Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 2 - GenBio1 BIOMOLECULES 1st Term SY 2021-2022
Week 2 - GenBio1 BIOMOLECULES 1st Term SY 2021-2022
Uploaded by
JAN PAULINE BABINAOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 2 - GenBio1 BIOMOLECULES 1st Term SY 2021-2022
Week 2 - GenBio1 BIOMOLECULES 1st Term SY 2021-2022
Uploaded by
JAN PAULINE BABINACopyright:
Available Formats
General Biology 1
BIOMOLECULES
Week 2 / August 23-27, 2021 / Lecture Notes
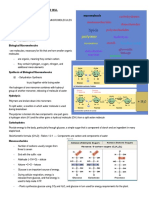
Introduction Condensation Reaction – a reaction that connects a
monomer to another monomer or polymer by
Element – simplest and purest form, cannot be covalent bond
broken down to other substances by chemical
reaction Dehydration Reaction – monomers to polymers, a
chemical reaction that covalently bonds two
Compound – consists of two or more elements molecules to each other with the removal of a water
Valence Electrons – the outermost part of the shell, molecule (adds OH and H bond)
interacts with other atoms to form chemical bonds Hydrolysis (Greek hydro ‘water’ & lysis ‘break’) –
Ionic Bond – transfer of electrons between a metal polymers to monomers, reverse of dehydration
and non-metal, attraction between an anion and reaction, the bond between monomers is broken by
cation the addition of a water molecule (breaks OH and H)
Covalent Bond – sharing of electrons between a Carbohydrates
non-metal and non-metal or metalloid Carbohydrates (building block: simple
Non-polar Covalent Bond – shares electrons equally sugar/monosaccharide) – CnH2nOn, include sugars
and polymers of sugars, commonly form rings
Polar Covalent Bond – do not share electron
equally, one is more electronegative Monosaccharides (Greek monos ‘single’ & sacchar
‘sugar’) (simple sugars) – C6H12O6, only 1 3-C, 5-C,
Cation – positively charged ion or 6-C chain, has 3-7 carbon skeleton, has a
Anion – negatively charged ion carbonyl and hydroxyl group [glyceraldehyde,
ribose, glucose, fructose, galactose]
Biomolecules – compounds found in living
organisms, organic and inorganic Triose – sugar with 3 carbons [glyceraldehyde,
dihydroxyacetone]
Macromolecules – large carbohydrates, proteins,
and nucleic acids Pentose – sugar with 5 carbons [ribose, ribulose]
Polymers (Greek polys ‘many’ & meros ‘part’) – Hexose – sugar with 6 carbons [glucose, fructose,
long molecule consisting of many similar building galactose]
blocks (monomers) linked by covalent bonds Aldose (Aldehyde Sugars) – carbonyl group at end
Monomers (Greek monos ‘single’) – smaller of carbon skeleton [glyceraldehyde, ribose, glucose,
molecules, the repeating units that serve as the galactose]
building blocks of polymers Ketose (Ketone Sugars) – carbonyl group within or
Carbon – all biomolecules contain Carbon, 4 at the center of carbon skeleton [dihydroxyacetone,
valence electron, bonding capacity is great, very ribulose, fructose]
stable once bound to other elements or Carbon Glucose – major nutrient for cells, component in
Polymerization – the chemical mechanisms by cell respiration
which cells make polymers Fructose – converted into glucose by the liver
Enzymes – specialized macromolecules (proteins) Galactose – transformed in the liver to be used as
that speed up chemical reactions energy
Jan Pauline B. Babina, 11 – STEM 01
1
General Biology 1
BIOMOLECULES
Week 2 / August 23-27, 2021 / Lecture Notes
Disaccharides (double sugars) – C12H22O11, formed *enzymes that digest starch (a link) cannot
by dehydration reaction, has 2 6-C chains or rings hydrolyze cellulose (b link); except for other
bonded together [sucrose, lactose, maltose] microorganisms that can digest cellulose [cow]*
Glycosidic Linkage (glycol ‘carbohydrate’) – Insoluble Fiber – cellulose in human food that
covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate to another passes through the digestive tract, cannot be
group or carbohydrate digested
Sucrose – glucose + fructose, table sugar, plants use Pasta Loading – eating a lot of carbohydrates to
to transport carbohydrates from leaves to roots and store energy (mostly by athletes before and after
other nonphotosynthetic organs games)
Lactose – glucose + galactose, sugar in milk Carbs in sweets (starch) – alpha linkage, easily
broken down by enzymes, converted to ATP, too
Maltose – glucose + glucose, malt sugar for much consumption raises sugar levels in body easily
brewing beer
Carbs in vegetables (cellulose) – beta linkage, not
Oligosaccharides – consists of 3 to 10 sugar easy to be broken down, does not add up to body’s
molecules sugar molecules as you consume carbohydrates
Polysaccharides (complex sugars) – for storage and Carbohydrates: Functions
structural roles [starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin]
Provide quick energy to the body
Amylose – unbranched
Dietary fiber can help lower blood
Amylopectin – somewhat branched cholesterol
Spares protein from being burned so it can
Starch (alpha configuration) – largely helical,
be used to build and repair
polymer of glucose, stored energy in plants
Stores energy
Cellulose (beta configuration) – polymer of glucose,
Lipids
straight and unbranched, main substance in plant
cell wall Lipids (building block: fatty acid) – hydrophobic,
present in all living organisms, constituent of cell
Glycogen – polymer of glucose, stored energy in
membrane, no true polymers, not big enough as
animals
other macromolecules [fats, oil, cholesterol,
Chitin – exoskeleton of arthropods, cellulose in lecithin]
fungi
Saturated Fats – single bond, raises less dense
Alpha Glucose Monomer/Configuration (1-4) – lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels in the blood,
downwards linkage, can be digested, raises sugar solid in room temperature, bad for you [animal fat,
levels in body dairy, coconut oil, cocoa butter]
Beta Glucose Monomer/Configuration (1-4) – Unsaturated Fats – at least 1 double bond that
upward downward pattern linkage, cannot be results to a kink or distortion of the structural
digested appearance, liquid in room temperature, good for
you
Jan Pauline B. Babina, 11 – STEM 01
2
General Biology 1
BIOMOLECULES
Week 2 / August 23-27, 2021 / Lecture Notes
Monounsaturated Fats – leave LDL and Proteins
HDL levels unchanged, 1 double bond in
fatty acid [olive oil, canola, peanut oil, Protein (Greek proteios ‘first/primary’) (building
avocado] block: amino acid) – basis for major structural
components of animal and human tissue, consists of
Polyunsaturated Fats – leave LDL 1 or more polypeptides (long chains of amino acids)
cholesterol unchanged, lower HDL
cholesterol, multiple double bonds in fatty Amino Acids – organic molecules with amino and
acid [safflower, corn oil] carboxyl groups, differs in R-groups (side chain)
Fatty Acid – one of three dehydration reactions in Peptide Bonds – covalent bonds that links amino
the synthesis of fat, joined to a glycerol, forms acids together to form polypeptide
triglyceride/fat molecule when joined together in Peptide – 2 or more amino acids joined by bonds
groups of 3, 16-18 carbon atoms
Polypeptides – chain of many amino acids, polymer
Fat Molecule (Triglycerides) – 3 fatty acid of amino acids, unbranched polymers, has carboxyl
molecules connected to a glycerol molecule with an end (C-terminus) and amino end (N-terminus)
ester linkage (hydroxyl + carboxyl), not polymers
*amino acid (peptide bond) > peptide > polypeptide
Phospholipid – 2 fatty acids and a phosphate group ‘chain’ > protein*
attached to a glycerol, amphipathic
Primary Structure – unique sequence of amino
Phospholipid Bilayer – hydrophilic head, acids, determines the shape of a protein
hydrophobic tail, found in cell membrane
Secondary Structure – coils and folds in the
Steroids – a carbon skeleton consisting 4 fused rings polypeptide chain
[cholesterol, cortisol, progesterone, testosterone]
Tertiary Structure – interactions among various side
Cis Fat – hydrogen is at the same direction, good chains (R-groups)
Trans Fat – hydrogen is at opposite directions, bad Quaternary Structure – when a protein consists of
LDL “bad” – carries dietary fats into your cells multiple polypeptide chains
HDL “good” – carries impurities out of your cells Sickle-cell Disease – inherited blood disorder,
single amino acid substitution, abnormal/deformed
Keto Diet –low in carbohydrates, more on RBC, substitution of Valine to the normal Glutamic
protein/fat Acid at the 6th position
Lipids: Functions Denaturation – will make the protein biologically
inactive, loss of protein’s structure because of pH
Energy source level, salt concentration, temperature
Protecting and structuring organs
Help in insulating the body Whey Protein – concentrated amino acids that the
Generate heat body does not need to break down anymore
Gives cell membrane’s structure
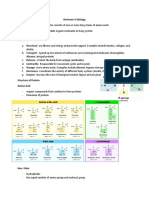
Proteins: Functions
Jan Pauline B. Babina, 11 – STEM 01
3
General Biology 1
BIOMOLECULES
Week 2 / August 23-27, 2021 / Lecture Notes
Enzymatic Proteins – accelerates chemical Pyrimidines – composed of 6-membered
reactions [digestive enzyme] ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms [cytosine,
Defensive Proteins – protection against thymine, uracil]
disease [antibodies]
Purines – composed of 2 fused rings (6-
Storage Proteins – stores amino acids membered ring fused to 5-membered ring)
[casein, ovalbumin] [adenine, guanine]
Transport Proteins – transport substances
[hemoglobin] Sugars/Pentose – component of DNA and RNA
Hormonal Proteins – coordination of together with nucleoside and phosphate group
organism activities [insulin] Deoxyribose – sugar in DNA, carbon 2 has
Receptor Proteins – response to chemical H attachment, lacks oxygen on the second
stimuli [receptors of a nerve cell] carbon (deoxy)
Contractile and Motor Proteins – movement
[cilia, flagella] Ribose – sugar in RNA, carbon 2 has OH
Structural Proteins – support [keratin, attachment
collagen] *slight changes in the amino acid sequencing leads
Nucleic Acids to a different organism*
Nucleic Acids (building block: nucleotide) – a.k.a. Gene Expression – information from a gene that is
polynucleotide, long thread-like water soluble extracted/converted to be used in synthesis to
macromolecules in all living cells, found in high produce end products
concentrated nuclei [DNA, RNA] Nucleic Acids: Functions
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – mainly found in Responsible for the transmission of inherent
nucleus; nitrogenous bases: A, T, G, C; controls
characters from parent to offspring
hereditary transmission; antiparallel double
Responsible for the synthesis of protein in
stranded/helix (sugar-phosphate backbones outside,
our body and direct its own replication,
nitrogenous bases pairs inside)
collectively known as gene expression
RNA (ribonucleic acid) – produced in nucleus but DNA fingerprinting is used to determine
mainly found in cytoplasm; nitrogenous bases: A, paternity/maternity
U, G, C; controls protein synthesis; single stranded Used for the identification of criminals
through secretion
*the basic components of DNA and RNA are
Played a major role in biological evolution
pentose sugar (5-carbon), nitrogenous bases, 1-3
and genetics
phosphate groups*
*DNA starts with 5’ (five prime) and ends with 3’*
Nucleotide/Nucleoside Monophosphate – monomer
of nucleic acid, composed of a phosphate group,
sugar/pentose, and nitrogenous base/nucleoside
Nitrogenous Bases/Nucleosides – the portion of
nucleotide without any phosphate groups (basically,
base + sugar) [A, T, G, C, U]
Jan Pauline B. Babina, 11 – STEM 01
4
General Biology 1
BIOMOLECULES
Week 2 / August 23-27, 2021 / Lecture Notes
Biomolecules: Comparison
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids
C, H, O in rings C, H, O in linear chain C, H, O, N, S C, H, O, N, P
Nucleotide/
Sugar Fatty Acid Amino Acid Nucleoside
Monophosphate
Monosaccharides,
Disaccharide, Peptide, Polypeptide
Fat Molecule
Oligosaccharide, Chain
Polysaccharide
Pentose Sugar,
Amino Group,
Carbonyl Group, Hydroxyl Fatty Acid, Glycerol Nitrogenous
Carboxyl Group, R-
Group (Hydroxyl + Carboxyl) Base/Nucleoside,
group
Phosphate Group
Triose, Pentose, Hexose Saturated, Unsaturated Fat Primary, Secondary, Pyrimidine, Purine
Monounsaturated, Tertiary, Quaternary -
Aldose, Ketose Structure Deoxyribose, Ribose
Polyunsaturated
Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose Oil, Wax, Phospholipid,
Enzyme DNA, RNA
Steroid
Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen,
Chitin
Glycosidic Linkage Ester Linkage Peptide Bond
Amylose, Amylopectin Cis, Trans Fat Denaturation
Alpha, Beta Linkage Sickle-Cell Disease Gene Expression
Pasta Loading Keto Diet Whey Protein
Heredity, Protein
Synthesis, DNA
Enzymatic, Defensive,
Energy Source, Protect Replication, DNA
Quick Energy, Lower Blood Storage, Transport,
and Structure Organs, fingerprinting,
Cholesterol, Spares Protein, Hormonal, Receptor,
Insulation, Generate Heat, Criminal
Stores Energy Contractile and Motor,
Cell Membrane Structure Identification,
Structural
Biological
Evolution, Genetics
Biomolecules: Structures
1. Carbohydrates – C, H, O (mostly in rings)
Jan Pauline B. Babina, 11 – STEM 01
5
General Biology 1
BIOMOLECULES
Week 2 / August 23-27, 2021 / Lecture Notes
2. Lipids – C, H, O (mostly in hydrocarbon chains) (carbon double bond)
3. Proteins – C, H, O, N, S (with amino NH2)
4. Nucleic Acid – C, H, O, N, P (with 4 oxygen around phosphorus)
Jan Pauline B. Babina, 11 – STEM 01
6
General Biology 1
BIOMOLECULES
Week 2 / August 23-27, 2021 / Lecture Notes
Jan Pauline B. Babina, 11 – STEM 01
7
You might also like
- Nutrition Guide by Petite PWRDocument39 pagesNutrition Guide by Petite PWRchallengekpsaveNo ratings yet
- AQA As-Level Biology Revision Notes - New SpecDocument38 pagesAQA As-Level Biology Revision Notes - New SpecjimboNo ratings yet
- Edexcel As Biology Revision Guide PDF FreeDocument108 pagesEdexcel As Biology Revision Guide PDF Freebody fayez100% (1)
- Eating To Win: Activity, Diet and Weight ControlDocument23 pagesEating To Win: Activity, Diet and Weight ControlAbraham SolomonNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Nutrition and Food PDFDocument1,613 pagesHandbook of Nutrition and Food PDFZahid Ali100% (1)
- Hello Fresh 36Document30 pagesHello Fresh 36Zuza Jedrychowski-Głowacka83% (6)
- Biology ReviewerDocument15 pagesBiology ReviewerIshie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Carbohydrates 2Document26 pagesWeek 3 Carbohydrates 2sabeera.ahmadNo ratings yet
- Biology ASDocument35 pagesBiology ASsalma mazruiNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules PDFDocument5 pagesBiomolecules PDFgabo uyNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument102 pagesDigestive Systemkavya nandhiNo ratings yet
- Organic MoleculesDocument7 pagesOrganic MoleculesJames CadizNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Structure of The Cell Biological MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesChemistry and Structure of The Cell Biological MacromoleculesJohn ManciaNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules. Monomers: Bio 11O Topic 5 - BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesMacromolecules. Monomers: Bio 11O Topic 5 - BiomoleculesYda TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Reviewer 2324Document7 pagesBiomolecules Reviewer 2324heraloesaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument40 pagesChemical Basis of LifeFloriza de LeonNo ratings yet
- Gr10 LifeSci ChemistryOfLife TheoryDocument6 pagesGr10 LifeSci ChemistryOfLife Theorymotauodette12No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document8 pagesChapter 2Kate Wen GuanNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes 1Document2 pagesBiology Notes 1Paulo AloroNo ratings yet
- (Poly, Many Mer, Unit) Monomers (Mono, One) : Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O) and Nitrogen (N) PolymersDocument5 pages(Poly, Many Mer, Unit) Monomers (Mono, One) : Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O) and Nitrogen (N) PolymersDaneth Julia TuberaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersJojo LouNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules RevisionDocument6 pagesBiological Molecules RevisioncocoNo ratings yet
- AQA Module All Revision NotesDocument82 pagesAQA Module All Revision NotesRS JNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument20 pagesBIOLOGYBlaire ReyesNo ratings yet
- C, L, P Notes No PicturesDocument35 pagesC, L, P Notes No PicturesFarhadullah KhanNo ratings yet
- All Biology LessonsDocument217 pagesAll Biology Lessonsadliabuwade3No ratings yet
- Gen Bio - 1 2.5 - The Organic Molecules of Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesGen Bio - 1 2.5 - The Organic Molecules of Living OrganismsBlaire ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Biomolecules: Major Types of Biomolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, andDocument12 pagesLesson 4: Biomolecules: Major Types of Biomolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, andJuselle Faith AtaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Biology Protein-A Large Macromolecules Consists of One or More Long Chains of Amino AcidsDocument9 pagesReviewer in Biology Protein-A Large Macromolecules Consists of One or More Long Chains of Amino AcidsDanilo PerezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Enzymes and The Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesUnit 2 - Enzymes and The Digestive SystemKatherine NunnNo ratings yet
- SBI4U Biochemistry NotesDocument13 pagesSBI4U Biochemistry NotesAli MalikNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of CellsDocument79 pagesBiochemistry of CellsketakeeNo ratings yet
- 3 Essential Chemicals of Life PPTDocument82 pages3 Essential Chemicals of Life PPTBhoni KumariNo ratings yet
- General Biology Reviewer:: - Synthesis of Biological MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewer:: - Synthesis of Biological MacromoleculesSarah Jane P. CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Notes Biological Molecules 3Document8 pagesNotes Biological Molecules 3abdul rehmanNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Biologically Important MoleculesDocument36 pages1.2 Biologically Important MoleculesSoleil R.No ratings yet
- Macromolecule: Polysacharide, Polypeptide - Protein and LipidsDocument56 pagesMacromolecule: Polysacharide, Polypeptide - Protein and Lipidsfahmi gunawanNo ratings yet
- Physical Science-Finals ReviewerDocument18 pagesPhysical Science-Finals ReviewerPrecious Miracle Lucas SacataniNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: A. Synthesis & Hydrolysis Reaction VocabDocument18 pagesBiomolecules: A. Synthesis & Hydrolysis Reaction Vocabrashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Transes-Chap 2 - MicrobioDocument4 pagesTranses-Chap 2 - MicrobioFReyes KarylleNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument6 pagesPhysical ScienceCAYABAN, RISHA MARIE DV.No ratings yet
- BIOA111 SN17 SummaryDocument6 pagesBIOA111 SN17 SummaryDorothy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument5 pagesBiology NotesFaith SNNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES-Any Molecules That Are Produced by A LivingDocument9 pagesBIOMOLECULES-Any Molecules That Are Produced by A LivingRuskin Jamir AquinoNo ratings yet
- Protein and FatDocument2 pagesProtein and FatOlin Jay HonrubiaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates SlidesDocument75 pagesCarbohydrates SlidesShiva PratheekNo ratings yet
- Worktext 1 - Biomol - Carbo & Lipids, PERALTADocument10 pagesWorktext 1 - Biomol - Carbo & Lipids, PERALTAKelsi Kyla PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Final Term ReviewerDocument27 pagesFinal Term ReviewerBenna Cyril OrbinoNo ratings yet
- Annotated GenbioDocument5 pagesAnnotated GenbioJarred HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules: When X y It's Simple So CX (H20) y When X Does Not y It's Simple So CX (H20) yDocument15 pagesBiological Molecules: When X y It's Simple So CX (H20) y When X Does Not y It's Simple So CX (H20) yteeeNo ratings yet
- l3 Biological Molecules - Without DnaDocument16 pagesl3 Biological Molecules - Without Dnaapi-239537002No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - 1A2-3 Carbohydrates I & IIDocument30 pagesLesson 3 - 1A2-3 Carbohydrates I & IIAlex SmirnovNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Enantiomers . These Are Mirror Images of Each Other. MirroredDocument17 pagesChapter 3: The Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Enantiomers . These Are Mirror Images of Each Other. Mirroredapi-524244445No ratings yet
- EED 5 Unit 2Document15 pagesEED 5 Unit 2Lara Mariz FragataNo ratings yet
- 2 Energy TransformationDocument138 pages2 Energy Transformationchizy bananaNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 10 Notes (Grade 11)Document12 pagesBio Chapter 10 Notes (Grade 11)Tammy Lam100% (4)
- Carbo HyDocument10 pagesCarbo HyLyka Joy RedobleNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Biological MoleculesDocument48 pagesCH 2 Biological Molecules9G11 Aulia KayanaNo ratings yet
- Animal AnatomyDocument11 pagesAnimal AnatomyTimothee KazunguNo ratings yet
- General Biology - EnzymesDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology - EnzymesHaze dashvilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Molecules of LifeDocument67 pagesChapter 2 Molecules of LifeNatalie GraceNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 ActivityDocument11 pagesWEEK 3 ActivityMai SasaNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- AQA Biology Unit 1: Revision Notes: myrevisionnotes, #1From EverandAQA Biology Unit 1: Revision Notes: myrevisionnotes, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Week 11 - GenBio1 GENETICS 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document2 pagesWeek 11 - GenBio1 GENETICS 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Week 3 - EarthSci EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document3 pagesWeek 3 - EarthSci EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Week 2 - EarthSci ORIGIN OF UNIVERSE&SOLAR SYSTEM 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document4 pagesWeek 2 - EarthSci ORIGIN OF UNIVERSE&SOLAR SYSTEM 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Week 8 - GenBio1 CELL RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document3 pagesWeek 8 - GenBio1 CELL RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Week 10 - GenBio1 CELL CYCLE 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document3 pagesWeek 10 - GenBio1 CELL CYCLE 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Week 9 - GenBio1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document2 pagesWeek 9 - GenBio1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Week 5 - GenBio1 CELLULAR RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document2 pagesWeek 5 - GenBio1 CELLULAR RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Week 4 - GenBio1 CELL MEMBRANE TRANSPORT 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document3 pagesWeek 4 - GenBio1 CELL MEMBRANE TRANSPORT 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Week 3 - GenBio1 CELLS 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document8 pagesWeek 3 - GenBio1 CELLS 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates LectureDocument74 pagesCarbohydrates LectureLars JayhawkNo ratings yet
- IssaDocument31 pagesIssaNayeem100% (1)
- Freshwater Fish NutritionDocument50 pagesFreshwater Fish NutritionGiuseppe AVNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Carbohydrates 2023Document37 pagesChemistry of Carbohydrates 2023andrade.sanchithaNo ratings yet
- Bio Biological Molecules AlevelsDocument28 pagesBio Biological Molecules AlevelsMunazzagulNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument2 pagesBIOLOGYMyraSimoraNo ratings yet
- 100 PDFDocument5 pages100 PDFyskdonNo ratings yet
- FSM 113Document113 pagesFSM 113ccatiishs100% (1)
- Healthy Eating HabitsDocument19 pagesHealthy Eating HabitsMarkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 47 NutritionDocument9 pagesChapter 47 NutritionKathleen FrugalidadNo ratings yet
- Science 10 4th Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesScience 10 4th Quarter ExamRamirez JazzNo ratings yet
- NSC 2410 INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY I Syllabus-1Document3 pagesNSC 2410 INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY I Syllabus-1Panashe MaluwaNo ratings yet
- Blood TypeDocument3 pagesBlood TypeMarina GevorgyanNo ratings yet
- Infant Growth and DevelopmentDocument111 pagesInfant Growth and DevelopmentAdnan QamarNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, EnzymesDocument11 pagesBiomolecules: Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, EnzymesJemiahNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Need Food?: A Balanced DietDocument3 pagesWhy Do We Need Food?: A Balanced DietTUNGAL KUMAR DHAMANo ratings yet
- Nutrients: African Sorghum-Based Fermented Foods: Past, Current and Future ProspectsDocument25 pagesNutrients: African Sorghum-Based Fermented Foods: Past, Current and Future ProspectsLestari PutriNo ratings yet
- Diet ChartDocument4 pagesDiet ChartAman KhanNo ratings yet
- 2122 Course Revision Questions Science J Solutions UpdatedDocument81 pages2122 Course Revision Questions Science J Solutions Updatedrokaya abotrikaNo ratings yet
- Sugar Types On Ethanol ProductionDocument5 pagesSugar Types On Ethanol ProductionGabriella NaomiNo ratings yet
- Glycemic IndexDocument4 pagesGlycemic IndexSunil BNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Chapter 1-5Document49 pagesNutrition Chapter 1-5Maria MarieNo ratings yet
- A Feasibility Study of The Production of Ethanol From Sugar CaneDocument239 pagesA Feasibility Study of The Production of Ethanol From Sugar CaneKhamda Aja Dulu100% (2)
- Holway & Spriet (2011) Sports NutritionDocument12 pagesHolway & Spriet (2011) Sports NutritionCallum BromleyNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules Structure and FunctionDocument16 pagesBiological Molecules Structure and FunctionJohn Romel Sicujan RiveraNo ratings yet