Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Kinetics
Chemical Kinetics
Uploaded by
MOHAMED HISHAM0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThis document provides an overview of chemical kinetics concepts including:
- The rate of a reaction is defined as well as the order of a reaction and activation energy.
- Questions are provided about rate laws, rate constants, reaction orders, and how temperature affects reaction rates.
- Integrated rate equations are derived for first and zero order reactions.
- An example examines the rate of disappearance of Cl2 in different experiments to determine the rate law and rate constant.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of chemical kinetics concepts including:
- The rate of a reaction is defined as well as the order of a reaction and activation energy.
- Questions are provided about rate laws, rate constants, reaction orders, and how temperature affects reaction rates.
- Integrated rate equations are derived for first and zero order reactions.
- An example examines the rate of disappearance of Cl2 in different experiments to determine the rate law and rate constant.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesChemical Kinetics
Chemical Kinetics
Uploaded by
MOHAMED HISHAMThis document provides an overview of chemical kinetics concepts including:
- The rate of a reaction is defined as well as the order of a reaction and activation energy.
- Questions are provided about rate laws, rate constants, reaction orders, and how temperature affects reaction rates.
- Integrated rate equations are derived for first and zero order reactions.
- An example examines the rate of disappearance of Cl2 in different experiments to determine the rate law and rate constant.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Chemical Kinetics
One Mark Questions (5*1=5) Total =40 marks
1. Define ‘rate of a reaction’.
2. Define ‘order of a reaction.
3. Define ‘activation energy’ of a reaction.
4. Express the rate of the following reaction in terms of the formation of ammonia :
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g).
5. If the rate constant of a reaction is k = 3 × 10-4 s-1, then identify the order of the
reaction.
Two Mark Questions (10*2=20)
1. What do you understand by the rate law and rate constant of a reaction? Identify the
order of a reaction if the units of its rate constant are : (i) L-1 mol s-1 (ii) L mol-1 s-1.
2. Define the following terms :
(a) Pseudo first order reaction.
(b) Half life period of reaction (t1/2).
3. (a) For a reaction, A + B → Product, the rate law is given by, Rate = k[A]1[B]2. What
is the order of the reaction?
(b) Write the unit of rate constant ‘k’ for the first order reaction.
4. Define the following terms :
(i) Rate constant (k)
(ii) Activation energy (Ea).
5. How does a change in temperature affect the rate, of a reaction? How can this effect
on the rate constant of a reaction be represented quantitatively?
6. Write units of rate constants for zero order and for the second order reactions if the
concentration is expressed in mol L-1 and time in second.
7. For a reaction: 2NH2(g) ⟶Pt N2(g) + 3H2(g)
Rate = k
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
8. What is meant by rate of a reaction? Differentiate between average rate and
instantaneous rate of a reaction.
9. The rate constant for a reaction of zero order in A is 0.0030 mol L-1 s-1. How long will
it take for the initial concentration of A to fall from 0.10 M to 0.075 M?
10. A first order gas phase reaction : A2B2(g) → 2A(g) + 2B(g) at the temperature 400°C
has the rate constant k = 2.0 × 10-4 sec-1. What percentage of A2B2 is decomposed on
heating for 900 seconds? (Antilog 0.0781 = 1.197).
Five mark Questions (5*3=15)
1. Derive integrated rate equation for rate constant of a first order reaction.
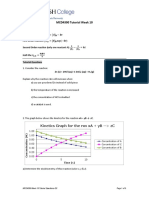
2. For the reaction
2NO(g) + Cl2(g) → 2NOCl(g) the following data were collected. All the
measurements were taken at 263 K :
Initial
Initial
Experiment No. Initial rate of tlisa/ipcarance of
[NO](M)
[Cl2](M) Cl2 (M/min)
1 0.15 0.15 0.60
2 0.15 0.30 1.20
3 0.30 0.15 2.40
4 0.25 0.25 ?
(a) Write the expression for rate law.
(b) Calculate the value of rate constant and specify its units.
(c) What is the initial rate of disappearance of Cl2 in exp. 4?
3. Derive integrated rate equation for rate constant of a Zero order reaction.
You might also like
- Converge 2.4 ManualDocument996 pagesConverge 2.4 ManualJaydip Hinsu100% (3)
- Ashrae C26 (97) Climatic Design InformationDocument53 pagesAshrae C26 (97) Climatic Design InformationDiegoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Radiation Lab ReportDocument13 pagesThermal Radiation Lab ReportHassan AnwerNo ratings yet
- Timber Beam Design PDFDocument5 pagesTimber Beam Design PDFnurulselangor50% (2)
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4khalidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Past PapersDocument2 pagesChemical Kinetics Past Papers10 A Pratyush Dubey50% (2)
- Chemical Kinetics Board Questions 2010Document5 pagesChemical Kinetics Board Questions 2010amone nNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument3 pagesChemical Kineticsnimitsigotiya2No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 StudentDocument6 pagesTutorial 2 StudentIrsyad KamilNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Lec-1 NEET ChalisaDocument35 pagesKinetics Lec-1 NEET Chalisaashustarguy005No ratings yet
- Big Idea 4 AnswersDocument4 pagesBig Idea 4 AnswersSreeyaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Reaction KineticsDocument142 pages1.0 Reaction KineticsKhairul Aswari Ab RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument10 pagesChemical Kineticsjayamadhavan2007No ratings yet
- Kinetics Assign 2020Document7 pagesKinetics Assign 2020SabaNo ratings yet
- Chemcal Kinetics (Tutorial Questions)Document3 pagesChemcal Kinetics (Tutorial Questions)renNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL KINETIC-worksheet - Module - 2Document3 pagesCHEMICAL KINETIC-worksheet - Module - 2sarahNo ratings yet
- PLTL Ch. 16 AssignmentDocument6 pagesPLTL Ch. 16 AssignmentJules BrunoNo ratings yet
- Kinetics and ElectroDocument3 pagesKinetics and Electropavithra KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical KinematicsDocument3 pagesChemical KinematicsLyra GurimbaoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Revision - 15.11.2016Document6 pagesChemical Kinetics Revision - 15.11.2016Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: Chung (Peter) Chieh Professor of Chemistry University of Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario, CanadaDocument34 pagesChemical Kinetics: Chung (Peter) Chieh Professor of Chemistry University of Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario, CanadaAngelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Reaction KineticsDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Reaction KineticsDinesh RamaNo ratings yet
- bài tập rateDocument2 pagesbài tập rateMys Genie100% (1)
- Tutorial 4Document3 pagesTutorial 4aliesyaNo ratings yet
- MCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsDocument5 pagesMCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsGabbar100% (1)
- CHM 096 Tutorial 1Document4 pagesCHM 096 Tutorial 1Muhammad ShafiqNo ratings yet
- 3 QP Chemical KineticsDocument4 pages3 QP Chemical KineticsSnehit RajNo ratings yet
- Practice Rate Law ProblemsDocument6 pagesPractice Rate Law ProblemsPatriciaNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument8 pagesChemical KineticsSnehashis BoseNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument3 pagesChemical KineticsakritiNo ratings yet
- 15-01-2021 Chemical & Isomerism (Autosaved)Document41 pages15-01-2021 Chemical & Isomerism (Autosaved)cric.indian.womenNo ratings yet
- Class XII Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesClass XII Chemical KineticsvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 8 - Chemical KineticsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 8 - Chemical KineticsAnushkaNo ratings yet
- Lecturers CHEMICAL KINETICSDocument36 pagesLecturers CHEMICAL KINETICSb.hamdi160No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Chemical KineticsDocument92 pagesChapter 2 - Chemical KineticssabNo ratings yet
- 1-8 Reaction Kinetics PDFDocument8 pages1-8 Reaction Kinetics PDFBerry101No ratings yet
- 02-Chemical Kinetic - Telegram - @JEE - BOOKSDocument11 pages02-Chemical Kinetic - Telegram - @JEE - BOOKSRdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 HOME WITH ANSDocument7 pagesChapter 14 HOME WITH ANSSerpicoNo ratings yet
- Phy Pharm - Kinetics Workshop 2Document2 pagesPhy Pharm - Kinetics Workshop 2koojunwei3624No ratings yet
- 4 BQ - Ans Chemical KineticsDocument7 pages4 BQ - Ans Chemical KineticsDawa PenjorNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Chemical KineticsDocument1 pageAssignment 3 Chemical Kineticsvegamaharajfaith02No ratings yet
- DPP5 Full Chemical KineticsDocument14 pagesDPP5 Full Chemical KineticsAbhishek SinglaNo ratings yet
- GZB - Xii - WS-8 - Chemistry - Chemical Kinetics - OctoberDocument3 pagesGZB - Xii - WS-8 - Chemistry - Chemical Kinetics - OctoberSaman PanwarNo ratings yet
- Chem 312 Test 1 2013 MemoDocument11 pagesChem 312 Test 1 2013 Memomatloa71No ratings yet
- 102 MSJC 13Document11 pages102 MSJC 13noelNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics CompleteDocument20 pagesChemical Kinetics CompleteNusrat ZahanNo ratings yet
- 08a. Chemical Kinetics SheetDocument33 pages08a. Chemical Kinetics SheetVIKRANTH KUMAR JAKKOJUNo ratings yet
- Chm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesChm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical Kineticsfiefy zmrNo ratings yet
- Chm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesChm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsisfaNo ratings yet
- CHM271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesCHM271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsisfaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 SolutionsDocument20 pagesTutorial 1 Solutionsanushka shagunNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics-I: Part - I: Subjective QuestionsDocument34 pagesChemical Kinetics-I: Part - I: Subjective Questionshorn blowNo ratings yet
- AP Ch. 12-13 Kinetics & Equilibrium Review AnswersDocument35 pagesAP Ch. 12-13 Kinetics & Equilibrium Review AnswersRucar Rad0% (1)
- CHM 112 Kinetics Practice Problems AnswersDocument13 pagesCHM 112 Kinetics Practice Problems AnswersReza RezaeiNo ratings yet
- Kinetics ReviewDocument5 pagesKinetics ReviewbrittanypriyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics-1Document50 pagesChemical Kinetics-1telangtanushreeNo ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 2Document18 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 2ridwan100% (2)
- Chapter 13 Chemical KineticsDocument10 pagesChapter 13 Chemical KineticsJacob McPhersonNo ratings yet
- CHM 112 Kinetics Practice Problems AnswersDocument14 pagesCHM 112 Kinetics Practice Problems AnswersHamzar MohammedNo ratings yet
- Kinetika KimiaDocument66 pagesKinetika KimiaMuhammad Thoriq AiNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL KINETICS Anilkumar HssliveDocument2 pagesCHEMICAL KINETICS Anilkumar HssliveMathew Yoyakky100% (1)
- Chemical Kinetics: Rate of Reaction MechanismDocument60 pagesChemical Kinetics: Rate of Reaction MechanismAneudis Javier BritoNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- 83 WaveOptics Short Ans 4Document2 pages83 WaveOptics Short Ans 4MOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- 3 WaveOptics - MCQ 1Document4 pages3 WaveOptics - MCQ 1MOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- 8 WaveOptics Short Answer 1Document2 pages8 WaveOptics Short Answer 1MOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- 4 WaveOptics - MCQ 2Document4 pages4 WaveOptics - MCQ 2MOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- 82 WaveOptics Short Ans 3Document2 pages82 WaveOptics Short Ans 3MOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- 7 Categories of AfaalDocument4 pages7 Categories of AfaalMOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- 6 WaveOptics Long Answer 1Document2 pages6 WaveOptics Long Answer 1MOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Amines NotesDocument8 pagesAmines NotesMOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- 81 WaveOptics Short Ans 2Document2 pages81 WaveOptics Short Ans 2MOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Biology Practicals Syllabus 22-23Document1 pageBiology Practicals Syllabus 22-23MOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Biology QPDocument12 pagesBiology QPMOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- 9WaveOptics MindMapDocument1 page9WaveOptics MindMapMOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Arabic Letters & EssaysDocument8 pagesArabic Letters & EssaysMOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules IMQ Board 22-23Document12 pagesBiomolecules IMQ Board 22-23MOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ip Cover Page 1Document1 pageChemistry Ip Cover Page 1MOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Long AnsDocument2 pagesAldehydes Long AnsMOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Maths ActivitiesDocument8 pagesClass 12 Maths ActivitiesMOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketone Carboxylic Acid IMQ Board 22-23Document22 pagesAldehyde Ketone Carboxylic Acid IMQ Board 22-23MOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Short AnsDocument2 pagesAldehydes Short AnsMOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Question PaperDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Question PaperMOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current 1Document2 pagesAlternating Current 1MOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument39 pagesBio NotesMOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- 2008 Suby BulletinDocument40 pages2008 Suby BulletinPiyush MohantyNo ratings yet
- Casing and TubingDocument7 pagesCasing and TubinglalalaNo ratings yet
- 4-2 Isentropic Flow Through NozzlesDocument25 pages4-2 Isentropic Flow Through NozzlesAlif Nur FirdausNo ratings yet
- Dr. Azealdeen Salih Al-Jawadi: Importance of Rock Mechanics and Its HistoryDocument5 pagesDr. Azealdeen Salih Al-Jawadi: Importance of Rock Mechanics and Its HistoryAzealdeen AlJawadiNo ratings yet
- KHBNKDocument20 pagesKHBNKJuventino VegaNo ratings yet
- Orifice Plate Sizing Calculation Using A New Labview TechniqueDocument6 pagesOrifice Plate Sizing Calculation Using A New Labview TechniquesyamsulNo ratings yet
- By Hamid R. Lotfi and P. Benson Shing, 2 Members, ASCE AbstractDocument18 pagesBy Hamid R. Lotfi and P. Benson Shing, 2 Members, ASCE AbstractafuhcivNo ratings yet
- Astm E8 / E8M: The Definitive Guide To Metals Tensile TestingDocument19 pagesAstm E8 / E8M: The Definitive Guide To Metals Tensile TestingashokkumarNo ratings yet
- Viscous Dissipation Term in Energy EquationsDocument14 pagesViscous Dissipation Term in Energy Equationsscience1990No ratings yet
- Space Time (ST) and Space Velocity (SV)Document2 pagesSpace Time (ST) and Space Velocity (SV)Marco A. Castillo LudeñaNo ratings yet
- Air Cooler 2023Document6 pagesAir Cooler 2023saheb167No ratings yet
- Lista de Precios VendedorDocument12 pagesLista de Precios VendedorSugeily MatosNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry 10th by ZumdahlDocument33 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry 10th by ZumdahlAmandaHarrissftia100% (98)
- Hooke Law Lab ReportDocument10 pagesHooke Law Lab ReportasifNo ratings yet
- Conservation LawsDocument33 pagesConservation Lawsafaq ahmad khanNo ratings yet
- Guide For The Design and Construction of Fixed Offshore Concrete StructuresDocument23 pagesGuide For The Design and Construction of Fixed Offshore Concrete StructuresYohannes GebreNo ratings yet
- ch03 PDFDocument11 pagesch03 PDFFarhan KhanNo ratings yet
- E 0211Document23 pagesE 0211Thinh ViproNo ratings yet
- Hoek Triaxial Cell: ApplicationsDocument2 pagesHoek Triaxial Cell: Applicationsvasudeva yasasNo ratings yet
- Pivot PointDocument31 pagesPivot PointJorge Quintas100% (2)
- Gallavotti Statistical MechanicsDocument359 pagesGallavotti Statistical MechanicsgerosaNo ratings yet
- Ce411 Ranola Ce42fa2Document42 pagesCe411 Ranola Ce42fa2Patrick AlimuinNo ratings yet
- Acfm To SCFMDocument1 pageAcfm To SCFMdit25195683No ratings yet
- R22 PDFDocument6 pagesR22 PDFZen JCNo ratings yet
- Activity-Spontaneous ReactionsDocument2 pagesActivity-Spontaneous ReactionsMagcayang, Presious Angel J.No ratings yet
- Modo Diagnostico ClimatronicDocument2 pagesModo Diagnostico Climatronichernanr76No ratings yet