Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7 Head and Neck
7 Head and Neck
Uploaded by
the someoneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7 Head and Neck
7 Head and Neck
Uploaded by
the someoneCopyright:
Available Formats
Bulacan State University
City of Malolos, Bulacan
COLLEGE OF NURSING
NCM 101-A : HEALTH ASSESSMENT
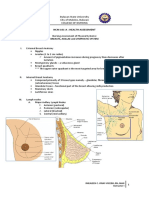
Nursing Assessment of Physical Systems:
HEAD and NECK
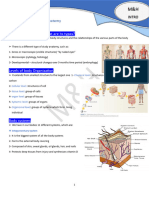
Head and neck assessment focuses on the cranium, face, thyroid gland, and lymph nodes
contained within the head and neck.
I. The Head
✓ A normal head size is referred to as normocephalic
A. Cranium
✓ Frontal (1 bone)
✓ Parietal (2 bones)
✓ Temporal (2 bones)
✓ Occipital (1 bone)
✓ Ethmoid (1 bone)
✓ Sphenoid (1 bone)
B. Face
✓ Maxilla (2 bones)
✓ Zygomatic (cheek) (2 bones)
✓ Inferior chonchae (2 bones)
✓ Nasal (2 bones)
✓ Lacrimal (2 bones)
✓ Palatine (2 bones)
✓ Vomer (1 bone)
✓ Mandible (jaw) (1 bone)
RHEALEEN VIRAY-VICEDO, RN, MAN
1
Instructor I
C. Developmental Considerations
o Infants
✓ Fontanels (“soft spots”) – anterior and posterior fontanels
✓ Voluntary head control should be present by about 6 months of age
II. The Neck
A. Muscles and Cervical Vertebrae
✓ Sternocleidomastoid muscle – rotates and flexes the head
✓ Trapezius muscle – extends the head and move the shoulders
✓ 11th cranial nerve (spinal accessory nerve) – responsible for muscle movements
that permits shrugging of the shoulders
✓ Cervical vertebrae – C1(atlas), C2 (axis) up to C7
B. Blood vessels
✓ Internal and/or external jugular vein
✓ Carotid arteries
✓ Nursing consideration: Avoid bilaterally compressing the carotid arteries when
assessing the neck as it might reduce blood supply to the brain
C. Thyroid Gland
✓ Largest endocrine gland producing thyroid hormones (T3, T4 and
Thyrocalcitonin) that increase metabolic rate of most body cells.
✓ Points of reference for accurate thyroid palpation – the trachea, cricoid cartilage
and the thyroid cartilage (“Adam’s apple” for male clients)
✓ Common thyroid disorders – hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism
(thyrotoxicosis)
III. Lymph Nodes of the Head and Neck
o Lymph nodes – they filter lymph
- a clear substance composed mostly of
excess tissue fluid which may or may not
contain bacteria or tumor cells; they also
produce lymphocytes and antibodies as
defense against foreign microbes of
substances.
✓ Normally not palpable but may
become overwhelmed with filtrates or
microbes leading to painful swelling on
palpation.
✓ Common types – preauricular,
postauricular, tonsillar, occipital,
submandibular, submental, superficial
cervical, posterior cervical, deep cervical
and supraclavicular
RHEALEEN VIRAY-VICEDO, RN, MAN
2
Instructor I
You might also like
- Ebook Vitamin C Archie Kalokerinos - Every Second ChildDocument83 pagesEbook Vitamin C Archie Kalokerinos - Every Second ChildAnonymous gwFqQcnaX100% (2)
- CirrhosisDocument54 pagesCirrhosisYani88% (8)
- Activity 6 - INFECTIONS OF THE SKIN GROUP 4 FINAL.Document6 pagesActivity 6 - INFECTIONS OF THE SKIN GROUP 4 FINAL.the someone100% (2)
- DIABETES in Pregnancy With NotesDocument84 pagesDIABETES in Pregnancy With NotesNeill CelesteNo ratings yet
- Mineral Nutrition and Suppression of Plant Disease - Elmer2014Document14 pagesMineral Nutrition and Suppression of Plant Disease - Elmer2014Dario BaronaNo ratings yet
- Dha & Scfhs ExamsDocument115 pagesDha & Scfhs Examsrayooona88100% (4)
- Microscopy Techniques: The Instrument & Dyes and Staining Summary of Microscopic Instruments and Their CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesMicroscopy Techniques: The Instrument & Dyes and Staining Summary of Microscopic Instruments and Their Characteristicsthe someoneNo ratings yet
- NCM 101-A: Health Assessment General Survey (Assessing The General Health Status)Document7 pagesNCM 101-A: Health Assessment General Survey (Assessing The General Health Status)the someoneNo ratings yet
- Clinical Laboratory LawDocument26 pagesClinical Laboratory Lawlwlski71% (7)
- HIGH RISK INFANT (1 Month - 12 Months) : 1. Failure To ThriveDocument14 pagesHIGH RISK INFANT (1 Month - 12 Months) : 1. Failure To ThriveRosaree Mae PantojaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 - Assessing Head, Neck, Breasts and Lymphatic SystemDocument11 pagesMODULE 5 - Assessing Head, Neck, Breasts and Lymphatic SystemKeila RosalesNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Transes Prelim 1Document7 pagesNCM 107 Transes Prelim 1Tatel JocelleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 9Document48 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 9Franc BlancNo ratings yet
- Nervous System and Endocrine SystemDocument90 pagesNervous System and Endocrine SystemCeres LucenteNo ratings yet
- Leopold's ManeuverDocument4 pagesLeopold's ManeuverDe Leon, Austine Sydney D.No ratings yet
- Head and Neck AssessmentDocument9 pagesHead and Neck AssessmentCrystal ARIETANo ratings yet
- Cestodes SummaryDocument6 pagesCestodes SummaryabigailNo ratings yet
- HA Notes (Prelim)Document20 pagesHA Notes (Prelim)Maria JuanilloNo ratings yet
- NCM 209 PediaDocument76 pagesNCM 209 PediaJohn Cyprian AbeloNo ratings yet
- Ed101 ReviewerDocument6 pagesEd101 ReviewerJeff selosaNo ratings yet
- Bioplasma Field: Compiled by Campbell M GoldDocument3 pagesBioplasma Field: Compiled by Campbell M GoldNorland IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- PAP Review KEY - Unit 7 CBA 2016-2017Document5 pagesPAP Review KEY - Unit 7 CBA 2016-2017Tom PunnenNo ratings yet
- 01 Organization of The Nervous SystemDocument6 pages01 Organization of The Nervous Systemlmdimaun8344valNo ratings yet
- 2.3a CELLS ARE GROUPED INTO TISSUESDocument6 pages2.3a CELLS ARE GROUPED INTO TISSUES2023820042No ratings yet
- HA Module 1Document6 pagesHA Module 1LACANARIA, ELLE BEA N.No ratings yet
- EINC Final Na Sorry Na GDDocument11 pagesEINC Final Na Sorry Na GDMaria JuanilloNo ratings yet
- W7 Intestinal CestodesDocument10 pagesW7 Intestinal CestodesPia PascualNo ratings yet
- Pediatric PT 9 HRIDocument52 pagesPediatric PT 9 HRINoby EbrahimNo ratings yet
- Close During Embryonic Development Generally in The Lumbosacral RegionDocument24 pagesClose During Embryonic Development Generally in The Lumbosacral RegionPotato BroNo ratings yet
- Pedia-Reviewer CompleteDocument36 pagesPedia-Reviewer CompletePotato BroNo ratings yet
- Week 1.3Document23 pagesWeek 1.3ginny.mycookiecanNo ratings yet
- Newborn AssessmentDocument3 pagesNewborn AssessmentangelaclaireramosNo ratings yet
- Labor and DeliveryDocument10 pagesLabor and DeliveryCharlmagne LinnamNo ratings yet
- Gynecology Tickets All 1Document34 pagesGynecology Tickets All 1moamen.nlNo ratings yet
- Retdem Interview GuideDocument2 pagesRetdem Interview GuideGlaiza Godalle TorresNo ratings yet
- Problems With The PassagewayDocument2 pagesProblems With The PassagewayPrilay Pring AlcopraNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of The Pediatric Client: Childhood Developmental StagesDocument14 pagesPhysical Examination of The Pediatric Client: Childhood Developmental Stagesshannon c. lewisNo ratings yet
- Ob HandoutsDocument22 pagesOb HandoutsKatriel Geryne ViloNo ratings yet
- 6 Months Old: 6-12 Months Old:: 0-3 Mos 0-3 MosDocument5 pages6 Months Old: 6-12 Months Old:: 0-3 Mos 0-3 MosLyan SamsonNo ratings yet
- Survival L1 and L1.2Document4 pagesSurvival L1 and L1.2RYZELLE SCHWEIN MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Ncm107 Summarization of MCNDocument40 pagesNcm107 Summarization of MCNArlyn Faith AlvarezNo ratings yet
- New Born, Infant and ToddlerDocument61 pagesNew Born, Infant and Toddlerمهند الرحيليNo ratings yet
- Artigo Publicado Dr. Andre FrareDocument6 pagesArtigo Publicado Dr. Andre FrareAndré FrareNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Reviewer 2Document5 pagesAnatomy Reviewer 2Jeanne Nicci OrcenaNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of The NewbornDocument7 pagesPhysical Examination of The NewbornurhighnxssNo ratings yet
- Ros Head and NeckDocument31 pagesRos Head and Neckshianize cilloNo ratings yet
- PTP - CorrectedDocument9 pagesPTP - CorrectedRaniNo ratings yet
- Maternal/Ob Notes: "Above Success There Is Excellence Beyond Impossible. " Skei Nursing Review & EnhancementDocument53 pagesMaternal/Ob Notes: "Above Success There Is Excellence Beyond Impossible. " Skei Nursing Review & EnhancementAbdullah, Atteya100% (1)
- Anglais Medical - Ranya OutmaniDocument6 pagesAnglais Medical - Ranya OutmaniLachgar SalmaNo ratings yet
- 2 Newborn AssesmentDocument23 pages2 Newborn Assesment.No ratings yet
- HA L2 Assessing Head, Neck, Breasts, and Lymphatic SystemDocument3 pagesHA L2 Assessing Head, Neck, Breasts, and Lymphatic SystemljtorreslriejyNo ratings yet
- Neuro - Sir Chavez - AS OF 12PMDocument5 pagesNeuro - Sir Chavez - AS OF 12PMCarl JustineNo ratings yet
- Newborn NotesDocument3 pagesNewborn NotesSharlotte EbayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. Pediatric WardDocument9 pagesLesson 1. Pediatric WardFlonamae AbiarNo ratings yet
- 8 EentDocument9 pages8 Eentthe someoneNo ratings yet
- ABRUPTIO PLACENTA Final 3.0Document51 pagesABRUPTIO PLACENTA Final 3.0Briandon CanlasNo ratings yet
- Assessing The NeckDocument18 pagesAssessing The NecksrslytrdNo ratings yet
- 8 EL Husseinys Essentials of Reproductive System @eduwaves360Document195 pages8 EL Husseinys Essentials of Reproductive System @eduwaves360ahmed_abu_alrobNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument9 pagesAnatomykhererer11No ratings yet
- Q1.5 Cell TypesDocument17 pagesQ1.5 Cell Typesminimoni kookiesNo ratings yet
- Normal Newborn PP Final-1Document97 pagesNormal Newborn PP Final-1ettevyviNo ratings yet
- Birth Trauma IN Newborns: DR Vanessa Lee Wan Mun Paediatrician Hospital Melaka 23 OCTOBER 2018Document28 pagesBirth Trauma IN Newborns: DR Vanessa Lee Wan Mun Paediatrician Hospital Melaka 23 OCTOBER 2018Cupin DeNo ratings yet
- DK Case 7 WrapDocument13 pagesDK Case 7 WrapSomaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Talipes Equinovarus (CTEV) : Nur Farhanah Binti Ariffin BJPA2019-0016 HSIDocument31 pagesCongenital Talipes Equinovarus (CTEV) : Nur Farhanah Binti Ariffin BJPA2019-0016 HSIfarhanah ariffinNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination Thyroid & Neck 2023-2024Document1 pagePhysical Examination Thyroid & Neck 2023-202482cxp4n46wNo ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and Physiology of The Head and NeckDocument11 pagesReview of Anatomy and Physiology of The Head and NeckDeborah Beatrice AlojadoNo ratings yet
- Elective - Neurologic Reporting 1Document23 pagesElective - Neurologic Reporting 1GenEsis CarandangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Overview of Professional Nursing PracticeDocument32 pagesLesson 2 Overview of Professional Nursing Practicethe someoneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 CommunicationDocument40 pagesLesson 3 Communicationthe someoneNo ratings yet
- Week 4: Part 1 Notes MBP 108 Lecture Medical and Surgical Asepsis Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesWeek 4: Part 1 Notes MBP 108 Lecture Medical and Surgical Asepsis Learning Objectivesthe someoneNo ratings yet
- 9 Breast Axilla and LymphaticsDocument3 pages9 Breast Axilla and Lymphaticsthe someoneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 History of Nursing Worldwide and in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesLesson 1 History of Nursing Worldwide and in The Philippinesthe someone100% (1)
- SYLLABUSDocument19 pagesSYLLABUSthe someoneNo ratings yet
- Criteria For Determining PrioritiesDocument1 pageCriteria For Determining Prioritiesthe someoneNo ratings yet
- 6 Skin Hair and NailsDocument5 pages6 Skin Hair and Nailsthe someoneNo ratings yet
- 8 EentDocument9 pages8 Eentthe someoneNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 MBP Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesWEEK 1 MBP Lecture Notesthe someoneNo ratings yet
- 4 Physical Examination and Pain AssessmentDocument8 pages4 Physical Examination and Pain Assessmentthe someoneNo ratings yet
- The Nursing Health History (NHH) : NCM 101-A: Health AssessmentDocument7 pagesThe Nursing Health History (NHH) : NCM 101-A: Health Assessmentthe someoneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Pharma Extra LectureDocument2 pagesLesson 5 Pharma Extra Lecturethe someoneNo ratings yet
- Please Search On The Filipino Cultural Characteristics and Health Care Beliefs and Practices in Health EducationDocument16 pagesPlease Search On The Filipino Cultural Characteristics and Health Care Beliefs and Practices in Health Educationthe someoneNo ratings yet
- E. History of Familial IllnessesDocument2 pagesE. History of Familial Illnessesthe someoneNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Community Quarantine MemorandumDocument7 pagesEnhanced Community Quarantine Memorandumthe someoneNo ratings yet
- Activity-4-TREMATODES GROUP 4 FINAL.Document10 pagesActivity-4-TREMATODES GROUP 4 FINAL.the someoneNo ratings yet
- DOCTYPE HTMLDocument6 pagesDOCTYPE HTMLthe someoneNo ratings yet
- April 6, 2020: Laboratory Assignment: TrematodesDocument9 pagesApril 6, 2020: Laboratory Assignment: Trematodesthe someoneNo ratings yet
- March 23, 2020: Laboratory Assignment: Amoeboid ProtozoansDocument11 pagesMarch 23, 2020: Laboratory Assignment: Amoeboid Protozoansthe someoneNo ratings yet
- Validation DictionaryDocument57 pagesValidation DictionaryPrince MoniNo ratings yet
- CoViTris2020 and ChloViD2020 A Striking PDFDocument16 pagesCoViTris2020 and ChloViD2020 A Striking PDFgygyNo ratings yet
- NSTP Group 3 First Aid ReportingDocument44 pagesNSTP Group 3 First Aid ReportingCindy GeverolaNo ratings yet
- Pulp Polyp - A Periapical Lesion: Radiographic Observational StudyDocument5 pagesPulp Polyp - A Periapical Lesion: Radiographic Observational StudyaabdoNo ratings yet
- Pain Management Us PharmacistDocument78 pagesPain Management Us PharmacistMarfu'ah Mar'ah100% (1)
- DeVore ErDocument96 pagesDeVore ErMelandes TamirisNo ratings yet
- SNCU Process in Madhya Pradesh NIPI DistrictsDocument7 pagesSNCU Process in Madhya Pradesh NIPI DistrictsDr Rajan Dubey100% (1)
- Benefits: Types of Nuts Good For Dogs?Document10 pagesBenefits: Types of Nuts Good For Dogs?Grace DNo ratings yet
- Bousema, Carbon FootprintDocument4 pagesBousema, Carbon FootprintChrisNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Control System in The PhilippinesDocument67 pagesFood Safety Control System in The PhilippinesjohnNo ratings yet
- Module in Mapeh 10: Healthcare Providers and Fraudulent ServicesDocument4 pagesModule in Mapeh 10: Healthcare Providers and Fraudulent ServicesChristian Gonzales Laron100% (1)
- Changing Our Understanding of HealthDocument4 pagesChanging Our Understanding of HealthNur HalimahNo ratings yet
- Low Cobalt Diet For Dyshidrotic Eczema PatientsDocument5 pagesLow Cobalt Diet For Dyshidrotic Eczema PatientsMaulidianaIndahNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Respiratory Delivery of Biologics Nucleic Acids and Vaccines 2Nd Edition Harry Perlstadt PDFDocument53 pagesFull Chapter Respiratory Delivery of Biologics Nucleic Acids and Vaccines 2Nd Edition Harry Perlstadt PDFkelly.bressette297100% (6)
- 14-Improving SVM Performance For Type II Diabetes Prediction With An Improved Non-Linear Kernel Insights From The PIMA DatasetDocument9 pages14-Improving SVM Performance For Type II Diabetes Prediction With An Improved Non-Linear Kernel Insights From The PIMA Datasetbeefypixel761No ratings yet
- DR Mohd Zawawi Abu Bakar KK Nabawan Kursus PSR PKK Keningau 12/4/2012Document27 pagesDR Mohd Zawawi Abu Bakar KK Nabawan Kursus PSR PKK Keningau 12/4/2012Zawawi Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Word Formation Easy ExerciseDocument44 pagesWord Formation Easy ExerciseKhoa DangNo ratings yet
- Therapy Tested Marker Predicted Response: Imatinib Sunitinib RegorafenibDocument11 pagesTherapy Tested Marker Predicted Response: Imatinib Sunitinib RegorafenibArif MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Parasitic PathologyDocument191 pagesAtlas of Parasitic PathologyAmina MeriemNo ratings yet
- Microbial Structures and Functions MoicroorganismsDocument390 pagesMicrobial Structures and Functions MoicroorganismssamsoatsNo ratings yet
- PARASITOLOGY-NEMATODESDocument14 pagesPARASITOLOGY-NEMATODESSonny Francisco Jr.No ratings yet
- This Oncologist Has Some Advice For MCI On Disability StudentsDocument3 pagesThis Oncologist Has Some Advice For MCI On Disability StudentsDisability Rights AllianceNo ratings yet
- Science Investigatory Project: Universidad de ManilaDocument7 pagesScience Investigatory Project: Universidad de ManilaCassandra AgustinNo ratings yet
- Rupture of Lenticulostriate Artery AneurysmsDocument8 pagesRupture of Lenticulostriate Artery Aneurysmsgeraldi radityaNo ratings yet