Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Noble Gases+reactions
Noble Gases+reactions
Uploaded by
GAURI GUPTA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageThe document discusses the properties and uses of noble gases. It notes that noble gases are colorless, monatomic nonmetals whose size and mass increase down the group. Their density and boiling points also increase down the group. Helium is the lightest noble gas. Common uses include argon in signs and lighting, helium in balloons, xenon in operating theaters, and krypton in car headlamps. The document also lists several types of chemical reactions such as neutralization, precipitation, thermal decomposition, displacement reactions, oxidation/reduction, and synthesis.
Original Description:
Original Title
noble gases+reactions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the properties and uses of noble gases. It notes that noble gases are colorless, monatomic nonmetals whose size and mass increase down the group. Their density and boiling points also increase down the group. Helium is the lightest noble gas. Common uses include argon in signs and lighting, helium in balloons, xenon in operating theaters, and krypton in car headlamps. The document also lists several types of chemical reactions such as neutralization, precipitation, thermal decomposition, displacement reactions, oxidation/reduction, and synthesis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageNoble Gases+reactions
Noble Gases+reactions
Uploaded by
GAURI GUPTAThe document discusses the properties and uses of noble gases. It notes that noble gases are colorless, monatomic nonmetals whose size and mass increase down the group. Their density and boiling points also increase down the group. Helium is the lightest noble gas. Common uses include argon in signs and lighting, helium in balloons, xenon in operating theaters, and krypton in car headlamps. The document also lists several types of chemical reactions such as neutralization, precipitation, thermal decomposition, displacement reactions, oxidation/reduction, and synthesis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
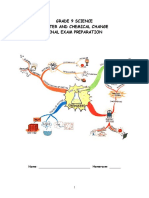
NOBLE GASES: GROUP VIII
● NON METALS
● COLOURLESS - PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
● MONOATOMIC
● SIZE AND MASS INCREASES DOWN THE GROUP
● HELIUM IS THE LIGHTEST GAS
● DENSITY ALSO INCREASES DOWN THE GROUP
● BOILING POINT INCREASES DOWN THE GROUP
USES OF NOBLE GASES
● ARGON: signs
● HELIUM: balloons because unreactive + lighter than air
● XENON: operation theatre
● ARGOM: light bulbs (why)
● KRYPTON: used in torch car headlamps
● RADON: laser
Reactions: CHAPTER 4.2
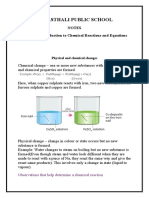
1. neutralisation: (acids+bases=salt+water) - (an exothermic reaction) when an acid and base react
with each-other to form salt and water.
2. precipitation - (an endothermic reaction) when two soluble salts react with each other to form one
soluble and one insoluble salt. ((double displacement))
3. thermal decomposition: it is a reaction in which a compound breaks into two or more elements or
compounds in presence of heat or a catalyst.
4. decomposition (any- thermal etc): endothermic reaction
5. displacement reaction: a reaction in which a more reactive element displaces the less reactive
element from its compound
6. endothermic, exothermic - heat taking in, heat given out
7. oxidation/redox:
1. oxidation is - adding oxygen, removal of hydrogen, loss of electrons
2. reduction is- removing oxygen, adding hydrogen, gain of electrons
3. redox reaction is- a reaction in which oxidation & reduction takes place simultaneously
8. synthesis- a reaction in which two or more elements or molecules combine to form a compound
(usually one product)
You might also like
- IGCSE Chemistry DefinitionsDocument5 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Definitionsjenifer100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsShabnam GolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsPrabhuPalanichamyNo ratings yet
- 10th NotesDocument7 pages10th NotesPratibha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equationsminimata100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science Chemistry Download in PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science Chemistry Download in PDFNaved ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 99998324Document7 pages99998324Ashish Urff ĐãkšhNo ratings yet
- Krish (Notes) : Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument20 pagesKrish (Notes) : Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsVivek saklaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science Matter and Chemical Change Final Exam PreparationDocument15 pagesGrade 9 Science Matter and Chemical Change Final Exam PreparationBekki VanderlendeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry GCSE NotesDocument4 pagesChemistry GCSE Notesbluebeary123No ratings yet
- 2324 T2 Chemistry C4 Chemical ReactionsDocument66 pages2324 T2 Chemistry C4 Chemical ReactionswilsonconcepcionNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 CH 21 Phy SciDocument29 pagesUnit-4 CH 21 Phy SciCarlyn VarelaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions NewDocument112 pagesChemical Reactions NewMaria Jamilla R. PuaNo ratings yet
- Changes in Matter 2019Document44 pagesChanges in Matter 2019api-423980580No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations Notes Gaurav SutharDocument9 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations Notes Gaurav SutharRaunik Motwani100% (1)
- Chem. - F8term 2 Chem 2019Document40 pagesChem. - F8term 2 Chem 2019Lobna ShabanNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument30 pagesChemical ReactionsAdeeba FatimaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes MYP4 5Document17 pagesChemistry Notes MYP4 5isharazil09No ratings yet
- Unit 5 (Energy Changes)Document16 pagesUnit 5 (Energy Changes)mya thet htar sweNo ratings yet
- Vanasthali Public School: Notes Chapter-1 Introduction To Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument8 pagesVanasthali Public School: Notes Chapter-1 Introduction To Chemical Reactions and EquationsPlatinum Gaming Warrior100% (1)
- Class 10 Chemical Reactions NotesDocument12 pagesClass 10 Chemical Reactions NotesShreyash VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction 4fb79727Document47 pagesChemical Reaction 4fb79727Tabish RahimNo ratings yet
- Group 18th Self Creating Project FileDocument17 pagesGroup 18th Self Creating Project FileDhairya VeerNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument36 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsASHRITH RASAKATLANo ratings yet
- Chem Notes pt-2Document7 pagesChem Notes pt-2Krish ThaparNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations - Docx NotesDocument9 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations - Docx NotesRodel AzaresNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations@RIMSDocument8 pagesChemical Equations@RIMSSAI PRANEETH REDDY DHADINo ratings yet
- Chemistry Thursday NotesDocument2 pagesChemistry Thursday Notesshaswatsathyamoorthy19No ratings yet
- Pressure and Temperature With Gas Brownian MotionDocument8 pagesPressure and Temperature With Gas Brownian Motiongabby tanNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class X Chemistry 086 Theory v1Document10 pagesCbse Class X Chemistry 086 Theory v1ARMANI ROYNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument36 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionsAira Villarin100% (3)
- English For ChemistsDocument27 pagesEnglish For ChemistsViet NguyenNo ratings yet
- Notes - Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument3 pagesNotes - Types of Chemical ReactionsJayasutha RamanNo ratings yet
- Yr 11 Chemistry Exam NotesDocument13 pagesYr 11 Chemistry Exam NotesadfknaljhNo ratings yet
- Non Metals ScienceDocument18 pagesNon Metals SciencekaleyakeaganNo ratings yet
- Chemistry I Study GuideDocument11 pagesChemistry I Study GuideDeepti SailappanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2, Inorganic Chemistry (2.11-2.15) Study GuideDocument22 pagesChemistry Unit 2, Inorganic Chemistry (2.11-2.15) Study Guidemannm26No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions - SYNOPSISDocument10 pagesChemical Reactions - SYNOPSISshashwatthegamerytNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Class 10 Chapter 1Document8 pagesChemistry Notes Class 10 Chapter 1Sandhya RaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry DefinitionsDocument4 pagesChemistry DefinitionsManiesegaran SagadevanNo ratings yet
- 2 Chemical ReactionDocument2 pages2 Chemical ReactionMohammad Jahid AlamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations and Reactions NotesDocument6 pagesChemical Equations and Reactions NotesLak WakNo ratings yet
- Type of Chemical Reaction: Prepared By-Abhay Bohra Guided by - Aakansha LalDocument8 pagesType of Chemical Reaction: Prepared By-Abhay Bohra Guided by - Aakansha LalVishal NandwanaNo ratings yet
- 2005 Chemistry NotesDocument6 pages2005 Chemistry NotesjzdoogNo ratings yet
- Made By:-Ruchika NigamDocument11 pagesMade By:-Ruchika NigamRuchika NigamNo ratings yet
- 5 WW XUJCSXdi Az MMHNT I6Document3 pages5 WW XUJCSXdi Az MMHNT I6varshatagade126No ratings yet
- ElementsDocument2 pagesElementsSyahmi RoslanNo ratings yet
- Final Research (Hady)Document6 pagesFinal Research (Hady)Hady SalehNo ratings yet
- Chem DefinitionsDocument6 pagesChem DefinitionsTariNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Elements (Positive Ion,)Document4 pagesGroup 1 Elements (Positive Ion,)BUMISAVERSNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument44 pagesChemistrymahrosh amirNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledWaggle The GreatNo ratings yet
- CDI 5 Complete Notes IIDocument49 pagesCDI 5 Complete Notes IIRhiteous Battateng BegeoNo ratings yet
- 68 Topper 21 101 2 2 22 Chemical Reactions and Equations Up201506181308 1434613126 7976Document6 pages68 Topper 21 101 2 2 22 Chemical Reactions and Equations Up201506181308 1434613126 7976VARUN SRIVASSNo ratings yet
- Name: Doaa Nassar Grade: 9B Teacher's Name: Ms. AfshariDocument35 pagesName: Doaa Nassar Grade: 9B Teacher's Name: Ms. AfshariDoaa NassarNo ratings yet
- Kỹ thuật xúc tácDocument12 pagesKỹ thuật xúc tácHoàng Phước KhảiNo ratings yet
- DRRR FireDocument3 pagesDRRR Firemarcian.cadayona1No ratings yet
- INORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Arshi (1905113797)Document6 pagesINORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Arshi (1905113797)Arsi NurNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Combining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandCombining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet