Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Deformation
1 Deformation
Uploaded by
R S Pappu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageThis document is from a Naval Materials Science and Engineering course and discusses material deformation. It covers stress-strain diagrams, material characteristics, elastic-plastic response of metals, true stress and strain measures, yielding of ductile metals under general stress states using the Mises yield condition, maximum shear stress condition, and creep. It defines engineering stress as the load divided by the cross-sectional area and elongation as the difference between the loaded and unloaded length of a bar subjected to tension loading.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document is from a Naval Materials Science and Engineering course and discusses material deformation. It covers stress-strain diagrams, material characteristics, elastic-plastic response of metals, true stress and strain measures, yielding of ductile metals under general stress states using the Mises yield condition, maximum shear stress condition, and creep. It defines engineering stress as the load divided by the cross-sectional area and elongation as the difference between the loaded and unloaded length of a bar subjected to tension loading.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 page1 Deformation
1 Deformation
Uploaded by
R S PappuThis document is from a Naval Materials Science and Engineering course and discusses material deformation. It covers stress-strain diagrams, material characteristics, elastic-plastic response of metals, true stress and strain measures, yielding of ductile metals under general stress states using the Mises yield condition, maximum shear stress condition, and creep. It defines engineering stress as the load divided by the cross-sectional area and elongation as the difference between the loaded and unloaded length of a bar subjected to tension loading.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
EN380 Naval Materials Science and Engineering Course Notes, U.S.
Naval Academy
CHAPTER 10
DEFORMATION
10.1 Stress-Strain Diagrams and Material Behavior
10.2 Material Characteristics
10.3 Elastic-Plastic Response of Metals
10.4 True stress and strain measures
10.5 Yielding of a Ductile Metal under a General Stress State - Mises Yield Condition.
10.6 Maximum shear stress condition
10.7 Creep
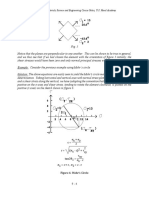
Consider the bar in figure 1 subjected to a simple tension loading F.
Figure 1: Bar in Tension
Engineering Stress () is the quotient of load (F) and area (A). The units of stress are normally
pounds per square inch (psi).
= F
A
where: is the stress (psi)
F is the force that is loading the object (lb)
A is the cross sectional area of the object (in2)
When stress is applied to a material, the material will deform. Elongation is defined as the
difference between loaded and unloaded length
∆𝑙 = L - Lo
where: ∆𝑙 is the elongation (ft)
L is the loaded length of the cable (ft)
Lo is the unloaded (original) length of the cable (ft)
10-1
You might also like
- Solenoid Actuators: Theory and Computational MethodsFrom EverandSolenoid Actuators: Theory and Computational MethodsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Emg 2303 NotesDocument65 pagesEmg 2303 NotesAnonymous UnchpksNo ratings yet
- Course Objectives 5. Properties of Naval MaterialsDocument31 pagesCourse Objectives 5. Properties of Naval MaterialsLenin ValerioNo ratings yet
- EN380 Naval Materials Science and Engineering Course Notes, U.S. Naval AcademyDocument16 pagesEN380 Naval Materials Science and Engineering Course Notes, U.S. Naval AcademyGuillaume Hervé POH'SIÉNo ratings yet
- Elasticity XIDocument5 pagesElasticity XIDark gaming liveNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Beam (LRFD, Load and Resistance Factor Design)Document5 pagesDesign of Steel Beam (LRFD, Load and Resistance Factor Design)surajoffshoreNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials 2018 by S K MondalDocument482 pagesStrength of Materials 2018 by S K MondalSnake BiteNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Fig. 1: Llyod Testing Machine in Materials Testing LabDocument34 pagesExperiment 1: Fig. 1: Llyod Testing Machine in Materials Testing LabRogie Neth AbatayoNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument32 pagesElasticityRannie Ayaay Jr.No ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - SOM Contents and PrefaceDocument429 pagesMicrosoft Word - SOM Contents and Prefacebrendonsithole6No ratings yet
- Mechanicslecture NotesDocument18 pagesMechanicslecture NotesleasterNo ratings yet
- Structures StiffnessDocument27 pagesStructures StiffnessFebri Al FaroukNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials by S K MondalDocument429 pagesStrength of Materials by S K MondalSaajal Sharma88% (26)
- SOMDocument431 pagesSOMPradeepvenugopalNo ratings yet
- Som Unit - IDocument24 pagesSom Unit - Inithesh kumar jNo ratings yet
- Material in ContactDocument3 pagesMaterial in Contactshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document26 pagesChapter 11arishaNo ratings yet
- Material PropertiesDocument42 pagesMaterial PropertiesDr_M_Soliman100% (2)
- 06 Strain SensorsDocument27 pages06 Strain SensorsGustavo CapillaNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 - 3rd WeekDocument28 pagesLec 3 - 3rd Weekrajpoot aliNo ratings yet
- 3.7 Young's Modulus of The Metal Bar TheoryDocument4 pages3.7 Young's Modulus of The Metal Bar TheoryOdilbek MarimovNo ratings yet
- MAE 351 Tension Test 2014Document10 pagesMAE 351 Tension Test 2014laura villarroelNo ratings yet
- Kyowa Strain GagesDocument16 pagesKyowa Strain GagesMurad AlamNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document34 pagesUnit 3moondonoo7No ratings yet
- Jsaer2015 02 02 01 11Document11 pagesJsaer2015 02 02 01 11jsaereditorNo ratings yet
- Lecture VVI 24 3 2020 10 40-12 40 Chitra Physics Electronics UPI-32511204Document10 pagesLecture VVI 24 3 2020 10 40-12 40 Chitra Physics Electronics UPI-32511204Chaitali KuteNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal Strain and Lateral StrainDocument8 pagesLongitudinal Strain and Lateral StrainMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials 2015 by S K MondalDocument473 pagesStrength of Materials 2015 by S K MondalNitik KumarNo ratings yet
- 3 - Basic PropertiesDocument24 pages3 - Basic Propertiesahmedmarwan82030No ratings yet
- Stresses and Strains PDFDocument44 pagesStresses and Strains PDFAnvi JainNo ratings yet
- ConcreteDocument23 pagesConcreteJoseph LantoNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material CH-1 Ppt-1Document26 pagesStrength of Material CH-1 Ppt-1Nura Guyo67% (3)
- Strength of Materials by S.K.mondalDocument429 pagesStrength of Materials by S.K.mondalKrishna Prakash100% (1)
- Fluids FluidsDocument66 pagesFluids Fluidsrolando maiso0% (1)
- YCT Mechanical Properties of Solids NEET JEE Questions PracticeDocument77 pagesYCT Mechanical Properties of Solids NEET JEE Questions Practicedrsantanuchakraborty91No ratings yet
- (Ebook) D Roylance - MIT - Mechanics of MaterialsDocument357 pages(Ebook) D Roylance - MIT - Mechanics of MaterialsmomenziNo ratings yet
- 05 ElasticityDocument29 pages05 ElasticityJoyce CulloNo ratings yet
- Tensil Test TDDocument3 pagesTensil Test TDKAOUKA AlaedinNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument61 pagesMechanical Properties of MaterialsSeira MolinaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of SolidsDocument12 pagesMechanical Properties of SolidskrutarthanasitNo ratings yet
- Engineering PhysicsDocument31 pagesEngineering PhysicsJoan VincentNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts Fluid PropertiesDocument71 pagesBasic Concepts Fluid PropertiesAbed Alrahman QaddourNo ratings yet
- XI. Solids and FluidsDocument21 pagesXI. Solids and FluidsMuhau ZvikomboreroNo ratings yet
- Strain Gage-WhatDocument16 pagesStrain Gage-WhatAshok JoshiNo ratings yet
- Mee 307 - Science of Engineering MaterialsDocument29 pagesMee 307 - Science of Engineering MaterialsDamilola OsubuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Elastic Properties of MatterDocument32 pagesChapter 3 - Elastic Properties of MatterNour HakamNo ratings yet
- Elasticity (Statics)Document25 pagesElasticity (Statics)Rizky PratamaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Stress and Strain PresentationDocument14 pagesLesson 1 Stress and Strain PresentationTashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Deformation of Solids: Tensile CompressiveDocument11 pagesChapter 11: Deformation of Solids: Tensile CompressiveAzmira AhmadNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PropertiesDocument37 pagesMechanical PropertiesMuhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Property 2Document33 pagesMechanical Property 2tazebNo ratings yet
- Plots, Graphs, and Sketches (1.1)Document43 pagesPlots, Graphs, and Sketches (1.1)abc123goNo ratings yet
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 6, Slice 8 "Conduction, Electric"From EverandEncyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 6, Slice 8 "Conduction, Electric"No ratings yet
- 5 StressDocument1 page5 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- 7 StressDocument1 page7 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- 6 StressDocument1 page6 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- 4 StressDocument1 page4 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Light Alloys - From Traditional To InnovativeDocument37 pagesLight Alloys - From Traditional To InnovativeR S PappuNo ratings yet
- 2 StressDocument1 page2 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- 1 StressDocument1 page1 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- 3 StressDocument1 page3 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Digestion of Animal Manures Methane Production Potential of Waste MaterialsDocument4 pagesAnaerobic Digestion of Animal Manures Methane Production Potential of Waste MaterialsR S PappuNo ratings yet
- LN 6Document1 pageLN 6R S PappuNo ratings yet
- LN 5Document1 pageLN 5R S PappuNo ratings yet
- Advanced Biofuel Demonstration Competition - Feasibility Study FINAL v3Document69 pagesAdvanced Biofuel Demonstration Competition - Feasibility Study FINAL v3R S PappuNo ratings yet
- Biofuel CompendiumDocument147 pagesBiofuel CompendiumR S PappuNo ratings yet
- International Journal For Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)Document1 pageInternational Journal For Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)R S PappuNo ratings yet
- LN 4Document1 pageLN 4R S PappuNo ratings yet
- LN 1Document1 pageLN 1R S PappuNo ratings yet
- LN 2Document1 pageLN 2R S PappuNo ratings yet
- Codevita Faqs, General Instructions and Best PracticesDocument10 pagesCodevita Faqs, General Instructions and Best PracticesR S PappuNo ratings yet
- LN 3Document1 pageLN 3R S PappuNo ratings yet
- Additional Specifications: - Rotational Range: 180° - Pulse Cycle: Ca. 20 Ms - Pulse Width: 500-2400 SDocument1 pageAdditional Specifications: - Rotational Range: 180° - Pulse Cycle: Ca. 20 Ms - Pulse Width: 500-2400 SR S PappuNo ratings yet
- International Journal For Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)Document1 pageInternational Journal For Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)R S PappuNo ratings yet
- AICTE Training LetterDocument1 pageAICTE Training LetterR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Why I Should Chose Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesWhy I Should Chose Mechanical EngineeringR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics 1Document6 pagesMechatronics 1R S PappuNo ratings yet
- Research Proj AbsDocument70 pagesResearch Proj AbsR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Four Decades of Research On Quality: Summarising, Trendspotting and Looking AheadDocument1 pageFour Decades of Research On Quality: Summarising, Trendspotting and Looking AheadR S PappuNo ratings yet
- International Journal For Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)Document1 pageInternational Journal For Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)R S PappuNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Applications in Used Academic BookstoresDocument1 pageSix Sigma Applications in Used Academic BookstoresR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Figure 2. The CRISP-DM Process (Wirth & Hipp,) Applied in The StudyDocument1 pageFigure 2. The CRISP-DM Process (Wirth & Hipp,) Applied in The StudyR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. Depiction of Qms Historical Development Weckenmann Et Al.Document1 pageFigure 1. Depiction of Qms Historical Development Weckenmann Et Al.R S PappuNo ratings yet