Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WLP Q2 Sci9 Week2
WLP Q2 Sci9 Week2
Uploaded by
Ronelyn SobrianoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WLP Q2 Sci9 Week2
WLP Q2 Sci9 Week2
Uploaded by
Ronelyn SobrianoCopyright:
Available Formats
WEEKLY LEARNING PLAN
Subject Ronelyn T. Sobriano Date November 14-18,2022
Teacher
Checked Ma. Regina A. Tan Grade 9
by Level
Quarter 2 Time/ Class CADMIUM/6:00-6:55(Tuesday- Friday)
Section DYSPROSSIUM/ 6:55-7:50(Monday- Wednesday &
Friday) GOLD/7:50-8:45((Tuesday-Friday)
BISMUTH/9:05-10:00(Monday,
Thursday,Friday)10:00-10:55(Tuesday)ARGON/10:00
-10:55(Monday, Wednesday-Friday)OHSP/10:55-
11:50((Tuesday)
Week 1 Learning
Area SCIENCE
MELCS Explain how the Quantum Mechanical Model of the atom describes the energies and
positions of the electrons
PERFOR
MANCE
STANDA
RD
Day Objectives Topic/s Activities
1 Recite at least 50 name Graded A. Preliminary Activities
and symbol in the Recitation 1. Prayer
periodic table of 2. Checking of Attendance
elements 3. Classroom Rules
B. Recall
C. Motivation
D. Discussion
E. Generalization
F. Evaluation
- The teacher will call a name f a students to
recite the names and symbols of the different
elements in the periodic table
- The students will have 2 minutes to do the task
G. Extend
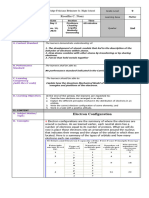
- What is Electron Configuration?
2 Describe electron Electron A. Preliminary Activities
configuration and write Configuratio 1. Prayer
the correct electron n 2. Checking of Attendance
configuration of given 3. Classroom Rules
elements B. Recall
- The students will the “Let’s Recall” part
Draw the structure of the atomic model of the
following scientists.
1. Dalton atomic model
4. Bohr’s Planetary model
2. Rutherford’s atomic model
5. Charged- cloud model
3. Thomson’s Plum-Pudding model
C. Motivation
- Let the students arrange the jumbled letters
LEONRTEC ONTIUGARFIONC
D. Discussion
- The students will describe electron
configuration
- The students will write the correct electron
configuration of an element
E. Generalization
- Let the students ask questions about the topic
- One student will give an element and let
another student write its electron configuration
F. Evaluation
Write the Electron configuration of the
following elements:
a. Au
b. Hg
c. Cu
d. C
e. Zn
G. Extend
- Write the definition of the following terms
a. Period
b. Group
c. Valence electron
d. Core electrons
Supply the following Electron A. Preliminary Activities
data from the electron Configuratio 1. Prayer
3 configuration such as: n 2. Checking of Attendance
period number, group 3. Classroom Rules
number, number of B. Recall
paired and unpaired - Let the students write the electron
electron/s, number of configuration of the following elements
valence electron/s, and 1. Co 2. Mn 3. Na
number of core C. Motivation
electrons D. Discussion
- Let the students identify the period number,
group number, paired and unpaired electrons,
number of valence electrons and number of
core electron of an element using its electron
configuration
The period of an element corresponds to the
principal quantum number of the valence shell.
The block of an element corresponds to the type
of orbital which receive the last electron.
The group of an element is predicted from the
number of electrons in the valence shell or/and
penultimate shell as follows:
a)For s block elements ,group number is equal to
the number of valence electrons.
b) For p block elements ,group number is equal to
10+number of electrons in the valence shell.
c)For d block elements ,group number is equal to
the number of electrons in a (n-1) sub shell + the
number of electrons in valence shell.
Generalization
- Let the students ask questions about the topic
- Let the students answer the questions given by
the teacher
What is the importance electron
configuration?
E. Evaluation
- The students will complete the table below.
F. Extend
- Let the students answer the following:
a. What is a Quantum Number?
b. What are the types of Quantum Number?
Define each.
Describe the set of Quantum A. Preliminary Activities
quantum numbers and Numbers 1. Prayer
4 complete the given set 2. Checking of Attendance
of quantum numbers for 3. Classroom Rules
each given element B. Recall
- Let the students complete the table below.
C. Motivation
- Let the students describe the energy of their
seatmate. They will rate it from 1-10. 1 being
the lowest and 10, the highest.
- Let the students discuss how they rate their
seatmate
D. Discussion
- Let the students define a quantum number
- Let the students identify the set of the quantum
numbers in each element.
Quantum Numbers - a value that is used when
describing the energy levels available to atoms and
molecules.
● Principal quantum number (n) – corresponds to
energy level numbers. It can have positive nonzero
integers as values, such as 1, 2, 3, and so on.
● Orbital quantum number (ℓ) – represents the
sublevel of a particular n, whose values are
integers from 0 to (n-1). Thus the orbital quantum
number (ℓ) describes the shape of the atomic
orbitals.
● Magnetic quantum number (mℓ) – describes the
orientation of the atomic orbital in space.
● Electron spin quantum number (ms) – describes
the spin direction of an electron. There are only
two possible values for the electron spin quantum
number, and these are + ½ (for clockwise spin)
and – ½ (counterclockwise spin)
E. Generalization
- Quantum numbers are important
because they can be used to determine the
electron configuration of an atom and the
probable location of the atom's electrons.
Quantum numbers are also used to
understand other characteristics of atoms,
such as ionization energy and the atomic
radius.
F. Evaluation
- Supply the missing parts of the table below.
G. Extend
- Let the students do the activity in “Let’s
Create” part.
Create a planetary model of the
atom. Use materials that can be
easily obtained from your home.
Recycled materials are always
welcome. Pay attention to the
details of your atomic model. Your
presentation will be rated based on
the following criteria:
Reflection
:
Prepared by: Checked:
RONELYN T. SOBRIANO MA. REGINA A. TAN
Subject Teacher Subject Coordinator
Noted by:
MARIA RHODORA P. ESPINO, Ed. D.
Principal III
You might also like
- SCIENCE 9 Second Quarter ModuleDocument41 pagesSCIENCE 9 Second Quarter ModuleKebu Yen78% (18)
- LE - GenPhysics2 - Week 1Document6 pagesLE - GenPhysics2 - Week 1Heilene Ethel AngcayaNo ratings yet
- Template - DLP - Atomic StructureDocument11 pagesTemplate - DLP - Atomic Structureargie joy marieNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 3Document2 pagesGrade 9 3king devesfruto0% (1)
- Introduction to Electromagnetic EngineeringFrom EverandIntroduction to Electromagnetic EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Q2 WLP Sci9 Week1Document7 pagesQ2 WLP Sci9 Week1Ronelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- DLL chemNOV15Document5 pagesDLL chemNOV15Rosallie Caaya-NuezNo ratings yet
- DLL chemNOV14Document5 pagesDLL chemNOV14Rosallie Caaya-NuezNo ratings yet
- WLP Sci9 Week3Document6 pagesWLP Sci9 Week3Ronelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- Final 7es Semi Detailed Lesson Plan GaringoDocument6 pagesFinal 7es Semi Detailed Lesson Plan GaringoJohnCrizNo ratings yet
- 2nd QTR MOD. 1 DLLDocument44 pages2nd QTR MOD. 1 DLLharold carbonelNo ratings yet
- DLL 1st Week Quarter 2Document5 pagesDLL 1st Week Quarter 2Anne McSciNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: First Row D-Block ElementsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: First Row D-Block ElementsMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Alejandria - Olive - COT - Genchem1 3rd QDocument3 pagesAlejandria - Olive - COT - Genchem1 3rd QOLIVE ALEJANDRIANo ratings yet
- WEEK-3-Q2-GEN CHEM-Nov 13-17-DLLDocument9 pagesWEEK-3-Q2-GEN CHEM-Nov 13-17-DLLJennette BelliotNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9-SY 2022-2023-Q2-W5-NOV 28-Dec 2,2022Document4 pagesSCIENCE 9-SY 2022-2023-Q2-W5-NOV 28-Dec 2,2022NOVA LESLIE AGAPAYNo ratings yet
- #4-Electronic Configuration-LpDocument13 pages#4-Electronic Configuration-LpirahlagguiNo ratings yet
- Dec 13-24Document3 pagesDec 13-24jezyl montealtoNo ratings yet
- SCI9Q2W1D2Document4 pagesSCI9Q2W1D2LA Lloyd Arvin MontesNo ratings yet
- WEEK-2-Q2-GEN CHEM-Nov 6-10-DLLDocument8 pagesWEEK-2-Q2-GEN CHEM-Nov 6-10-DLLJennette BelliotNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration Lesson 2Document9 pagesElectron Configuration Lesson 2brian catianNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Observation (G9)Document7 pagesLesson Plan For Observation (G9)Obrique AljanNo ratings yet
- Weekly Lesson LogDocument5 pagesWeekly Lesson LogCAROLYN CAYBOTNo ratings yet
- Weekly-Lesson-Log-SCIENCE 9Document7 pagesWeekly-Lesson-Log-SCIENCE 9CAROLYN CAYBOTNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Teacher's Weekly Learning PlanDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Teacher's Weekly Learning PlanmarjunampoNo ratings yet
- DLL in Science 9Document3 pagesDLL in Science 9Judith Abarquez100% (2)
- 2nd QTR MOD. 1 DLLDocument191 pages2nd QTR MOD. 1 DLLleiziah xyrille maturanNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 9 Week 1 Second QuarterDocument6 pagesDLL Science 9 Week 1 Second QuarterRosel Gamana LibradoNo ratings yet
- DLL chemNOV21Document3 pagesDLL chemNOV21Rosallie Caaya-NuezNo ratings yet
- COT1 2nd Quarter 2021-2022Document5 pagesCOT1 2nd Quarter 2021-2022Aszet Feraer San MiguelNo ratings yet
- Learning Area UNIT 1 Matter QUARTER Third Quarter MODULE 2 ATOMS: Atomic Structure Date Date Sections SectionsDocument37 pagesLearning Area UNIT 1 Matter QUARTER Third Quarter MODULE 2 ATOMS: Atomic Structure Date Date Sections SectionsAdrian Suladay100% (1)
- G8 Week 5Document6 pagesG8 Week 5PRIMELYN WAGASNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 4Document2 pagesGrade 9 4king devesfrutoNo ratings yet
- Westbury High School: Science Department Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesWestbury High School: Science Department Lesson PlanChrs TomNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week 1 Copy 1Document5 pagesQ2 Week 1 Copy 1Roberto Misola Jr.No ratings yet
- DLL Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesDLL Atomic StructureMichelle Baguio100% (2)
- Week 1 - LeDocument6 pagesWeek 1 - LeRodney BarbaNo ratings yet
- DLP On Periodic TableDocument4 pagesDLP On Periodic TableRachel AbrahamNo ratings yet
- DLL 2nd Week Quarter 2Document5 pagesDLL 2nd Week Quarter 2Anne McSciNo ratings yet
- Physical Science NOV. 13-15, 2019 DLPDocument2 pagesPhysical Science NOV. 13-15, 2019 DLPJedidiah Jara QuidetNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Day 1 Q3 Science 5Document7 pagesWeek 2 Day 1 Q3 Science 5Mary Cristine DuranNo ratings yet
- DLL chemNOV20Document3 pagesDLL chemNOV20Rosallie Caaya-NuezNo ratings yet
- G S Electron-ConfigurationDocument7 pagesG S Electron-ConfigurationShyra May GalendezNo ratings yet
- Science 9 WHLP q2 Week1Document2 pagesScience 9 WHLP q2 Week1Glynnise DalitNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science VDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science VJhezmae Rose Pasion AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Wave Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic Wave Lesson Planjose miranda100% (1)
- November 20 24Document5 pagesNovember 20 24ALIZA MARIE SAGUNNo ratings yet
- 2nd QTR MOD. 1 DLLDocument39 pages2nd QTR MOD. 1 DLLanewflorescaNo ratings yet
- Phy Sci LC4Document5 pagesPhy Sci LC4John Nerlo DequiñaNo ratings yet
- DLL - G8 Science - Q3 - F2FDocument2 pagesDLL - G8 Science - Q3 - F2FRAMIR BECOYNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Plan: Department of EducationDocument6 pagesWeekly Learning Plan: Department of EducationRonald ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Riessa Jane Cañete's LPDocument4 pagesRiessa Jane Cañete's LPRjane CañeteNo ratings yet
- Ii. Content Iii. Learning Resources: Pencil/ Pen Crayon or Colored PencilsDocument2 pagesIi. Content Iii. Learning Resources: Pencil/ Pen Crayon or Colored Pencilsjanice alquizarNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The Philippinesjerome100% (1)
- Science 9-Sy 2022-2023-Q2-W3-Nov 14-18,2022Document4 pagesScience 9-Sy 2022-2023-Q2-W3-Nov 14-18,2022NOVA LESLIE AGAPAYNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 9Document6 pagesDLL Science 9May Shyll BugtaiNo ratings yet
- DLL chemNOV16Document3 pagesDLL chemNOV16Rosallie Caaya-NuezNo ratings yet
- DLL ScienceDocument35 pagesDLL ScienceJesson ClutarioNo ratings yet
- LP in Electronic Structure of Matter - 121127Document17 pagesLP in Electronic Structure of Matter - 121127Xandria SabrosoNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Partial Differential Equations: Second EditionFrom EverandIntroduction to Partial Differential Equations: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Q2 WLP Sci9 Week1Document7 pagesQ2 WLP Sci9 Week1Ronelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- WLP Sci9 Week3Document6 pagesWLP Sci9 Week3Ronelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- Science9 Q2 TosDocument2 pagesScience9 Q2 TosRonelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- R.sobriano WLP Sci9 Week 8Document4 pagesR.sobriano WLP Sci9 Week 8Ronelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- Q2 PT Scie9 Key To CorrectionDocument1 pageQ2 PT Scie9 Key To CorrectionRonelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- Q2 PT Scie9Document3 pagesQ2 PT Scie9Ronelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- R.sobriano WLP Sci9 Week 9Document3 pagesR.sobriano WLP Sci9 Week 9Ronelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- R.sobriano WLP Sci9 Week 5Document5 pagesR.sobriano WLP Sci9 Week 5Ronelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- R.sobriano WLP Sci9 Week 10Document2 pagesR.sobriano WLP Sci9 Week 10Ronelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- R.sobriano WLP Sci9 Week 2Document5 pagesR.sobriano WLP Sci9 Week 2Ronelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- R.sobriano WLP Sci9 Week 6Document4 pagesR.sobriano WLP Sci9 Week 6Ronelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- Wlp-Sci9-Week 7Document4 pagesWlp-Sci9-Week 7Ronelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- R.sobriano WLP Sci9 Week 4Document5 pagesR.sobriano WLP Sci9 Week 4Ronelyn SobrianoNo ratings yet
- Punjab Police SI Intelligence Officer Model PapersDocument33 pagesPunjab Police SI Intelligence Officer Model Papershk3987gmailcomNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 Solutions - ECE6553, Spring 2011: H U T H U TDocument2 pagesHomework 1 Solutions - ECE6553, Spring 2011: H U T H U TmusalmanmusalmanNo ratings yet
- P102LN2021BDocument25 pagesP102LN2021BJeji HirboraNo ratings yet
- Efficient Calculation of Clebsch-Gordan CoefficientsDocument5 pagesEfficient Calculation of Clebsch-Gordan CoefficientsweylguyNo ratings yet
- The Rotation of Logarithmic-Spiral-Shaped GearsDocument3 pagesThe Rotation of Logarithmic-Spiral-Shaped GearsAdam Jaffe100% (1)
- The Invariance of Spacetime IntervalDocument11 pagesThe Invariance of Spacetime IntervalGeorge Mpantes mathematics teacherNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-HSPTA-2.1 Electric Charges and Fields 2021-FDocument17 pagesHsslive-HSPTA-2.1 Electric Charges and Fields 2021-FBhagyaNo ratings yet
- Acceleration: Sunil Kumar SinghDocument6 pagesAcceleration: Sunil Kumar SinghphultushiblsNo ratings yet
- Midterm Review 3 ANSWERSDocument4 pagesMidterm Review 3 ANSWERSar02No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument17 pagesPhysics ProjectPrerana Chaithra0% (1)
- Lecture 01 Laser & OpticsDocument2 pagesLecture 01 Laser & OpticsAsad RazaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document10 pagesLecture 3Charitha Prasad LiyanagamaNo ratings yet
- Kresse Vasp PhononDocument54 pagesKresse Vasp PhononNamrata JaykhedkarNo ratings yet
- Molecular SymmetryDocument2 pagesMolecular SymmetryRD's Academy100% (1)
- Lesson 1 - Implicit DifferentiationDocument17 pagesLesson 1 - Implicit DifferentiationElvis Kadagi0% (1)
- Solutions For Homework Set 7: X Z X I (K X+K Z)Document3 pagesSolutions For Homework Set 7: X Z X I (K X+K Z)rahul krNo ratings yet
- Hartree Fock TheoryDocument56 pagesHartree Fock TheoryAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Laplace UpdateDocument17 pages2.1 Laplace UpdateNasir AiyubNo ratings yet
- Gathering Kurdish Mathematics Researchers: Meeting With Caucher BirkarDocument1 pageGathering Kurdish Mathematics Researchers: Meeting With Caucher BirkarMuhammed FuadNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Quantum MechanicsDocument41 pagesUnit 1 Quantum MechanicsVimala H CNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Ex 4.1Document6 pagesChapter 4-Ex 4.1FAISAL RAHIMNo ratings yet
- Advanced Calculus - Department of Mathematics - Harvard University (PDFDrive) - CompressedDocument592 pagesAdvanced Calculus - Department of Mathematics - Harvard University (PDFDrive) - CompressedDavid ReyesNo ratings yet
- 09 ps2Document2 pages09 ps2Ismady SihombingNo ratings yet
- 3-6 Practice WorksheetDocument1 page3-6 Practice WorksheetantonylukNo ratings yet
- Green's Theorem ExamplesDocument4 pagesGreen's Theorem ExamplesFahad ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Physics For High School Students PDFDocument5 pagesLagrangian and Hamiltonian Physics For High School Students PDFJaimeNo ratings yet
- 2011-2 QT Siesta Tutorial-1Document15 pages2011-2 QT Siesta Tutorial-1Ozan ArıNo ratings yet
- Special Determinants and Matrices and Their Use in EconomicsDocument30 pagesSpecial Determinants and Matrices and Their Use in Economicstohmina tultuliNo ratings yet
- 2b Maths ImportantDocument2 pages2b Maths ImportantSyed Salman80% (20)
- Solutions Manual For Introduction To RobDocument10 pagesSolutions Manual For Introduction To RobAndy Tan Fu YangNo ratings yet