Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9th Lecture
9th Lecture
Uploaded by
محمد عدنان مصطفى0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesThe document provides examples and solutions for calculating forces in systems involving cords, weights, and bars. The first example calculates the tensile forces in cords supporting different weights. The second determines the angle and normal force between cylinders supporting hanging weights. The third finds the forces along bars pinned together and supporting a 35 kN load.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides examples and solutions for calculating forces in systems involving cords, weights, and bars. The first example calculates the tensile forces in cords supporting different weights. The second determines the angle and normal force between cylinders supporting hanging weights. The third finds the forces along bars pinned together and supporting a 35 kN load.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pages9th Lecture
9th Lecture
Uploaded by
محمد عدنان مصطفىThe document provides examples and solutions for calculating forces in systems involving cords, weights, and bars. The first example calculates the tensile forces in cords supporting different weights. The second determines the angle and normal force between cylinders supporting hanging weights. The third finds the forces along bars pinned together and supporting a 35 kN load.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Al-Najaf Technical Institute Engineering Mechanics
St
Civil Techniques Department 1 . Academic year, 2020-2021
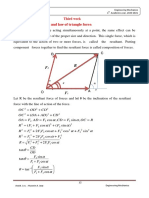
Example: The system of knotted cords
showing in figure support the
indicated weights. Compute the tensile
force in each cord.
اﻟﻤﻄﻠﻮب ﺣﺴﺎب ﻛﻞ ﻗﻮى اﻟﺸﺪ ﻟﻜﻞ ﺣﺒﻞ ﻓﻲ اﻟﻤﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ
Solution:
The lower part:
+→ΣFx=0
DSin75∘- CSin30∘=0
D=0.5176C …….1
+↑ΣFy=0
DCos75∘+CCos30∘-400=0 ….2
Sub (1)in (2)
(0.5176C)Cos75∘+CCos30∘-400=0
C=400 lb
D=0.5176(400)
D=207.06 lb
The upper part:
+↑ΣFy=0
BSin45∘-300-CCos30∘=0
BSin45∘=300+400Cos30∘
B=914.16 lb
+→ΣFx=0
BCos45∘+Csin30∘-A=0
A=914.16Cos45∘+400Sin30∘
Free-body diagram
A=846.41 lb
Lecturer : Hussein A. Jaaz 33 Building and construction Engineering Branch
Al-Najaf Technical Institute Engineering Mechanics
St
Civil Techniques Department 1 . Academic year, 2020-2021
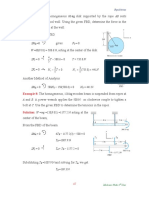
Example: Cords are passing through
frictionless pulleys to weights of 200 lb
and 400 lb and tensioned to the weighting
cylinder. Determine the angle θ and the
normal pressure N between the cylinders
and the smooth horizontal surface.
Solution:
+→ΣFx=0
400Cosθ-200=0
Cosθ=0.5 → θ=60∘
N+400Sinθ-800=0
N+400Sin60∘=800 → N=453.59 lb
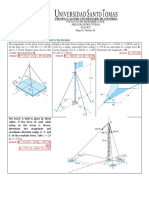
Example : Two weightless bars pinned
together and support a load of 35 kN.
Determine the forces P and F acting
respectively along bars AB and AC that
maintain equilibrium of pin A.
Solution:
+→ΣFx=0
5 2
-F( 41
)+P( )=0
√ √13
F=0.7104P ….1
+↑ΣFy=0
3 4
P( )-F( )-35=0
√13 √41
3 4
P( )=F( )+35
√13 √41
0.3883P=35 ….2 sub(1) in (2)
P=90.14 kN
F=0.7104(90.14) → F=64.03 kN
Lecturer : Hussein A. Jaaz 34
You might also like
- 5.14 Rigid Bar ABCD Is Loaded and Supported As: SolutionDocument19 pages5.14 Rigid Bar ABCD Is Loaded and Supported As: SolutionKaren QuitianNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics - Part27Document9 pagesEngineering Mechanics - Part27nikhil modgil100% (1)
- HW4 SolutionsDocument11 pagesHW4 Solutionsglttcgamer100% (2)
- 8th LectureDocument6 pages8th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 4th LectureDocument4 pages4th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- IRENEMAEBACAS - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesDocument9 pagesIRENEMAEBACAS - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesjonathanNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ejercicios de Estudio Resultante de Un Sistema de Fuerzas Concurrentes en El Espacio PDFDocument3 pages1.2 Ejercicios de Estudio Resultante de Un Sistema de Fuerzas Concurrentes en El Espacio PDFAndrésDíazNo ratings yet
- CE 9 HW Solutions 3Document25 pagesCE 9 HW Solutions 3XCyborgX25% (4)
- OMBOYGENELL - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesDocument10 pagesOMBOYGENELL - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesjonathanNo ratings yet
- HANNIE T. PANAMOGAN - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesDocument10 pagesHANNIE T. PANAMOGAN - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesKennyNo ratings yet
- RJ VAN C LORONO in Stattics of Rigid BodiesDocument10 pagesRJ VAN C LORONO in Stattics of Rigid BodiesKennyNo ratings yet
- Examples 7:: Chapter Three EquilibriumDocument9 pagesExamples 7:: Chapter Three EquilibriumReafe Carla Bustamante MabalotNo ratings yet
- 10th LectureDocument2 pages10th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- Type I: Examples Based On Components in SpaceDocument13 pagesType I: Examples Based On Components in SpaceAmeya1823100% (1)
- MALASAGAJONATHAN - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesDocument9 pagesMALASAGAJONATHAN - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesjonathanNo ratings yet
- م-9 كولومDocument9 pagesم-9 كولومنور عليNo ratings yet
- ENGR-1100 Introduction To Engineering AnalysisDocument21 pagesENGR-1100 Introduction To Engineering AnalysisHarshit MathurNo ratings yet
- ACEDILLA LEVY - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesDocument10 pagesACEDILLA LEVY - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesKennyNo ratings yet
- TANAREKEMberly - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesDocument10 pagesTANAREKEMberly - Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesjonathanNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Lesson 3 Design of Square Footing Subjected To BendingDocument4 pagesUnit 5 Lesson 3 Design of Square Footing Subjected To BendingFaher Gaosel WatamamaNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering and Information TechnologyDocument6 pagesCollege of Engineering and Information Technologydave baroroNo ratings yet
- ENGR-1100 Introduction To Engineering AnalysisDocument34 pagesENGR-1100 Introduction To Engineering AnalysisHappy Formidable SmileNo ratings yet
- JAPHET CABAJES-Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesDocument10 pagesJAPHET CABAJES-Comprehensive Examination in Stattics of Rigid BodiesKennyNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 6th Edition: CHAPTER 12Document22 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers 6th Edition: CHAPTER 12Fredy Arana Rodríguez100% (1)
- Chapter2 286 29Document16 pagesChapter2 286 29NUR AFIFAH BINTI JAMALUDIN STUDENTNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM 6.90: SolutionDocument10 pagesPROBLEM 6.90: SolutionJose Antonio P BNo ratings yet
- Ce1013 09Document42 pagesCe1013 09Durga SharmaNo ratings yet
- LBYCVD2 Compex 2Document7 pagesLBYCVD2 Compex 2sg.comNo ratings yet
- Lec.8 - Eccentrically-Loaded Short Columns Using TablesDocument9 pagesLec.8 - Eccentrically-Loaded Short Columns Using Tablesمحمد حاج اسماعيلNo ratings yet
- Eccentrically-Loaded Short Columns Using Interaction DiagramsDocument9 pagesEccentrically-Loaded Short Columns Using Interaction Diagramsنور عليNo ratings yet
- Unit - I (Deflections of Determinate Structures) : Classical Methods Ce6501-Structural AnalysisDocument21 pagesUnit - I (Deflections of Determinate Structures) : Classical Methods Ce6501-Structural AnalysisAnonymous SEDun6PWNo ratings yet
- Homework Solutions For Chapter 11: W W T T F T T W W TDocument4 pagesHomework Solutions For Chapter 11: W W T T F T T W W TkimseonhoNo ratings yet
- Chap 55555Document25 pagesChap 55555Jean Zyrelle AuronNo ratings yet
- Module 02: Approximate Analysis of Indeterminate Structures: Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO's)Document41 pagesModule 02: Approximate Analysis of Indeterminate Structures: Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO's)Mac KYNo ratings yet
- Turorial 1 PresentationDocument11 pagesTurorial 1 PresentationSujith DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- Steps in Designing Beam Reinforced For TensionDocument12 pagesSteps in Designing Beam Reinforced For TensionRogen Graciano DelgadoNo ratings yet
- PHN001 - Unit1st - Assisgnment1st - 2022 2Document12 pagesPHN001 - Unit1st - Assisgnment1st - 2022 2harshitaNo ratings yet
- Lec.35 Long Columns IIDocument5 pagesLec.35 Long Columns IIHassan AssyNo ratings yet
- Equations of Equilibrium (2D) : 440:221 Intro To Engineering Mechanics: StaticsDocument21 pagesEquations of Equilibrium (2D) : 440:221 Intro To Engineering Mechanics: StaticsVatsal PandyaNo ratings yet
- ch2 69 76Document10 pagesch2 69 76Gonçalo CruzeiroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - StructuresDocument34 pagesChapter 4 - StructuresThirukumar Sandra67% (3)
- ch2 26 37Document12 pagesch2 26 37Keilly CasanovaNo ratings yet
- HW3 SolutionDocument5 pagesHW3 SolutiondcasaliNo ratings yet
- Dec 2018 EmechDocument25 pagesDec 2018 Emechchaitanyasn0508No ratings yet
- Siao, Benjie Jr. F. - StaticsDocument9 pagesSiao, Benjie Jr. F. - Staticsbenjie siaoNo ratings yet
- HW 06Document11 pagesHW 06Don ValentinoNo ratings yet
- 07 Es202Document19 pages07 Es202Moguri OwowNo ratings yet
- 4 2 (Welded Connection)Document7 pages4 2 (Welded Connection)vladyflores529100% (1)
- CDocument17 pagesCaischosNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Mechanics J L MariamDocument75 pagesSolution Manual Mechanics J L MariamKhalid Yousaf86% (7)
- 02.01a Ch1 HW Solutions Update 21 May 2019Document17 pages02.01a Ch1 HW Solutions Update 21 May 2019EnriqueNo ratings yet
- StaticsDocument20 pagesStaticsAngelyn Rey71% (7)
- HW 1 Solutions 2012Document10 pagesHW 1 Solutions 2012Dustin Brown100% (1)
- 5 - RCE-design-of-Tbeam-and-double-reinforcedDocument33 pages5 - RCE-design-of-Tbeam-and-double-reinforced'Riky Dwi Prasetyo'No ratings yet
- Jurusan Teknik Sipil Sekolah Tinggi Teknologi YPKP: Ir. Muhamad Ryanto, MTDocument9 pagesJurusan Teknik Sipil Sekolah Tinggi Teknologi YPKP: Ir. Muhamad Ryanto, MTRumah DesainNo ratings yet
- 13th LectureDocument4 pages13th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 10th LectureDocument2 pages10th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 8th LectureDocument6 pages8th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 5th LectureDocument4 pages5th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 7th LectureDocument3 pages7th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 6th LectureDocument6 pages6th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 4th LectureDocument4 pages4th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 0 Lecture 0Document63 pages0 Lecture 0محمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 1st LectureDocument7 pages1st Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet