Professional Documents
Culture Documents
05 Handout 1
05 Handout 1
Uploaded by
JohnCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Core Java Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedDocument36 pagesCore Java Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedVibrant Publishers100% (1)
- Basic Elements of Programming LanguageDocument82 pagesBasic Elements of Programming LanguagePM 2014 1st year summer studentsNo ratings yet
- CMP-2123-Object Oriented Programming: by Mohammad NomanDocument52 pagesCMP-2123-Object Oriented Programming: by Mohammad NomanMohammad NomanNo ratings yet
- 002) Variables and Data Types in Java - 1Document12 pages002) Variables and Data Types in Java - 1day2 testingNo ratings yet
- Java ScriptDocument8 pagesJava ScriptchristmashipolitoNo ratings yet
- Java MynotesDocument17 pagesJava MynotesAditi GoelNo ratings yet
- ICSE Mind Maps & On Tips Notes Class 10 - Computer ApplicationsDocument5 pagesICSE Mind Maps & On Tips Notes Class 10 - Computer Applicationsks.ashwiniNo ratings yet
- Java Quick ReferenceDocument35 pagesJava Quick ReferenceNitin MenonNo ratings yet
- TrainingMaterials Day2Document22 pagesTrainingMaterials Day2Arindam BasuNo ratings yet
- Ata Types: Department of Computer Science & Engineering Web Technologies-Kcs-602 Unit-IDocument8 pagesAta Types: Department of Computer Science & Engineering Web Technologies-Kcs-602 Unit-Ia2021cse7825No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 2Document49 pagesUnit 1 - 2Vinayak kalelNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Programming Structures in JavaDocument23 pagesFundamental Programming Structures in JavaVinayKumarSinghNo ratings yet
- Nirmal Jha NotesDocument17 pagesNirmal Jha NotesSatyam DevNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 OperatorsDocument16 pagesLesson 5 OperatorsJhezryll MayNo ratings yet
- Notes of Bluej For STD 10Document17 pagesNotes of Bluej For STD 10Ab. Funny100% (2)
- Lecture2 2020Document17 pagesLecture2 2020Jmaes SukuinaNo ratings yet
- Java (2) Lectures (6)Document33 pagesJava (2) Lectures (6)Mojtaba AlrasheedNo ratings yet
- Java OperatorsDocument17 pagesJava OperatorsMohammad ImthiyazNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument9 pagesReviewerAXL JOHN CEDRICK DEMATENo ratings yet
- About JavaScriptDocument49 pagesAbout JavaScriptheroku5151No ratings yet
- Introduction To JavaScriptDocument13 pagesIntroduction To JavaScriptkhaliqjaveria12No ratings yet
- Module 4.1 Java ScriptDocument40 pagesModule 4.1 Java Scriptshefaligupta0408No ratings yet
- Java Part 2Document10 pagesJava Part 2Ch. Rahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Part II Java TokensDocument43 pagesChapter 2 Part II Java TokensFiromsa DineNo ratings yet
- Java Script CheatSheetDocument31 pagesJava Script CheatSheethkush78No ratings yet
- Unit - 02Document70 pagesUnit - 02Bhavya ParikhNo ratings yet
- DFC20113 - Programming Fundamentals: Chapter 2: Basic Program ElementsDocument78 pagesDFC20113 - Programming Fundamentals: Chapter 2: Basic Program ElementsNurul AsyiqinNo ratings yet
- Javascript DatatypesDocument52 pagesJavascript DatatypesAmna TofiqueNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 1Document5 pages02 Handout 1Nor Jhon BruzonNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Introduction To JavaDocument39 pagesObjectives: Introduction To JavavishalakiteNo ratings yet
- JavaScript IntroDocument46 pagesJavaScript Introqwerty uiopNo ratings yet
- 02 C++ OperatorsDocument15 pages02 C++ OperatorsRaza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document63 pagesModule 1kumarNo ratings yet
- Ceng1004 Lecture 2Document35 pagesCeng1004 Lecture 2ozlemNo ratings yet
- Java FundamentalsDocument85 pagesJava FundamentalsKene BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Using DataDocument38 pagesUsing DataChesley CarolinoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document49 pagesUnit 3Akshay TeotiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Java Datatypes and Control Constructs (1) As SIRDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Java Datatypes and Control Constructs (1) As SIRADITYA PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Basics TheoryDocument7 pagesBasics Theoryzemo kumarNo ratings yet
- LessonsDocument46 pagesLessonsChristian LaguidaoNo ratings yet
- MIC ch4Document51 pagesMIC ch4Diksha KatakdhondNo ratings yet
- HNVN TR JavaScript 1-3 PresentationDocument99 pagesHNVN TR JavaScript 1-3 PresentationPhạm Quang HiếuNo ratings yet
- Core JavaScript NotesDocument62 pagesCore JavaScript NotesSujay VadavadagiNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Operators Operands Expressions 2Document26 pages4.1 Operators Operands Expressions 2Sumedha ReddyNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument36 pagesUntitledAkash KaleNo ratings yet
- The Five Basic Data Types: VariablesDocument12 pagesThe Five Basic Data Types: VariablesvrrengasNo ratings yet
- C OperatorsDocument4 pagesC Operatorssonu1070No ratings yet
- 1.1 OCA - 1Z0-808 - Module03 - Operators - Control - Structures - ReviewDocument26 pages1.1 OCA - 1Z0-808 - Module03 - Operators - Control - Structures - ReviewcarutsaNo ratings yet
- Data TypesDocument27 pagesData TypesREESHU RANJANNo ratings yet
- Python For Security - Chapter 1Document75 pagesPython For Security - Chapter 1oobaa bbbssaNo ratings yet
- Unit V JavascriptDocument25 pagesUnit V JavascriptDeepak VarmaNo ratings yet
- Computer ProjectDocument71 pagesComputer ProjectACCELALORDNo ratings yet
- OperatorsDocument33 pagesOperatorsadarsh rajNo ratings yet
- JAVA Lecture 2Document9 pagesJAVA Lecture 2vishalNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts: I. Introduction To Java Microsystems, and Currently Owned by OracleDocument4 pagesBasic Concepts: I. Introduction To Java Microsystems, and Currently Owned by OracleMharv Jesrael hinayoNo ratings yet
- Activity 5Document2 pagesActivity 5Julianna LeeNo ratings yet
- Basics of Javascript Programming: K. K. Wagh Polytechnic, Nashik-3Document29 pagesBasics of Javascript Programming: K. K. Wagh Polytechnic, Nashik-3Sakshi SatheNo ratings yet
- Javascript & DOMDocument68 pagesJavascript & DOMNyoman Adi MuliawanNo ratings yet
- College of Science Department of Computer Programing Fundamentals (Java) First StageDocument23 pagesCollege of Science Department of Computer Programing Fundamentals (Java) First StagebashdarNo ratings yet
- NIIT Vile ParleDocument24 pagesNIIT Vile ParleGauravMakhechaNo ratings yet
- 321 The Lord Has Come (Dec 26)Document9 pages321 The Lord Has Come (Dec 26)JohnNo ratings yet
- 63 Trust in God (Mar 6)Document7 pages63 Trust in God (Mar 6)JohnNo ratings yet
- 1 PrayerFasting (Jan 2)Document8 pages1 PrayerFasting (Jan 2)JohnNo ratings yet
- 4 The Tent Meeting (Jan 5)Document9 pages4 The Tent Meeting (Jan 5)JohnNo ratings yet
- 3 Alive in Jesus (Jan 4)Document12 pages3 Alive in Jesus (Jan 4)JohnNo ratings yet
- 35 Worship Thorough Giving (Feb 5)Document7 pages35 Worship Thorough Giving (Feb 5)JohnNo ratings yet
- 10 The Virtue of Humility (Jan 11)Document7 pages10 The Virtue of Humility (Jan 11)JohnNo ratings yet
- 9 Blessed To Servee (Jan 10)Document7 pages9 Blessed To Servee (Jan 10)JohnNo ratings yet
- 13 What Makes God Smilae (Jan 14)Document7 pages13 What Makes God Smilae (Jan 14)JohnNo ratings yet
- 29 Responses That Pleases God During Crisis (Jan 30)Document9 pages29 Responses That Pleases God During Crisis (Jan 30)JohnNo ratings yet
- Revised PVCH Reflection On Gods Restoring LoveDocument20 pagesRevised PVCH Reflection On Gods Restoring LoveJohnNo ratings yet
- The Power of ObedienceDocument6 pagesThe Power of ObedienceJohnNo ratings yet
- True RepentanceDocument17 pagesTrue RepentanceJohnNo ratings yet
- 01 Presentation TemplateDocument9 pages01 Presentation TemplateJohnNo ratings yet
- Prelims: WebinarDocument9 pagesPrelims: WebinarJohnNo ratings yet
- Among The Multimedia Businesses That Were Given As An ExampleDocument1 pageAmong The Multimedia Businesses That Were Given As An ExampleJohnNo ratings yet
- 01 Presentation TemplateDocument9 pages01 Presentation TemplateJohnNo ratings yet
- Team Taimtim Yapak E Commerce WebsiteDocument5 pagesTeam Taimtim Yapak E Commerce WebsiteJohnNo ratings yet
- Jjann00 Skiff Recovery KeyDocument1 pageJjann00 Skiff Recovery KeyJohnNo ratings yet
- Manipon Jerome, Garcia Clariza, Ledesma Berjon, Tome Jann Raqui, Recile James, Abenes Richard BMMA 321 March 15, 2023Document2 pagesManipon Jerome, Garcia Clariza, Ledesma Berjon, Tome Jann Raqui, Recile James, Abenes Richard BMMA 321 March 15, 2023JohnNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument2 pagesLetterJohnNo ratings yet
- Morpho FormsDocument49 pagesMorpho FormsJohnNo ratings yet
- 2023 The Stairs Notes by Diego LuciaDocument15 pages2023 The Stairs Notes by Diego LuciaJohnNo ratings yet
- Assignment: 1) Write A Program Which Checks If Two Strings Are Anagram or Not?Document8 pagesAssignment: 1) Write A Program Which Checks If Two Strings Are Anagram or Not?Premi RamsingNo ratings yet
- Java DeveloperDocument7 pagesJava DeveloperSyeda AnmolNo ratings yet
- CV (Java Software Developer)Document1 pageCV (Java Software Developer)Illia MelnykNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document31 pagesChapter 11abdalhq xNo ratings yet
- Development With WebLogic Server 12c and MavenDocument50 pagesDevelopment With WebLogic Server 12c and MavenWilson VerardiNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Aplikasi Materi Kursus Fundamental LepkomDocument2 pagesSpesifikasi Aplikasi Materi Kursus Fundamental LepkomSultan AdityaNo ratings yet
- QCM Chap4Document25 pagesQCM Chap4abdelkader maatallahNo ratings yet
- LogDocument4 pagesLogMujianiNo ratings yet
- Java 4Document65 pagesJava 4Kavya MamillaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To JavaDocument5 pagesIntroduction To JavaSHEETANSHU BHANDARINo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Pair RDD and DataFrameDocument38 pagesLecture 4 - Pair RDD and DataFrameKhánh Hoàng VănNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 Object Oriented Paradigms, Abstraction, PrinciplesDocument55 pagesLecture1 Object Oriented Paradigms, Abstraction, PrinciplesAbdul HaseebNo ratings yet
- 02 Stack QueueDocument12 pages02 Stack QueuevarykNo ratings yet
- Maven Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesMaven Interview QuestionsDinesh KarthickNo ratings yet
- AsasDocument2 pagesAsasriyazudheenNo ratings yet
- Java PolymorphismDocument14 pagesJava PolymorphismSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Collections in JavaDocument19 pagesCollections in JavaPhani PHNo ratings yet
- Crash 2020 12 30 - 13.28.33 ServerDocument9 pagesCrash 2020 12 30 - 13.28.33 ServerTar OgreNo ratings yet
- Oopc++ Assignment G.Vaishnavi Btech Cse (2 Sem) ENR. NO:-A80105219022 Section:ADocument8 pagesOopc++ Assignment G.Vaishnavi Btech Cse (2 Sem) ENR. NO:-A80105219022 Section:ASanjana PulapaNo ratings yet
- AWP FinalDocument63 pagesAWP FinalColab PracticalNo ratings yet
- Portal Info StubDocument15 pagesPortal Info Stubnungkoiramono51No ratings yet
- Docker Zero To HeroDocument16 pagesDocker Zero To HeroShamshad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Bank SimulatorDocument8 pagesBank SimulatorAnkit MainiNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Android Development: CS231M - Alejandro TroccoliDocument22 pagesAn Introduction To Android Development: CS231M - Alejandro TroccolisinteNo ratings yet
- Welcome To: JDBC Programming IDocument27 pagesWelcome To: JDBC Programming IUnknownNo ratings yet
- CrashDocument7 pagesCrashNaveen KNo ratings yet
- Practical Assignment: SYBCA-DIV-1-SEM-4 Java Roll No:84Document12 pagesPractical Assignment: SYBCA-DIV-1-SEM-4 Java Roll No:84pNo ratings yet
- 5 Primary Key Mappings For JPA and Hibernate Every Developer Should KnowDocument7 pages5 Primary Key Mappings For JPA and Hibernate Every Developer Should KnowAdolfNo ratings yet
- Java IODocument23 pagesJava IOJohn BerkmansNo ratings yet
05 Handout 1
05 Handout 1
Uploaded by
JohnOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
05 Handout 1
05 Handout 1
Uploaded by
JohnCopyright:
Available Formats
IT1804
JavaScript Basics
JavaScript
- It is a scripting language used to manipulate the contents of a Web page. It can be both HTML and CSS.
- Using JavaScript, it can animate, move, transition, and hide HTML elements.
- JavaScript is different from Java. Java is a compiled, object-oriented programming language known for its ability to
run on any platform with a Java Virtual Machine installed, while JavaScript only runs in a browser.
- JavaScript's file extension is .js
Comment
- The comment in JavaScript prevents the execution of the program or explain the JavaScript Code.
- There are two (2) styles of comment:
o The single line or end-of-line comment starts with two (2) forward slashes //.
o The block or multi-line comment begins with /* and ends with */.
Locations
- JavaScript can be linked in a number of ways in an HTML file. It can be inline, embedded (internal), and external
JavaScript.
- Inline JavaScript
o The inline JavaScript refers to including or placing the JavaScript code directly within certain attributes of an
HTML.
- Embedded (Internal) JavaScript
o This refers to including or placing the JavaScript code inside the <script> element.
- External JavaScript
o This refers to the external file of a JavaScript that is placed within the <head> element, similar to the case
of external CSS files. It is also possible to include this external file inside the <body> element, and it is
recommended to place it at the bottom.
Variables
- Variables in JavaScript are dynamically typed. It means that the variable can be a string, an integer, and then later an
object.
- In declaring a variable, the var keyword is usually followed by the desired variable name and a semicolon. It simplifies
the variable declarations, and it doesn't need or require the common data types, such as int, char, double or float,
and string, once the value is set as a string (var str = "hello world!";). It is already set as a string variable,
and if the value is a number (var num = 5;), then it is set as an integer.
05 Handout 1 *Property of STI
student.feedback@sti.edu Page 1 of 8
IT1804
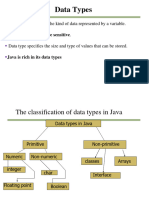
Data Type
- In JavaScript, data type specifies which type of value a variable contains.
- There are six (6) primitive data types that are supported in JavaScript:
o String – The string data type represents textual data.
o Boolean – The Boolean data type contains a logical entity that may return a value of TRUE or FALSE.
o Number – The number data type can be an integer or a decimal.
o Null – This data type represents an unknown or missing value.
o Undefined – It refers to a variable that has no value. The undefined keyword can be set in the variable.
JavaScript Output
- In JavaScript, there are different ways to display the data in the browser:
o innerHTML
▪ The innerHTML is used to display the output in an HTML element.
o document.write();
▪ This syntax is used to display the data in the HTML document.
o window.alert();
▪ The alert function shows a pop-up message to the browser.
o console.log();
▪ This function displays the output in a console. The console for JavaScript can be seen in the developer
tools of a Web browser.
▪ The console object refers to the console of developer tools in a Web browser, while the log
method prints the data.
Control Flow
Control Flow Statement
- The control flow statement refers to the decisions or conditions that the executed program may depend on its
output.
- This control statement contains the following:
o if – the if statement returns true if the specified condition is true.
05 Handout 1 *Property of STI
student.feedback@sti.edu Page 2 of 8
IT1804
o if-else – the if-else statement returns true if the condition is true; otherwise, it returns false.
o else if – the else if statement is used if the first condition is false; otherwise, the second condition is
true and so on.
o switch – The switch statement is the same as the if-else statement. It evaluates an expression and
matches the expression's value but in the case label.
05 Handout 1 *Property of STI
student.feedback@sti.edu Page 3 of 8
IT1804
o try…catch – The try…catch statement is used to block a statement(s) to try and respond with an
exception.
▪ This statement consists of the following:
• try – The try block contains one (1) or more statements.
• catch – The catch block contains a statement of what to do when the try block throws an
exception.
Operator
- It is used to assign values in a variable.
- The following types are operators in JavaScript:
o Assignment operator
▪ The assignment operator is used to assign the value to its left operand or variable.
▪ The following are the common assignment operators in JavaScript:
• =
o Assigns the value to a variable
• +=
o Adds the value to a variable
• -=
o Subtracts the value from a variable
• *=
o Multiplies the value by a variable
• /=
o Divides the value by a variable
o Comparison operators
▪ The comparison operator compares the two (2) variables or operands.
▪ The following comparison operators are:
• ==
o Equal to the value of the variable or operand.
• ===
o Equal value and equal type
• < , >
o Less than and greater than
• <= , >=
o Less than or equal to and greater than or equal to
• !=
o Not equal to the value of the variable or operand.
o Arithmetic operators
▪ The arithmetic operator performs addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
▪ The following arithmetic operators are:
• Addition ( + )
o This arithmetic operator adds two (2) operands or two (2) variables that contain
number values.
• Subtraction ( - )
o This arithmetic operator subtracts two (2) operands or two (2) variables that
contain number values.
• Multiplication ( * )
o This arithmetic operator multiplies two (2)operands or two (2) variables that contain
number values.
05 Handout 1 *Property of STI
student.feedback@sti.edu Page 4 of 8
IT1804
• Division ( / )
o This arithmetic operator divides two (2) operands or two (2) variables that contain
number values.
• Modulus ( % )
o The modulus operator gets the remainder of the division of the two (2) numbers.
• Increment ( ++ )
o This operator adds one (1) in the operand.
• Decrement ( -- )
o This operator subtracts one (1) from the operand.
o Logical operators
▪ The logical operator uses Boolean values.
▪ There are three (3) logical operators, and they are the following:
• AND ( && )
o The AND operator returns true if both values are true.
• OR ( || )
o The OR operator returns true if either expression1 or expression2 is true.
• NOT ( ! )
o The NOT operator will return true if the expression1 is false.
o Ternary operator
▪ The ternary operator is the same as the if-else statement that if the condition is true, then
execute the statement; otherwise, return false.
Loops and Iterations
for Loop
- A for loop specifies the number of loops of an object.
- The for loop contains three (3) expressions:
o Initialization
▪ The first expression is known as the counter of the for loop.
o Condition
▪ The second expression is condition; it will check if the condition will return true or false.
o Increment/Decrement
▪ The third expression specifies the number of loops based on the condition; it may increment or
decrement this loop.
05 Handout 1 *Property of STI
student.feedback@sti.edu Page 5 of 8
IT1804
for in
- It is used to loop the properties of an object or an array.
do-while
- It is used to loop the statement until it evaluates to false.
- The do-while will execute the block of code first before checking if the condition will evaluate to true.
while
- The while loop is the most basic loop. It only uses a condition. The while loop is like an if statement that
repeatedly runs until a condition is satisfied.
05 Handout 1 *Property of STI
student.feedback@sti.edu Page 6 of 8
IT1804
label
- The label statement identifies a statement and uses a break or continue statement to indicate whether the
executed code will interrupt a loop or continue its execution.
break
- The break statement is used to terminate a loop, switch, and a labeled statement.
05 Handout 1 *Property of STI
student.feedback@sti.edu Page 7 of 8
IT1804
continue
- The continue statement is used to repeat a loop, condition, or a labeled statement.
Functions
Functions
- A function is a block of code or modular code in JavaScript that performs a specific task. The function is defined in
the
function keyword followed by the function name and parameters enclosed in parentheses.
- Parameters in a function are accessible within the body of the function.
- The function may also return a value once you declare the parameters.
REFERENCES:
1. Connolly, R. & Hoar, R. (2015). Fundamentals of web development. New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc.
2. Lemay, L., Colburn, R., & Kyrnin, J. (2016). Sams teach yourself html, CSS and JavaScript web publishing in one hour a day (7th Ed.).
New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc.
3. Krause, J. (2016). Introducing web development. California: Apress Media, LLC.
05 Handout 1 *Property of STI
student.feedback@sti.edu Page 8 of 8
You might also like
- Core Java Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedDocument36 pagesCore Java Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedVibrant Publishers100% (1)
- Basic Elements of Programming LanguageDocument82 pagesBasic Elements of Programming LanguagePM 2014 1st year summer studentsNo ratings yet
- CMP-2123-Object Oriented Programming: by Mohammad NomanDocument52 pagesCMP-2123-Object Oriented Programming: by Mohammad NomanMohammad NomanNo ratings yet
- 002) Variables and Data Types in Java - 1Document12 pages002) Variables and Data Types in Java - 1day2 testingNo ratings yet
- Java ScriptDocument8 pagesJava ScriptchristmashipolitoNo ratings yet
- Java MynotesDocument17 pagesJava MynotesAditi GoelNo ratings yet
- ICSE Mind Maps & On Tips Notes Class 10 - Computer ApplicationsDocument5 pagesICSE Mind Maps & On Tips Notes Class 10 - Computer Applicationsks.ashwiniNo ratings yet
- Java Quick ReferenceDocument35 pagesJava Quick ReferenceNitin MenonNo ratings yet
- TrainingMaterials Day2Document22 pagesTrainingMaterials Day2Arindam BasuNo ratings yet
- Ata Types: Department of Computer Science & Engineering Web Technologies-Kcs-602 Unit-IDocument8 pagesAta Types: Department of Computer Science & Engineering Web Technologies-Kcs-602 Unit-Ia2021cse7825No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 2Document49 pagesUnit 1 - 2Vinayak kalelNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Programming Structures in JavaDocument23 pagesFundamental Programming Structures in JavaVinayKumarSinghNo ratings yet
- Nirmal Jha NotesDocument17 pagesNirmal Jha NotesSatyam DevNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 OperatorsDocument16 pagesLesson 5 OperatorsJhezryll MayNo ratings yet
- Notes of Bluej For STD 10Document17 pagesNotes of Bluej For STD 10Ab. Funny100% (2)
- Lecture2 2020Document17 pagesLecture2 2020Jmaes SukuinaNo ratings yet
- Java (2) Lectures (6)Document33 pagesJava (2) Lectures (6)Mojtaba AlrasheedNo ratings yet
- Java OperatorsDocument17 pagesJava OperatorsMohammad ImthiyazNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument9 pagesReviewerAXL JOHN CEDRICK DEMATENo ratings yet
- About JavaScriptDocument49 pagesAbout JavaScriptheroku5151No ratings yet
- Introduction To JavaScriptDocument13 pagesIntroduction To JavaScriptkhaliqjaveria12No ratings yet
- Module 4.1 Java ScriptDocument40 pagesModule 4.1 Java Scriptshefaligupta0408No ratings yet
- Java Part 2Document10 pagesJava Part 2Ch. Rahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Part II Java TokensDocument43 pagesChapter 2 Part II Java TokensFiromsa DineNo ratings yet
- Java Script CheatSheetDocument31 pagesJava Script CheatSheethkush78No ratings yet
- Unit - 02Document70 pagesUnit - 02Bhavya ParikhNo ratings yet
- DFC20113 - Programming Fundamentals: Chapter 2: Basic Program ElementsDocument78 pagesDFC20113 - Programming Fundamentals: Chapter 2: Basic Program ElementsNurul AsyiqinNo ratings yet
- Javascript DatatypesDocument52 pagesJavascript DatatypesAmna TofiqueNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 1Document5 pages02 Handout 1Nor Jhon BruzonNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Introduction To JavaDocument39 pagesObjectives: Introduction To JavavishalakiteNo ratings yet
- JavaScript IntroDocument46 pagesJavaScript Introqwerty uiopNo ratings yet
- 02 C++ OperatorsDocument15 pages02 C++ OperatorsRaza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document63 pagesModule 1kumarNo ratings yet
- Ceng1004 Lecture 2Document35 pagesCeng1004 Lecture 2ozlemNo ratings yet
- Java FundamentalsDocument85 pagesJava FundamentalsKene BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Using DataDocument38 pagesUsing DataChesley CarolinoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document49 pagesUnit 3Akshay TeotiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Java Datatypes and Control Constructs (1) As SIRDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Java Datatypes and Control Constructs (1) As SIRADITYA PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Basics TheoryDocument7 pagesBasics Theoryzemo kumarNo ratings yet
- LessonsDocument46 pagesLessonsChristian LaguidaoNo ratings yet
- MIC ch4Document51 pagesMIC ch4Diksha KatakdhondNo ratings yet
- HNVN TR JavaScript 1-3 PresentationDocument99 pagesHNVN TR JavaScript 1-3 PresentationPhạm Quang HiếuNo ratings yet
- Core JavaScript NotesDocument62 pagesCore JavaScript NotesSujay VadavadagiNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Operators Operands Expressions 2Document26 pages4.1 Operators Operands Expressions 2Sumedha ReddyNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument36 pagesUntitledAkash KaleNo ratings yet
- The Five Basic Data Types: VariablesDocument12 pagesThe Five Basic Data Types: VariablesvrrengasNo ratings yet
- C OperatorsDocument4 pagesC Operatorssonu1070No ratings yet
- 1.1 OCA - 1Z0-808 - Module03 - Operators - Control - Structures - ReviewDocument26 pages1.1 OCA - 1Z0-808 - Module03 - Operators - Control - Structures - ReviewcarutsaNo ratings yet
- Data TypesDocument27 pagesData TypesREESHU RANJANNo ratings yet
- Python For Security - Chapter 1Document75 pagesPython For Security - Chapter 1oobaa bbbssaNo ratings yet
- Unit V JavascriptDocument25 pagesUnit V JavascriptDeepak VarmaNo ratings yet
- Computer ProjectDocument71 pagesComputer ProjectACCELALORDNo ratings yet
- OperatorsDocument33 pagesOperatorsadarsh rajNo ratings yet
- JAVA Lecture 2Document9 pagesJAVA Lecture 2vishalNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts: I. Introduction To Java Microsystems, and Currently Owned by OracleDocument4 pagesBasic Concepts: I. Introduction To Java Microsystems, and Currently Owned by OracleMharv Jesrael hinayoNo ratings yet
- Activity 5Document2 pagesActivity 5Julianna LeeNo ratings yet
- Basics of Javascript Programming: K. K. Wagh Polytechnic, Nashik-3Document29 pagesBasics of Javascript Programming: K. K. Wagh Polytechnic, Nashik-3Sakshi SatheNo ratings yet
- Javascript & DOMDocument68 pagesJavascript & DOMNyoman Adi MuliawanNo ratings yet
- College of Science Department of Computer Programing Fundamentals (Java) First StageDocument23 pagesCollege of Science Department of Computer Programing Fundamentals (Java) First StagebashdarNo ratings yet
- NIIT Vile ParleDocument24 pagesNIIT Vile ParleGauravMakhechaNo ratings yet
- 321 The Lord Has Come (Dec 26)Document9 pages321 The Lord Has Come (Dec 26)JohnNo ratings yet
- 63 Trust in God (Mar 6)Document7 pages63 Trust in God (Mar 6)JohnNo ratings yet
- 1 PrayerFasting (Jan 2)Document8 pages1 PrayerFasting (Jan 2)JohnNo ratings yet
- 4 The Tent Meeting (Jan 5)Document9 pages4 The Tent Meeting (Jan 5)JohnNo ratings yet
- 3 Alive in Jesus (Jan 4)Document12 pages3 Alive in Jesus (Jan 4)JohnNo ratings yet
- 35 Worship Thorough Giving (Feb 5)Document7 pages35 Worship Thorough Giving (Feb 5)JohnNo ratings yet
- 10 The Virtue of Humility (Jan 11)Document7 pages10 The Virtue of Humility (Jan 11)JohnNo ratings yet
- 9 Blessed To Servee (Jan 10)Document7 pages9 Blessed To Servee (Jan 10)JohnNo ratings yet
- 13 What Makes God Smilae (Jan 14)Document7 pages13 What Makes God Smilae (Jan 14)JohnNo ratings yet
- 29 Responses That Pleases God During Crisis (Jan 30)Document9 pages29 Responses That Pleases God During Crisis (Jan 30)JohnNo ratings yet
- Revised PVCH Reflection On Gods Restoring LoveDocument20 pagesRevised PVCH Reflection On Gods Restoring LoveJohnNo ratings yet
- The Power of ObedienceDocument6 pagesThe Power of ObedienceJohnNo ratings yet
- True RepentanceDocument17 pagesTrue RepentanceJohnNo ratings yet
- 01 Presentation TemplateDocument9 pages01 Presentation TemplateJohnNo ratings yet
- Prelims: WebinarDocument9 pagesPrelims: WebinarJohnNo ratings yet
- Among The Multimedia Businesses That Were Given As An ExampleDocument1 pageAmong The Multimedia Businesses That Were Given As An ExampleJohnNo ratings yet
- 01 Presentation TemplateDocument9 pages01 Presentation TemplateJohnNo ratings yet
- Team Taimtim Yapak E Commerce WebsiteDocument5 pagesTeam Taimtim Yapak E Commerce WebsiteJohnNo ratings yet
- Jjann00 Skiff Recovery KeyDocument1 pageJjann00 Skiff Recovery KeyJohnNo ratings yet
- Manipon Jerome, Garcia Clariza, Ledesma Berjon, Tome Jann Raqui, Recile James, Abenes Richard BMMA 321 March 15, 2023Document2 pagesManipon Jerome, Garcia Clariza, Ledesma Berjon, Tome Jann Raqui, Recile James, Abenes Richard BMMA 321 March 15, 2023JohnNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument2 pagesLetterJohnNo ratings yet
- Morpho FormsDocument49 pagesMorpho FormsJohnNo ratings yet
- 2023 The Stairs Notes by Diego LuciaDocument15 pages2023 The Stairs Notes by Diego LuciaJohnNo ratings yet
- Assignment: 1) Write A Program Which Checks If Two Strings Are Anagram or Not?Document8 pagesAssignment: 1) Write A Program Which Checks If Two Strings Are Anagram or Not?Premi RamsingNo ratings yet
- Java DeveloperDocument7 pagesJava DeveloperSyeda AnmolNo ratings yet
- CV (Java Software Developer)Document1 pageCV (Java Software Developer)Illia MelnykNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document31 pagesChapter 11abdalhq xNo ratings yet
- Development With WebLogic Server 12c and MavenDocument50 pagesDevelopment With WebLogic Server 12c and MavenWilson VerardiNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Aplikasi Materi Kursus Fundamental LepkomDocument2 pagesSpesifikasi Aplikasi Materi Kursus Fundamental LepkomSultan AdityaNo ratings yet
- QCM Chap4Document25 pagesQCM Chap4abdelkader maatallahNo ratings yet
- LogDocument4 pagesLogMujianiNo ratings yet
- Java 4Document65 pagesJava 4Kavya MamillaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To JavaDocument5 pagesIntroduction To JavaSHEETANSHU BHANDARINo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Pair RDD and DataFrameDocument38 pagesLecture 4 - Pair RDD and DataFrameKhánh Hoàng VănNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 Object Oriented Paradigms, Abstraction, PrinciplesDocument55 pagesLecture1 Object Oriented Paradigms, Abstraction, PrinciplesAbdul HaseebNo ratings yet
- 02 Stack QueueDocument12 pages02 Stack QueuevarykNo ratings yet
- Maven Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesMaven Interview QuestionsDinesh KarthickNo ratings yet
- AsasDocument2 pagesAsasriyazudheenNo ratings yet
- Java PolymorphismDocument14 pagesJava PolymorphismSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Collections in JavaDocument19 pagesCollections in JavaPhani PHNo ratings yet
- Crash 2020 12 30 - 13.28.33 ServerDocument9 pagesCrash 2020 12 30 - 13.28.33 ServerTar OgreNo ratings yet
- Oopc++ Assignment G.Vaishnavi Btech Cse (2 Sem) ENR. NO:-A80105219022 Section:ADocument8 pagesOopc++ Assignment G.Vaishnavi Btech Cse (2 Sem) ENR. NO:-A80105219022 Section:ASanjana PulapaNo ratings yet
- AWP FinalDocument63 pagesAWP FinalColab PracticalNo ratings yet
- Portal Info StubDocument15 pagesPortal Info Stubnungkoiramono51No ratings yet
- Docker Zero To HeroDocument16 pagesDocker Zero To HeroShamshad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Bank SimulatorDocument8 pagesBank SimulatorAnkit MainiNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Android Development: CS231M - Alejandro TroccoliDocument22 pagesAn Introduction To Android Development: CS231M - Alejandro TroccolisinteNo ratings yet
- Welcome To: JDBC Programming IDocument27 pagesWelcome To: JDBC Programming IUnknownNo ratings yet
- CrashDocument7 pagesCrashNaveen KNo ratings yet
- Practical Assignment: SYBCA-DIV-1-SEM-4 Java Roll No:84Document12 pagesPractical Assignment: SYBCA-DIV-1-SEM-4 Java Roll No:84pNo ratings yet
- 5 Primary Key Mappings For JPA and Hibernate Every Developer Should KnowDocument7 pages5 Primary Key Mappings For JPA and Hibernate Every Developer Should KnowAdolfNo ratings yet
- Java IODocument23 pagesJava IOJohn BerkmansNo ratings yet