Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8th Lecture
8th Lecture
Uploaded by
محمد عدنان مصطفىCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- En 14582Document33 pagesEn 14582Vladimir Krzalic100% (1)
- Lab Report Experiment 4 - CHE145Document3 pagesLab Report Experiment 4 - CHE145Nur Aqilah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Lab Flow SheetDocument2 pagesLab Flow SheetRyan LazatinNo ratings yet
- 9th LectureDocument2 pages9th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 10th LectureDocument2 pages10th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 4th LectureDocument4 pages4th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ejercicios de Estudio Resultante de Un Sistema de Fuerzas Concurrentes en El Espacio PDFDocument3 pages1.2 Ejercicios de Estudio Resultante de Un Sistema de Fuerzas Concurrentes en El Espacio PDFAndrésDíazNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Force System Cont 2Document5 pagesModule 4 Force System Cont 2Johannes Frucz RadaNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions Subject-Physics Class-Xii Adesh Patel - PGT (Physics)Document107 pagesFrequently Asked Questions Subject-Physics Class-Xii Adesh Patel - PGT (Physics)Shreya SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit - I (Deflections of Determinate Structures) : Classical Methods Ce6501-Structural AnalysisDocument21 pagesUnit - I (Deflections of Determinate Structures) : Classical Methods Ce6501-Structural AnalysisAnonymous SEDun6PWNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04.3Document6 pagesLesson 04.3Patrick Jamiel TorresNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04.1Document9 pagesLesson 04.1Patrick Jamiel TorresNo ratings yet
- 1-Concept of Stress and Strain PDFDocument29 pages1-Concept of Stress and Strain PDFMohamad Zaid83% (6)
- 6th LectureDocument6 pages6th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 5th LectureDocument4 pages5th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- Ia - 1Document3 pagesIa - 1krishnamoorthipsgNo ratings yet
- QB-em-1 - Mem202Document19 pagesQB-em-1 - Mem202rahuljaiswal1931No ratings yet
- Problems in Unit - 1Document25 pagesProblems in Unit - 1Prakasini SakthivelNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Mechanics J L MariamDocument75 pagesSolution Manual Mechanics J L MariamKhalid Yousaf86% (7)
- Engineering Mechanics Static PDFDocument7 pagesEngineering Mechanics Static PDFVeronica ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 1090 997Document7 pagesPaper 1 1090 997IlYas NimiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.c (Equilibrium in Plane 2D)Document27 pagesChapter 2.c (Equilibrium in Plane 2D)LogarithemNo ratings yet
- Module 02: Approximate Analysis of Indeterminate Structures: Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO's)Document41 pagesModule 02: Approximate Analysis of Indeterminate Structures: Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO's)Mac KYNo ratings yet
- PHN001 - Unit1st - Assisgnment1st - 2022 2Document12 pagesPHN001 - Unit1st - Assisgnment1st - 2022 2harshitaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material-Shear Force and Bending MomentsDocument25 pagesStrength of Material-Shear Force and Bending MomentszakeriyaNo ratings yet
- Pretest Mechanics StaticsDocument20 pagesPretest Mechanics Staticsdarlene zaraNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering ProjectDocument11 pagesControl Engineering Projectglennmarc.mejascoNo ratings yet
- EngineeringMechanics by J L Meriam 6th Solutions by Khalid YousafDocument70 pagesEngineeringMechanics by J L Meriam 6th Solutions by Khalid YousafKhalid Yousaf84% (25)
- s2 Bending MomentDocument22 pagess2 Bending MomentismailNo ratings yet
- Chapter III A Equilibrium 2D: Engineering MechanicsDocument85 pagesChapter III A Equilibrium 2D: Engineering MechanicsYue FeiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics-Statics ReferencesDocument92 pagesEngineering Mechanics-Statics Referencesfazeel100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Forces and EquilibriumDocument53 pagesChapter 2 Forces and EquilibriumvinoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics VectorsDocument12 pagesEngineering Mechanics VectorsMankush Jain100% (1)
- Electric Charges 2Document7 pagesElectric Charges 2Namita SinhaNo ratings yet
- 3) Displacement Method of Analysis: Moment Distribution: General Principles and DefinitionsDocument14 pages3) Displacement Method of Analysis: Moment Distribution: General Principles and DefinitionsAyad SlabyNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of 2d Force System 20-21-1Document34 pagesEquilibrium of 2d Force System 20-21-1Hemant JadhaoNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Force SystemsDocument8 pagesEquilibrium of Force SystemsIra James AbanesNo ratings yet
- Topic1 2to1 4Document35 pagesTopic1 2to1 4Sesha Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- Equations of Equilibrium (2D) : 440:221 Intro To Engineering Mechanics: StaticsDocument21 pagesEquations of Equilibrium (2D) : 440:221 Intro To Engineering Mechanics: StaticsVatsal PandyaNo ratings yet
- 16th Week Review and Preparation For Final ExaminationDocument107 pages16th Week Review and Preparation For Final ExaminationNguyênNguyễnAnNo ratings yet
- 1-1 Stress Analysis and DesignDocument25 pages1-1 Stress Analysis and Design陈韦权No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Electric FieldDocument19 pagesLesson 5 - Electric FieldGino CruzNo ratings yet
- Applied Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 1Document10 pagesApplied Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 1keith magakaNo ratings yet
- Fem Mid 1 Question BankDocument2 pagesFem Mid 1 Question BankallakagopichandNo ratings yet
- Tut 1-5Document7 pagesTut 1-5Dipanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Assignment - 1Document3 pagesMechanics Assignment - 1karanshah19112005No ratings yet
- A1786119601 - 16379 - 30 - 2019 - T1.2 Unit 1 Moment of ForceDocument5 pagesA1786119601 - 16379 - 30 - 2019 - T1.2 Unit 1 Moment of ForceSHIVAM NANDANo ratings yet
- Lab Manual FormatDocument22 pagesLab Manual FormatSahil PatelNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics 1Document57 pagesEngineering Mechanics 1Dahlak AfricaNo ratings yet
- Shear Force and Bending MomentssDocument32 pagesShear Force and Bending Momentssمحمد شمسNo ratings yet
- Examples 7:: Chapter Three EquilibriumDocument9 pagesExamples 7:: Chapter Three EquilibriumReafe Carla Bustamante MabalotNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 6th Edition: CHAPTER 12Document22 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers 6th Edition: CHAPTER 12Fredy Arana Rodríguez100% (1)
- Paper 12 21843 997Document5 pagesPaper 12 21843 997Ali Essa khNo ratings yet
- Solved QP-Mechanics-Ktunote - in PDFDocument16 pagesSolved QP-Mechanics-Ktunote - in PDFThaanya sNo ratings yet
- Design of Beam ColumnDocument8 pagesDesign of Beam ColumnRan YahyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Normal Stress Under Axial Loading PDFDocument12 pagesLecture 2-Normal Stress Under Axial Loading PDFomed RekaniNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and FieldsDocument33 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and FieldsPrakhar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11From EverandIntroduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11No ratings yet
- 13th LectureDocument4 pages13th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 10th LectureDocument2 pages10th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 7th LectureDocument3 pages7th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 9th LectureDocument2 pages9th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 6th LectureDocument6 pages6th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 4th LectureDocument4 pages4th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 5th LectureDocument4 pages5th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 0 Lecture 0Document63 pages0 Lecture 0محمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 1st LectureDocument7 pages1st Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- ELA Heat of SolutionDocument15 pagesELA Heat of SolutionJim100% (2)
- ASTM C813-90 Standard Test Method For Hydrophobic Contamination On Glass by Contact Angle MeasurementDocument3 pagesASTM C813-90 Standard Test Method For Hydrophobic Contamination On Glass by Contact Angle MeasurementgustavoesanchezNo ratings yet
- Electrocoagulation Process For Stevia Extract Treatment PDFDocument11 pagesElectrocoagulation Process For Stevia Extract Treatment PDFMatichon ChamchooklinNo ratings yet
- 2021 Article 419Document27 pages2021 Article 419Parsa PourbakhtNo ratings yet
- Report Lab Experiment 2 (Plastic Limit & Liquid Limit) Group 3Document17 pagesReport Lab Experiment 2 (Plastic Limit & Liquid Limit) Group 3NURFARZANA ABDUL RAZAK KTNNo ratings yet
- Percentage Composition and Empirical FormulaDocument36 pagesPercentage Composition and Empirical FormulaNeeta PandeyNo ratings yet
- Sarnacol®-2142 S: Product Data SheetDocument3 pagesSarnacol®-2142 S: Product Data SheetAhmed MontashNo ratings yet
- Check List of Organic Chemistry Topics For B17CA and B17CB AppendedDocument6 pagesCheck List of Organic Chemistry Topics For B17CA and B17CB AppendedSarah FeyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class Xii Blue Prints For Board Exam 2023Document1 pageChemistry Class Xii Blue Prints For Board Exam 2023aniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- Empirical and Molecular Formulae 1Document4 pagesEmpirical and Molecular Formulae 1mybusinesscompany781No ratings yet
- JAC604Document2 pagesJAC604Mohd Afiq AminNo ratings yet
- SP7021M00U24 000 A PDFDocument3 pagesSP7021M00U24 000 A PDFPedro Casimiro GámizNo ratings yet
- Product Brochure Aurubis Shapes - 2014 - enDocument10 pagesProduct Brochure Aurubis Shapes - 2014 - enTrầnHữuHòaNo ratings yet
- Coating Failures - Causes, Identification, and AnalysisDocument36 pagesCoating Failures - Causes, Identification, and AnalysisSUBODH100% (1)
- Springer - 2001 - J. - Electrochem. - Soc. - 148 - A11Document14 pagesSpringer - 2001 - J. - Electrochem. - Soc. - 148 - A11Faseeh KKNo ratings yet
- Polyester ValsparDocument2 pagesPolyester ValsparsuksesNo ratings yet
- HCU Chemistry 2011-2017 - Career EndeavourDocument78 pagesHCU Chemistry 2011-2017 - Career EndeavourSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Manual ViewerDocument12 pagesManual ViewerCeleynes RTNo ratings yet
- Absorbent GauzeDocument2 pagesAbsorbent GauzeRaquel BcNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Section-1Document6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Section-1dinesh kumarNo ratings yet
- A Level ChemistryDocument302 pagesA Level ChemistryStuart DawsonNo ratings yet
- Improving Gas Dehydration With Preinhibited GlycolDocument5 pagesImproving Gas Dehydration With Preinhibited Glycol1412091090No ratings yet
- TOM Chi-All Are ConnectedDocument15 pagesTOM Chi-All Are ConnectedDebasish DeyNo ratings yet
- TD - Rhenus LKZ 2Document1 pageTD - Rhenus LKZ 2Teknik LasallefoodNo ratings yet
- CN113321577 Preparation Method of 5-Bromo-2-Chlorobenzoic AcidDocument7 pagesCN113321577 Preparation Method of 5-Bromo-2-Chlorobenzoic AcidrgNo ratings yet
- Post Treatment of Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet-Chromating, Phosphating and Other Alternative Passivation TechnologiesDocument22 pagesPost Treatment of Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet-Chromating, Phosphating and Other Alternative Passivation TechnologiesAmirtharaaj VijayanNo ratings yet
- Special StainsDocument18 pagesSpecial StainsJil BellaNo ratings yet
8th Lecture
8th Lecture
Uploaded by
محمد عدنان مصطفىOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8th Lecture
8th Lecture
Uploaded by
محمد عدنان مصطفىCopyright:
Available Formats
Al-Najaf Technical Institute Engineering Mechanics
St
Civil Techniques Department 1 . Academic year, 2020-2021
Equilibrium of force system ﺗﻮازن اﻟﻘﻮى
In static, a body is said to be in equilibrium when the force system acting upon it has a
zero resultant. When a body is in equilibrium, the resultant of all forces acting on it is
zero. Thus, the resultant force Rand the resultant couple Mare both zero, and we have
the equilibrium equations.
. ﯾﻘﺎل ﻟﻼﺟﺴﺎم ﻓﻲ ﺣﺎﻟﺔ اﻟﺴﻜﻮن ﺑﺎﻧﮭﺎ ﻓﻲ ﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﺗﻮازن ﻋﻨﻤﺎ ﺗﻜﻮن ﻣﺤﺼﻠﺔ اﻟﻘﻮى اﻟﻤﺆﺛﺮة ﻋﻠﯿﮭﺎ ﻣﺴﺎوﯾﺔ ﻟﻠﺼﻔﺮ
وﺗﻜﻮن ھﺬه اﻻﺟﺴﺎم ﺧﺎﺿﻌﺔ ﻟﻤﻌﺎدﻟﺘﻲ اﻟﺘﻮازن
R = ΣF=0
M =ΣM=0
These requirements are both necessary and sufficient conditions for equilibrium.
Free Body Diagram (F B D)
Lecturer : Hussein A. Jaaz 27
Al-Najaf Technical Institute Engineering Mechanics
St
Civil Techniques Department 1 . Academic year, 2020-2021
Lecturer : Hussein A. Jaaz 28
Al-Najaf Technical Institute Engineering Mechanics
St
Civil Techniques Department 1 . Academic year, 2020-2021
Lecturer : Hussein A. Jaaz 30 Building and construction Engineering Branch
Al-Najaf Technical Institute Engineering Mechanics
St
Ci
vil Techniques Department 1 . Academic year, 2020-2021
Example: Determine the magnitude T of
the tension in the supporting cable and the
magnitude of the force on the pin at A for the
jib crane shown. The beam AB is a standard
0.5m I-beam with a mass of 95 kg/m length.
اﻟﻤﻄﻠﻮب ﺣﺴﺎب ﻗﻮة اﻟﺸﺪ ﻓﻲ اﻟﺴﻠﻚ وﻗﻮة رد اﻟﻔﻌﻞ ﻓﻲ ﻧﻘﻄﺔ
A اﻻﺳﻨﺎد
Solution:
Mass = 95 kg/m * 5 m = 475 kg
W= mass * g = 475 kg * 9.81 N/kg = 4660 N
= 4.66 KN
+↻ ∑ 𝑀𝐴 = 0
TCos25°*(0.25)+TSin25°
*(5-0.12)-10*(5-0.12-1.5)-4.66(2.5-0.12)=0
T=19.61kN
+→ ∑ Fx = 0 → Ax -19.61Cos25°=0
Ax =17.77kN
+↑ ∑ Fy = 0 → Ay +19.61*Sin25°-4.66-10=0
Ay =6.37kN
A = √Ax 2 + Ay 2 → A = √17.772 + 6.372
A = 18.88 kN
Lecturer : Hussein A. Jaaz 32 Building and construction Engineering Branch
Al-Najaf Technical Institute Engineering Mechanics
St
Civil Techniques Department 1 . Academic year, 2020-2021
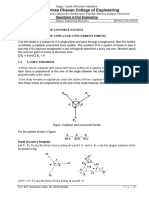
Example: The system of knotted cords
showing in figure support the
indicated weights. Compute the tensile
force in each cord.
اﻟﻤﻄﻠﻮب ﺣﺴﺎب ﻛﻞ ﻗﻮى اﻟﺸﺪ ﻟﻜﻞ ﺣﺒﻞ ﻓﻲ اﻟﻤﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ
Solution:
The lower part:
+→ΣFx=0
DSin75∘- CSin30∘=0
D=0.5176C …….1
+↑ΣFy=0
DCos75∘+CCos30∘-400=0 ….2
Sub (1)in (2)
(0.5176C)Cos75∘+CCos30∘-400=0
C=400 lb
D=0.5176(400)
D=207.06 lb
The upper part:
+↑ΣFy=0
BSin45∘-300-CCos30∘=0
BSin45∘=300+400Cos30∘
B=914.16 lb
+→ΣFx=0
BCos45∘+Csin30∘-A=0
A=914.16Cos45∘+400Sin30∘
Free-body diagram
A=846.41 lb
Lecturer : Hussein A. Jaaz 33 Building and construction Engineering Branch
Al-Najaf Technical Institute Engineering Mechanics
St
Civil Techniques Department 1 . Academic year, 2020-2021
Example: Cords are passing through
frictionless pulleys to weights of 200 lb
and 400 lb and tensioned to the weighting
cylinder. Determine the angle θ and the
normal pressure N between the cylinders
and the smooth horizontal surface.
Solution:
+→ΣFx=0
400Cosθ-200=0
Cosθ=0.5 → θ=60∘
N+400Sinθ-800=0
N+400Sin60∘=800 → N=453.59 lb
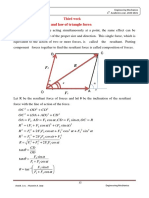
Example : Two weightless bars pinned
together and support a load of 35 kN.
Determine the forces P and F acting
respectively along bars AB and AC that
maintain equilibrium of pin A.
Solution:
+→ΣFx=0
5 2
-F( 41
)+P( )=0
√ √13
F=0.7104P ….1
+↑ΣFy=0
3 4
P( )-F( )-35=0
√13 √41
3 4
P( )=F( )+35
√13 √41
0.3883P=35 ….2 sub(1) in (2)
P=90.14 kN
F=0.7104(90.14) → F=64.03 kN
Lecturer : Hussein A. Jaaz 34
You might also like
- En 14582Document33 pagesEn 14582Vladimir Krzalic100% (1)
- Lab Report Experiment 4 - CHE145Document3 pagesLab Report Experiment 4 - CHE145Nur Aqilah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Lab Flow SheetDocument2 pagesLab Flow SheetRyan LazatinNo ratings yet
- 9th LectureDocument2 pages9th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 10th LectureDocument2 pages10th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 4th LectureDocument4 pages4th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ejercicios de Estudio Resultante de Un Sistema de Fuerzas Concurrentes en El Espacio PDFDocument3 pages1.2 Ejercicios de Estudio Resultante de Un Sistema de Fuerzas Concurrentes en El Espacio PDFAndrésDíazNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Force System Cont 2Document5 pagesModule 4 Force System Cont 2Johannes Frucz RadaNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions Subject-Physics Class-Xii Adesh Patel - PGT (Physics)Document107 pagesFrequently Asked Questions Subject-Physics Class-Xii Adesh Patel - PGT (Physics)Shreya SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit - I (Deflections of Determinate Structures) : Classical Methods Ce6501-Structural AnalysisDocument21 pagesUnit - I (Deflections of Determinate Structures) : Classical Methods Ce6501-Structural AnalysisAnonymous SEDun6PWNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04.3Document6 pagesLesson 04.3Patrick Jamiel TorresNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04.1Document9 pagesLesson 04.1Patrick Jamiel TorresNo ratings yet
- 1-Concept of Stress and Strain PDFDocument29 pages1-Concept of Stress and Strain PDFMohamad Zaid83% (6)
- 6th LectureDocument6 pages6th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 5th LectureDocument4 pages5th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- Ia - 1Document3 pagesIa - 1krishnamoorthipsgNo ratings yet
- QB-em-1 - Mem202Document19 pagesQB-em-1 - Mem202rahuljaiswal1931No ratings yet
- Problems in Unit - 1Document25 pagesProblems in Unit - 1Prakasini SakthivelNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Mechanics J L MariamDocument75 pagesSolution Manual Mechanics J L MariamKhalid Yousaf86% (7)
- Engineering Mechanics Static PDFDocument7 pagesEngineering Mechanics Static PDFVeronica ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 1090 997Document7 pagesPaper 1 1090 997IlYas NimiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.c (Equilibrium in Plane 2D)Document27 pagesChapter 2.c (Equilibrium in Plane 2D)LogarithemNo ratings yet
- Module 02: Approximate Analysis of Indeterminate Structures: Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO's)Document41 pagesModule 02: Approximate Analysis of Indeterminate Structures: Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO's)Mac KYNo ratings yet
- PHN001 - Unit1st - Assisgnment1st - 2022 2Document12 pagesPHN001 - Unit1st - Assisgnment1st - 2022 2harshitaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material-Shear Force and Bending MomentsDocument25 pagesStrength of Material-Shear Force and Bending MomentszakeriyaNo ratings yet
- Pretest Mechanics StaticsDocument20 pagesPretest Mechanics Staticsdarlene zaraNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering ProjectDocument11 pagesControl Engineering Projectglennmarc.mejascoNo ratings yet
- EngineeringMechanics by J L Meriam 6th Solutions by Khalid YousafDocument70 pagesEngineeringMechanics by J L Meriam 6th Solutions by Khalid YousafKhalid Yousaf84% (25)
- s2 Bending MomentDocument22 pagess2 Bending MomentismailNo ratings yet
- Chapter III A Equilibrium 2D: Engineering MechanicsDocument85 pagesChapter III A Equilibrium 2D: Engineering MechanicsYue FeiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics-Statics ReferencesDocument92 pagesEngineering Mechanics-Statics Referencesfazeel100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Forces and EquilibriumDocument53 pagesChapter 2 Forces and EquilibriumvinoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics VectorsDocument12 pagesEngineering Mechanics VectorsMankush Jain100% (1)
- Electric Charges 2Document7 pagesElectric Charges 2Namita SinhaNo ratings yet
- 3) Displacement Method of Analysis: Moment Distribution: General Principles and DefinitionsDocument14 pages3) Displacement Method of Analysis: Moment Distribution: General Principles and DefinitionsAyad SlabyNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of 2d Force System 20-21-1Document34 pagesEquilibrium of 2d Force System 20-21-1Hemant JadhaoNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Force SystemsDocument8 pagesEquilibrium of Force SystemsIra James AbanesNo ratings yet
- Topic1 2to1 4Document35 pagesTopic1 2to1 4Sesha Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- Equations of Equilibrium (2D) : 440:221 Intro To Engineering Mechanics: StaticsDocument21 pagesEquations of Equilibrium (2D) : 440:221 Intro To Engineering Mechanics: StaticsVatsal PandyaNo ratings yet
- 16th Week Review and Preparation For Final ExaminationDocument107 pages16th Week Review and Preparation For Final ExaminationNguyênNguyễnAnNo ratings yet
- 1-1 Stress Analysis and DesignDocument25 pages1-1 Stress Analysis and Design陈韦权No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Electric FieldDocument19 pagesLesson 5 - Electric FieldGino CruzNo ratings yet
- Applied Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 1Document10 pagesApplied Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 1keith magakaNo ratings yet
- Fem Mid 1 Question BankDocument2 pagesFem Mid 1 Question BankallakagopichandNo ratings yet
- Tut 1-5Document7 pagesTut 1-5Dipanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Assignment - 1Document3 pagesMechanics Assignment - 1karanshah19112005No ratings yet
- A1786119601 - 16379 - 30 - 2019 - T1.2 Unit 1 Moment of ForceDocument5 pagesA1786119601 - 16379 - 30 - 2019 - T1.2 Unit 1 Moment of ForceSHIVAM NANDANo ratings yet
- Lab Manual FormatDocument22 pagesLab Manual FormatSahil PatelNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics 1Document57 pagesEngineering Mechanics 1Dahlak AfricaNo ratings yet
- Shear Force and Bending MomentssDocument32 pagesShear Force and Bending Momentssمحمد شمسNo ratings yet
- Examples 7:: Chapter Three EquilibriumDocument9 pagesExamples 7:: Chapter Three EquilibriumReafe Carla Bustamante MabalotNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 6th Edition: CHAPTER 12Document22 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers 6th Edition: CHAPTER 12Fredy Arana Rodríguez100% (1)
- Paper 12 21843 997Document5 pagesPaper 12 21843 997Ali Essa khNo ratings yet
- Solved QP-Mechanics-Ktunote - in PDFDocument16 pagesSolved QP-Mechanics-Ktunote - in PDFThaanya sNo ratings yet
- Design of Beam ColumnDocument8 pagesDesign of Beam ColumnRan YahyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Normal Stress Under Axial Loading PDFDocument12 pagesLecture 2-Normal Stress Under Axial Loading PDFomed RekaniNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and FieldsDocument33 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and FieldsPrakhar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11From EverandIntroduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11No ratings yet
- 13th LectureDocument4 pages13th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 10th LectureDocument2 pages10th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 7th LectureDocument3 pages7th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 9th LectureDocument2 pages9th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 6th LectureDocument6 pages6th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 4th LectureDocument4 pages4th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 5th LectureDocument4 pages5th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 0 Lecture 0Document63 pages0 Lecture 0محمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 1st LectureDocument7 pages1st Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- ELA Heat of SolutionDocument15 pagesELA Heat of SolutionJim100% (2)
- ASTM C813-90 Standard Test Method For Hydrophobic Contamination On Glass by Contact Angle MeasurementDocument3 pagesASTM C813-90 Standard Test Method For Hydrophobic Contamination On Glass by Contact Angle MeasurementgustavoesanchezNo ratings yet
- Electrocoagulation Process For Stevia Extract Treatment PDFDocument11 pagesElectrocoagulation Process For Stevia Extract Treatment PDFMatichon ChamchooklinNo ratings yet
- 2021 Article 419Document27 pages2021 Article 419Parsa PourbakhtNo ratings yet
- Report Lab Experiment 2 (Plastic Limit & Liquid Limit) Group 3Document17 pagesReport Lab Experiment 2 (Plastic Limit & Liquid Limit) Group 3NURFARZANA ABDUL RAZAK KTNNo ratings yet
- Percentage Composition and Empirical FormulaDocument36 pagesPercentage Composition and Empirical FormulaNeeta PandeyNo ratings yet
- Sarnacol®-2142 S: Product Data SheetDocument3 pagesSarnacol®-2142 S: Product Data SheetAhmed MontashNo ratings yet
- Check List of Organic Chemistry Topics For B17CA and B17CB AppendedDocument6 pagesCheck List of Organic Chemistry Topics For B17CA and B17CB AppendedSarah FeyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class Xii Blue Prints For Board Exam 2023Document1 pageChemistry Class Xii Blue Prints For Board Exam 2023aniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- Empirical and Molecular Formulae 1Document4 pagesEmpirical and Molecular Formulae 1mybusinesscompany781No ratings yet
- JAC604Document2 pagesJAC604Mohd Afiq AminNo ratings yet
- SP7021M00U24 000 A PDFDocument3 pagesSP7021M00U24 000 A PDFPedro Casimiro GámizNo ratings yet
- Product Brochure Aurubis Shapes - 2014 - enDocument10 pagesProduct Brochure Aurubis Shapes - 2014 - enTrầnHữuHòaNo ratings yet
- Coating Failures - Causes, Identification, and AnalysisDocument36 pagesCoating Failures - Causes, Identification, and AnalysisSUBODH100% (1)
- Springer - 2001 - J. - Electrochem. - Soc. - 148 - A11Document14 pagesSpringer - 2001 - J. - Electrochem. - Soc. - 148 - A11Faseeh KKNo ratings yet
- Polyester ValsparDocument2 pagesPolyester ValsparsuksesNo ratings yet
- HCU Chemistry 2011-2017 - Career EndeavourDocument78 pagesHCU Chemistry 2011-2017 - Career EndeavourSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Manual ViewerDocument12 pagesManual ViewerCeleynes RTNo ratings yet
- Absorbent GauzeDocument2 pagesAbsorbent GauzeRaquel BcNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Section-1Document6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Section-1dinesh kumarNo ratings yet
- A Level ChemistryDocument302 pagesA Level ChemistryStuart DawsonNo ratings yet
- Improving Gas Dehydration With Preinhibited GlycolDocument5 pagesImproving Gas Dehydration With Preinhibited Glycol1412091090No ratings yet
- TOM Chi-All Are ConnectedDocument15 pagesTOM Chi-All Are ConnectedDebasish DeyNo ratings yet
- TD - Rhenus LKZ 2Document1 pageTD - Rhenus LKZ 2Teknik LasallefoodNo ratings yet
- CN113321577 Preparation Method of 5-Bromo-2-Chlorobenzoic AcidDocument7 pagesCN113321577 Preparation Method of 5-Bromo-2-Chlorobenzoic AcidrgNo ratings yet
- Post Treatment of Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet-Chromating, Phosphating and Other Alternative Passivation TechnologiesDocument22 pagesPost Treatment of Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet-Chromating, Phosphating and Other Alternative Passivation TechnologiesAmirtharaaj VijayanNo ratings yet
- Special StainsDocument18 pagesSpecial StainsJil BellaNo ratings yet