T Cell ActivationDocument37 pagesAntigen Presentation and T Cell ActivationAzkayra AzzahraNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Immune FunctionDocument13 pages4.1 Immune FunctionJohn Anthony de GùzmanNo ratings yet
- Guide Questions Answers: 14.01A. Describe The Functions of The Lymphatic System. 14.01B. Explain How Lymph Is FormedDocument5 pagesGuide Questions Answers: 14.01A. Describe The Functions of The Lymphatic System. 14.01B. Explain How Lymph Is FormedPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- S6 Blood & ImmunityDocument41 pagesS6 Blood & ImmunityZoltan FodorNo ratings yet
- Bythe End of This Chapter You Should Be Able To:: The Lymphoid SystemDocument13 pagesBythe End of This Chapter You Should Be Able To:: The Lymphoid SystemMac Kevin MandapNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument18 pagesLymphatic SystemAlliyah SalindoNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues of The Immune SystemDocument32 pagesCells and Tissues of The Immune SystemSathiyaraj100% (13)
- Week 4 - Drugs Acting On The Immune SystemDocument16 pagesWeek 4 - Drugs Acting On The Immune SystemDino MicaNo ratings yet
- CBS Imm1Document31 pagesCBS Imm1tyhbbhhNo ratings yet
- theimmunesystem-130430115239-phpapp02Document31 pagestheimmunesystem-130430115239-phpapp02Aegon TargeryanNo ratings yet
- Besana 121106035558 Phpapp02 PDFDocument9 pagesBesana 121106035558 Phpapp02 PDFAtu KaushalNo ratings yet
- Pres. Histo. Sist. Imun - SNW '13Document34 pagesPres. Histo. Sist. Imun - SNW '13Septian PutraNo ratings yet
- ImmunoSero Side NotesDocument2 pagesImmunoSero Side NotesReca Marie FRIASNo ratings yet
- 8 Lymphoid TissueDocument3 pages8 Lymphoid TissueMary Dianne MosuelaNo ratings yet
- BIOL25441 Class 5 and 6 Winter 2013Document58 pagesBIOL25441 Class 5 and 6 Winter 2013raunak .comNo ratings yet
- Immuno Notes LectureDocument30 pagesImmuno Notes LectureSteph TabasaNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Dr. A.K.M. Akbar KabirDocument29 pagesImmunology: Dr. A.K.M. Akbar KabirRakib's exploration worldNo ratings yet
- Elearning LymphaticOrgans 1 2023newDocument49 pagesElearning LymphaticOrgans 1 2023newpiano357sidNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument11 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemmeowzartNo ratings yet
- MergeResult 2022 09 12 01 31 19Document3 pagesMergeResult 2022 09 12 01 31 19Reca Marie FRIASNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System and Body DefensesDocument12 pagesThe Lymphatic System and Body DefensesGuenevere DamasinNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemrazondiegoNo ratings yet
- Elearning Lymphatic Organs 2 2023newDocument28 pagesElearning Lymphatic Organs 2 2023newpiano357sidNo ratings yet
- LM 1 - Introduction To Concept With Immunity and InflammationDocument3 pagesLM 1 - Introduction To Concept With Immunity and InflammationMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument10 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemChloe MercadoNo ratings yet
- Histology BloodDocument6 pagesHistology BloodNeneng Cutin GanzonNo ratings yet
- Why There Are New Strain of Viruses?: Pathogens EvolveDocument30 pagesWhy There Are New Strain of Viruses?: Pathogens EvolveDRANo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument2 pagesThe Lymphatic Systemabi dimatulacNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of The Immune SystemDocument53 pagesCells and Organs of The Immune SystemZyma EmaNo ratings yet
- Histology 10 ImmunosystemDocument79 pagesHistology 10 ImmunosystemAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses: Part BDocument67 pagesThe Lymphatic System and Body Defenses: Part BJovelle AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Histology LymphaticDocument4 pagesHistology LymphaticIsaac DoringoNo ratings yet
- ÓRGÃOS e TECIDOS LINFOIDES PDFDocument4 pagesÓRGÃOS e TECIDOS LINFOIDES PDFPatricia CostaNo ratings yet
- Immune System by Asif PresentationDocument35 pagesImmune System by Asif PresentationHassan AsifNo ratings yet
- Assignment Adv. in ImmunologyDocument7 pagesAssignment Adv. in ImmunologyM Sikandar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Author(s) : Matthew Velkey, 2009 License: Unless Otherwise Noted, This Material Is Made Available Under The Terms ofDocument88 pagesAuthor(s) : Matthew Velkey, 2009 License: Unless Otherwise Noted, This Material Is Made Available Under The Terms ofEunice PalloganNo ratings yet
- MTEC 3790 Chapter 9Document37 pagesMTEC 3790 Chapter 9turkeyonryeNo ratings yet
- 2.introduction To ImmunologyDocument39 pages2.introduction To ImmunologyZakaria MakereNo ratings yet
- Our Immune System-CassDocument27 pagesOur Immune System-CassSaira BanuNo ratings yet
- Lymph NodeDocument13 pagesLymph NodeNurul Ilma AllauwNo ratings yet
- Reticuloendothelial SystemDocument26 pagesReticuloendothelial SystemNashreen QtqtNo ratings yet
- Group 11 HistoDocument40 pagesGroup 11 HistoJAWAD, JAINA A.No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 159q4x4fxyrNo ratings yet
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityFrom EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityNo ratings yet
- Module01 AnOverviewofClinicalLaboratoryHemtologyDocument52 pagesModule01 AnOverviewofClinicalLaboratoryHemtologyKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Module 01 HematopeisisDocument15 pagesModule 01 HematopeisisKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Loyzaga - (BK5) - #AnongAmbagMoDocument1 pageLoyzaga - (BK5) - #AnongAmbagMoKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- BK1 - Be Brave, Be Self-Reliant - LOYZAGADocument1 pageBK1 - Be Brave, Be Self-Reliant - LOYZAGAKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43 - MycobacteriaDocument3 pagesChapter 43 - MycobacteriaKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41 - 42 - Anaerobic OrganimsDocument4 pagesChapter 41 - 42 - Anaerobic OrganimsKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 46 - The SpirochetesDocument2 pagesChapter 46 - The SpirochetesKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 44 - Obligate Intracellular and Nonculturable BacteriaDocument2 pagesChapter 44 - Obligate Intracellular and Nonculturable BacteriaKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Performance of Sysmex XN-3100 Automated Hematology Analyzer Regarding The Sysmex XE-2100 and Microscopic ExaminationDocument9 pagesEvaluation of The Performance of Sysmex XN-3100 Automated Hematology Analyzer Regarding The Sysmex XE-2100 and Microscopic ExaminationbalkisNo ratings yet
- White Blood CellDocument8 pagesWhite Blood Cellsai calderNo ratings yet
- Analisis Kuantitas Dan Hitung Jenis Leuk 39572b02 PDFDocument7 pagesAnalisis Kuantitas Dan Hitung Jenis Leuk 39572b02 PDFFerminia Putri RukmawatiNo ratings yet
- CBC ReportDocument1 pageCBC ReportKamal DeepNo ratings yet
- Durdans Lab - Panadura MR .Josep Perera: Location:: Time:: 3:26PM Patient Name / 76 Y M Age / GenderDocument1 pageDurdans Lab - Panadura MR .Josep Perera: Location:: Time:: 3:26PM Patient Name / 76 Y M Age / GenderHush PereraNo ratings yet
- Nomenklatur Sel DarahDocument27 pagesNomenklatur Sel DarahAsyha KantifaNo ratings yet
- Wiki T CellDocument12 pagesWiki T Cellالولد الخطير تابعونيNo ratings yet
- Asim Saud&Saif Alawadi Asim Saud: Rakan Fayez El-HamadDocument14 pagesAsim Saud&Saif Alawadi Asim Saud: Rakan Fayez El-HamadInnocent L NdambakuwaNo ratings yet
- Erythroid PrecursorsDocument1 pageErythroid PrecursorsMezouar AbdennacerNo ratings yet
- ErythropoisisDocument47 pagesErythropoisisDisha SuvarnaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument1 pageReportM.Raheel GhoriNo ratings yet
- Rubriblast/ Pronormoblast: Size: Nucleus: Cytoplasm: N:C Ratio: Additional NotesDocument13 pagesRubriblast/ Pronormoblast: Size: Nucleus: Cytoplasm: N:C Ratio: Additional NotesOsannah Irish InsongNo ratings yet
- Blood: Types of Blood Cells and Their Average NumberDocument32 pagesBlood: Types of Blood Cells and Their Average NumberSumayya KabeerNo ratings yet
- Department of Laboratory Services - Laboratory: Biological Reference Interval Unit Result ParameterDocument2 pagesDepartment of Laboratory Services - Laboratory: Biological Reference Interval Unit Result ParameterParchuri PraveenNo ratings yet
- G89858 Id No: Haematology ReportDocument1 pageG89858 Id No: Haematology Reportতৌফিক আহমেদNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Mast Cell and BasophilDocument2 pagesDifference Between Mast Cell and BasophilponbohacopNo ratings yet
- Nucleated Red Blood Cell (NRBC) - QSP Newsletter Issue 44Document2 pagesNucleated Red Blood Cell (NRBC) - QSP Newsletter Issue 44Gaurav MauryaNo ratings yet
- Kuby Immunology, 7e: Chapter 2: Cells, Organs, and Microenvironments of The Immune SystemDocument37 pagesKuby Immunology, 7e: Chapter 2: Cells, Organs, and Microenvironments of The Immune Systemnemezienna100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Cells and Organs of The Immune System PDFDocument61 pagesChapter 2 Cells and Organs of The Immune System PDFanaraudhatulNo ratings yet
- Leucemia Limfatica CronicaDocument52 pagesLeucemia Limfatica CronicaAnghel BogdanNo ratings yet
- Components of BloodDocument20 pagesComponents of BloodVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Parham Ch. 1: An Overview of The Immune System: (Fig. 1.3) Pathogen An Organism That Causes Disease Eg: BacteriaDocument10 pagesParham Ch. 1: An Overview of The Immune System: (Fig. 1.3) Pathogen An Organism That Causes Disease Eg: BacteriaAbhishek Isaac MathewNo ratings yet
- MegakaryopoiesisDocument41 pagesMegakaryopoiesisHazel FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Humoral and Cell Mediated Immunity: September 2017Document9 pagesDifference Between Humoral and Cell Mediated Immunity: September 2017Shivraj JadhavNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Hematopoiesis I. General Principles of HematopoiesisDocument13 pagesModule 2: Hematopoiesis I. General Principles of HematopoiesisJane JapoleNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise On Blood: .What Is The Blood Volume of An Avernge-Sized Adult Male?Document4 pagesLab Exercise On Blood: .What Is The Blood Volume of An Avernge-Sized Adult Male?سهى الغامديNo ratings yet
- Classification Functions of WBCsDocument22 pagesClassification Functions of WBCsirajput 001No ratings yet
- Hematology I ArconadoDocument37 pagesHematology I ArconadoReizel GaasNo ratings yet
- SNAB 7.18 Immunity FlashcardsDocument2 pagesSNAB 7.18 Immunity FlashcardsMeidayNo ratings yet
Immuno Sero Lec Week 2 Transes
Immuno Sero Lec Week 2 Transes
Uploaded by
Koarie Frae ZuleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Immuno Sero Lec Week 2 Transes
Immuno Sero Lec Week 2 Transes
Uploaded by
Koarie Frae ZuleCopyright:
Available Formats
LOYZAGA, ANDREA MAE.
2019-2023 IMMUNOLOGY & SEROLOGY | CHAPTER 1
Lymphoid Organs
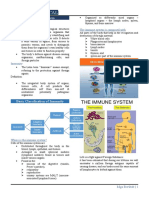
Provides a location where contact with foreign antigens
Introduction can occur
Organs of the Immune System have 2 types: Spleen, lymph nodes, and various types of mucosal-
associated lymphoid tissues, and cutaneous-associated
Primary Lymphoid Organs lymphoid tissue
Where maturation of B and T cells takes place Circulation of lymphocytes between secondary organs
Bone marrow and Thymus is complex and is regulated by cell surface adhesion
Secondary Lymphoid Organs molecules and cytokines
Provides a location where contact with foreign Lymphocytes travel through tissue and bloodstream via
antigens can occur thoracic duct
Spleen, lymph nodes, and various types of mucosal Lymphopoiesis (multiplication of lymphocytes) occurs
associated lymphoid tissues in these tissues and is antigen-dependent vs in the bone
marrow (antigen independent)
Primary Lymphoid Organs Spleen
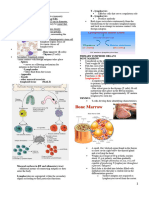
Bone Marrow
Serve as central collecting points for lymph fluid
One of the largest tissues in the body and a main
from adjacent tissues.
source of hematopoietic stem cells
Filtration of interstitial fluid from around cells in
Some lymphocyte precursors remain in the marrow
the tissues is an important function of these organs
to mature and become NK and B cells (T cells
Provide the ideal environment for contact with
mature at thymus)
foreign antigens that have penetrated the tissues
If contact with an antigen takes place, lymphocyte
traffic shuts down. Lymphocytes able to respond to
a particular antigen proliferate in the node
Thymus
A small, flat, bilobed organ found in the thorax Other Secondary Lymphoid Organs
Diminishes in size as humans age Mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
Site where T cells mature Ex. Tonsils, appendix, Peyer’s patches
Thought initially to produce enough virgin T
lymphocytes early in life to seed the entire immune Skin (lined with intra epidermal lymphocytes and
system WBCs)
2 portions: Thymic cortex and medulla collectively termed as Cutaneous-associated
lymphoid tissue (CALT)
T-cell maturation and differentiation happens as it
moves through these areas
Mature T lymphocytes are then released from the
medulla
Secondary Lymphoid Organs
Page 1|1
You might also like
- Immunology MCQ DrNaeem PDFDocument163 pagesImmunology MCQ DrNaeem PDFA-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOLOGY - 2 - Lymphoid SystemDocument2 pagesIMMUNOLOGY - 2 - Lymphoid SystemFelix NepumocenoNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Immune System NotesDocument7 pagesAdaptive Immune System Notesolmilloanne02No ratings yet
- Tissue and Organs of The Immune System: Learning GoalsDocument113 pagesTissue and Organs of The Immune System: Learning Goalsbright nvachirawit100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Basic ImmunologyDocument64 pagesChapter 2 Basic ImmunologykelifamohammadsaniabdulfatahNo ratings yet
- DermatitisDocument31 pagesDermatitisJoanne LagusadNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Immune SystemDocument19 pagesOrgans of The Immune SystemprabuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010Document85 pagesChapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010TofikNo ratings yet
- By The End of This Chapter You Should Be Able ToDocument13 pagesBy The End of This Chapter You Should Be Able ToMac Kevin MandapNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument10 pagesLymphatic SystemPasipanodya MuzendaNo ratings yet
- 3 Organs of The Immune SystemDocument30 pages3 Organs of The Immune SystemRayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Function of Lymphoid Tissues: Wesam Mohammed EmharibDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Function of Lymphoid Tissues: Wesam Mohammed Emharibنسيم حامدNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System ReviewerDocument5 pagesLymphatic System ReviewerCHRISTIAN JUSTINE NARVAZANo ratings yet
- 1 - Hema Lec FinalsDocument8 pages1 - Hema Lec FinalsFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Immunology - Nursing HandoutsDocument22 pagesImmunology - Nursing HandoutsRayePrudente100% (1)
- Powerlecture: ImmunityDocument107 pagesPowerlecture: Immunitymr. nicartNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument21 pagesImmune SystemAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Antigen Presentation and T Cell ActivationDocument37 pagesAntigen Presentation and T Cell ActivationAzkayra AzzahraNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Immune FunctionDocument13 pages4.1 Immune FunctionJohn Anthony de GùzmanNo ratings yet
- Guide Questions Answers: 14.01A. Describe The Functions of The Lymphatic System. 14.01B. Explain How Lymph Is FormedDocument5 pagesGuide Questions Answers: 14.01A. Describe The Functions of The Lymphatic System. 14.01B. Explain How Lymph Is FormedPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- S6 Blood & ImmunityDocument41 pagesS6 Blood & ImmunityZoltan FodorNo ratings yet
- Bythe End of This Chapter You Should Be Able To:: The Lymphoid SystemDocument13 pagesBythe End of This Chapter You Should Be Able To:: The Lymphoid SystemMac Kevin MandapNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument18 pagesLymphatic SystemAlliyah SalindoNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues of The Immune SystemDocument32 pagesCells and Tissues of The Immune SystemSathiyaraj100% (13)
- Week 4 - Drugs Acting On The Immune SystemDocument16 pagesWeek 4 - Drugs Acting On The Immune SystemDino MicaNo ratings yet
- CBS Imm1Document31 pagesCBS Imm1tyhbbhhNo ratings yet
- theimmunesystem-130430115239-phpapp02Document31 pagestheimmunesystem-130430115239-phpapp02Aegon TargeryanNo ratings yet
- Besana 121106035558 Phpapp02 PDFDocument9 pagesBesana 121106035558 Phpapp02 PDFAtu KaushalNo ratings yet
- Pres. Histo. Sist. Imun - SNW '13Document34 pagesPres. Histo. Sist. Imun - SNW '13Septian PutraNo ratings yet
- ImmunoSero Side NotesDocument2 pagesImmunoSero Side NotesReca Marie FRIASNo ratings yet
- 8 Lymphoid TissueDocument3 pages8 Lymphoid TissueMary Dianne MosuelaNo ratings yet
- BIOL25441 Class 5 and 6 Winter 2013Document58 pagesBIOL25441 Class 5 and 6 Winter 2013raunak .comNo ratings yet
- Immuno Notes LectureDocument30 pagesImmuno Notes LectureSteph TabasaNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Dr. A.K.M. Akbar KabirDocument29 pagesImmunology: Dr. A.K.M. Akbar KabirRakib's exploration worldNo ratings yet
- Elearning LymphaticOrgans 1 2023newDocument49 pagesElearning LymphaticOrgans 1 2023newpiano357sidNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument11 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemmeowzartNo ratings yet
- MergeResult 2022 09 12 01 31 19Document3 pagesMergeResult 2022 09 12 01 31 19Reca Marie FRIASNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System and Body DefensesDocument12 pagesThe Lymphatic System and Body DefensesGuenevere DamasinNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemrazondiegoNo ratings yet
- Elearning Lymphatic Organs 2 2023newDocument28 pagesElearning Lymphatic Organs 2 2023newpiano357sidNo ratings yet
- LM 1 - Introduction To Concept With Immunity and InflammationDocument3 pagesLM 1 - Introduction To Concept With Immunity and InflammationMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument10 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemChloe MercadoNo ratings yet
- Histology BloodDocument6 pagesHistology BloodNeneng Cutin GanzonNo ratings yet
- Why There Are New Strain of Viruses?: Pathogens EvolveDocument30 pagesWhy There Are New Strain of Viruses?: Pathogens EvolveDRANo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument2 pagesThe Lymphatic Systemabi dimatulacNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of The Immune SystemDocument53 pagesCells and Organs of The Immune SystemZyma EmaNo ratings yet
- Histology 10 ImmunosystemDocument79 pagesHistology 10 ImmunosystemAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses: Part BDocument67 pagesThe Lymphatic System and Body Defenses: Part BJovelle AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Histology LymphaticDocument4 pagesHistology LymphaticIsaac DoringoNo ratings yet
- ÓRGÃOS e TECIDOS LINFOIDES PDFDocument4 pagesÓRGÃOS e TECIDOS LINFOIDES PDFPatricia CostaNo ratings yet
- Immune System by Asif PresentationDocument35 pagesImmune System by Asif PresentationHassan AsifNo ratings yet
- Assignment Adv. in ImmunologyDocument7 pagesAssignment Adv. in ImmunologyM Sikandar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Author(s) : Matthew Velkey, 2009 License: Unless Otherwise Noted, This Material Is Made Available Under The Terms ofDocument88 pagesAuthor(s) : Matthew Velkey, 2009 License: Unless Otherwise Noted, This Material Is Made Available Under The Terms ofEunice PalloganNo ratings yet
- MTEC 3790 Chapter 9Document37 pagesMTEC 3790 Chapter 9turkeyonryeNo ratings yet
- 2.introduction To ImmunologyDocument39 pages2.introduction To ImmunologyZakaria MakereNo ratings yet
- Our Immune System-CassDocument27 pagesOur Immune System-CassSaira BanuNo ratings yet
- Lymph NodeDocument13 pagesLymph NodeNurul Ilma AllauwNo ratings yet
- Reticuloendothelial SystemDocument26 pagesReticuloendothelial SystemNashreen QtqtNo ratings yet
- Group 11 HistoDocument40 pagesGroup 11 HistoJAWAD, JAINA A.No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 159q4x4fxyrNo ratings yet
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityFrom EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityNo ratings yet
- Module01 AnOverviewofClinicalLaboratoryHemtologyDocument52 pagesModule01 AnOverviewofClinicalLaboratoryHemtologyKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Module 01 HematopeisisDocument15 pagesModule 01 HematopeisisKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Loyzaga - (BK5) - #AnongAmbagMoDocument1 pageLoyzaga - (BK5) - #AnongAmbagMoKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- BK1 - Be Brave, Be Self-Reliant - LOYZAGADocument1 pageBK1 - Be Brave, Be Self-Reliant - LOYZAGAKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43 - MycobacteriaDocument3 pagesChapter 43 - MycobacteriaKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41 - 42 - Anaerobic OrganimsDocument4 pagesChapter 41 - 42 - Anaerobic OrganimsKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 46 - The SpirochetesDocument2 pagesChapter 46 - The SpirochetesKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 44 - Obligate Intracellular and Nonculturable BacteriaDocument2 pagesChapter 44 - Obligate Intracellular and Nonculturable BacteriaKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Performance of Sysmex XN-3100 Automated Hematology Analyzer Regarding The Sysmex XE-2100 and Microscopic ExaminationDocument9 pagesEvaluation of The Performance of Sysmex XN-3100 Automated Hematology Analyzer Regarding The Sysmex XE-2100 and Microscopic ExaminationbalkisNo ratings yet
- White Blood CellDocument8 pagesWhite Blood Cellsai calderNo ratings yet
- Analisis Kuantitas Dan Hitung Jenis Leuk 39572b02 PDFDocument7 pagesAnalisis Kuantitas Dan Hitung Jenis Leuk 39572b02 PDFFerminia Putri RukmawatiNo ratings yet
- CBC ReportDocument1 pageCBC ReportKamal DeepNo ratings yet
- Durdans Lab - Panadura MR .Josep Perera: Location:: Time:: 3:26PM Patient Name / 76 Y M Age / GenderDocument1 pageDurdans Lab - Panadura MR .Josep Perera: Location:: Time:: 3:26PM Patient Name / 76 Y M Age / GenderHush PereraNo ratings yet
- Nomenklatur Sel DarahDocument27 pagesNomenklatur Sel DarahAsyha KantifaNo ratings yet
- Wiki T CellDocument12 pagesWiki T Cellالولد الخطير تابعونيNo ratings yet
- Asim Saud&Saif Alawadi Asim Saud: Rakan Fayez El-HamadDocument14 pagesAsim Saud&Saif Alawadi Asim Saud: Rakan Fayez El-HamadInnocent L NdambakuwaNo ratings yet
- Erythroid PrecursorsDocument1 pageErythroid PrecursorsMezouar AbdennacerNo ratings yet
- ErythropoisisDocument47 pagesErythropoisisDisha SuvarnaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument1 pageReportM.Raheel GhoriNo ratings yet
- Rubriblast/ Pronormoblast: Size: Nucleus: Cytoplasm: N:C Ratio: Additional NotesDocument13 pagesRubriblast/ Pronormoblast: Size: Nucleus: Cytoplasm: N:C Ratio: Additional NotesOsannah Irish InsongNo ratings yet
- Blood: Types of Blood Cells and Their Average NumberDocument32 pagesBlood: Types of Blood Cells and Their Average NumberSumayya KabeerNo ratings yet
- Department of Laboratory Services - Laboratory: Biological Reference Interval Unit Result ParameterDocument2 pagesDepartment of Laboratory Services - Laboratory: Biological Reference Interval Unit Result ParameterParchuri PraveenNo ratings yet
- G89858 Id No: Haematology ReportDocument1 pageG89858 Id No: Haematology Reportতৌফিক আহমেদNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Mast Cell and BasophilDocument2 pagesDifference Between Mast Cell and BasophilponbohacopNo ratings yet
- Nucleated Red Blood Cell (NRBC) - QSP Newsletter Issue 44Document2 pagesNucleated Red Blood Cell (NRBC) - QSP Newsletter Issue 44Gaurav MauryaNo ratings yet
- Kuby Immunology, 7e: Chapter 2: Cells, Organs, and Microenvironments of The Immune SystemDocument37 pagesKuby Immunology, 7e: Chapter 2: Cells, Organs, and Microenvironments of The Immune Systemnemezienna100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Cells and Organs of The Immune System PDFDocument61 pagesChapter 2 Cells and Organs of The Immune System PDFanaraudhatulNo ratings yet
- Leucemia Limfatica CronicaDocument52 pagesLeucemia Limfatica CronicaAnghel BogdanNo ratings yet
- Components of BloodDocument20 pagesComponents of BloodVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Parham Ch. 1: An Overview of The Immune System: (Fig. 1.3) Pathogen An Organism That Causes Disease Eg: BacteriaDocument10 pagesParham Ch. 1: An Overview of The Immune System: (Fig. 1.3) Pathogen An Organism That Causes Disease Eg: BacteriaAbhishek Isaac MathewNo ratings yet
- MegakaryopoiesisDocument41 pagesMegakaryopoiesisHazel FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Humoral and Cell Mediated Immunity: September 2017Document9 pagesDifference Between Humoral and Cell Mediated Immunity: September 2017Shivraj JadhavNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Hematopoiesis I. General Principles of HematopoiesisDocument13 pagesModule 2: Hematopoiesis I. General Principles of HematopoiesisJane JapoleNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise On Blood: .What Is The Blood Volume of An Avernge-Sized Adult Male?Document4 pagesLab Exercise On Blood: .What Is The Blood Volume of An Avernge-Sized Adult Male?سهى الغامديNo ratings yet
- Classification Functions of WBCsDocument22 pagesClassification Functions of WBCsirajput 001No ratings yet
- Hematology I ArconadoDocument37 pagesHematology I ArconadoReizel GaasNo ratings yet
- SNAB 7.18 Immunity FlashcardsDocument2 pagesSNAB 7.18 Immunity FlashcardsMeidayNo ratings yet