Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsNucleic Acids Fact Sheet
Nucleic Acids Fact Sheet
Uploaded by
asieee chimmyNucleic acids such as DNA and RNA are organic compounds that store and transmit genetic information from one generation to the next. DNA carries the genetic code and exists as a double-stranded helix structure. RNA is a single-stranded molecule that is involved in protein synthesis. The key differences between DNA and RNA are that DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose and bases adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine while RNA contains the sugar ribose and replaces thymine with uracil.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Sba MekpresentationDocument11 pagesSba MekpresentationPrashit JainNo ratings yet
- Biol313 M5Document2 pagesBiol313 M5Fares SamirNo ratings yet
- (SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and PhotosynthesisDocument2 pages(SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and Photosynthesisitz.jdv1694No ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer FinalsDocument18 pagesBiochem Reviewer Finalscha cuteNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument23 pagesCell Cyclefrank menshaNo ratings yet
- Expt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetDocument9 pagesExpt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetMary Ella Mae PilaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: Assignment Biochem-700Document29 pagesNucleic Acids: Assignment Biochem-700Arslan AliNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Pre FinalsDocument31 pagesBiochemistry Pre FinalsArah Lyn ApiagNo ratings yet
- Week 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- Group 4 PresentationDocument14 pagesGroup 4 PresentationJanrei Devilla TeNo ratings yet
- 04-Chemical Basis of HeredityDocument10 pages04-Chemical Basis of HeredityBen Abella100% (1)
- Nu Cleo ShitDocument4 pagesNu Cleo ShitPretty Grace101No ratings yet
- Jeeheheb GRRDocument22 pagesJeeheheb GRRahhhyiNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA Compared Supplementary WorksheetsDocument4 pagesDNA and RNA Compared Supplementary WorksheetsVena Grace MendezNo ratings yet
- GenBIO REVIEWERDocument39 pagesGenBIO REVIEWERblismae genotivaNo ratings yet
- LEC 11 - NucleotidesDocument11 pagesLEC 11 - Nucleotideserikapana09No ratings yet
- Biochemistry BrochureDocument2 pagesBiochemistry BrochureCaryl Alvarado SilangNo ratings yet
- WK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2Document7 pagesWK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2opingaangelamae.opingaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio 3rd QuarterzafmustaphaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of DNADocument27 pagesStructure and Function of DNAHaniya RijaNo ratings yet
- Basic Structures of Dna and Rna 2Document38 pagesBasic Structures of Dna and Rna 2Herajen DeadoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec Midterm TransesDocument17 pagesBiochem Lec Midterm Transescathryna gaylanNo ratings yet
- Abo, Margaret Nicole Bsmls 2C Nucleic Acids FinalsDocument5 pagesAbo, Margaret Nicole Bsmls 2C Nucleic Acids FinalsMargaret Nicole AboNo ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNADocument16 pagesDNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNAady.rogo.plnnpNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionGreatel Elijah TorregosaNo ratings yet
- D - BW DNA & RNADocument2 pagesD - BW DNA & RNAWahaj MazherNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Nucleic AcidsDocument62 pagesUnit 7 Nucleic AcidsGlory MuedaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument23 pagesNucleic AcidsShenne Ann MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Aid NoteDocument5 pagesNucleic Aid NoteKaye BaguhinNo ratings yet
- The Nucleic AcidsDocument94 pagesThe Nucleic Acidsmeklit birhanuNo ratings yet
- Heredity and VariationsDocument18 pagesHeredity and VariationsLovely Syre LaysonNo ratings yet
- HMB 100 Lect. 5Document58 pagesHMB 100 Lect. 5Sylvia NjauNo ratings yet
- Materi GenetikDocument3 pagesMateri GenetikAKMELIA NAJWANo ratings yet
- AS - Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesAS - Nucleic AcidsAraijan AbaiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Nucleic AcidDocument33 pagesStructure and Function of Nucleic AcidLaiba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid ChemistryDocument47 pagesNucleic Acid Chemistryjohn2001royNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument8 pagesNucleic AcidhbmbzfnttpNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five GeneticsDocument28 pagesChapter Five GeneticsYahya AbdiwahabNo ratings yet
- How Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityDocument5 pagesHow Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityAdonis Besa100% (1)
- 1 Nucleic AcidsDocument11 pages1 Nucleic AcidsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Comparison Chart: DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, Is Like A Blueprint of BiologicalDocument5 pagesComparison Chart: DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, Is Like A Blueprint of BiologicalNova Divine De la PeñaNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument10 pagesDeoxyribonucleic AcidAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna StructureDocument26 pagesDna and Rna StructureVince Lenzer BeliganioNo ratings yet
- Types of Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesTypes of Nucleic AcidsJomari Alipante100% (1)
- Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNucleic AcidsAntonette SolaresNo ratings yet
- DR Linda Molecular BiosDocument73 pagesDR Linda Molecular BiosValency BathoNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 4th QTDocument7 pagesGen Bio 4th QTZuri MaeNo ratings yet
- Genetic MaterialDocument31 pagesGenetic MaterialANBC- 24- Safa AfreenNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna-101Document30 pagesDna Rna-101Hazel SioseNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Vitamins Digestion and EnzymesDocument9 pagesNucleic Acids Vitamins Digestion and Enzymesjlinuel' StNo ratings yet
- What You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsDocument35 pagesWhat You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsSeemaNo ratings yet
- Notes MolbioDocument8 pagesNotes Molbiochristineeraymundo02No ratings yet
- Biochem ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiochem ReviewerKathleenNo ratings yet
- Nucleiuc AcidDocument18 pagesNucleiuc AcidJunelle Ramos AquinoNo ratings yet
- Acidos Nucleicos (Nucleic Acids) : Ana Jimena González Perez Andrea Tatiana Tiedra Bayona Maria Fernanda Avila RubianoDocument11 pagesAcidos Nucleicos (Nucleic Acids) : Ana Jimena González Perez Andrea Tatiana Tiedra Bayona Maria Fernanda Avila RubianoJimena GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Differences Between DNA and RNADocument2 pagesDifferences Between DNA and RNAmonishaNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Lesson 2 - Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesCytogenetics - Lesson 2 - Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionAli TaguibaoNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Material-1Document48 pagesThe Genetic Material-1Windra TrivenNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument9 pagesNucleic Acidgelary sousaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Genetic MaterialDocument22 pages8 - Genetic MaterialCrisha LimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics (Lecture)Document50 pagesNursing Informatics (Lecture)asieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- P.E ReportingDocument1 pageP.E Reportingasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Digital Footprint LiyahDocument3 pagesDigital Footprint Liyahasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- PhilosophersDocument7 pagesPhilosophersasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Lesson 1Document1 pagePhilosophy Lesson 1asieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Lao Tzu BiographyDocument3 pagesLao Tzu Biographyasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Persons and RightsDocument3 pagesPersons and Rightsasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- People As MediaDocument2 pagesPeople As Mediaasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Information LiteracyDocument1 pageInformation Literacyasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- N EtiquetteDocument3 pagesN Etiquetteasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Ubiquitous LearningDocument1 pageUbiquitous Learningasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Cerae 2-1Document3 pagesCerae 2-1asieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument1 pageProteinsasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- The 20 Century Music: Igor StravinskyDocument1 pageThe 20 Century Music: Igor Stravinskyasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- QURANDocument5 pagesQURANasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Writing Broadcast NewsDocument14 pagesWriting Broadcast Newsasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Unit - E Chapter OneDocument2 pagesUnit - E Chapter Oneasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Valence ElectronsDocument23 pagesValence Electronsasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Julliet Adubo: Well Completion FluidsDocument15 pagesJulliet Adubo: Well Completion FluidsJOHN KOKASNo ratings yet
- Creep of Materials-LatestDocument65 pagesCreep of Materials-Latestmm22b015No ratings yet
- 24 Astm A815Document8 pages24 Astm A815FYNo ratings yet
- New Draft Data Sheet Soil StabilizerDocument1 pageNew Draft Data Sheet Soil StabilizerEraNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document3 pagesExp 2Farhatul Abrar AnandaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties Palm OilDocument21 pagesChemical Properties Palm OilAmirah Mohd ZuberNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Chemical EquilibriumDocument74 pagesChapter 6 Chemical Equilibriumnoor syahirahNo ratings yet
- NTPC Project ReportDocument31 pagesNTPC Project ReportDeepak Ranjan ParidaNo ratings yet
- Leaflet Ultra Pompe 2018Document2 pagesLeaflet Ultra Pompe 2018Prince Chaudhary0% (1)
- Business Math Final ReportDocument99 pagesBusiness Math Final ReportAbubakar MehmoodNo ratings yet
- 04 Abstract-Central WorkshopDocument75 pages04 Abstract-Central Workshopumesh prustyNo ratings yet
- Pentens T-250 Data SheetDocument2 pagesPentens T-250 Data Sheetamelinda jocelinNo ratings yet
- Quizlet Chapter 16Document10 pagesQuizlet Chapter 16EUNAH LimNo ratings yet
- Engineering Specification Process PTPN IIIDocument8 pagesEngineering Specification Process PTPN IIIandrieysyah2525No ratings yet
- NOAC Comparison ChartDocument1 pageNOAC Comparison ChartrsouzaNo ratings yet
- Chickpea Manual FullDocument28 pagesChickpea Manual Fullfarooqzai1No ratings yet
- Chemical Hazard Bulletin: Baker Hughes E-31Document1 pageChemical Hazard Bulletin: Baker Hughes E-31mohamed thabetNo ratings yet
- Solution - Advanced Problems in OC by MSC 15th Edi - 231216 - 101206Document306 pagesSolution - Advanced Problems in OC by MSC 15th Edi - 231216 - 101206M.L.C Public SchoolNo ratings yet
- Dayton Close Coupled Centrifugal Pumps OIPM PDFDocument48 pagesDayton Close Coupled Centrifugal Pumps OIPM PDFstepa79No ratings yet
- Biology Form 4&5Document16 pagesBiology Form 4&5Ka Mun LeongNo ratings yet
- WB Environment MonitorDocument35 pagesWB Environment MonitorRonnie EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Introduction To WWTPs DesignDocument55 pagesIntroduction To WWTPs Designalvaro.roldan1No ratings yet
- Y8 RespirationDocument26 pagesY8 RespirationJohan Sukweenadhi100% (3)
- 16527Document22 pages16527Jaikrishna SukumarNo ratings yet
- 3500-Mn Manganese (Editorial Revisions, 2011)Document3 pages3500-Mn Manganese (Editorial Revisions, 2011)Gustavo Baccho Jorge FilhoNo ratings yet
- 8001-9000 GokulDocument23 pages8001-9000 GokulVenkatram PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Delgado 2 Media: Teacher(s) Subject Group and Discipline Unit Title MYP Year Unit Duration (HRS) 13Document12 pagesMrs. Delgado 2 Media: Teacher(s) Subject Group and Discipline Unit Title MYP Year Unit Duration (HRS) 13SaraA.DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Paints, CoatingsDocument9 pagesPaints, CoatingsazozinlcNo ratings yet
- Gizmo - Solubility and TemperatureDocument5 pagesGizmo - Solubility and TemperatureGarnet LeeNo ratings yet
Nucleic Acids Fact Sheet
Nucleic Acids Fact Sheet
Uploaded by
asieee chimmy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageNucleic acids such as DNA and RNA are organic compounds that store and transmit genetic information from one generation to the next. DNA carries the genetic code and exists as a double-stranded helix structure. RNA is a single-stranded molecule that is involved in protein synthesis. The key differences between DNA and RNA are that DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose and bases adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine while RNA contains the sugar ribose and replaces thymine with uracil.
Original Description:
A fact sheets about Nucleic Acids.
Original Title
Nucleic-Acids-fact-sheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNucleic acids such as DNA and RNA are organic compounds that store and transmit genetic information from one generation to the next. DNA carries the genetic code and exists as a double-stranded helix structure. RNA is a single-stranded molecule that is involved in protein synthesis. The key differences between DNA and RNA are that DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose and bases adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine while RNA contains the sugar ribose and replaces thymine with uracil.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageNucleic Acids Fact Sheet
Nucleic Acids Fact Sheet
Uploaded by
asieee chimmyNucleic acids such as DNA and RNA are organic compounds that store and transmit genetic information from one generation to the next. DNA carries the genetic code and exists as a double-stranded helix structure. RNA is a single-stranded molecule that is involved in protein synthesis. The key differences between DNA and RNA are that DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose and bases adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine while RNA contains the sugar ribose and replaces thymine with uracil.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
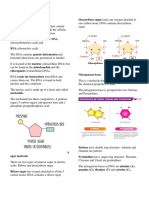
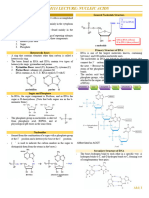
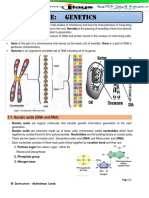
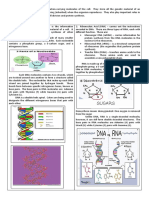
Nucleic Acids o Nitrogenous base are either double-
ringed purines that consists of a nine-
- Are organic compounds that function for the
membered molecule with four nitrogen
storage of genetic information, which is atoms such as: Adenine and Guanine or
transmitted from one generation to the next in single-ringed pyramidines that has just
all living organisms. six members and two nitrogen atoms
- It is the physical carrier of inheritance that is such as Cytosine, Uracil, and Thymine.
passed from parents to offspring.
- Also function in protein synthesis as they carry The structure of DNA as a double-stranded
code needed in the formation of specific molecule was first described by James
proteins. Watson and Francis Crick in 1953.
- The two strands that make up a
2 types of Nucleotides DNA molecule winds around each
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) other forming a double spiral
- Is the molecule that carries genetic molecule that resembles a twisted
information for the development and ladder.
functioning of an organism. - The backbone of the helix consists
- In a shape form called Double Helix. of alternating sugar and
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) phosphates, while the steps of the
- Is a nucleic acid present in all living cells ladders are made up of
that has structural similar to DNA. A type nitrogenous base pairs.
of nucleic acid made by cells that Chargaff's rule - different nitrogenous
contains information that has been bases form specific pairs, such as that A
copied from DNA. pairs with T, while C pairs with G. (A is
- Carriers genetic information that is adenine, T is thymine, C is cytosine, and G
translated by ribosomes into various is guanine.)
proteins necessary for cellular process.
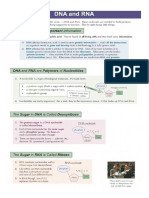
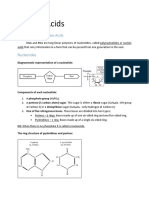
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN DNA & RNA
Both types of Nucleic Acid are made up of
Nucleotide. SUMMARY OF THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN
DNA and RNA
Nucleotide DNA RNA
- Is the building block of DNA and RNA. It is Deoxyribose Ribose
Sugar
particularly essential for replication of DNA and (C5H10O9) (C5H10O5)
transcription of RNA. Strand Double Strand Single-Strand
- It is made up of: Adenine Adenine
Five-carbon Sugar or Pentose sugar - a 5- Nitrogenous Thymine Uracil
carbon monosaccharide with the formula bases Cytosine Cytosine
(CH2O)5. Guanine Guanine
o Sugar molecule in DNA is called Mainly in Nucleus
Found in
but also found in
Deoxyribose while in RNA is Ribose. Location cytoplasm and
mitochondria and
Phosphate group - they form phosphodiester nucleus
chloroplast
bonds with the pentose sugars to create the
sides of the DNA “ladder”.
Nitrogenous Base - an organic molecule that
contains nitrogen.
You might also like
- Sba MekpresentationDocument11 pagesSba MekpresentationPrashit JainNo ratings yet
- Biol313 M5Document2 pagesBiol313 M5Fares SamirNo ratings yet
- (SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and PhotosynthesisDocument2 pages(SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and Photosynthesisitz.jdv1694No ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer FinalsDocument18 pagesBiochem Reviewer Finalscha cuteNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument23 pagesCell Cyclefrank menshaNo ratings yet
- Expt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetDocument9 pagesExpt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetMary Ella Mae PilaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: Assignment Biochem-700Document29 pagesNucleic Acids: Assignment Biochem-700Arslan AliNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Pre FinalsDocument31 pagesBiochemistry Pre FinalsArah Lyn ApiagNo ratings yet
- Week 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- Group 4 PresentationDocument14 pagesGroup 4 PresentationJanrei Devilla TeNo ratings yet
- 04-Chemical Basis of HeredityDocument10 pages04-Chemical Basis of HeredityBen Abella100% (1)
- Nu Cleo ShitDocument4 pagesNu Cleo ShitPretty Grace101No ratings yet
- Jeeheheb GRRDocument22 pagesJeeheheb GRRahhhyiNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA Compared Supplementary WorksheetsDocument4 pagesDNA and RNA Compared Supplementary WorksheetsVena Grace MendezNo ratings yet
- GenBIO REVIEWERDocument39 pagesGenBIO REVIEWERblismae genotivaNo ratings yet
- LEC 11 - NucleotidesDocument11 pagesLEC 11 - Nucleotideserikapana09No ratings yet
- Biochemistry BrochureDocument2 pagesBiochemistry BrochureCaryl Alvarado SilangNo ratings yet
- WK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2Document7 pagesWK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2opingaangelamae.opingaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio 3rd QuarterzafmustaphaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of DNADocument27 pagesStructure and Function of DNAHaniya RijaNo ratings yet
- Basic Structures of Dna and Rna 2Document38 pagesBasic Structures of Dna and Rna 2Herajen DeadoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec Midterm TransesDocument17 pagesBiochem Lec Midterm Transescathryna gaylanNo ratings yet
- Abo, Margaret Nicole Bsmls 2C Nucleic Acids FinalsDocument5 pagesAbo, Margaret Nicole Bsmls 2C Nucleic Acids FinalsMargaret Nicole AboNo ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNADocument16 pagesDNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNAady.rogo.plnnpNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionGreatel Elijah TorregosaNo ratings yet
- D - BW DNA & RNADocument2 pagesD - BW DNA & RNAWahaj MazherNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Nucleic AcidsDocument62 pagesUnit 7 Nucleic AcidsGlory MuedaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument23 pagesNucleic AcidsShenne Ann MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Aid NoteDocument5 pagesNucleic Aid NoteKaye BaguhinNo ratings yet
- The Nucleic AcidsDocument94 pagesThe Nucleic Acidsmeklit birhanuNo ratings yet
- Heredity and VariationsDocument18 pagesHeredity and VariationsLovely Syre LaysonNo ratings yet
- HMB 100 Lect. 5Document58 pagesHMB 100 Lect. 5Sylvia NjauNo ratings yet
- Materi GenetikDocument3 pagesMateri GenetikAKMELIA NAJWANo ratings yet
- AS - Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesAS - Nucleic AcidsAraijan AbaiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Nucleic AcidDocument33 pagesStructure and Function of Nucleic AcidLaiba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid ChemistryDocument47 pagesNucleic Acid Chemistryjohn2001royNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument8 pagesNucleic AcidhbmbzfnttpNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five GeneticsDocument28 pagesChapter Five GeneticsYahya AbdiwahabNo ratings yet
- How Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityDocument5 pagesHow Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityAdonis Besa100% (1)
- 1 Nucleic AcidsDocument11 pages1 Nucleic AcidsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Comparison Chart: DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, Is Like A Blueprint of BiologicalDocument5 pagesComparison Chart: DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, Is Like A Blueprint of BiologicalNova Divine De la PeñaNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument10 pagesDeoxyribonucleic AcidAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna StructureDocument26 pagesDna and Rna StructureVince Lenzer BeliganioNo ratings yet
- Types of Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesTypes of Nucleic AcidsJomari Alipante100% (1)
- Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNucleic AcidsAntonette SolaresNo ratings yet
- DR Linda Molecular BiosDocument73 pagesDR Linda Molecular BiosValency BathoNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 4th QTDocument7 pagesGen Bio 4th QTZuri MaeNo ratings yet
- Genetic MaterialDocument31 pagesGenetic MaterialANBC- 24- Safa AfreenNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna-101Document30 pagesDna Rna-101Hazel SioseNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Vitamins Digestion and EnzymesDocument9 pagesNucleic Acids Vitamins Digestion and Enzymesjlinuel' StNo ratings yet
- What You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsDocument35 pagesWhat You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsSeemaNo ratings yet
- Notes MolbioDocument8 pagesNotes Molbiochristineeraymundo02No ratings yet
- Biochem ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiochem ReviewerKathleenNo ratings yet
- Nucleiuc AcidDocument18 pagesNucleiuc AcidJunelle Ramos AquinoNo ratings yet
- Acidos Nucleicos (Nucleic Acids) : Ana Jimena González Perez Andrea Tatiana Tiedra Bayona Maria Fernanda Avila RubianoDocument11 pagesAcidos Nucleicos (Nucleic Acids) : Ana Jimena González Perez Andrea Tatiana Tiedra Bayona Maria Fernanda Avila RubianoJimena GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Differences Between DNA and RNADocument2 pagesDifferences Between DNA and RNAmonishaNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Lesson 2 - Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesCytogenetics - Lesson 2 - Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionAli TaguibaoNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Material-1Document48 pagesThe Genetic Material-1Windra TrivenNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument9 pagesNucleic Acidgelary sousaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Genetic MaterialDocument22 pages8 - Genetic MaterialCrisha LimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics (Lecture)Document50 pagesNursing Informatics (Lecture)asieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- P.E ReportingDocument1 pageP.E Reportingasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Digital Footprint LiyahDocument3 pagesDigital Footprint Liyahasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- PhilosophersDocument7 pagesPhilosophersasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Lesson 1Document1 pagePhilosophy Lesson 1asieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Lao Tzu BiographyDocument3 pagesLao Tzu Biographyasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Persons and RightsDocument3 pagesPersons and Rightsasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- People As MediaDocument2 pagesPeople As Mediaasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Information LiteracyDocument1 pageInformation Literacyasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- N EtiquetteDocument3 pagesN Etiquetteasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Ubiquitous LearningDocument1 pageUbiquitous Learningasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Cerae 2-1Document3 pagesCerae 2-1asieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument1 pageProteinsasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- The 20 Century Music: Igor StravinskyDocument1 pageThe 20 Century Music: Igor Stravinskyasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- QURANDocument5 pagesQURANasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Writing Broadcast NewsDocument14 pagesWriting Broadcast Newsasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Unit - E Chapter OneDocument2 pagesUnit - E Chapter Oneasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Valence ElectronsDocument23 pagesValence Electronsasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Julliet Adubo: Well Completion FluidsDocument15 pagesJulliet Adubo: Well Completion FluidsJOHN KOKASNo ratings yet
- Creep of Materials-LatestDocument65 pagesCreep of Materials-Latestmm22b015No ratings yet
- 24 Astm A815Document8 pages24 Astm A815FYNo ratings yet
- New Draft Data Sheet Soil StabilizerDocument1 pageNew Draft Data Sheet Soil StabilizerEraNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document3 pagesExp 2Farhatul Abrar AnandaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties Palm OilDocument21 pagesChemical Properties Palm OilAmirah Mohd ZuberNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Chemical EquilibriumDocument74 pagesChapter 6 Chemical Equilibriumnoor syahirahNo ratings yet
- NTPC Project ReportDocument31 pagesNTPC Project ReportDeepak Ranjan ParidaNo ratings yet
- Leaflet Ultra Pompe 2018Document2 pagesLeaflet Ultra Pompe 2018Prince Chaudhary0% (1)
- Business Math Final ReportDocument99 pagesBusiness Math Final ReportAbubakar MehmoodNo ratings yet
- 04 Abstract-Central WorkshopDocument75 pages04 Abstract-Central Workshopumesh prustyNo ratings yet
- Pentens T-250 Data SheetDocument2 pagesPentens T-250 Data Sheetamelinda jocelinNo ratings yet
- Quizlet Chapter 16Document10 pagesQuizlet Chapter 16EUNAH LimNo ratings yet
- Engineering Specification Process PTPN IIIDocument8 pagesEngineering Specification Process PTPN IIIandrieysyah2525No ratings yet
- NOAC Comparison ChartDocument1 pageNOAC Comparison ChartrsouzaNo ratings yet
- Chickpea Manual FullDocument28 pagesChickpea Manual Fullfarooqzai1No ratings yet
- Chemical Hazard Bulletin: Baker Hughes E-31Document1 pageChemical Hazard Bulletin: Baker Hughes E-31mohamed thabetNo ratings yet
- Solution - Advanced Problems in OC by MSC 15th Edi - 231216 - 101206Document306 pagesSolution - Advanced Problems in OC by MSC 15th Edi - 231216 - 101206M.L.C Public SchoolNo ratings yet
- Dayton Close Coupled Centrifugal Pumps OIPM PDFDocument48 pagesDayton Close Coupled Centrifugal Pumps OIPM PDFstepa79No ratings yet
- Biology Form 4&5Document16 pagesBiology Form 4&5Ka Mun LeongNo ratings yet
- WB Environment MonitorDocument35 pagesWB Environment MonitorRonnie EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Introduction To WWTPs DesignDocument55 pagesIntroduction To WWTPs Designalvaro.roldan1No ratings yet
- Y8 RespirationDocument26 pagesY8 RespirationJohan Sukweenadhi100% (3)
- 16527Document22 pages16527Jaikrishna SukumarNo ratings yet
- 3500-Mn Manganese (Editorial Revisions, 2011)Document3 pages3500-Mn Manganese (Editorial Revisions, 2011)Gustavo Baccho Jorge FilhoNo ratings yet
- 8001-9000 GokulDocument23 pages8001-9000 GokulVenkatram PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Delgado 2 Media: Teacher(s) Subject Group and Discipline Unit Title MYP Year Unit Duration (HRS) 13Document12 pagesMrs. Delgado 2 Media: Teacher(s) Subject Group and Discipline Unit Title MYP Year Unit Duration (HRS) 13SaraA.DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Paints, CoatingsDocument9 pagesPaints, CoatingsazozinlcNo ratings yet
- Gizmo - Solubility and TemperatureDocument5 pagesGizmo - Solubility and TemperatureGarnet LeeNo ratings yet