Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maths Mock-03 (08.03.21)
Maths Mock-03 (08.03.21)
Uploaded by
rahul kumarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Schaum's Outline of Physics For Engineering and ScienceDocument473 pagesSchaum's Outline of Physics For Engineering and Sciencemexx4u2nv100% (5)
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (ITF) JEE Main and Advanced (IIT-JEE)Document5 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions (ITF) JEE Main and Advanced (IIT-JEE)Er. Vineet Loomba (IIT Roorkee)67% (6)
- Determinants & Matrices - Ex.1 (A)Document7 pagesDeterminants & Matrices - Ex.1 (A)happyNo ratings yet
- 024efcb68fc74-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 09 09.04.2020Document8 pages024efcb68fc74-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 09 09.04.2020Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024e99d5874b2-Mock Test (Maths) - 05Document8 pages024e99d5874b2-Mock Test (Maths) - 05Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- KCET 2020 MATHEMATICS DR AcademyDocument5 pagesKCET 2020 MATHEMATICS DR AcademypullagalkNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions - DPP 04Document2 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions - DPP 04jeemainsmaterial97No ratings yet
- XII-PTS-21 (2023-24) - by O.P. GUPTADocument8 pagesXII-PTS-21 (2023-24) - by O.P. GUPTAmaanya.ailawadi3No ratings yet
- Maths SQP 1Document7 pagesMaths SQP 1qutubkhan.nalwalaNo ratings yet
- 01-Indefinite Integration PDFDocument11 pages01-Indefinite Integration PDFShubhankar SinhaNo ratings yet
- Full Book 1st Year MathDocument2 pagesFull Book 1st Year MathkamranNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper-1: in This Section, Attempt Any 16 Questions (From 01 - 20)Document6 pagesPractice Paper-1: in This Section, Attempt Any 16 Questions (From 01 - 20)Shivangi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 02571792c9ae4-DPT Inverse Trigonometry 16.12.2020Document2 pages02571792c9ae4-DPT Inverse Trigonometry 16.12.2020HeartbeatssNo ratings yet
- 125 Class TestDocument2 pages125 Class Testjaiswal23456No ratings yet
- Practice Paper-3: in This Section, Attempt Any 16 Questions (From 01 - 20)Document6 pagesPractice Paper-3: in This Section, Attempt Any 16 Questions (From 01 - 20)Shivangi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 12th Maths Preboard-1 2021Document7 pages12th Maths Preboard-1 2021Little GardenNo ratings yet
- 026795351f95d-Inverse Trigonometry DPT - 01 (11.05.22)Document2 pages026795351f95d-Inverse Trigonometry DPT - 01 (11.05.22)Farhan SalimNo ratings yet
- MCQ Uestion On PolynomialsDocument5 pagesMCQ Uestion On PolynomialsMosisa SufaNo ratings yet
- Complex Number Exercise Book PDFDocument26 pagesComplex Number Exercise Book PDFRitik KumarNo ratings yet
- Maths XII Q 3-08-2021Document5 pagesMaths XII Q 3-08-2021Ashwani JhaNo ratings yet
- Paper: Iit-Jam 2012: X X X y N NDocument5 pagesPaper: Iit-Jam 2012: X X X y N NMr MNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper 1: Section ADocument5 pagesSample Question Paper 1: Section Agunjan bhalikaNo ratings yet
- Test On CalculusDocument10 pagesTest On CalculusKarthik NNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Imb2Document6 pagesSample Paper Imb2Aryan VermaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: MathematicsDocument12 pagesSample Paper: MathematicsSABARI SRINIVAS ANo ratings yet
- Determinant NewDocument14 pagesDeterminant NewAbhinav PipalNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trignometric Function Paper-1Document4 pagesInverse Trignometric Function Paper-1jagannivasNo ratings yet
- MathDocument50 pagesMathYOGESHWAR SINGH YADAVNo ratings yet
- 025dd369008c4-Determinants DPT - 02 (14.07.2021)Document2 pages025dd369008c4-Determinants DPT - 02 (14.07.2021)MD REHANNo ratings yet
- Definite Integration AssignmentDocument9 pagesDefinite Integration AssignmentJayNsteinNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 of 20 MCQ PDFDocument3 pagesUNIT 2 of 20 MCQ PDFpraveen kumarNo ratings yet
- XII-PTS-26 (2023-24) - by O.P. GUPTADocument7 pagesXII-PTS-26 (2023-24) - by O.P. GUPTAronitsuniyaNo ratings yet
- Xii - Maths QP - Kum Campus TestDocument3 pagesXii - Maths QP - Kum Campus TestraghuNo ratings yet
- 024eec5a83031-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 08 (07.04.2020)Document8 pages024eec5a83031-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 08 (07.04.2020)Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- Class-XII-Maths-QP-KV NERISTDocument6 pagesClass-XII-Maths-QP-KV NERISTBot1234No ratings yet
- Revision Test - 02Document7 pagesRevision Test - 02Ankit RoyNo ratings yet
- 024e500ce0750-NIT New Test Series NT - 02Document7 pages024e500ce0750-NIT New Test Series NT - 02Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- Maths 12Document7 pagesMaths 12Prince bhadaniaNo ratings yet
- St. Paul Education Centre: Code: Wqp-Mm-1 Mathematics Model - SADocument7 pagesSt. Paul Education Centre: Code: Wqp-Mm-1 Mathematics Model - SAsudevs_unniNo ratings yet
- Annual Exam 11th Math PrestigeDocument4 pagesAnnual Exam 11th Math PrestigeVarun PatilNo ratings yet
- O.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnerDocument6 pagesO.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnersusenthilNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII MCQ TEST (CH 2-8) 2019-20-1Document4 pagesCLASS XII MCQ TEST (CH 2-8) 2019-20-1JIVANSHU SHARMANo ratings yet
- 12 Math Eng PP 2023 24 1Document7 pages12 Math Eng PP 2023 24 1narangdiya602No ratings yet
- XI Maths RevisionDocument37 pagesXI Maths Revisionbansaljayash740No ratings yet
- 024e6042fa437-CBT - 04Document3 pages024e6042fa437-CBT - 04Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- M14 - Indefinite IntegrationDocument24 pagesM14 - Indefinite IntegrationBhawna SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1st Assignment-Inequalities With Answer KeyDocument2 pages1st Assignment-Inequalities With Answer KeyPrince DhananiNo ratings yet
- DPT - Determinants - 02 - Updated Answer Key - 21482656Document2 pagesDPT - Determinants - 02 - Updated Answer Key - 21482656dicen506No ratings yet
- Xii - Maths - All Examples QP - Kum Campus TestDocument3 pagesXii - Maths - All Examples QP - Kum Campus TestraghuNo ratings yet
- 12th Maths Preboard-1 2021Document7 pages12th Maths Preboard-1 2021dev sharmaNo ratings yet
- Nit New Test Series NT-04Document7 pagesNit New Test Series NT-04Mohommad ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Ruby Park, Kolkata: UNIT TEST - II (2021-22) Class - Xii Subject - MathematicsDocument2 pagesDelhi Public School Ruby Park, Kolkata: UNIT TEST - II (2021-22) Class - Xii Subject - MathematicsAryan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Limits Quiz-1: Single Correct Type 1Document2 pagesMathematics Limits Quiz-1: Single Correct Type 1sikkaNo ratings yet
- Limits, Continuity & Derivative Exercise + ANS KEYDocument24 pagesLimits, Continuity & Derivative Exercise + ANS KEYAshwani ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Xii Main Full Test-1 PCM 02.01.2023Document17 pagesXii Main Full Test-1 PCM 02.01.2023MeetNo ratings yet
- Revision Test-Mock-1 - XIIDocument7 pagesRevision Test-Mock-1 - XIIdev sharmaNo ratings yet
- 024e500c71824-BHU MOCK - 01Document10 pages024e500c71824-BHU MOCK - 01Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Function: Subject: Mathematics DATE: 18-03-2024Document2 pagesInverse Trigonometric Function: Subject: Mathematics DATE: 18-03-2024abhayalways1rajpootNo ratings yet
- Nda 2Document22 pagesNda 2Gurpartap SinghNo ratings yet
- O.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnerDocument6 pagesO.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnersusenthilNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Pondicherry University: Provisional Overall Merit List (Based On Cuet Score)Document82 pagesPondicherry University: Provisional Overall Merit List (Based On Cuet Score)rahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Pondicherry University: Provisional Overall Merit List (Based On Cuet Score)Document31 pagesPondicherry University: Provisional Overall Merit List (Based On Cuet Score)rahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Seq & SeriesDocument9 pagesSeq & Seriesrahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Mca Mhcutoff 2021 22Document98 pagesMca Mhcutoff 2021 22rahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Maintenant Part - Recc. ListDocument4 pagesMaintenant Part - Recc. ListNguyen TrungNo ratings yet
- Progress in Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 139, 229-245, 2013Document17 pagesProgress in Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 139, 229-245, 2013Vivek KushwahNo ratings yet
- 5 - Friction Ex. Module-1Document16 pages5 - Friction Ex. Module-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18-Fundamentals of Metal FormingDocument33 pagesChapter 18-Fundamentals of Metal FormingMuhammad Qasim QureshiNo ratings yet
- Bin Tariq Pipes Intro 2013Document61 pagesBin Tariq Pipes Intro 2013Munir Ahmed MusianiNo ratings yet
- 03/10 - Rock Excavation Handbook / Rock ExcavationDocument39 pages03/10 - Rock Excavation Handbook / Rock ExcavationHakan_KURUNo ratings yet
- Mechanical BeltsDocument9 pagesMechanical BeltstorresgiovanniNo ratings yet
- Panel Operator About MeDocument2 pagesPanel Operator About MeMunirul ChaqimNo ratings yet
- VISCOELASTICITY Power Point PresentationDocument26 pagesVISCOELASTICITY Power Point PresentationNathaly CuasialpudNo ratings yet
- Pvsyst Trial Pvsyst Trial Pvsyst Trial Pvsyst TrialDocument11 pagesPvsyst Trial Pvsyst Trial Pvsyst Trial Pvsyst TrialGheorghe SilviuNo ratings yet
- SputteringDocument17 pagesSputteringTonmoy PaulNo ratings yet
- Government College of Engineering, Amravati: Industrial Visit Report On 220 KV Substation Power House, AmravatiDocument20 pagesGovernment College of Engineering, Amravati: Industrial Visit Report On 220 KV Substation Power House, AmravatiShourya Prasad100% (1)
- Principles of Electricity PDFDocument371 pagesPrinciples of Electricity PDFJohn C. Stephens100% (5)
- Vdocuments - MX - Internship Report TNB Distribution SelangorDocument87 pagesVdocuments - MX - Internship Report TNB Distribution Selangormuhd faizNo ratings yet
- 1920SEM1 ExamDocument9 pages1920SEM1 ExamBenedict ChinNo ratings yet
- Designing and Managing Drilling Fluid: Plano, Texas, USADocument22 pagesDesigning and Managing Drilling Fluid: Plano, Texas, USAAl-Shargabi MohaNo ratings yet
- 3.2.3 Notes Thin Converging Lens P4 TeacherDocument10 pages3.2.3 Notes Thin Converging Lens P4 TeacherYokeLing ChangNo ratings yet
- PDC TR-06-02 Rev 1 SBEDS Users Guide DistribADocument95 pagesPDC TR-06-02 Rev 1 SBEDS Users Guide DistribAmirko huaranccaNo ratings yet
- Ibong Tiririt (MDSP 3) : MM 25 M 025 - 0 400 10 N V L 25 Tan D L TanDocument31 pagesIbong Tiririt (MDSP 3) : MM 25 M 025 - 0 400 10 N V L 25 Tan D L TanSYBRELLE CRUZNo ratings yet
- Datasheet LFU119XDocument2 pagesDatasheet LFU119XMohammed Tausif AhmedNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Void Growth and Fiber Volume Fraction Based On Filament Winding Process MechanicsDocument10 pagesPrediction of Void Growth and Fiber Volume Fraction Based On Filament Winding Process MechanicsHassan HabibNo ratings yet
- Compact Design of Planar Stepped Micro Combustor For PortableDocument11 pagesCompact Design of Planar Stepped Micro Combustor For PortableHERDI SUTANTONo ratings yet
- 2022 - Bazli - Long-Span Timber Flooring SystemsDocument17 pages2022 - Bazli - Long-Span Timber Flooring SystemsThomas ManderNo ratings yet
- Solenoid Valve Namur Fig 33580 AluminiumDocument1 pageSolenoid Valve Namur Fig 33580 AluminiumNam Nguyễn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Project On Reinforced Concrete Design (Cotm 447)Document5 pagesProject On Reinforced Concrete Design (Cotm 447)Zoom LionNo ratings yet
- Datasheet b393g Impactpp eDocument2 pagesDatasheet b393g Impactpp eEmre UzunogluNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Paper-IDocument13 pagesElectrical Engineering Paper-Ikpv294No ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering Lab and HeatDocument87 pagesThermal Engineering Lab and Heatsaadzamel67No ratings yet
- Acoustic LevitatorDocument62 pagesAcoustic LevitatorJulianSalazarNo ratings yet
Maths Mock-03 (08.03.21)
Maths Mock-03 (08.03.21)
Uploaded by
rahul kumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maths Mock-03 (08.03.21)
Maths Mock-03 (08.03.21)
Uploaded by
rahul kumarCopyright:
Available Formats
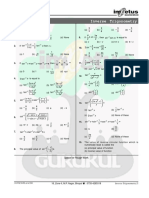
MATHS MOCK TEST- 03
dy 10. If A x : x N, and x 6 ,
1. If y sin 1 x (1 x 2 ) then at x = 0 equals :
dx B x : x N, and 3 x 8 ,
1 1 u x : x N and x 10 , then elements of A´ B´ are
(a) 1 (b) (c) 0 (d)
2 2
(a) {1, 2} (b) {3, 4} (c) {7, 8} (d) {9, 10}
dy 11. Out of 10000 people surveyed, 3700 liked city A, 4000
2. If y sin x sin x.... then equals liked city B and 5000 liked city C . 700 people liked A
dx
and B, 1200 liked A and C and 1000 liked B and C.
y cot x y cot x Each person liked at least one city .
(a) 1 y log sin x (b) 1 y log sin x
The number of people liking all the three cities is :
(a) 100 (b) 200 (c) 300 (d) 400
y 2 cot x
(c) (d) none of these 12. If the sum of all the coefficients in the expansion
1 y log sin x
( x 3 2 x 1 3 )n is 128, then the coefficients of x will
5
3 3x be:
3. Value of 0 3x
dx is
(a) 7 (b) 21 (c) 35 (d) 45
13
The value of the sum (i n i n 1) , where i 1 ,
(a) 3( 1) (b) 3 2 1 13.
n 1
equal
(a) i (b) i 1 (c) –i (d) 0
(c) 3(1 ) (d) 3 1 2
14. If z1, z2 , z3 are complex numbers such that
sin x cos x
4. 1 sin 2 x
dx is | z1 | | z2 | | z3 |
1
1
z1 z2 z3
1
1, then
(a) sin x (b) x (c) cos x (d) tan x
| z1 z2 z3 | is
5. Length of tangent drawn from point (2, 5) to the circle
(a) Equal to 1 (b) Less than 1
x 2 y 2 2 x 3 y 1 0 is (c) Greater than 3 (d) Equal to 3
(a) 3 3 (b) 3 (c) 6 (d) 6 3 1 iz
15. If z x iy and then | | 1 show that in
6. The probability of getting one head in live tosses of a zi
complex plane
coin is
(a) z will be at imaginary axis
5 5 5 5 (b) z will be at real axis
(a) (b) (c) (d)
8 16 32 64 (c) z will be at unity circle
7. W hich of following is affected most by extreme (d) None of these
observations?
16. If , are the roots of ax 2 bx b 0 , then
(a) Median (b) Mode
(c) Harmonic mean (d) Arithmetic mean b
is equal to
8. Which of following is correct relation ? a
(a) H.M > G.M > A.M (b) H.M.>A.M>G.M b
(c) A.M > G.M > H.M (d) G.M > H.M > A.M (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 2
a
9. Which of the following is a true statement ?
17. If one root of the equation x 2 px 12 0 is 4, while
(a) { a, b, c, 1, 2, 3 } is not a set
(b) a,b a,b,c the equation x 2 px q 0 has equal roots, then the
value of q is
(c) x R :| x | 1 f (a) 49/4 (b) 4/49 (c) 4 (d) None
(d) x R : 1 x 2 is finite
18, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319 MT-03|1
18. If A is any m n matrix such that AB and BA are both 28. The product of perpendiculars drawn from the foci of
defined, then B is an ellipse to any tangent of ellipse is equal to
(a) m n matrix (b) n m matrix (a) u 2 (b) a2e2 (c) b2 (d) none
(c) n n matrix (d) m m matrix
19. If A is a skew symmetric and n is an odd positive integer, x2 y 2
29. The length of latus rectum of hyperbola 1
then A isn 16 25
(a) a symmetric matrix is
(b) a skew symmetric matrix 16 18 32
(a) (b) (c) (d) none
(c) a diagonal 5 5 5
(d) none of these 30. A die and two coins are tossed. The probability that both
the coins show heads and die shows 1 or 2, is
20. If A [aij ]mn is a matrix of rank r and B is a square
submatrix of A of the order r + 1, then 1 7 4 5
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(a) B is invertible (b) B is not invertible 12 12 7 12
(c) B may of may not be invertible (d) none 31. The variance is independent of change of
(a) scale only (b) origin and Scale both
2 2
21. The equation x 1 has (c) origin only (d) none of these
1 x 1 x
(a) no real root (b) one real root 32. If log 2, log( 2n 1) and log( 2n 3) are in A.P., then n =
(c) two equal roots (d) infinitely.
(a) 5/2 (b) log2 5 (c) log3 5 (d) 3/2
33. Two men are on the opposite side of a tower. They
22. If a, b, c are positive real numbers not all equal the value
measure the angles of elevation of the top of the tower
a b c 45° and 30° respectively. If the height of the tower is
40m. find the distance between the men.
of b c a is
c a b (a) 40m (b) 40 3 m (c) 68.280 m (d) 109.28 m
(a) positive (b) negative 34. The coefficient of skewenss in Karl Pearson formula
lies between
(c) zero (d) noting can be said
(a) – 1 and + 1 (b) – 1.5 and + 1.5
23. If is a cube root of unity, then the value of (c) – 2 and + 2 (d) – 3 and + 3
(1 2 )5 (1 2 )5 35. If two lines of regression are coincident, then it implies
(a) r = 0 (b) r = – 1/2 (c) r = 1/2 (d) r 1
(a) 16 (b) 32 (c) 48 (d) –32
36. The least value of natural number n satisfying
2
24. The roots of the quadratic equation ax bx c 0 will
C (n, 5) C (n, 6) C (n 1, 5) is
be reciprocal to each other if
(a) 11 (b) 10 (c) 12 (d) 13
(a) a 1 / c (b) a c (c) b ac (d) a b
B C A
25. Let A be a non-singular square matrix of order n then 37. If tan x cot , then x =
2 2
| adj A | equals
c a ab bc
(a) | A |n (b) | A |n 1 (c) | A |n 2 (d) none (a)
c a
(b)
ab
(c)
bc
(d) None
26. There are 4 parcels and 5 post-offices. In how many 1 x 2
1 2 x
sec 1 dy
different ways the registration of parcel can be made. 38. If y sin 2 2 then , equals
1 x 1 x dx
(a) 20 (b) 45 (c) 54 (d) 54 45
4 4 4
(a) (b) (c) (d) 1 x 2
dy 1 x 2 1 x 2 1 x 2
27. If y sin x , then equals
dx 39. If circle x 2 y 2 2gx a 2 0 and
180
(a) cos x (b) cos x x 2 y 2 2fy a 2 0 touch each other, then relation
between g, f and a is
(a) g 2 f 1 a 1 (b) g 1 f 1 a 1
(c) cos x (d) none of these
180
(c) g 1 f 2 a 2 (d) g 2 f 2 a 2
2| MT-03 18, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319
50. The system of equation
40. The locus of the mid points of the chords of parabola
x 2y 3z 6
y 2 4ax which passes through the vertex is a parabola 2x 4y z 7
whose latus rectum is 3 x 2y z 14
(a) a (b) 2a (c) 3a (d) a/2
(a) is inconsistent
41. A line L is perpendicular to the line 5 x y 1 and age
(b) has a unique solution x = 5, y = –1, z = 1
area of the triangle formed by the line L and coordinate
axes is 5. The equation of the line L is (c) has a unique solution x = y = z = 1
(d) none of these
(a) x 5y 5 (b) x 5y 5 2
51. The centre of the circle which intersect circles
(c) x 5y 5 (d) x 5y 5 2 x 2 y 2 2 x 17 y 4 0, x 2 y 2 7 x 6 y 11 0
42. If the line y mx meets the lines x 2 y 1 0 and and x 2 y 2 – x 22 y 3 0 orthogonally is :
2 x y 3 0 at the same point, then m is equal to : (a) (2, 3) (b) (3, 2)
(a) 1 (b) – 1 (c) 2 (d) – 2 (c) (–2, 3) (d) (–3, 2)
43. If B is a non-singular matrix and A is a square matrix of
52. The equation of the tangents to the circle
same order, then det B 1( AB ) equals
x 2 y 2 2 x – 4 y 1 0 which passes through (0, 0)
(a) det (A) 1
(b) det (B) (c) det (B ) (d) det ( A ) 1
are:
44. If p and p’ be perpendiculars from the origin upon the (a) x 0, 3 y 4 x (b) x 0, 4 y 3 x
straight lines x sec y cosec a and
(c) y 0, 3 y 4 x (d) y 0, 4 y 3 x
x cos y sin a cos 2 respectively, then the value of
53. The mode of a symmetrical series is 18 and mean is
expression 4 p 2 p'2 is : 24 then median is :
(a) 18 (b) 24 (c) 22 (d) 21
(a) a2 (b) 3a 2 (c) 2 a 2 (d) 4 a 2
45. The ends of a rod of length l move on two mutually 54. The correct empirical relation between the measures
perpendicular lines. The locus of the point on the rod of dispersion is :
which divides it in the ratio 1 : 2 is 3 4
2 2 2 2 2 2 (a) M . D. S . D. (b) M . D. S . D.
(a) 36 x 9 y 4l (b) 36 x 9 y l 4 3
2 2
(c) 9 x 36 y 4l 2
(d) None of these 5 4
(c) M . D. S . D. (d) M . D. S . D.
46. The distance between the lines 3 x 4 y 9 and 4 5
6 x 8 y 15 is :
55. The common area between two curves y 2 4ax 0
(a) 3/2 (b) 3/10 (c) 6 (d) None
47. Algebraic sum of deviations of a set of n observations and x 2 4ay lies in
from their mean is
(a) first quadrant (b) second quadrant
n(n 1) (c) third quadrant (d) fourth quadrant
(a) 0 (b)
2
2
1
n(n 1) n 1 56. The value of dx is :
(c) (d) 0 1 tan x
2 2
48. For the circle x 2 y 2 – 2x 4y – 4 0 the line (a) (b) (c) (d)
2 4 8
2 x – y 1 0 is a 57. The order and degree of the differential equation of all
(a) tangent (b) chord (c) diameter (d) None parabolas which have x axis as their common axis are
(a) 1, 1 (b) 2, 1 (c) 2, 2 (d) 3, 1
49. The integral part of the expression (7 4 3 )n is : 58. The line lx + my + n = 0 is a tangent of parabola
(a) odd integer (b) even integer y 2 4ax , if
(c) 0 (d) none of these
(a) mn al 2 (b) lm an 2
(c) ln am 2 (d) am ln2
59. The locus of foot of perpendicular drawn from a fucus,
18, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319 MT-03|3
III. A constant function is continuous in an interval.
x2 y2
upon the tangents of ellipse 1 is Out of these correct statements are :
a2 b2 (a) I and II (b) II and III
(c) I and III (d) all the above
2 2 a 2b 2
(a) x 2 y 2 ab (b) x y 67. The probability of happening at least one of the events A
a2 b2
and B is 0.6. If events A and B happen simultaneously
(c) x 2 y 2 a 2 b 2 (d) none of these with probability 0.2 then P(A)+P(B) is equal to :
60. If e is the eccentricity of a hyperbola then centricity of it's (a) 1.2 (b) 0.8 (c) 0.4 (d) 1.0
conjugate hyperbola is given by 68. An integer is chosen at random from the number ranging
from 1 to 50. The probability that the integer chosen is a
1 1
(a) (b) multiple of 2 or 3 or 10 is
e e2 1
3 5 7 9
(a) (b) (c) (d)
1 10 10 10 10
(c) (d) none of these
e2 1 69. Out of 40 consecutive natural numbers, two are chosen
at random. Probability that the sum of the numbers is
61. A matrix A [aij ] is an upper triangular matrix if odd is :
(a) it is a square matrix and aij 0, i j 14 20 1
(a) (b) (c) (d) none
29 39 2
(b) it is a square matrix and aij 0, i j
(c) it is not a square matrix and aij 0, i j x
70. The domain of the function f ( x ) sin1 log3 is :
3
(d) it is not a square matrix and aij 0, i j
(a) [– 1, 9] (b) [1, 9]
cos sin (c) [– 9, 1] (d) [– 9, – 1]
62. If E () then E ( )·E ( ) is equal to
sin cos x2
(a) E( 0 ) (b) E( ) (c) E( ) (d) E( ) 71. Value of lim 0
sec 2 t dt
is :
x 0 x sin x
3ax b , x 1 (a) 2 (b) 1 (c) 0 (d) 3
63. If f ( x ) 11 , x 1 is continuous at x = 1,
5ax 2b , x 1 | x 3 | ; x 1
72. The function defined by f ( x ) 1 2 3 13
then : 4 x 2 x 4 ; x 1
(a) a = 2, b = 3 (b) a = 3, b = 2
is :
(c) a = 5, b = 1 (d) a = 1, b = 5
(a) Continuous at x = 1
2 3 (b) Continuous at x = 3
64. If A 3 2
then A 4 A A is equal to
1 2 (c) Differentiable at x = 1
(a) I (b) A (c) O (d) none (d) All the above
65. If A is a square matrix of order n such that elements of A
5
1
are polynomials in x and it's r rows become identical for 73. The value of (| x 3 | | 1 x |) dx is :
x = k, then
(a) ( x k )r is a factor of | A | 5
(a) 10 (b) (c) 21 (d) 12
6
(b) ( x k ) n r is a factor of | A |
3
x
(c) ( x k )r is factor A 74. The value of 2 5x x
dx is :
(d) none of these
(a) 1 (b) 0 (c) –1 (d) 1/2
66. Consider the following statement :
I. A function f is continuous at a point x0 Dom (f ) if 75. In a ABC, a 2 sin 2C c 2 sin 2 A
lim f ( x ) f ( x )
0 . (a) (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4
x x0
II. f is continuous in [a, b] if f is continuous in (a, b) and
f (a ) f ( b ) .
4| MT-03 18, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319
a
76. The d.r’s of normal to the plane through (1, 0, 0 ), (0, 1, 0 ) 88.
a
[g ( x ) g ( x )][f ( x ) f ( x )] dx equals:
a
which makes an angle
4
with plane x y 3 , are (a) 2 0
[g ( x ) g ( x )] [f ( x ) f ( x )] dx
a
(a) 1, 2 ,1 (b) 1,1, 2 (b) 2 0
g ( x ) . f ( x ) dx
(c) 1,1,2 (d) none of these (c) 0
77. Given A sin2 cos 4 , then for all real values of a a
(a) 1 A 2 (b) 3 / 4 A 1
(d) 2
0
g(x ) f (x )
0
f ( x ) g ( x ) dx
(c) 13 / 16 A 1 (d) 3 / 4 A 13 / 16
e (1 tan x ) sec x dx
78. Which of the following is correct : x
89. equals:
cot A cot B 1
(a) cot( A B )
cot A cot B (a) e x sec x (b) e x sec x
1 sin (c) e x sec x tan x (d) none of these
(b) tan
1 sin 4 2
(c) tan A cot A 2 cot 2 A 90. If m is the slope of the tangent to the curve e y 1 x 2 ,
then:
AB AB
(d) cos B cos A 2 sin sin (a) |m| > 1 (b) m < 1 (c) |m| < 1 (d) | m | 1
2 2
79. tan 1 tan 2 tan 3 ........ tan 179
d 2y
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) (d) 91. If x = a (t – sin t) y = a(1 + cos t) then equals:
dx 2
80. If r represents the coefficient of correlation then correct
relation is 1 4 t 1 2 t
(a) r 1 (b) r 1 (c) | r | 1 (d) | r | 1 (a) 2a cos ec 2 (b) 4a cos ec 2
81. Out of 800 families with 4 children each. How many
families are expected to have 2 boys and 2 girls 1 4 t 1 2 t
(a) 500 (b) 400 (c) 300 (d) 200 (c) 4a cos ec 2 (d) 4a cos ec 4
82. Which of the following relations is correct :
(a) sin 1 sin 1 (b) sin 1 sin 1 92. The value of the expression
C0 3C1 5C2 ... (2n 1)Cn :
(c) sin 1 sin 1 (d) sin 1 sin 1
180 (a) ( n 1) 2 n (b) n 2n 1 (c) 2n 2 (d) none
83. A binary number 101101 is equivalent to octal number
(a) 65 (b) 55 (c) 51 (d) 45 93. Distance between two parallel planes
84. Minimum value of 5 sin2 4 cos2 is : 2x y 2z 8 and 4 x 2y 4 z 5 0 is
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4
9 5 7 3
85. tan 9 tan 27 tan 63 tan 81 (a) (b) (c) (d)
2 2 2 2
(a) 1/2 (b) 2 (c) 4 (d) 8
86. Area bounded by curve y x 0 and y x 2 0 is:
2 x 2 y 3 z 4 x 1
94. The line and
(a) 7/3 sq. unit (b) 1/3 sq. unit 1 1 k k
(c) 5/3 sq. unit (d) 1 sq. unit
y 4 z 5
87. Equation of the chord of ellipse 2 x 2 5 y 2 20 which are coplanar, if
2 1
is bisected at point (2, 1) is: (a) k = 0 or -1 (b) k = 0 or 1
(a) 4x + 5y +13 = 0 (b) 4x + 5y –13 = 0 (c) k = 0 or – 3 (d) k = 3 or – 3
(c) 2x + 5y +13 = 0 (d) none of these
B C
95. In a ABC , if 3a b c , then the value of cot cot
2 2
is :
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 2
18, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319 MT-03|5
1 x
xdx 1
96. 4 equals: (c) x , y 4, z 10 (d) x 1, y 2, z 5
2
1 103. If three vectors a, b, c satisfy a + b + c = 0 and | a | = 3,
(a) tan1 x 2 c (b) tan 1 x 2 c
2 | b | = 5, | c | = 7, then the angle between a and b is
(c) log(1 x 4 ) c (d) none of these (a) 30 (b) 45 (c) 60 (d) 90
97. The coefficient of correlation between x and y is 0.6 104. Let a 2i – j 2k and b i 2 j and c is a vector
their covariance is 4.8 and var(x)= 9 then y is : such that angle between a b and c is 30 . If a . c | c |
8 3 8 and | c – a | 3 , then | ( a b ) c |
(a) (b) (c) (d) none
3 8 9
(a) 2 5 (b) 3 5 (c) 3 2 (d) 2 3
105. If a, b, c are three non-zero vectors, then
98. A spherical balloon is being pumped at the rate of
a (b c ) b (c a ) c ( a b ) is equal to :
a cm 3 / second. Then rate at which the surface area of (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) –1 (d) 2
the balloon is increasing, when it's radius is b cm, is:
106. The average age of a class of 40 boys is 16.95 years
2a2 a but by the admission of a new boy the average age is
(a) cm2 / sec ond (b) cm 2 / sec ond raised to 17 years. Then the age of the new boy.
b4 2b
(a) 18 years (b) 16.95 years
2a (c) 19 years (d) 41 years
(c) cm 2 / sec ond (d) none
b 107. Which of the following is true for the set of numbers 3, 5,
2, 6, 5, 9, 5, 2, 8, 6 ?
4 5 cos x
dx (a) (b) A.M. = Mode
99. is equal to—
A . M . = M
d
(c) Md = Mode (d) A.M. = 2Md
108. A purse contains two 20 paise coins and four 10 paise
x x
3 tan 1 tan 3 coins. A second purse contains four 20 paise coins and
(b) log
1 2
(a) log 2 three 10 paise coins. If a coin is selected at random
3 3 tan x 3 tan x 3 from one of the two purses, then the probability that it is
2 2 a 20 paise coin is :
(a) 6/13 (b) 3/13 (c) 19/42 (d) 19/21
x x
tan 3 1 3 tan 109. If Y 2 2 x 10 tangent to x 2 y 2 2 y 1 a 2 0 ,
1
(c) log 2 (d) log 2
3 tan x 3 3 3 tan x then a =
2 2 (a) – 3 (b) 4 (c) 5 (d) 10/3
110. (3232 )8 (1256 )8
100. Solution of differential equation (y – x)
(a) 4600 (b) 4510
dy ( y 2 x 2 )dx 0 , given y (0) = – 1 is : (c) 4508 (d) 4610
(a) y = –( x + 1) (b) y = 1 + x 111. A box contain 9 tickets numbered from 1 to 9. If 3 tickets
(c) y = 1 – x (d) y (1 x )2 are drawn from the box, one by one then probability that
the numbers on these are alternately either even, odd,
101. If ABCD is a rhombus whose diagonals cut at the origin even or odd; even, odd is :
(a) 4/9 (b) 5/18 (c) 20/63 (d) 5/42
O, then OA OB OC OD
a
(a) AB AC (b) 2 BC 112. If (a x ) ( x ) , then
0
x( x ) dx is equal to :
(c) O (d) AC BD
a a
1
(a) a ( x ) dx (b) a ( x ) dx
102. The vectors a xi 2 j 5k and b i yj zk are 0 2 0
collinear if : a
(a) x 1, y 2, z 5
1
(b) x , y 4, z 10
2
(c) 2a 0
( x ) dx (d) none of these
6| MT-03 18, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319
118. Let E and F be two independent events. The probability
x that both E and F happens is 1/12 and the probability
113. if f ( x ) A sin B, f ' (1 / 2) 2
2 that neither E nor F happens is 1/2. Then :
1 (a) P(E) 1/ 3, P (F) 1/ 4 or P (E) 1/ 4, P(F) 1/ 3
2A
and f ( x ) dx , then values of A and B are :
0 (b) P(E) 1/ 2, P (F ) 1/ 6
(a) / 2, / 2 (b) 2 / , 3 / (c) P(E) 1/ 6, P (F ) 1/ 2
(c) 4 / , 0 (d) 0, 4 / (d) P(E) 1/ 4, P (F) 1/ 3
119. The radius of the circle in which the sphere
114. Domain of definition of the
x 2 y 2 z 2 2x 2y 4 z 19 0 is cut by the
3 3
function f ( x ) log10 ( x – x ) is
4 – x2 plane x 2y 2z 7 0 is
(a) (–1, 0 ) (1, 2) ( 2, ) (b) (1, 2) ( a ) 1 ( b ) 2 ( c ) 3 ( d ) 4
(c) (–1, 0 ) (1, 2) (d) (1, 2) ( 2, )
120. The equations of the line passing through the point
115. A vector whose modulus is (1,2,–4) and perpendicular to the two lines
51 and makes the same
x 8 y 19 z 10 x 15 y 29 z 5
i – 2 j 2k –4i – 3k and ,
angle with a , b and c = j , will 3 16 7 3 8 5
3 5
be will be
(a) 5i 5 j k (b) 5i j – 5k x 1 y 2 z 4
(a)
(c) 5i j 5k (d) (5i – j – 5k )
2 3 6
x 1 y 2 z 4
x cosec 2 30 sec 2 45 (b)
116. If 2 2
tan 60 tan 30 , then x = 2 3 8
8 cos2 45 sin2 60
x 1 y 2 z 4
(a) 1 (b) – 1 (c) 2 (d) 0
(c)
3 2 8
117. f (0 ) f ' (0 ) 0 and f ' ' ( x ) tan2 x , then f (x ) is
(d)None of these
x2 x2
(a) log sec x (b) log cos x
2 2
x2
(c) log sec x (d) none of these
2
18, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319 MT-03|7
SMATHS MOCK TEST -03N
1. (a) 2. (c) 3. (b) 4. (b) 5. (b) 6. (c) 7. (d) 8. (c) 9. (c) 10. (d)
11. (b) 12. (c) 13. (b) 14. (a) 15. (b) 16. (a) 17. (a) 18. (b) 19. (b) 20. (b)
21. (a) 22. (b) 23. (b) 24. (b) 25. (b) 26. (c) 27. (c) 28. (c) 29. (c) 30. (a)
31. (c) 32. (b) 33. (d) 34. (d) 35. (d) 36. (a) 37. (c) 38. (c) 39. (d) 40. (b)
41. (d) 42. (b) 43. (a) 44. (a) 45. (c) 46. (c) 47. (a) 48. (b) 49. (a) 50. (b)
51. (b) 52. (c) 53. (c) 54. (d) 55. (b) 56. (b) 57. (b) 58. (c) 59. (d) 60. (d)
61. (b) 62. (c) 63. (b) 64. (c) 65. (a) 66. (c) 67. (b) 68. (c) 69. (b) 70. (b)
71. (b) 72. (d) 73. (d) 74. (d) 75. (d) 76. (b) 77. (b) 78. (d) 79. (d) 80. (c)
81. (c) 82. (b) 83. (b) 84. (d) 85. (c) 86. (b) 87. (b) 88. (c) 89. (a) 90. (d)
91. (c) 92. (a) 93. (c) 94. (c) 95. (b) 96. (b) 97. (a) 98. (c) 99. (c) 100. (a)
101. (c) 102. (c) 103. (c) 104. (b) 105. (b) 106. (c) 107. (c) 108. (c) 109. (a) 110. (b)
111. (b) 112. (b) 113. (c) 114. (a) 115. (d) 116. (a) 117. (a) 118. (a) 119. (c) 120. (a)
SMATHS MOCK TEST -03N
1. (a) 2. (c) 3. (b) 4. (b) 5. (b) 6. (c) 7. (d) 8. (c) 9. (c) 10. (d)
11. (b) 12. (c) 13. (b) 14. (a) 15. (b) 16. (a) 17. (a) 18. (b) 19. (b) 20. (b)
21. (a) 22. (b) 23. (b) 24. (b) 25. (b) 26. (c) 27. (c) 28. (c) 29. (c) 30. (a)
31. (c) 32. (b) 33. (d) 34. (d) 35. (d) 36. (a) 37. (c) 38. (c) 39. (d) 40. (b)
41. (d) 42. (b) 43. (a) 44. (a) 45. (c) 46. (c) 47. (a) 48. (b) 49. (a) 50. (b)
51. (b) 52. (c) 53. (c) 54. (d) 55. (b) 56. (b) 57. (b) 58. (c) 59. (d) 60. (d)
61. (b) 62. (c) 63. (b) 64. (c) 65. (a) 66. (c) 67. (b) 68. (c) 69. (b) 70. (b)
71. (b) 72. (d) 73. (d) 74. (d) 75. (d) 76. (b) 77. (b) 78. (d) 79. (d) 80. (c)
81. (c) 82. (b) 83. (b) 84. (d) 85. (c) 86. (b) 87. (b) 88. (c) 89. (a) 90. (d)
91. (c) 92. (a) 93. (c) 94. (c) 95. (b) 96. (b) 97. (a) 98. (c) 99. (c) 100. (a)
101. (c) 102. (c) 103. (c) 104. (b) 105. (b) 106. (c) 107. (c) 108. (c) 109. (a) 110. (b)
111. (b) 112. (b) 113. (c) 114. (a) 115. (d) 116. (a) 117. (a) 118. (a) 119. (c) 120. (a)
SMATHS MOCK TEST -03N
1. (a) 2. (c) 3. (b) 4. (b) 5. (b) 6. (c) 7. (d) 8. (c) 9. (c) 10. (d)
11. (b) 12. (c) 13. (b) 14. (a) 15. (b) 16. (a) 17. (a) 18. (b) 19. (b) 20. (b)
21. (a) 22. (b) 23. (b) 24. (b) 25. (b) 26. (c) 27. (c) 28. (c) 29. (c) 30. (a)
31. (c) 32. (b) 33. (d) 34. (d) 35. (d) 36. (a) 37. (c) 38. (c) 39. (d) 40. (b)
41. (d) 42. (b) 43. (a) 44. (a) 45. (c) 46. (c) 47. (a) 48. (b) 49. (a) 50. (b)
51. (b) 52. (c) 53. (c) 54. (d) 55. (b) 56. (b) 57. (b) 58. (c) 59. (d) 60. (d)
61. (b) 62. (c) 63. (b) 64. (c) 65. (a) 66. (c) 67. (b) 68. (c) 69. (b) 70. (b)
71. (b) 72. (d) 73. (d) 74. (d) 75. (d) 76. (b) 77. (b) 78. (d) 79. (d) 80. (c)
81. (c) 82. (b) 83. (b) 84. (d) 85. (c) 86. (b) 87. (b) 88. (c) 89. (a) 90. (d)
91. (c) 92. (a) 93. (c) 94. (c) 95. (b) 96. (b) 97. (a) 98. (c) 99. (c) 100. (a)
101. (c) 102. (c) 103. (c) 104. (b) 105. (b) 106. (c) 107. (c) 108. (c) 109. (a) 110. (b)
111. (b) 112. (b) 113. (c) 114. (a) 115. (d) 116. (a) 117. (a) 118. (a) 119. (c) 120. (a)
You might also like
- Schaum's Outline of Physics For Engineering and ScienceDocument473 pagesSchaum's Outline of Physics For Engineering and Sciencemexx4u2nv100% (5)
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (ITF) JEE Main and Advanced (IIT-JEE)Document5 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions (ITF) JEE Main and Advanced (IIT-JEE)Er. Vineet Loomba (IIT Roorkee)67% (6)
- Determinants & Matrices - Ex.1 (A)Document7 pagesDeterminants & Matrices - Ex.1 (A)happyNo ratings yet
- 024efcb68fc74-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 09 09.04.2020Document8 pages024efcb68fc74-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 09 09.04.2020Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024e99d5874b2-Mock Test (Maths) - 05Document8 pages024e99d5874b2-Mock Test (Maths) - 05Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- KCET 2020 MATHEMATICS DR AcademyDocument5 pagesKCET 2020 MATHEMATICS DR AcademypullagalkNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions - DPP 04Document2 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions - DPP 04jeemainsmaterial97No ratings yet
- XII-PTS-21 (2023-24) - by O.P. GUPTADocument8 pagesXII-PTS-21 (2023-24) - by O.P. GUPTAmaanya.ailawadi3No ratings yet
- Maths SQP 1Document7 pagesMaths SQP 1qutubkhan.nalwalaNo ratings yet
- 01-Indefinite Integration PDFDocument11 pages01-Indefinite Integration PDFShubhankar SinhaNo ratings yet
- Full Book 1st Year MathDocument2 pagesFull Book 1st Year MathkamranNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper-1: in This Section, Attempt Any 16 Questions (From 01 - 20)Document6 pagesPractice Paper-1: in This Section, Attempt Any 16 Questions (From 01 - 20)Shivangi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 02571792c9ae4-DPT Inverse Trigonometry 16.12.2020Document2 pages02571792c9ae4-DPT Inverse Trigonometry 16.12.2020HeartbeatssNo ratings yet
- 125 Class TestDocument2 pages125 Class Testjaiswal23456No ratings yet
- Practice Paper-3: in This Section, Attempt Any 16 Questions (From 01 - 20)Document6 pagesPractice Paper-3: in This Section, Attempt Any 16 Questions (From 01 - 20)Shivangi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 12th Maths Preboard-1 2021Document7 pages12th Maths Preboard-1 2021Little GardenNo ratings yet
- 026795351f95d-Inverse Trigonometry DPT - 01 (11.05.22)Document2 pages026795351f95d-Inverse Trigonometry DPT - 01 (11.05.22)Farhan SalimNo ratings yet
- MCQ Uestion On PolynomialsDocument5 pagesMCQ Uestion On PolynomialsMosisa SufaNo ratings yet
- Complex Number Exercise Book PDFDocument26 pagesComplex Number Exercise Book PDFRitik KumarNo ratings yet
- Maths XII Q 3-08-2021Document5 pagesMaths XII Q 3-08-2021Ashwani JhaNo ratings yet
- Paper: Iit-Jam 2012: X X X y N NDocument5 pagesPaper: Iit-Jam 2012: X X X y N NMr MNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper 1: Section ADocument5 pagesSample Question Paper 1: Section Agunjan bhalikaNo ratings yet
- Test On CalculusDocument10 pagesTest On CalculusKarthik NNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Imb2Document6 pagesSample Paper Imb2Aryan VermaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: MathematicsDocument12 pagesSample Paper: MathematicsSABARI SRINIVAS ANo ratings yet
- Determinant NewDocument14 pagesDeterminant NewAbhinav PipalNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trignometric Function Paper-1Document4 pagesInverse Trignometric Function Paper-1jagannivasNo ratings yet
- MathDocument50 pagesMathYOGESHWAR SINGH YADAVNo ratings yet
- 025dd369008c4-Determinants DPT - 02 (14.07.2021)Document2 pages025dd369008c4-Determinants DPT - 02 (14.07.2021)MD REHANNo ratings yet
- Definite Integration AssignmentDocument9 pagesDefinite Integration AssignmentJayNsteinNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 of 20 MCQ PDFDocument3 pagesUNIT 2 of 20 MCQ PDFpraveen kumarNo ratings yet
- XII-PTS-26 (2023-24) - by O.P. GUPTADocument7 pagesXII-PTS-26 (2023-24) - by O.P. GUPTAronitsuniyaNo ratings yet
- Xii - Maths QP - Kum Campus TestDocument3 pagesXii - Maths QP - Kum Campus TestraghuNo ratings yet
- 024eec5a83031-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 08 (07.04.2020)Document8 pages024eec5a83031-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 08 (07.04.2020)Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- Class-XII-Maths-QP-KV NERISTDocument6 pagesClass-XII-Maths-QP-KV NERISTBot1234No ratings yet
- Revision Test - 02Document7 pagesRevision Test - 02Ankit RoyNo ratings yet
- 024e500ce0750-NIT New Test Series NT - 02Document7 pages024e500ce0750-NIT New Test Series NT - 02Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- Maths 12Document7 pagesMaths 12Prince bhadaniaNo ratings yet
- St. Paul Education Centre: Code: Wqp-Mm-1 Mathematics Model - SADocument7 pagesSt. Paul Education Centre: Code: Wqp-Mm-1 Mathematics Model - SAsudevs_unniNo ratings yet
- Annual Exam 11th Math PrestigeDocument4 pagesAnnual Exam 11th Math PrestigeVarun PatilNo ratings yet
- O.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnerDocument6 pagesO.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnersusenthilNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII MCQ TEST (CH 2-8) 2019-20-1Document4 pagesCLASS XII MCQ TEST (CH 2-8) 2019-20-1JIVANSHU SHARMANo ratings yet
- 12 Math Eng PP 2023 24 1Document7 pages12 Math Eng PP 2023 24 1narangdiya602No ratings yet
- XI Maths RevisionDocument37 pagesXI Maths Revisionbansaljayash740No ratings yet
- 024e6042fa437-CBT - 04Document3 pages024e6042fa437-CBT - 04Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- M14 - Indefinite IntegrationDocument24 pagesM14 - Indefinite IntegrationBhawna SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1st Assignment-Inequalities With Answer KeyDocument2 pages1st Assignment-Inequalities With Answer KeyPrince DhananiNo ratings yet
- DPT - Determinants - 02 - Updated Answer Key - 21482656Document2 pagesDPT - Determinants - 02 - Updated Answer Key - 21482656dicen506No ratings yet
- Xii - Maths - All Examples QP - Kum Campus TestDocument3 pagesXii - Maths - All Examples QP - Kum Campus TestraghuNo ratings yet
- 12th Maths Preboard-1 2021Document7 pages12th Maths Preboard-1 2021dev sharmaNo ratings yet
- Nit New Test Series NT-04Document7 pagesNit New Test Series NT-04Mohommad ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Ruby Park, Kolkata: UNIT TEST - II (2021-22) Class - Xii Subject - MathematicsDocument2 pagesDelhi Public School Ruby Park, Kolkata: UNIT TEST - II (2021-22) Class - Xii Subject - MathematicsAryan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Limits Quiz-1: Single Correct Type 1Document2 pagesMathematics Limits Quiz-1: Single Correct Type 1sikkaNo ratings yet
- Limits, Continuity & Derivative Exercise + ANS KEYDocument24 pagesLimits, Continuity & Derivative Exercise + ANS KEYAshwani ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Xii Main Full Test-1 PCM 02.01.2023Document17 pagesXii Main Full Test-1 PCM 02.01.2023MeetNo ratings yet
- Revision Test-Mock-1 - XIIDocument7 pagesRevision Test-Mock-1 - XIIdev sharmaNo ratings yet
- 024e500c71824-BHU MOCK - 01Document10 pages024e500c71824-BHU MOCK - 01Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Function: Subject: Mathematics DATE: 18-03-2024Document2 pagesInverse Trigonometric Function: Subject: Mathematics DATE: 18-03-2024abhayalways1rajpootNo ratings yet
- Nda 2Document22 pagesNda 2Gurpartap SinghNo ratings yet
- O.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnerDocument6 pagesO.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnersusenthilNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Pondicherry University: Provisional Overall Merit List (Based On Cuet Score)Document82 pagesPondicherry University: Provisional Overall Merit List (Based On Cuet Score)rahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Pondicherry University: Provisional Overall Merit List (Based On Cuet Score)Document31 pagesPondicherry University: Provisional Overall Merit List (Based On Cuet Score)rahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Seq & SeriesDocument9 pagesSeq & Seriesrahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Mca Mhcutoff 2021 22Document98 pagesMca Mhcutoff 2021 22rahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Maintenant Part - Recc. ListDocument4 pagesMaintenant Part - Recc. ListNguyen TrungNo ratings yet
- Progress in Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 139, 229-245, 2013Document17 pagesProgress in Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 139, 229-245, 2013Vivek KushwahNo ratings yet
- 5 - Friction Ex. Module-1Document16 pages5 - Friction Ex. Module-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18-Fundamentals of Metal FormingDocument33 pagesChapter 18-Fundamentals of Metal FormingMuhammad Qasim QureshiNo ratings yet
- Bin Tariq Pipes Intro 2013Document61 pagesBin Tariq Pipes Intro 2013Munir Ahmed MusianiNo ratings yet
- 03/10 - Rock Excavation Handbook / Rock ExcavationDocument39 pages03/10 - Rock Excavation Handbook / Rock ExcavationHakan_KURUNo ratings yet
- Mechanical BeltsDocument9 pagesMechanical BeltstorresgiovanniNo ratings yet
- Panel Operator About MeDocument2 pagesPanel Operator About MeMunirul ChaqimNo ratings yet
- VISCOELASTICITY Power Point PresentationDocument26 pagesVISCOELASTICITY Power Point PresentationNathaly CuasialpudNo ratings yet
- Pvsyst Trial Pvsyst Trial Pvsyst Trial Pvsyst TrialDocument11 pagesPvsyst Trial Pvsyst Trial Pvsyst Trial Pvsyst TrialGheorghe SilviuNo ratings yet
- SputteringDocument17 pagesSputteringTonmoy PaulNo ratings yet
- Government College of Engineering, Amravati: Industrial Visit Report On 220 KV Substation Power House, AmravatiDocument20 pagesGovernment College of Engineering, Amravati: Industrial Visit Report On 220 KV Substation Power House, AmravatiShourya Prasad100% (1)
- Principles of Electricity PDFDocument371 pagesPrinciples of Electricity PDFJohn C. Stephens100% (5)
- Vdocuments - MX - Internship Report TNB Distribution SelangorDocument87 pagesVdocuments - MX - Internship Report TNB Distribution Selangormuhd faizNo ratings yet
- 1920SEM1 ExamDocument9 pages1920SEM1 ExamBenedict ChinNo ratings yet
- Designing and Managing Drilling Fluid: Plano, Texas, USADocument22 pagesDesigning and Managing Drilling Fluid: Plano, Texas, USAAl-Shargabi MohaNo ratings yet
- 3.2.3 Notes Thin Converging Lens P4 TeacherDocument10 pages3.2.3 Notes Thin Converging Lens P4 TeacherYokeLing ChangNo ratings yet
- PDC TR-06-02 Rev 1 SBEDS Users Guide DistribADocument95 pagesPDC TR-06-02 Rev 1 SBEDS Users Guide DistribAmirko huaranccaNo ratings yet
- Ibong Tiririt (MDSP 3) : MM 25 M 025 - 0 400 10 N V L 25 Tan D L TanDocument31 pagesIbong Tiririt (MDSP 3) : MM 25 M 025 - 0 400 10 N V L 25 Tan D L TanSYBRELLE CRUZNo ratings yet
- Datasheet LFU119XDocument2 pagesDatasheet LFU119XMohammed Tausif AhmedNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Void Growth and Fiber Volume Fraction Based On Filament Winding Process MechanicsDocument10 pagesPrediction of Void Growth and Fiber Volume Fraction Based On Filament Winding Process MechanicsHassan HabibNo ratings yet
- Compact Design of Planar Stepped Micro Combustor For PortableDocument11 pagesCompact Design of Planar Stepped Micro Combustor For PortableHERDI SUTANTONo ratings yet
- 2022 - Bazli - Long-Span Timber Flooring SystemsDocument17 pages2022 - Bazli - Long-Span Timber Flooring SystemsThomas ManderNo ratings yet
- Solenoid Valve Namur Fig 33580 AluminiumDocument1 pageSolenoid Valve Namur Fig 33580 AluminiumNam Nguyễn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Project On Reinforced Concrete Design (Cotm 447)Document5 pagesProject On Reinforced Concrete Design (Cotm 447)Zoom LionNo ratings yet
- Datasheet b393g Impactpp eDocument2 pagesDatasheet b393g Impactpp eEmre UzunogluNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Paper-IDocument13 pagesElectrical Engineering Paper-Ikpv294No ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering Lab and HeatDocument87 pagesThermal Engineering Lab and Heatsaadzamel67No ratings yet
- Acoustic LevitatorDocument62 pagesAcoustic LevitatorJulianSalazarNo ratings yet