Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Healtheduc 4
Healtheduc 4
Uploaded by
Mark Aparici0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesThe document discusses Bloom's Taxonomy, which classifies learning objectives into different domains and levels of complexity. It details the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains. The cognitive domain involves thinking skills and has six levels - remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. The affective domain focuses on attitudes, beliefs, and emotions. The psychomotor domain involves physical skills and movements. Bloom's Taxonomy provides a framework for designing instructional objectives that align with different learning levels.
Original Description:
Original Title
HEALTHEDUC-4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses Bloom's Taxonomy, which classifies learning objectives into different domains and levels of complexity. It details the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains. The cognitive domain involves thinking skills and has six levels - remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. The affective domain focuses on attitudes, beliefs, and emotions. The psychomotor domain involves physical skills and movements. Bloom's Taxonomy provides a framework for designing instructional objectives that align with different learning levels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesHealtheduc 4
Healtheduc 4
Uploaded by
Mark ApariciThe document discusses Bloom's Taxonomy, which classifies learning objectives into different domains and levels of complexity. It details the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains. The cognitive domain involves thinking skills and has six levels - remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. The affective domain focuses on attitudes, beliefs, and emotions. The psychomotor domain involves physical skills and movements. Bloom's Taxonomy provides a framework for designing instructional objectives that align with different learning levels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Principles & Strategies of Teaching in Medical Laboratory Science
First Semester / SY. 2022-2023 / Cycle 2 / Module 4
DOMAINS OF LEARNING
○ Analyzing
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY ○ Applying
➢ Benjamin Bloom (1956) developed a ● Lower-order Thinking Skills
classification of levels of intellectual ★ Also known as the Basic
behavior in learning. Requirements
➢ The taxonomy is a way to classify ○ Understanding
instructional activities or questions as ○ Remembering/ Knowing
they progress in difficulty.
➢ This taxonomy contained three
overlapping domains:
● Cognitive (knowledge/mental
skills) - THINKING
- Involves thoughts
● Affective
(attitude/feelings/emotions) –
FEELING
- Targets the emotional
aspect
● Psychomotor (manual/physical Create- Produce new or original work
skills)- DOING (design, assemble, construct, conjecture,
- Touching on the motor develop, formulate, author, investigate)
skills. It requires Evaluate- Justify a stand or decision
students to do actions (appraise, argue, defend, judge, select,
on what is being support, value, critique,weigh)
presented. Analyze- Draw connections among ideas
(differentiate, organize, relate, compare,
contrast, distinguish, examine,
experiment,question, test)
COGNITIVE DOMAIN
Apply- Use information in new situations
> It is concerned with intellectual activities (execute, implement, solve, use,
such as thinking, remembering, reasoning, demonstrate, interpret, operate, schedule,
and using language. sketch)
> It is anchored on the processes that we do Understand- Explain ideas or concepts (
in our brains. classify, describe, discuss, explain, identify,
> Used to exercise judgment, draw locate, recognize, report, select, translate)
inferences, arrive at conclusions, and make Remember- Recall facts and basic concepts
decisions. (define, duplicate, list, memorize, repeat,
> Involves the learning and application of state)
knowledge
> Being Dependent at First at the same time > Remembering: Retrieving, recognizing,
learning to be Independent and recalling relevant knowledge from
long‐term memory
LEVELS OF COGNITION > Understanding: Constructing meaning
from oral, written, and graphic messages
● Higher-order Thinking Skills through interpreting, exemplifying, classifying,
○ Creating summarizing, inferring, comparing, and
○ Evaluating explaining.
> Applying: Carrying out or using a AFFECTIVE DOMAIN
procedure for executing, or implementing.
> Analyzing: Breaking material into > Deals with personal issues: attitudes,
constituent parts, determining how the parts beliefs, behaviors, and emotions.
relate to one another and to an overall > Focuses on helping learners understand
structure or purpose through differentiating, what their own values are and how they have
organizing, and attributing. developed
> Evaluating: Making judgments ba
> Creating: Putting elements together to form
a coherent or functional whole; reorganizing
elements into a new pattern or structure
through generating, planning, or producing.
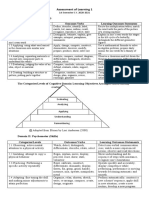
Level Description Verbs Example
Knowledge To recall or Define Define the levels of
recognize List cognitive domain
information in
some
pre-arranged
form.
Comprehens To Describe Explain the
ion understand Explain purpose of the
mening of Interpret cognitive
information
based on
prior learning.
Application To utilize Compute Write objectives for
information to Solve the levels of
complete a Use cognitive domain.
task with ● Five (5) Levels:
limited
direction.
Receiving: is being aware of or sensitive to
Analysis To classify Contrast Compare the
and relate Examine cognitive &
the existence of certain ideas, material, or
assumptions affective domains. phenomena and being willing to tolerate
or evidence.
them.
Evaluation Crique iea Appraise Judge the - Examples include: to differentiate, to
based on
specific
Judge
Justify
effectiveness of
writing objectives
accept, to listen (for), to respond to
standards using Bloom’s
and criteria taxonomy.
Responding is committed in some small
Synthesis To integrate Design Design ways to measure to the ideas, materials, or
or combine
ideas into a
Develop
Organize
write objectives
that combines 3
phenomena involved by actively responding
new product domains. to them.
or a plan.
- Examples are: to comply with, to
relative to
follow, to commend, to volunteer, to other
spend leisure time in, to acclaim priorities
Characterization Acting Act on Join the team
Valuing is willing to be perceived by others as consistently Depict in-charge of
valuing certain ideas, materials, or with the new
value; person
Exemplify warding
(specimen
phenomena. is known by collection).
the value
- Examples include: to increase
measured proficiency in, to relinquish,
to subsidize, to support, to debate.
PSYCHOMOTOR DOMAIN
Organization is to relate the value to those
already held and bring it into a harmonious > Characterized by progressive levels of
and internally consistent philosophy. behaviors from observation to mastery of a
- Examples are: to discuss, to theorize, physical skill
to formulate, to balance, to examine > Involves physical movement and the use of
motor skills
Characterization by value or value set is to
act consistently in accordance with the values
he or she has internalized.
- Examples include: to revise, to
require, to be rated high in the value,
to avoid, to resist, to manage, to
resolve.
Level Description Verbs Example
Receiving Being aware Listen Listen
of, or Notice attentively to the
attending to Tolerate orientation
something in regarding
the specimen
environment handling
Responding Showing Comply Voluntarily helps
some new Enjoy set up a
behavior as a Follow collection
result of tray/box.
experience
Valuing Showing Carry out Assist staff/
some definite Express co-intern in
involvement warding the
or morning pick Level Description Verbs Example
commitment
Perceiving Recognizing Listen > Discover
Organization Integrating a Choose Accommodate movement Observe headstand
new value Consider requests for position or movement
into one’s Prefer specimen pattern. principles.
general set of collections >Observe/ watch
values how to extract or
collect blood.
to impart learning. It helps teachers
Patterning Reproducing Imitate > Perform make decisions about the
movement Practice headstand classification of content.
position or following modeling.
pattern. >Recognize the ● It also helps teachers map content to
correct way of
collecting blood.
tasks that students need to perform.
● It serves as a guide to teachers to
Accommo Using or Adjust >Use headstand in develop higher levels of thinking
dating modifying Modify routine.
movement > Performs blood process for critical thinking or creative
position or extraction. thinking.
pattern
● It helps teachers to create class
Refining Demonstratin Improve > Perform activities based on Bloom’s Taxonomy
g efficient Master headstand with
control in pointed stand.
that work from LOTS to HOTS.
performing > Adopts personal
pattern. style of blood
extraction.
Varying Performing Design >Perform
movement Develop headstand in three
pattern in position
different > Tries to use a
ways. vecutainer instead
of syringe and
needle.
Improvising Originating Construct > Combine
novel Invent headstand with
movement or new skill
movement > Perform multiple
combinations. draw.
Composing Creating Create > Create floor
unique Invent exercise routine.
movement > Able to perform
pattern. blood extraction
from other sites of
the patient.
COGNITIVE AFFECTIVE PSYCHOMOTOR
Creating Characterizing Composing
Evaluating Organizing Improvising
Analyzing Valuing Varying
Applying Responding Refining
Understanding Receiving Accommodating
Remembering Patterning
Perceiving
EDUCATIONAL IMPLICATIONS OF
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY
● It provides a universally effective
strategy for creating all type of content
You might also like
- Answers To QuestionsDocument3 pagesAnswers To QuestionsL-yeah Traifalgar52% (21)
- DLP Format - FilipinoDocument4 pagesDLP Format - FilipinoLissa Mae MacapobreNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper FormatDocument9 pagesConcept Paper FormatMohammad Naeem79% (28)
- Detailed Lesson Plan For Concept PaperDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan For Concept PaperMaria Connie A. Arcenal100% (1)
- Program Outcomes and Learning OutcomesDocument18 pagesProgram Outcomes and Learning OutcomesApril Claire Pineda Manlangit100% (3)
- UPM BS BIO Curriculum As of JAN 28 2020Document4 pagesUPM BS BIO Curriculum As of JAN 28 2020Paula Joy AliposaNo ratings yet
- Mthltheduc - m4Document3 pagesMthltheduc - m4Michelle VargasNo ratings yet
- Ecb 2306 - 1Document22 pagesEcb 2306 - 1peterambrose009No ratings yet
- Cognitive Domain: Cooperative LearningDocument6 pagesCognitive Domain: Cooperative LearningCherry BobierNo ratings yet
- I-Plan Cot 2 GTCDocument6 pagesI-Plan Cot 2 GTCeyadcampNo ratings yet
- BloomDocument11 pagesBloomTalab_DeepakNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - TEACHING and The TEACHING PROCESSDocument88 pagesTopic 1 - TEACHING and The TEACHING PROCESSmanrhe pilanNo ratings yet
- Implementing A Curriculum in A Daily ClassroomDocument34 pagesImplementing A Curriculum in A Daily ClassroomHazel LavapizNo ratings yet
- Bloom'S Texanomy: Dr. M. Zafar IqbalDocument11 pagesBloom'S Texanomy: Dr. M. Zafar IqbalZohaibKhanNo ratings yet
- 1 Revised Blooms For UnpackingDocument37 pages1 Revised Blooms For UnpackingYvonne Alonzo De BelenNo ratings yet
- Program Outcomes & Student Learning OutcomesDocument15 pagesProgram Outcomes & Student Learning OutcomesMark Anthony DancalanNo ratings yet
- The Three Types of Learning: Bloom'S TaxonomyDocument21 pagesThe Three Types of Learning: Bloom'S TaxonomyGlennson LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Milq2 LC11Document5 pagesMilq2 LC11renzmarion.penalesNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument6 pagesBloom's TaxonomyJisiamar GeromoNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DomainDocument14 pagesCognitive DomainJemuel DalanaNo ratings yet
- DLP CS RS11-IIIb-2Document5 pagesDLP CS RS11-IIIb-2michelle mijarezNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provisions of D.O. No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, S. 2016)Document5 pagesInstructional Planning (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provisions of D.O. No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, S. 2016)Krizza Marie AtonNo ratings yet
- Blooms TaxDocument12 pagesBlooms TaxHelen CandelariaNo ratings yet
- FABM - Accounting Concepts and Principles IplanDocument9 pagesFABM - Accounting Concepts and Principles IplanBP Cabrera100% (1)
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsDocument16 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsummerbilalNo ratings yet
- Presentationcurricylum 1Document10 pagesPresentationcurricylum 1Jubelle SumilangNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Instructional ObjectivesDocument4 pagesLecture - Instructional ObjectivesAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Content 1. Cognitive ProcessesDocument14 pagesSummary of Content 1. Cognitive ProcessesCel Edi CelNo ratings yet
- The Three Types of LearningDocument5 pagesThe Three Types of LearningJonah A. RecioNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Present A Novel Concept or Project With Accompanying Visuals/graphic AidsDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Present A Novel Concept or Project With Accompanying Visuals/graphic AidsMa LouNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument8 pagesBloom's TaxonomyMarissaM.PerezNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Revised Taxonomy: Cognitive, Affective, and PsychomotorDocument4 pagesBloom's Revised Taxonomy: Cognitive, Affective, and PsychomotorsumonNo ratings yet
- Dev't ReadingDocument16 pagesDev't ReadingPee BaradasNo ratings yet
- ABM - BM11BS IIa 11Document6 pagesABM - BM11BS IIa 11Junard AsentistaNo ratings yet
- Learning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content CodeDocument9 pagesLearning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content CodeJuvyGonzalesNo ratings yet
- BLOOM For PrintingDocument17 pagesBLOOM For PrintingVincentAlejandroNo ratings yet
- Writing Instructional Objectives: January 2006Document10 pagesWriting Instructional Objectives: January 2006Wahyu HidayatNo ratings yet
- Alejandro - WRITTEN ACTIVITY NO. 3 PRINCIPLES OF TEACHINGDocument25 pagesAlejandro - WRITTEN ACTIVITY NO. 3 PRINCIPLES OF TEACHINGAngelica AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Presentation Curric y Lum 1Document10 pagesPresentation Curric y Lum 1Jubelle SumilangNo ratings yet
- PrEd 146 & 161n - Assessment in LearningDocument8 pagesPrEd 146 & 161n - Assessment in Learningshiela maeNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsDocument5 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsNuruel HassanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningArgie Corbo BrigolaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DomainDocument20 pagesCognitive DomainNadeem ShakeelNo ratings yet
- 3 Domains of LearningDocument5 pages3 Domains of LearningFeinrirNo ratings yet
- Bloomsrevisedtaxonomyofeducationalobjectives 150907103449 Lva1 App6892Document36 pagesBloomsrevisedtaxonomyofeducationalobjectives 150907103449 Lva1 App6892Mariane Joy TecsonNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Learning 1: Domain:1 Cognitive (Knowledge) Categories/Level Outcomes Verbs Learning Outcomes StatementsDocument3 pagesAssessment of Learning 1: Domain:1 Cognitive (Knowledge) Categories/Level Outcomes Verbs Learning Outcomes StatementsElpid Soleng BadongNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument3 pagesInstructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument4 pagesInstructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 12Document2 pagesLearning Task 12kenneth57% (7)
- Bloom's Taxonomy: Note That The Top Two Levels Are Essentially Exchanged From The Old To The New VersionDocument17 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: Note That The Top Two Levels Are Essentially Exchanged From The Old To The New VersionNur ZaraNo ratings yet
- Outcome Statement That Captures Specifically What Knowledge, Skills, AttitudesDocument6 pagesOutcome Statement That Captures Specifically What Knowledge, Skills, AttitudesJessel GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Revised Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesDocument36 pagesBloom's Revised Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesPax GarciaNo ratings yet
- CO Q3 RW Langauge UseDocument8 pagesCO Q3 RW Langauge UseFelisaMae Boyboy JaymeNo ratings yet
- Iplan - DLP - Format - PR1 - Identifying The Inquiry and StatingDocument5 pagesIplan - DLP - Format - PR1 - Identifying The Inquiry and Statingjenenn ann cacayanNo ratings yet
- KognisainsDocument9 pagesKognisainsnurfifahNo ratings yet
- DLP Week 1.1Document9 pagesDLP Week 1.1Shiela Castardo EjurangoNo ratings yet
- LRMDS DLP FormatDocument24 pagesLRMDS DLP FormatRochelle AdlaoNo ratings yet
- Principles of High Quality AssessmentDocument54 pagesPrinciples of High Quality AssessmentAngelito S. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy: Objectives Action Words Examples RememberingDocument7 pagesBlooms Taxonomy: Objectives Action Words Examples RememberingPaul DalumayNo ratings yet
- How To Write COs, Procedure 1 - CO PO Mapping 20-9Document26 pagesHow To Write COs, Procedure 1 - CO PO Mapping 20-9girishgandhiNo ratings yet
- Maam Hadir2,.0Document4 pagesMaam Hadir2,.0Julius Rusiana CatubigNo ratings yet
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Tools of History Part 1 3Document45 pagesTools of History Part 1 3qwertyNo ratings yet
- Kaist Graduated Admission 2019Document16 pagesKaist Graduated Admission 2019Đỗ Duy ThảoNo ratings yet
- What Is AFM - ICSPI PDFDocument10 pagesWhat Is AFM - ICSPI PDFnehaNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Penerapan Model Discovery Learning Terhadap Hasil Belajar Matematika SiswaDocument16 pagesPengaruh Penerapan Model Discovery Learning Terhadap Hasil Belajar Matematika SiswaMI MALIHATUL HIKAMNo ratings yet
- Top 7 Reasons Why Math Is So HardDocument3 pagesTop 7 Reasons Why Math Is So HardNacylene UbasNo ratings yet
- Ali Shariati - An Approach To The Understanding of Islam 2Document11 pagesAli Shariati - An Approach To The Understanding of Islam 2Scottie GreenNo ratings yet
- استدامة المدن التقليدية بين الامس والمعاصرة اليوم PDFDocument16 pagesاستدامة المدن التقليدية بين الامس والمعاصرة اليوم PDFAliaa Ahmed ShemariNo ratings yet
- CKS 2014 Education and Sociology Art.097Document10 pagesCKS 2014 Education and Sociology Art.097Ana Maria MonicaNo ratings yet
- NF148 Protocole-General-Validation enDocument47 pagesNF148 Protocole-General-Validation enPiruzi Maghlakelidze100% (1)
- Lab 10 ReportDocument4 pagesLab 10 ReportDavid Jesus MoralesNo ratings yet
- M&e NotesDocument183 pagesM&e NotesAravind SureshNo ratings yet
- The Mystery of MathematicsDocument2 pagesThe Mystery of MathematicsMC Aberca100% (2)
- Electromagnetic Waves (Report)Document22 pagesElectromagnetic Waves (Report)astria alos100% (1)
- Ajzen - Tpb.obhdp 1991Document34 pagesAjzen - Tpb.obhdp 1991Jose A OrdinolaNo ratings yet
- Postgraduate Programmes OfferedDocument1 pagePostgraduate Programmes OfferedLucie BulyabaNo ratings yet
- 10 Wild Theories About The Universe Live ScienceDocument33 pages10 Wild Theories About The Universe Live Sciencepurnata PatidarNo ratings yet
- KHDA - Dubai Modern Education School 2015 2016Document31 pagesKHDA - Dubai Modern Education School 2015 2016Edarabia.comNo ratings yet
- Atr Ftir 3Document8 pagesAtr Ftir 3akosi gantNo ratings yet
- The Problem Centred Expert Interview Combining Qualitative Interviewing Approaches For Investigating Implicit Expert KnowledgeDocument15 pagesThe Problem Centred Expert Interview Combining Qualitative Interviewing Approaches For Investigating Implicit Expert KnowledgeUdayan DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Date Sheet For 2nd Pre Board Exam of Class X & XII (2023-24) Reg (16!12!2023)Document1 pageDate Sheet For 2nd Pre Board Exam of Class X & XII (2023-24) Reg (16!12!2023)Aman RazzNo ratings yet
- Cognizant GenC Model PaperDocument29 pagesCognizant GenC Model PaperKeerthi MurthyNo ratings yet
- Inquiries, Investigations and Immersion: 3 Quarter Week6Document7 pagesInquiries, Investigations and Immersion: 3 Quarter Week6Pegeeey100% (1)
- Rational Planning Model - Planning TankDocument6 pagesRational Planning Model - Planning TankAnugrah RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Podsakoff 1996 HFHFHFGDocument40 pagesPodsakoff 1996 HFHFHFGVali GhitaNo ratings yet
- Quantum TeleportationDocument15 pagesQuantum Teleportationraghav_20752100% (2)
- Teaching Guide Statistics and ProbabilityDocument5 pagesTeaching Guide Statistics and ProbabilityNestor Abante Valiao Jr.No ratings yet
- Rusen RankeDocument16 pagesRusen RankeElisa Silva CaetanoNo ratings yet