Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math Summary
Math Summary
Uploaded by
YAGOUB MUSA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views7 pagesThe document summarizes key concepts from geometry and algebra. In geometry, it outlines the polygon angle-sum theorem, properties of kites, trapezoids and parallelograms, and ways to prove a quadrilateral is a parallelogram. In algebra, it covers exponential growth and decay, compound interest, geometric sequences, and transformations of exponential functions through vertical and horizontal translation.
Original Description:
Geometry and Algebra.
Savvas pearson
Original Title
MATH SUMMARY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key concepts from geometry and algebra. In geometry, it outlines the polygon angle-sum theorem, properties of kites, trapezoids and parallelograms, and ways to prove a quadrilateral is a parallelogram. In algebra, it covers exponential growth and decay, compound interest, geometric sequences, and transformations of exponential functions through vertical and horizontal translation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views7 pagesMath Summary
Math Summary
Uploaded by
YAGOUB MUSAThe document summarizes key concepts from geometry and algebra. In geometry, it outlines the polygon angle-sum theorem, properties of kites, trapezoids and parallelograms, and ways to prove a quadrilateral is a parallelogram. In algebra, it covers exponential growth and decay, compound interest, geometric sequences, and transformations of exponential functions through vertical and horizontal translation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
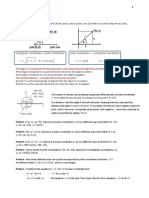
GEOMETRY SUMMARY
L. 6-1: The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem
The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a convex
n-gon is 180 x ( n-2 ).
180 x ( n-2 )
_________
The measure of an interior angle of a regular n-gon is _________
n
The sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a _
convex polygon, one at each vertex, is 360.
L. 6-2: Kites and Trapezoids
The diagonals of a kite are perpendicular.
In an isosceles trapezoid, each pair of bases angles are
congruent.
The diagonals of an isosceles trapezoid are congruent.
The midsegment of a trapezoid is parallel to the bases, and
it’s length is the sum of the bases.
XY ll AD , XY ll BC. XY = ½ (AD + BC).
L. 6-3 : Properties of Parallelograms
If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram , then it’s opposite sides
are congruent.
If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then it’s consecutive
angles are supplementary.
If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then opposite angles are
congruent.
If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, the it’s diagonals are
bisectors.
L. 6-4 : Proving a Quadrilateral is a Parallelogram
If both pairs of opposite sides of a quadrilateral are
congruent, then the quadrilateral is a parallelogram.
If an angle of quadrilateral is supplementary to both of it’s
consecutive angles, then the it’s a parallelogram.
If both pairs of opposite angles of quadrilateral are
congruent, then the quadrilateral is a parallelogram.
If the diagonals of a quadrilateral are bisectors, then the
quadrilateral is a parallelogram.
If one pair of opposite sides of a quadrilateral is both
congruent and parallel, then the quadrilateral is a
parallelogram.
ALGEBRA SUMMARY
L. 6-3: Exponential Growth and Decay
Exponential growth: f(x)= a ( 1+r ) [to the power of x]
a = initial amount , r = growth rate , x = time in years ,
1+r = growth factor
Exponential decay: f(x)= a ( 1-r ) [to the power of x]
a = initial amount , r = decay rate , x = time in years ,
1-r = decay factor
r
Compound Interest: f(x)= a (1+ ____ ) [ to the power of n
n
____
times t] __
a = initial amount , p = principal amount , r = interest rate , n =
number of times per year [ annually n:1 , semiannually n:2 ,
quarterly n:4 , monthly n:12 ] , t = time in years
L. 6-4: Geometric Sequence
Recursive formula: An= r ( An-1 ) , A1: ? [you have to include
the first value]
n: nth term , r: common ratio , An-1: previous term
Explicit formula: An= A1(r) [to the power of n-1]
n: nth term , A1: first term , r: common ratio
L.6-5: Transformation of Exponential Functions
Vertical Translation: f(x)= a [ to the power of x] + k
Ex. F(x)= 0.5[to the power of x]
g(x)= 0.5[to the power of x] + 2
g(x) is translated 2 units up
Horizontal Translation: f(x)= a [ to the power of x + k]
F(x)= 0.5[to the power of x]
g(x)= 0.5[to the power of x + 2]
g(x) is translated 2 units left
You might also like
- Maths Formula Sheet of Icse StudentsDocument13 pagesMaths Formula Sheet of Icse Studentsvidhiseth89% (109)
- Heriot-Watt University Dubai Campus: ReceiptDocument2 pagesHeriot-Watt University Dubai Campus: ReceiptMuhammadnasidiNo ratings yet
- Lect 2 Coordinate SystemsDocument57 pagesLect 2 Coordinate SystemsBarış DuranNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi Thorax FotoDocument38 pagesInterpretasi Thorax FotoSinta SintaaNo ratings yet
- Binomial TheoremDocument14 pagesBinomial TheoremSahaj SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Linear Correlation CoefficientDocument3 pagesLinear Correlation CoefficientyoyoyoNo ratings yet
- Linear Correlation CoefficientDocument3 pagesLinear Correlation CoefficientyoyoyoNo ratings yet
- Finding Number of Digits in A Number: Solution 1Document24 pagesFinding Number of Digits in A Number: Solution 1Deepak ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- DM20Document18 pagesDM20YashwanthNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic and Geometric Progressions APGP SummaryDocument4 pagesArithmetic and Geometric Progressions APGP SummaryFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- INT5Document14 pagesINT5bamunobaNo ratings yet
- Series Parallel Duality in The MathematiDocument14 pagesSeries Parallel Duality in The MathematiAristoclesNo ratings yet
- Mensuration PDFDocument33 pagesMensuration PDFSudhanshu Kumar100% (1)
- ED536913Document16 pagesED536913shirleyyy.idoloNo ratings yet
- Great Math Formula With ExamplesDocument37 pagesGreat Math Formula With Examplessandesh negi100% (1)
- 2 Maths Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument2 pages2 Maths Multiple Choice Questionsmohamedeyssa88No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Mathematics Guide QuestionsDocument18 pagesGrade 10 Mathematics Guide QuestionsDEUCE ZANYNo ratings yet
- Mathematics4024-22 (Mayjun2019-Octnov2022) 07mar2023++looseformDocument200 pagesMathematics4024-22 (Mayjun2019-Octnov2022) 07mar2023++looseformAHMADNo ratings yet
- Article On GP Using LatexDocument3 pagesArticle On GP Using LatexPreyanshMitharwalNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic and Geometric Progressions APGP SummaryDocument4 pagesArithmetic and Geometric Progressions APGP SummaryGyoWool EunNo ratings yet
- ملزمة خامس علميDocument40 pagesملزمة خامس علميBetool AlghalbiNo ratings yet
- Unit 11: Complex Numbers Chapter 12.1, 12.2, 12.3, 12.4, 12.5, 12.6Document10 pagesUnit 11: Complex Numbers Chapter 12.1, 12.2, 12.3, 12.4, 12.5, 12.6Rob GchukNo ratings yet
- 2021 PH101 Lecture03Document17 pages2021 PH101 Lecture03Vivek ParleyNo ratings yet
- Maths Formulas AllDocument22 pagesMaths Formulas Alladitya chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics4024-12 (Mayjun2019-Octnov2022) 07mar2023++looseformDocument186 pagesMathematics4024-12 (Mayjun2019-Octnov2022) 07mar2023++looseformAHMADNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Systems: ContinueDocument18 pagesCoordinate Systems: ContinueVaijantiNo ratings yet
- Schoolisfun's Math Level 2 Subject Test Guide and FormulasDocument40 pagesSchoolisfun's Math Level 2 Subject Test Guide and Formulassudhakaralla1100% (2)
- 7 Measure of RelationshipDocument6 pages7 Measure of RelationshipRonald LanotNo ratings yet
- Vector Addition LabDocument16 pagesVector Addition LabJasdeepSinghNo ratings yet
- SNSDocument4 pagesSNShchawla421No ratings yet
- SequenceDocument4 pagesSequenceJak RichardNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series: (Barisan Dan Deret)Document3 pagesSequences and Series: (Barisan Dan Deret)Sharon RivaniNo ratings yet
- B0BDJKB3M5Document37 pagesB0BDJKB3M5thabris73No ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument78 pagesMathematicsJohneil Perea Asi100% (2)
- Formulas of 2015Document17 pagesFormulas of 2015kris_gn54No ratings yet
- Correlation Analysis and Its TypesDocument50 pagesCorrelation Analysis and Its TypesAnshika MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- G10 - Key Points Formulae 2023Document10 pagesG10 - Key Points Formulae 2023hersheys boiNo ratings yet
- 01 Plane and Solid GeometryDocument3 pages01 Plane and Solid GeometryJohn Randel SanchezNo ratings yet
- Weatherwax Contest Problem BooksDocument329 pagesWeatherwax Contest Problem BooksMkanNo ratings yet
- G10 - Key Points & FormulaeDocument10 pagesG10 - Key Points & FormulaePlayer dude65No ratings yet
- 141 10.1 Lecture Notes Polar CordinatesDocument4 pages141 10.1 Lecture Notes Polar CordinatesHaroon ShahNo ratings yet
- Coordinate SystemsDocument10 pagesCoordinate SystemsKazeem FataiNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Polar Coordinates and Polar Graphs PDFDocument10 pages4.2 Polar Coordinates and Polar Graphs PDFLarsen Atega AlexanderssonNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines Slides-239 PDFDocument465 pagesStraight Lines Slides-239 PDFYash Chaudhaury100% (1)
- Lecture 1 - Polygons, Triangle, QuadrilateralDocument40 pagesLecture 1 - Polygons, Triangle, QuadrilateralPaulo Bonifacio100% (1)
- Arithmetic Progression, AP: ElementsDocument6 pagesArithmetic Progression, AP: ElementsJohnray CastroNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Firstsem PrecalculusDocument9 pagesReviewer Firstsem PrecalculusChricellFNo ratings yet
- Glossary of MathsDocument52 pagesGlossary of MathsManduri Nagamalleswara Prasad100% (1)
- Short Notes and Formulae Class XII MathsDocument30 pagesShort Notes and Formulae Class XII Mathsshashankkr4831No ratings yet
- Important Math FormulasDocument5 pagesImportant Math FormulasMighty MayukhNo ratings yet
- Add Math DefaultDocument19 pagesAdd Math DefaultFatin Nadzirah YusofNo ratings yet
- IB AASL Exam Prep Lecture 1Document8 pagesIB AASL Exam Prep Lecture 1girlydoggirl23No ratings yet
- Important Points and Formulae: Mathematics Grade 9 BmiDocument6 pagesImportant Points and Formulae: Mathematics Grade 9 BmiZulfiqar Ali MirNo ratings yet
- Sequences (Part 1)Document68 pagesSequences (Part 1)tejaswini muralidharanNo ratings yet
- Precal SHS 1 - W3Document4 pagesPrecal SHS 1 - W3Chaelin CLNo ratings yet
- Buckingham's Pi-Theorem: TheoryDocument4 pagesBuckingham's Pi-Theorem: TheorymlkndnzNo ratings yet
- Polar Coordinates LESSONDocument10 pagesPolar Coordinates LESSONHawraa HawraaNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics: CBMA2103Document11 pagesDiscrete Mathematics: CBMA2103hamizonaNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Rag & Bone - Fragments: Free Content Friday - Outbreak: Undead.. September 2021Document7 pagesRag & Bone - Fragments: Free Content Friday - Outbreak: Undead.. September 2021Brian PayneNo ratings yet
- Peopleware Chapter 20Document14 pagesPeopleware Chapter 20Umar AshrafNo ratings yet
- 17Document105 pages17Ahmad TurmiziNo ratings yet
- 10 Known Issues: Tusbaudio Driver For WindowsDocument4 pages10 Known Issues: Tusbaudio Driver For WindowsWillian LimaNo ratings yet
- Arkeryd, L. Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 45, 1 (1972) - On The Boltzmann Equation - Part I - ExistenceDocument16 pagesArkeryd, L. Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 45, 1 (1972) - On The Boltzmann Equation - Part I - ExistencejahernandesNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument50 pagesDefinitionsRaajeshkrishnaNo ratings yet
- SCF 020 - Ship Shore Safety ChecklistDocument8 pagesSCF 020 - Ship Shore Safety ChecklistSutarmoNo ratings yet
- GST RegistrationDocument3 pagesGST RegistrationJabagodu SP & CoNo ratings yet
- SS 550 Amendement 1 CBCA141017Document5 pagesSS 550 Amendement 1 CBCA141017Yunos GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Laya Marxlenin - CE152P-2 - E02 - Experiment2 - Module1Document5 pagesLaya Marxlenin - CE152P-2 - E02 - Experiment2 - Module1Marxlenin LayaNo ratings yet
- Career & Technical Education Month (January 2024)Document2 pagesCareer & Technical Education Month (January 2024)The Livingston County NewsNo ratings yet
- Commodore Magazine Vol-08-N09 1987 SepDocument132 pagesCommodore Magazine Vol-08-N09 1987 SepSteven DNo ratings yet
- AsDocument602 pagesAsnareshNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument4 pagesProject ProposalQueenie Diane MontañoNo ratings yet
- Kondensasi Aldol Silang PDFDocument7 pagesKondensasi Aldol Silang PDFRiska Elya VenilitaNo ratings yet
- Holy Child College of DavaoDocument33 pagesHoly Child College of DavaoMara LabanderoNo ratings yet
- Lzizj: Comprehensive Manuals of Surgical SpecialtiesDocument288 pagesLzizj: Comprehensive Manuals of Surgical SpecialtiesBeatriz BelottiNo ratings yet
- Light Millennium Man - LM 12-04 F SesamoDocument24 pagesLight Millennium Man - LM 12-04 F SesamoFranky AlbarranNo ratings yet
- K80000 Technical Datasheet PDFDocument1 pageK80000 Technical Datasheet PDFKhalid ZghearNo ratings yet
- Diamond Kipah For JDocument3 pagesDiamond Kipah For JM MilliganNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Math High School G 7 4rth QDocument8 pagesSupplemental Math High School G 7 4rth QdapitomaryjoyNo ratings yet
- 2252-Article Text-3992-1-10-20190421Document22 pages2252-Article Text-3992-1-10-20190421Etab BarakatNo ratings yet
- Inspyrus - White PaperDocument8 pagesInspyrus - White PaperBayCreativeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/32Document12 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/32davieNo ratings yet
- IT GovernanceDocument16 pagesIT Governanceterdesak100% (2)
- English 1-2-1Document7 pagesEnglish 1-2-1Arlene Suan Paña SevensixfourzeroNo ratings yet
- NEW GEPC Lesson 2 - Interactive LectureDocument5 pagesNEW GEPC Lesson 2 - Interactive LectureHazel MaeeeNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Protection RelaysDocument10 pagesLab 2 - Protection RelaysLeo GeeNo ratings yet