Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6 Stress
6 Stress
Uploaded by
R S PappuOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
6 Stress
6 Stress
Uploaded by
R S PappuCopyright:
Available Formats
EN380 Naval Materials Science and Engineering Course Notes, U.S.
Naval Academy
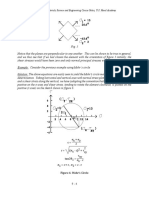
Where
The roots of the equation, usually determined numerically, are the principal stresses. To find the
direction cosines, nx, ny, and nz of the plane in which, say σ1 acts, we may use the above equations
with σ = σ1, together with the geometric condition
nx2 + ny2 + nz2 = 1
Similar procedures apply for σ2 and σ3.
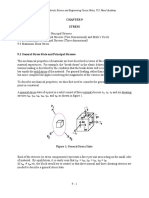
9.4 Maximum Shear Stress
It is not difficult to show, using methods of analysis similar to those applied above, that the
maximum shear stress existing at a point is given by the greatest of the quantities
σ1 - σ2 σ2 - σ3 σ3 - σ1
, ,
2 2 2
if we label the principal stresses such that σ1 > σ2 > σ3, then
θ1 - θ3
τmax =
2
This greatest shear stress acts on a plane perpendicular to the principal plane associated with σ 2
and at 45o to those associated with σ1 and σ3.
9-6
You might also like
- Maximum and Minimum Normal StressDocument3 pagesMaximum and Minimum Normal StressRajesh KhadkaNo ratings yet
- EN380 Naval Materials Science and Engineering Course Notes, U.S. Naval AcademyDocument7 pagesEN380 Naval Materials Science and Engineering Course Notes, U.S. Naval Academysrinivas pavan kumar ANo ratings yet
- Steady Load Failure TheoriesDocument17 pagesSteady Load Failure Theoriesapi-3710585No ratings yet
- FailureNotes PDFDocument8 pagesFailureNotes PDFsameshni pillayNo ratings yet
- MEC 3611: Structural Mechanics: Lecture 3: REVIEWDocument22 pagesMEC 3611: Structural Mechanics: Lecture 3: REVIEWhellolover0% (1)
- Mechanic of MaterialsDocument16 pagesMechanic of MaterialsjokoNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Plane Stress and Strain PDFDocument14 pagesTransformation of Plane Stress and Strain PDFFitsum OmituNo ratings yet
- 7 1theoriesoffailureDocument11 pages7 1theoriesoffailureLeul AchawNo ratings yet
- Amsiejus Dirgeliene Et Al (TX P'-Q)Document6 pagesAmsiejus Dirgeliene Et Al (TX P'-Q)laloNo ratings yet
- 4-2 Fatigue Under Combined Stresses - BDocument5 pages4-2 Fatigue Under Combined Stresses - BkandeabigaelNo ratings yet
- Principal Stresses Mohr CircleDocument10 pagesPrincipal Stresses Mohr CircleMohammed GamNo ratings yet
- Sex 1Document4 pagesSex 1Ibrahim HussainNo ratings yet
- Griffith TheoryDocument24 pagesGriffith TheorysarvannnNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress TransformDocument24 pagesPlane Stress Transformsandrock92No ratings yet
- Mohr-Coulomb Failure PDFDocument25 pagesMohr-Coulomb Failure PDFHugo Damian AvalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Yeleti FamilyNo ratings yet
- Stresses Transformation: In-Class Activities:: To: A)Document30 pagesStresses Transformation: In-Class Activities:: To: A)Random Emails From EverywhereNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering, Architecture and Technology:: Course Title: Course Number: Course DescriptionDocument13 pagesCollege of Engineering, Architecture and Technology:: Course Title: Course Number: Course DescriptionEdmil Jhon AriquesNo ratings yet
- Chap 7Document24 pagesChap 7Georgio GhossainNo ratings yet
- Surface Wear and FatigueDocument7 pagesSurface Wear and Fatiguebeaver85No ratings yet
- 3 StressDocument1 page3 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Shear Strength of SoilsDocument18 pagesChapter-1 Shear Strength of Soilsmidju100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Stress TransformationDocument48 pagesChapter 5 - Stress TransformationLai Swee YongNo ratings yet
- Multiaxial Loading - Tresca and Von-Mises Yield Criteria: PlasticityDocument3 pagesMultiaxial Loading - Tresca and Von-Mises Yield Criteria: Plasticityazizieh5701No ratings yet
- Module-1: Lecture-3 (Principal Stress and Principal Planes) : February 9, 2017Document9 pagesModule-1: Lecture-3 (Principal Stress and Principal Planes) : February 9, 2017rangavaliNo ratings yet
- EOSC364: Rock Deformation Theory of Homogeneous Stress in Two-DimensionsDocument1 pageEOSC364: Rock Deformation Theory of Homogeneous Stress in Two-DimensionsMiguel CastillejoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 1 PDFDocument22 pagesTutorial 1 1 PDFSuresh g.s.No ratings yet
- CE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations: Stresses in A Soil Mass I (Das, Ch. 9)Document27 pagesCE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations: Stresses in A Soil Mass I (Das, Ch. 9)jorge.jimenezNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Theories of Failure: Introduction: Due To Large Numbers of Examples of Compound Stresses MetDocument23 pagesUnit IV Theories of Failure: Introduction: Due To Large Numbers of Examples of Compound Stresses MetMohtasham NaeemNo ratings yet
- Theories of FailureDocument14 pagesTheories of FailuresushilNo ratings yet
- Unlocksify+ +chegg 1684300130840Document2 pagesUnlocksify+ +chegg 1684300130840AdrianRahmantoPutraNo ratings yet
- 2 StressDocument1 page2 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- 101 PDFDocument21 pages101 PDFThaung Myint OoNo ratings yet
- Principal StressesDocument15 pagesPrincipal StressesTibebu MerideNo ratings yet
- Complex Stress Condition CAE FatigueDocument77 pagesComplex Stress Condition CAE FatigueN.g. NagarajNo ratings yet
- Geomechanics GlossaryDocument5 pagesGeomechanics GlossarysomsubhraNo ratings yet
- FEA&CM Lecture-17Document22 pagesFEA&CM Lecture-17shivaNo ratings yet
- Review: Stress: Defined As The Force Applied Per Until Area. Normal Stresses: Shear StressesDocument11 pagesReview: Stress: Defined As The Force Applied Per Until Area. Normal Stresses: Shear StressesGaurav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Advanced Soil Mechanics 1 - Chapter 1-1-12Document12 pagesAdvanced Soil Mechanics 1 - Chapter 1-1-12mmike9179No ratings yet
- Chapter Three The Yield CriteriaDocument9 pagesChapter Three The Yield CriteriaAbdalmalek ShamsanNo ratings yet
- ENTC 376 Chapter 9 Lecture Notes-III-Stress TransformationDocument27 pagesENTC 376 Chapter 9 Lecture Notes-III-Stress TransformationYahia Raad Al-AniNo ratings yet
- Theories of Yielding PDFDocument13 pagesTheories of Yielding PDFJowesh Avisheik GoundarNo ratings yet
- PS6 SolDocument10 pagesPS6 SolgarridolopezNo ratings yet
- Strain Failures: 10.7 Theories of FailureDocument56 pagesStrain Failures: 10.7 Theories of FailureginoNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 SolidDocument2 pagesSheet 2 Solidmariam.ahmed03No ratings yet
- Principal Stresses (Civil Engg. For AUST EEE 1/1)Document25 pagesPrincipal Stresses (Civil Engg. For AUST EEE 1/1)Fazlay ElahiNo ratings yet
- Theories of FailureDocument27 pagesTheories of FailureRaviShankarDuggirala88% (57)
- Solutions To Problem Set 9Document10 pagesSolutions To Problem Set 9Patrick SibandaNo ratings yet
- Thick Walled Cylinders (Plane Stress)Document16 pagesThick Walled Cylinders (Plane Stress)Alvaro FabianNo ratings yet
- Complex Stress Tutorial 3 Complex Stress and Strain: © D.J.Dunn 1Document22 pagesComplex Stress Tutorial 3 Complex Stress and Strain: © D.J.Dunn 1Php TutorialsNo ratings yet
- 14 RESISTENCIA 1.desbloqueadoDocument47 pages14 RESISTENCIA 1.desbloqueadoVíctor Obregón MartínezNo ratings yet
- Metal Working DerivationsDocument17 pagesMetal Working DerivationsShrutiNo ratings yet
- Dundee Final HDRDocument13 pagesDundee Final HDRFranco BrownNo ratings yet
- Lecture Class2Document15 pagesLecture Class2Kibrom MenasboNo ratings yet
- Principal StressesDocument5 pagesPrincipal Stressesavinashn1No ratings yet
- 5 StressDocument1 page5 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- 1 DeformationDocument1 page1 DeformationR S PappuNo ratings yet
- 7 StressDocument1 page7 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- 4 StressDocument1 page4 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Light Alloys - From Traditional To InnovativeDocument37 pagesLight Alloys - From Traditional To InnovativeR S PappuNo ratings yet
- 2 StressDocument1 page2 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- 1 StressDocument1 page1 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- 3 StressDocument1 page3 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Digestion of Animal Manures Methane Production Potential of Waste MaterialsDocument4 pagesAnaerobic Digestion of Animal Manures Methane Production Potential of Waste MaterialsR S PappuNo ratings yet
- LN 6Document1 pageLN 6R S PappuNo ratings yet
- LN 5Document1 pageLN 5R S PappuNo ratings yet
- Advanced Biofuel Demonstration Competition - Feasibility Study FINAL v3Document69 pagesAdvanced Biofuel Demonstration Competition - Feasibility Study FINAL v3R S PappuNo ratings yet
- Biofuel CompendiumDocument147 pagesBiofuel CompendiumR S PappuNo ratings yet
- International Journal For Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)Document1 pageInternational Journal For Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)R S PappuNo ratings yet
- LN 4Document1 pageLN 4R S PappuNo ratings yet
- LN 1Document1 pageLN 1R S PappuNo ratings yet
- LN 2Document1 pageLN 2R S PappuNo ratings yet
- Codevita Faqs, General Instructions and Best PracticesDocument10 pagesCodevita Faqs, General Instructions and Best PracticesR S PappuNo ratings yet
- LN 3Document1 pageLN 3R S PappuNo ratings yet
- Additional Specifications: - Rotational Range: 180° - Pulse Cycle: Ca. 20 Ms - Pulse Width: 500-2400 SDocument1 pageAdditional Specifications: - Rotational Range: 180° - Pulse Cycle: Ca. 20 Ms - Pulse Width: 500-2400 SR S PappuNo ratings yet
- International Journal For Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)Document1 pageInternational Journal For Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)R S PappuNo ratings yet
- AICTE Training LetterDocument1 pageAICTE Training LetterR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Why I Should Chose Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesWhy I Should Chose Mechanical EngineeringR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics 1Document6 pagesMechatronics 1R S PappuNo ratings yet
- Research Proj AbsDocument70 pagesResearch Proj AbsR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Four Decades of Research On Quality: Summarising, Trendspotting and Looking AheadDocument1 pageFour Decades of Research On Quality: Summarising, Trendspotting and Looking AheadR S PappuNo ratings yet
- International Journal For Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)Document1 pageInternational Journal For Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)R S PappuNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Applications in Used Academic BookstoresDocument1 pageSix Sigma Applications in Used Academic BookstoresR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Figure 2. The CRISP-DM Process (Wirth & Hipp,) Applied in The StudyDocument1 pageFigure 2. The CRISP-DM Process (Wirth & Hipp,) Applied in The StudyR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. Depiction of Qms Historical Development Weckenmann Et Al.Document1 pageFigure 1. Depiction of Qms Historical Development Weckenmann Et Al.R S PappuNo ratings yet