Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ohms Law NEW
Ohms Law NEW
Uploaded by
Krish JainOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ohms Law NEW
Ohms Law NEW
Uploaded by
Krish JainCopyright:
Available Formats
Date:
Experiment Number:
Aim: To determine resistivity of two / three wires by plotting a
graph for potential difference versus current.
Apparatus Required: Battery eliminator, Ammeter, Voltmeter,
Resistance wire, Rheostat, One way key, Connecting wires.
Theory: According to Ohm’s law “The current flowing through a
conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference
across its ends provided the physical conditions like
temperature, dimensions etc. remain constant.”
V = IR
V
Or R=
I
Where R is resistance of given wire
V is potential difference across given wire
I is current flowing through given wire
Specific resistance can be calculated using
𝑹𝑨
ρ=
L
𝑹𝜋𝑑2
or ρ=
4L
where 𝜌 is specific resistance
d is diameter of cross section of given resistance wire
L is length of given resistance wire.
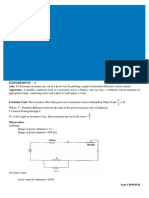
Diagram:
Observations:
Range of ammeter = 0A to 3A
Least count of ammeter = 0.05A
Range of voltmeter = 0V to 3V
Least count of voltmeter = 0.05V
Length of resistance wire 1 (l1) = 50 cm = 0.5 m
Diameter of resistance wire 1 (d1) = 0.5 mm = 5 𝑋 10−4 m
Length of resistance wire 2 (l2) = 40 cm = 0.4 m
Diameter of resistance wire 2 (d2) = 0.5 mm = 5 𝑋 10−4 m
Observation Table:
Sr.No. Voltmeter Reading Ammeter Reading
V I
volts amperes
Wire 1 Wire 2 Wire 1 Wire 2
1. 0 X 0.05 = 0 0 X 0.05 = 0 0 X 0.05 = 0 0 X 0.05 = 0
2. 4 X 0.05 = 0.2 5 X 0.05 = 0.25 3 X 0.05 = 0.15 6 X 0.05 = 0.3
3. 8 X 0.05 = 0.4 10 X 0.05 = 0.5 7 X 0.05 = 0.35 12 X 0.05 = 0.6
4. 12 X 0.05 = 0.6 15 X 0.05 = 0.75 9 X 0.05 = 0.45 17 X 0.05 = 0.85
5. 16 X 0.05 = 0.8 20 X 0.05 = 1 11 X 0.05 = 0.55 23 X 0.05 = 1.15
6. 20 X 0.05 = 1 25 X 0.05 = 1.25 16 X 0.05 = 0.8 30 X 0.05 = 1.5
7. 24 X 0.05 = 1.2 30 X 0.05 = 1.5 18 X 0.05 = 0.9 37 X 0.05 = 1.85
Graph:
V-I Graph
Calculations
From V-I graph
For wire 1 For wire 2
𝐴𝐵 𝑃𝑄
R1 = R2 =
𝐵𝐶 𝑄𝑅
1.2−0.6 1.25−0.5
R1 = R2 =
0.9−0.45 1.5−0.6
0.6 0.75
R1 = R2 =
0.45 0.9
R1 = 1.34 Ω R2 = 0.84 Ω
For Wire 1 For Wire 1
R𝜋𝑑 2 R𝜋𝑑 2
ρ= ρ=
4L 4L
1.34 X 3.14 𝑋 5 𝑋 10−4 𝑋 5 𝑋 10−4 0.84 X 3.14 𝑋 5 𝑋 10−4 𝑋 5 𝑋 10−4
ρ= ρ=
4 X 0.5 4 X 0.4
105.19 𝑋 10−8 65.94 𝑋 10−8
ρ= ρ=
2 1.6
−8 −8
ρ = 52.595 𝑋 10 Ωm ρ = 41.2125 𝑋 10 Ωm
Result:
I. Resistance from V-I graph
For given wire 1 = 1.34 Ω
For given wire 2 = 0.84 Ω
II. Specific resistance
−8
For given wire 1 = 52.595 𝑋 10 Ωm
−8
For given wire 2 = 41.2125 𝑋 10 Ωm
Sources of errors:
1. Screws of the instruments may be loose.
2. There may be parallax error while taking reading from
instruments.
3. Instruments may have internal faults.
Precautions:
1. All connections must be tight.
2. Voltmeter must be connected in parallel.
3. Ammeter must be connected in series.
You might also like
- Change On The Rise: Transcribed by David LiuDocument7 pagesChange On The Rise: Transcribed by David Liuveromejhdo57% (7)
- Physics Practical Class 12Document14 pagesPhysics Practical Class 12Sahil Midha67% (3)
- 2.basic Electrical Engineering Lecture Part 2Document22 pages2.basic Electrical Engineering Lecture Part 2Cedric Zamora100% (1)
- Resistive Circuit PracticeDocument11 pagesResistive Circuit PracticeBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Metatonin & Pineal GlandDocument107 pagesMetatonin & Pineal GlandSoman100% (2)
- Physics Practical File 2021-22Document17 pagesPhysics Practical File 2021-22Raushan KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Experiment FileDocument36 pagesPhysics Experiment Fileriyanshis892No ratings yet
- Physics Practical FileDocument31 pagesPhysics Practical FileAyushNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics Experiment 1Document5 pagesXii Physics Experiment 1Solomon Peter SunilNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics Experiment 1Document5 pagesXii Physics Experiment 1Solomon Peter SunilNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSREPORT4Document5 pagesPHYSICSREPORT4Daud Bin NasarNo ratings yet
- AIM: To Determine Resistance Per CM of A Given Wire by Plotting A Graph of Potential Apparatus RequiredDocument6 pagesAIM: To Determine Resistance Per CM of A Given Wire by Plotting A Graph of Potential Apparatus RequiredMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- Ramos Exp02Document3 pagesRamos Exp02Khen RamosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Basic Electric CircuitsDocument9 pagesLesson 4 Basic Electric Circuits1 Vallanta, Jonathan Jr. P.No ratings yet
- Physics Lab Manual For ClassXII (2024-2025) Madhavi 24.4.24Document40 pagesPhysics Lab Manual For ClassXII (2024-2025) Madhavi 24.4.24krishnaa8001sasiNo ratings yet
- Calculating Equivalent Resistence When 2 Resistors Are Connected in Series and Parellel ConnectionDocument22 pagesCalculating Equivalent Resistence When 2 Resistors Are Connected in Series and Parellel ConnectionSajjan KamalNo ratings yet
- CBSE XII Chemistry Project Variation of Conductance With Temperature in ElectrolytesDocument19 pagesCBSE XII Chemistry Project Variation of Conductance With Temperature in ElectrolytesSubhash MittalNo ratings yet
- Electrical LabDocument17 pagesElectrical LabBlack HeartNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Work XII 2023-24 - 240114 - 203222Document25 pagesPhysics Lab Work XII 2023-24 - 240114 - 203222ريحان بن إكرامNo ratings yet
- LP - Akomah Seth8GMATH NYU-POLY LESSON B1Document9 pagesLP - Akomah Seth8GMATH NYU-POLY LESSON B1Jay SeaNo ratings yet
- Resistors in CircuitsDocument10 pagesResistors in CircuitsKcirex GarinNo ratings yet
- ResistivityDocument6 pagesResistivity15598330809No ratings yet
- Velammal Vidhyashram Chem ProjectDocument14 pagesVelammal Vidhyashram Chem ProjectOpenArtifact339No ratings yet
- Physics Lab ExperimentsDocument13 pagesPhysics Lab ExperimentsNO WORRY-copyright free music libraryNo ratings yet
- Laboratorio Sistemas ElectricosDocument12 pagesLaboratorio Sistemas ElectricosLaura Tatiana Rojas RozoNo ratings yet
- Exp Section-ADocument10 pagesExp Section-ABilal MalikNo ratings yet
- Exp - 1 - Ohm's Law ExperimentDocument5 pagesExp - 1 - Ohm's Law Experimentmfassociates188No ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Electric CircuitsDocument96 pagesChapter 2-Electric Circuitsn nudgeNo ratings yet
- Electricity Circuits)Document33 pagesElectricity Circuits)Princess de VeraNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project-1Document11 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project-1kavinvishnu3No ratings yet
- Physics Practical PDF - 12hhhDocument54 pagesPhysics Practical PDF - 12hhhmyjadavfamilyNo ratings yet
- Apply Electrical CircuitsDocument22 pagesApply Electrical Circuitsn asniNo ratings yet
- Practical Notes-Mock ExamDocument8 pagesPractical Notes-Mock ExamannalisaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Basic LawsDocument5 pagesTopic 2 - Basic LawsUmakandan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Laboratory Experiment 1 Determination of Inductance in An LR CircuitDocument10 pagesElectromagnetism Laboratory Experiment 1 Determination of Inductance in An LR CircuitAryan yadavNo ratings yet
- Circuits II Practice No. 1: Nodal Analysis, Mesh Analysis and Superposition TheoremsDocument12 pagesCircuits II Practice No. 1: Nodal Analysis, Mesh Analysis and Superposition TheoremsJorge vasquezNo ratings yet
- Physics Icse Projects PDFDocument3 pagesPhysics Icse Projects PDFSourajit DasguptaNo ratings yet
- EE21L Experiment 4Document11 pagesEE21L Experiment 4asnajhjas asashladaNo ratings yet
- EE21L Experiment 8Document12 pagesEE21L Experiment 8Jian TumaliNo ratings yet
- Phys 1 TV LectDocument3 pagesPhys 1 TV LectEerah Jane EspinarNo ratings yet
- Practical Record Book - 24-25Document28 pagesPractical Record Book - 24-25pushkar.aashritNo ratings yet
- 0hms LawDocument34 pages0hms LawJaslinn FayeNo ratings yet
- Experiment On: Measurement of DC Currents, Voltage, Resistances and Study of Resistance Colour CodeDocument8 pagesExperiment On: Measurement of DC Currents, Voltage, Resistances and Study of Resistance Colour CodeHenok BelaynehNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Aim: To Verify Ohm's Law Using The Voltmeter-Ammeter of Measuring ElectricalDocument3 pagesOhm's Law: Aim: To Verify Ohm's Law Using The Voltmeter-Ammeter of Measuring ElectricalKefentse HincksonNo ratings yet
- Physics 12th Practicals File 2022-23Document12 pagesPhysics 12th Practicals File 2022-23Harsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Series Parallel CircuitsDocument26 pagesModule 6 Series Parallel CircuitsGanancias, Angel Kate R.No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ElectronicsDocument68 pagesFundamentals of ElectronicsbrightieNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics - Practical - 2021 - 22 Term 1 Term 2Document12 pages12th Physics - Practical - 2021 - 22 Term 1 Term 2NAYAN DARYANINo ratings yet
- (Class Xii Physics Practicals) : Physics Practical Term-1 Experiment - 1Document17 pages(Class Xii Physics Practicals) : Physics Practical Term-1 Experiment - 1Aksar AlamNo ratings yet
- GRADE 12 PRACTICALS 2024-25Document48 pagesGRADE 12 PRACTICALS 2024-25qhubaib789No ratings yet
- DC CircuitsDocument34 pagesDC CircuitsPeach BubbleNo ratings yet
- EE-Lab-2 (0124)Document6 pagesEE-Lab-2 (0124)ali burhan tahirNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Part 2Document10 pagesExperiment 5 Part 2Jakob Dylan0717No ratings yet
- Expt 2 Ohms Law PagayonanDocument6 pagesExpt 2 Ohms Law PagayonanAlienrayNo ratings yet
- Investigation Task Physics 2019Document5 pagesInvestigation Task Physics 2019Agent DNo ratings yet
- 11zon - Prac 10 - Current - 2023Document3 pages11zon - Prac 10 - Current - 2023soumyadiptalukdar311No ratings yet
- Practicals and activities-XII 2023-24Document24 pagesPracticals and activities-XII 2023-24krishnapradhani091No ratings yet
- MQ OMjia 19 Zo 0634 QTMPGDocument28 pagesMQ OMjia 19 Zo 0634 QTMPGROYAL JAATNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument52 pagesElectric CircuitsTejesh Shami100% (1)
- Fow Seng Joe (B1757) - Lab 2 IEEDocument12 pagesFow Seng Joe (B1757) - Lab 2 IEERobert Fow JOENo ratings yet
- Phys2 Week9 Ohm's LawDocument5 pagesPhys2 Week9 Ohm's LawSahirNo ratings yet
- Front Page BasketballDocument1 pageFront Page BasketballKrish JainNo ratings yet
- Project (P.ed.)Document4 pagesProject (P.ed.)Krish JainNo ratings yet
- Series MBDocument3 pagesSeries MBKrish JainNo ratings yet
- Faulty Circuit ActivityDocument2 pagesFaulty Circuit ActivityKrish JainNo ratings yet
- Half DeflectionDocument4 pagesHalf DeflectionKrish JainNo ratings yet
- Assembling Components ActivityDocument2 pagesAssembling Components ActivityKrish JainNo ratings yet
- Metre Bridge ResistanceDocument2 pagesMetre Bridge ResistanceKrish Jain100% (8)
- Household Circuit ActivityDocument2 pagesHousehold Circuit ActivityKrish JainNo ratings yet
- Fourth Quarter Exam in TLE Grade SevenDocument5 pagesFourth Quarter Exam in TLE Grade SevenShabby Gay Trogani83% (12)
- Covellite PDFDocument1 pageCovellite PDFRyoga RizkyNo ratings yet
- WoPhO 2012 Q9Document5 pagesWoPhO 2012 Q9Mohammed AlsawafiNo ratings yet
- Optoma DS325 DLP ProjectorDocument6 pagesOptoma DS325 DLP ProjectorWebAntics.com Online Shopping StoreNo ratings yet
- EW74Ëó+ Á+ ÚDocument9 pagesEW74Ëó+ Á+ Úundibal rivasNo ratings yet
- ControlDocument58 pagesControlRobinson CardenasNo ratings yet
- Uasin Gishu - 2Document77 pagesUasin Gishu - 2peeteoNo ratings yet
- Transformer MaintenanceDocument22 pagesTransformer MaintenanceAugustine Owo UkpongNo ratings yet
- GCSE-Biology-7-Summer2019-Foundation Tier, Unit 1-PaperDocument24 pagesGCSE-Biology-7-Summer2019-Foundation Tier, Unit 1-PaperjramatlhakolaneNo ratings yet
- Circuito Integrado BA05STDocument10 pagesCircuito Integrado BA05STEstefano EspinozaNo ratings yet
- ENGG 10 PreCalculus For EngineersDocument11 pagesENGG 10 PreCalculus For EngineersMariel Erica RootNo ratings yet
- Dissertation - Balancing Heritage and Contemporary ArchitectureDocument62 pagesDissertation - Balancing Heritage and Contemporary Architecturekavyagupta92100% (7)
- Electric Vehicles Case StudyDocument2 pagesElectric Vehicles Case StudyVaibhav RaulkarNo ratings yet
- DIAGRAMA - 2007 - NEW YarisDocument1 pageDIAGRAMA - 2007 - NEW YarisLuis M. Valenzuela Arias50% (2)
- Service Manual: No. SEB-83ACEDocument129 pagesService Manual: No. SEB-83ACEThein Htoon lwin100% (3)
- RFIDDocument18 pagesRFIDKulavardan ThalapulaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemMary Joyce RamosNo ratings yet
- CROSS REFERENCE DE VALVULAS SOLENOIDES - Danfoss - Alco - Sporlan-ParkerDocument4 pagesCROSS REFERENCE DE VALVULAS SOLENOIDES - Danfoss - Alco - Sporlan-ParkerJoss CastellNo ratings yet
- End-Of-Year Test: ListeningDocument3 pagesEnd-Of-Year Test: ListeningRox Purdea0% (1)
- Academic Reading TestDocument14 pagesAcademic Reading Testjade kamboj0% (1)
- English FinalDocument71 pagesEnglish FinalKhadeeja MarjanNo ratings yet
- Full Download Strategies For Teaching Learners With Special Needs 11th Edition Polloway Test BankDocument36 pagesFull Download Strategies For Teaching Learners With Special Needs 11th Edition Polloway Test Banklevidelpnrr100% (31)
- Artikel Review BiodegradasiDocument6 pagesArtikel Review BiodegradasiEka Ayu NingtyasNo ratings yet
- Metasploit FrameworkDocument1 pageMetasploit FrameworkPAUL VINCENT FAJARDONo ratings yet
- Nabcep AppendixesDocument32 pagesNabcep AppendixeshockpinNo ratings yet
- Up ListDocument200 pagesUp Listprashant guptaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Past PaperDocument36 pagesIgcse Past PaperfaiyazNo ratings yet
- M20 LatticeDocument30 pagesM20 LatticeKerwin Cley UgaleNo ratings yet