Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Colligative Properties of Solutions Reviewer
Colligative Properties of Solutions Reviewer
Uploaded by
Precious Lara MangobaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Colligative Properties of Solutions Reviewer
Colligative Properties of Solutions Reviewer
Uploaded by
Precious Lara MangobaCopyright:
Available Formats
Colligative Properties of Solutions ➢ VAPOR PRESSURE LOWERING
When a nonvolatile solute is added to a solvent, physical • The vapor pressure of solution is lower than the vapor
properties of the solvent will change. pressure of pure solvent
• The greater the concentration of solution, the greater
Colligative properties of a solution depend only on the
the vapor pressure is lowered.
number of solute particles in a solution and not on the
• Since the number of solute is greater in solution
nature of those particles.
containing electrolyte solute, the vapor pressure will be
Colligative Property lower than that of solution with non-electrolyte solutes.
• the interaction between the solute and solvent changes
the property of solution form that of the pure solvent
• properties that depend solely on the number of particles
of solute present but not on the kind and nature of
solute
• depend on the amount of the solute and not on their
chemical identities
Electrolyte vs. Non- Electrolyte solutes
• Non-electrolyte solute does not ionizes in solution, the
number of solute particles will be less in a solution
containing non-electrolyte solute than in a solution
containing electrolyte solute
• The effect of an electrolyte solute will be greater than a
non-electrolyte solute in a solution
Colligative Property
1. VAPOR PRESSURE LOWERING Calculate the vapor pressure of a solution made by
2. BOILING POINT ELEVATION dissolving 50.0 g glucose, C6H12O6 ,in 500 g of water.
3. FREEZING POINT DEPRESSION The vapor pressure of pure water is 47.1 torr at 37°C
4. OSMOTIC PRESSURE
Kb
VAPOR PRESSURE
The ebullioscopic constant is also called the molal
A substance that evaporates readily is called VOLATILE. elevation constant.
*escaping tendency is high It is defined as the elevation in boiling point when one
* high vapor pressure mole of non-volatile solute is added to one kilogram of
solvent.
A nonvolatile substance has low vapor pressure and low It is denoted by Kb.
escaping tendency. The unit of an ebullioscopic constant is K Kg mol-1.
If a nonvolatile solute is dissolved in water, the solute Kf
molecules take up space at the surface and thus preventing Cryoscopic constant or the Molal depression constant is
the escape of solvent molecules. defined as the depression in freezing point when one mole
of non-volaitile solute is dissolved in one kilogram of
solvent.
Its unit is K.Kg.mol-1.
➢ BOILING POINT ELEVATION
• The boiling point of pure water is 100OC.
• Sea water boils at higher temperature.
• The burn caused by boiling syrup is more severe than
that is caused by boiling pure water.
The interaction between solute-solvent is greater than
solvent-solvent and solute-solute
Thus, longer time to equalize the vapor pressure of the
liquid (solution) and the atmospheric pressure.
The boiling point of solution, therefore; is greater than the
boiling point of the pure solvent.
Symbols used in the calculation of colligative properties:
FREEZING POINT
• The temperature at which the solid and liquid phases
coexist
➢ FREEZING POINT DEPRESSION
• If a nonvolatile solute is added to a solvent, the freezing
point of the solvent is lowered and the reduction in the
freezing point depends on the number of moles of
solute present.
• The freezing point of solution is lower than the freezing
point of the pure solvent.
Osmosis is the diffusion of water, either from a dilute
solution or from pure water, through a semipermeable
membrane into a solution of higher concentration.
Semipermeable membrane: A semipermeable membrane
allows the passage of water (solvent) molecules through it
in either direction, but it prevents the passage of larger
solute molecules.
Osmotic pressure is the pressure that must be exerted to
prevent osmosis of solvent particles through a
semipermeable membrane that is separating two solutions
of different solute concentrations.
Osmotic pressure is a colligative property.
➢ OSMOTIC PRESSURE
You might also like
- Battery Charger: Standard EquipmentDocument2 pagesBattery Charger: Standard EquipmentlejocolsaNo ratings yet
- Hart Chapter 3 SolutionsDocument32 pagesHart Chapter 3 SolutionsCAMILO100% (1)
- Colligative Properties of Solution: General Chemistry 2 Lesson 6.2Document48 pagesColligative Properties of Solution: General Chemistry 2 Lesson 6.2Mark Lorens StaanaNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 3rdsem EndTerm ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenChem2 3rdsem EndTerm ReviewerJames Andre DionedaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7. Electrolyte and Non ElectrolyteDocument29 pagesLesson 7. Electrolyte and Non ElectrolyteAnthony CreationNo ratings yet
- Ways of Expressing Concentrations of SolutionsDocument57 pagesWays of Expressing Concentrations of SolutionsKearly Joy VictorioNo ratings yet
- Razzel Quinones Chemistry SolutionDocument5 pagesRazzel Quinones Chemistry SolutionRazzel QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of Non ElectrolytesDocument20 pagesColligative Properties of Non ElectrolytesHans Sicangco0% (1)
- Water &MC: in Food SystemDocument23 pagesWater &MC: in Food SystemFISIA AQRORINANo ratings yet
- M4 Colligative PropertiesDocument46 pagesM4 Colligative Propertiesicebear1333No ratings yet
- Mod 3.2 Colligative, Tonicity and Mod 4 Solubility (PDF - Io)Document62 pagesMod 3.2 Colligative, Tonicity and Mod 4 Solubility (PDF - Io)Charles DapitoNo ratings yet
- 5211 - Colligative Properties of Solution-1Document33 pages5211 - Colligative Properties of Solution-1Muhammad Sameer RasheedNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of Solution - ChemDocument23 pagesColligative Properties of Solution - Chemkatherine corveraNo ratings yet
- Solution Conc Raoults ClligativeDocument66 pagesSolution Conc Raoults ClligativeHeather WrightNo ratings yet
- Solution ChemistryDocument27 pagesSolution ChemistryZarahbeth Claire G. ArcederaNo ratings yet
- Simple Mixture DrShikin 2 ConDocument59 pagesSimple Mixture DrShikin 2 ConPutriNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of Solution (3rd Week)Document41 pagesColligative Properties of Solution (3rd Week)SomeThingNo ratings yet
- เอกสารประกอบรายวิชา pc205 ครั้งที่ 5 solutionDocument57 pagesเอกสารประกอบรายวิชา pc205 ครั้งที่ 5 solutionVeliyana Londong AlloNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 12-Colligative Properties - UPDocument50 pagesLECTURE 12-Colligative Properties - UPJimmy Jim DakaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 SolutionsDocument81 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 SolutionsLol lolNo ratings yet
- SolubilityDocument59 pagesSolubilityNadem DreemNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument66 pagesColligative Properties of Solutionspalitpa moreNo ratings yet
- Lecture30 f05Document27 pagesLecture30 f05احمد الدلالNo ratings yet
- Solutios, Solutions of Non Electrolyte - 2019-2020Document80 pagesSolutios, Solutions of Non Electrolyte - 2019-2020hazo hazNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Q2Document3 pagesChemistry Q2Kristel Anne Magaru-Macauggal-LugoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry2 - Lesson2Document2 pagesGeneral Chemistry2 - Lesson2Ronalda GuevarraNo ratings yet
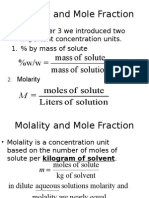
- Molality and Mole Fraction: % 100 Solution of Mass Solute of Mass W/W %Document26 pagesMolality and Mole Fraction: % 100 Solution of Mass Solute of Mass W/W %keshavNo ratings yet
- Solutios, Solutions of Non Electrolyte - 2019-2020 v2Document80 pagesSolutios, Solutions of Non Electrolyte - 2019-2020 v2hazo hazNo ratings yet
- It 4 - SolutionsDocument74 pagesIt 4 - SolutionsRafika Novianti CikovaNo ratings yet
- MixturesDocument30 pagesMixturesSubir BiswasNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Lesson 7 Colligative PropertiesDocument29 pagesGen Chem 2 Lesson 7 Colligative PropertiesB-Quinain, Don Joachim V.No ratings yet
- SOLUBILITYDocument62 pagesSOLUBILITYHaroon RazaNo ratings yet
- Cheme Cheme Lang:: An Academic Guide and Tutorial Towards LiteracyDocument32 pagesCheme Cheme Lang:: An Academic Guide and Tutorial Towards LiteracySpace MonkeyNo ratings yet
- 4 SolutionsDocument139 pages4 SolutionslwenselchristineNo ratings yet
- Edsci 112Document8 pagesEdsci 112Meah Angela GulacNo ratings yet
- (Lec7) Properties of SolutionsDocument51 pages(Lec7) Properties of SolutionsdinurjNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument12 pagesColligative PropertiesDivay VermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13aulectureslides 000 PDFDocument105 pagesChapter 13aulectureslides 000 PDFFrances Valerie Cambronero PaceteNo ratings yet
- Solutions G Colligative PropDocument14 pagesSolutions G Colligative PropHusnul YaqinNo ratings yet
- Solution & Solubilit yDocument28 pagesSolution & Solubilit yChristine MalibiranNo ratings yet
- Solutions & Colligative Properties2Document15 pagesSolutions & Colligative Properties2Uzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Solutes and SolubilityDocument19 pagesSolutes and Solubilitylucas zhangNo ratings yet
- GC2 ColligativeDocument20 pagesGC2 Colligativejosemarie kunNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument34 pagesColligative Properties of Solutionstatskopling100% (1)
- Dr. Saidane Lecture Notes Properties of Solutions: Chem 200Document10 pagesDr. Saidane Lecture Notes Properties of Solutions: Chem 200Marko QuebralNo ratings yet
- Mixtures & SolutionsDocument28 pagesMixtures & Solutionsapi-239855791No ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument8 pagesColligative Properties of SolutionspieNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saDocument34 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saapi-19824406100% (1)
- Solubility and DissolutionDocument87 pagesSolubility and Dissolutionm7md3del2015No ratings yet
- 14 SolutionsDocument60 pages14 SolutionsGlen MangaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Solutions NotesDocument37 pagesChapter 2 Solutions NotesAbhishek PatelNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab Hand OutsDocument12 pagesBiochemistry Lab Hand Outsrica sebabillonesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Properties of SolutionsDocument66 pagesChapter 13 Properties of SolutionsRoxanne UrmenetaNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties: Chemistry AssignmentDocument10 pagesColligative Properties: Chemistry AssignmentJubin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Hand Out 3 For Grade 12Document5 pagesChemistry Hand Out 3 For Grade 12Nigatu MAmoNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument47 pagesColligative Propertiespipay vlogsNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Day 4 Session - Gen Chem 2Document43 pagesWeek 1 Day 4 Session - Gen Chem 2louiseputoyNo ratings yet
- L 3 - SolutionsDocument51 pagesL 3 - SolutionsJayRiveraNo ratings yet
- 02 - Colligative PropertiesDocument46 pages02 - Colligative PropertiesamirNo ratings yet
- Solution ChemistryDocument24 pagesSolution ChemistryJisna JaisonNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceFrom EverandFluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Earth and Life Science LESSON 1Document28 pagesEarth and Life Science LESSON 1Precious Lara MangobaNo ratings yet
- Sugar RushDocument1 pageSugar RushPrecious Lara MangobaNo ratings yet
- PhiloDocument3 pagesPhiloPrecious Lara MangobaNo ratings yet
- Career Study PlannerDocument13 pagesCareer Study PlannerPrecious Lara MangobaNo ratings yet
- Free and Forced Vortices PDFDocument6 pagesFree and Forced Vortices PDFdemiseNo ratings yet
- Transactions Apparatus Systems, Vol - PAS-98, No.1: 97 Ieee Power and Jan/Feb 1979Document13 pagesTransactions Apparatus Systems, Vol - PAS-98, No.1: 97 Ieee Power and Jan/Feb 1979awolNo ratings yet
- Ansys Coupled Field AnalysisDocument307 pagesAnsys Coupled Field AnalysisUmesh Vishwakarma100% (1)
- Solarflex - X H1Z2Z2-K: 1500 V DC, EN 50618Document2 pagesSolarflex - X H1Z2Z2-K: 1500 V DC, EN 50618Solar ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Eee 3204Document22 pagesEee 3204Sarwar Hosen SimonNo ratings yet
- E650 Series 3: Industrial and CommercialDocument12 pagesE650 Series 3: Industrial and Commercialashish sahaNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationHaider AliNo ratings yet
- 3 160428055251Document30 pages3 160428055251arifNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual Communication Systems An Introduction Signals Noise in Electrical Communication 5th Edition CarlsonDocument150 pagesSolutions Manual Communication Systems An Introduction Signals Noise in Electrical Communication 5th Edition Carlsondede ogag100% (1)
- Mto 2 Expt PDFDocument44 pagesMto 2 Expt PDFSai DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Bc141 Baldor Manual EspañolDocument20 pagesBc141 Baldor Manual Españoljohn kenneth vasquez vasquez100% (1)
- Load Curves and Selection of Generating Units: From 12 Midnight To 7 A.M. Only Unit No.1 Is Put in OperationDocument11 pagesLoad Curves and Selection of Generating Units: From 12 Midnight To 7 A.M. Only Unit No.1 Is Put in OperationHarNo ratings yet
- 1951-Jacobsen-Hydrodynamic Experiments With Rigid Cylindrical Tanks Subjected To Transient MontionsDocument34 pages1951-Jacobsen-Hydrodynamic Experiments With Rigid Cylindrical Tanks Subjected To Transient MontionsEuge CompagnoniNo ratings yet
- Tugas 29 April 2016Document3 pagesTugas 29 April 2016api-316036600No ratings yet
- CHE 416 Reaction KineticsDocument133 pagesCHE 416 Reaction KineticsElijahNo ratings yet
- Final Quiz 2 - CIV191.PDF Version 1Document1 pageFinal Quiz 2 - CIV191.PDF Version 1Harvey MorosNo ratings yet
- RLC Svu006a E4 0414Document32 pagesRLC Svu006a E4 0414Emerson PenaforteNo ratings yet
- Motion of Particles Through FluidsDocument9 pagesMotion of Particles Through FluidsFarman AliNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Testing of Power Distribution TransformersDocument8 pagesPower Factor Testing of Power Distribution TransformersfvicunaeNo ratings yet
- MT Lab - B1 Batch-ScheduleDocument3 pagesMT Lab - B1 Batch-ScheduleNanditha ANo ratings yet
- Xe2 e DC Current Relay For Loss of Exciation ProtectionDocument16 pagesXe2 e DC Current Relay For Loss of Exciation ProtectionUdara AmilaNo ratings yet
- (Deich) - Technical Gas DynamicsDocument649 pages(Deich) - Technical Gas DynamicsRaphael Pugliesi100% (1)
- Test in Physics - Docx Answer KeyDocument2 pagesTest in Physics - Docx Answer KeyZzaiRraNo ratings yet
- CTV SLB033 en - 03242010Document2 pagesCTV SLB033 en - 03242010Emerson PenaforteNo ratings yet
- Saturated Steam Metal Wall 1 Outer Asbestos 3Document8 pagesSaturated Steam Metal Wall 1 Outer Asbestos 3raras atiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ProblemsDocument15 pagesTutorial Problemsrebekah mahabirNo ratings yet
- Development of Wireless Charging For Mobile Application Using PVDocument47 pagesDevelopment of Wireless Charging For Mobile Application Using PVYasirNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab ManualDocument48 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab ManualArsi Rajput100% (1)