Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsReference Angle
Reference Angle
Uploaded by
Ana May BanielA reference angle is the acute angle formed between a reflex angle's terminal side and the x-axis when drawn on a coordinate plane, allowing trigonometric functions to be simplified for angles of any value. Reference angles are always between 0 and 90 degrees, using the x-axis as a frame of reference. While an angle and its reference angle give the same value for trig functions, the sign may differ depending on the angle's quadrant.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Module in Techno Week 3 4Document8 pagesModule in Techno Week 3 4Ana May BanielNo ratings yet
- The Use of Trigonometry in NavigationDocument5 pagesThe Use of Trigonometry in NavigationJanPoulPoscabol100% (2)
- Analytic Geometry MATH 004 (TIP Reviewer)Document9 pagesAnalytic Geometry MATH 004 (TIP Reviewer)James Lindo100% (1)
- Reference Angle (Trigo)Document2 pagesReference Angle (Trigo)Nadine Clare FloresNo ratings yet
- Pelham Trigonometry Vocabulary (Article) Author Pelham School DistrictDocument2 pagesPelham Trigonometry Vocabulary (Article) Author Pelham School DistrictCarl YapNo ratings yet
- EngrdrawDocument2 pagesEngrdrawriegonationNo ratings yet
- Math 12-1 NotesDocument12 pagesMath 12-1 NotesJulliene Angela CarpioNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Notes and VideosDocument31 pagesTrigonometry Notes and VideosAnibor EzekielNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Imp QuesDocument23 pagesComputer Graphics Imp QuesDr. MANU SINGH KEC (CSE)No ratings yet
- Angles in Standard Position: Mathematics Iv Mr. Carlo R. Dela CruzDocument23 pagesAngles in Standard Position: Mathematics Iv Mr. Carlo R. Dela CruzPaolo DavidNo ratings yet
- The Unit CircleDocument4 pagesThe Unit CircleNuur AiisyaahNo ratings yet
- MATHS ProjectDocument40 pagesMATHS ProjectShrija Padhi100% (1)
- Experiment No.3: "To Calculate Area of Irregular Shapes by Using Planimeter." ObjectiveDocument10 pagesExperiment No.3: "To Calculate Area of Irregular Shapes by Using Planimeter." ObjectiveMahrukh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Cris PPT 3Document16 pagesCris PPT 3JUDE BALDOVISONo ratings yet
- MAJ 3 - Handout 2Document12 pagesMAJ 3 - Handout 2Annalie LobianoNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument65 pagesTrigonometryChristine BalladNo ratings yet
- Maths PresentationDocument19 pagesMaths PresentationAbha BansalNo ratings yet
- If You Know The Coordinates of A Group of Points You CanDocument16 pagesIf You Know The Coordinates of A Group of Points You CanSanaka LogesNo ratings yet
- Angles LM'SDocument2 pagesAngles LM'S22-70282No ratings yet
- Interactive Unit Circle ActivityDocument10 pagesInteractive Unit Circle Activityapi-260038645No ratings yet
- Basic Functions and The Right TriangleDocument15 pagesBasic Functions and The Right TriangleChetan Tolia100% (1)
- Geometry Reference: Points, Lines and Planes CirclesDocument2 pagesGeometry Reference: Points, Lines and Planes Circlesmarko1234No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions - WikipediaDocument14 pagesTrigonometric Functions - WikipediaAlone EulerNo ratings yet
- Dictionary PDFDocument95 pagesDictionary PDFFaiza Faizan100% (1)
- Graphs of SineDocument6 pagesGraphs of SineMary Jasmine AzulNo ratings yet
- Shear MappingDocument2 pagesShear MappingTheLuckS; ラッキー矢印No ratings yet
- Principal Moments of InertiaDocument13 pagesPrincipal Moments of Inertiabruno_matos7No ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration: Mr. Mark Jave C. Gualberto, RME Lecturer IDocument12 pagesSolid Mensuration: Mr. Mark Jave C. Gualberto, RME Lecturer IAzha Clarice VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Engineering BertolineDocument49 pagesEngineering BertolineKami BabaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 (8) .PDF YilaDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 3 (8) .PDF YilaFasiko AsmaroNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 DLS 26-27Document6 pagesMathematics 10 DLS 26-27Ivan Miguel MariNo ratings yet
- Module 5 TrigonometryDocument0 pagesModule 5 TrigonometryManish MishraNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions Topic SummaryDocument13 pagesTrigonometric Functions Topic SummaryPerson GainableNo ratings yet
- Angles and Circles: Drawing Angles in Standard PositionDocument4 pagesAngles and Circles: Drawing Angles in Standard PositionFrancesca RicafortNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument13 pagesEngineering DrawingVIVEK V SNo ratings yet
- KKKDocument6 pagesKKKKavi MukilanNo ratings yet
- Angle Measurement: Instruments Used For Angular MeasurementDocument8 pagesAngle Measurement: Instruments Used For Angular MeasurementSayanSanyalNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument12 pagesTrigonometryGwyneth Lei T. ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Formulas For 2D Shapes - VPDocument21 pagesMensuration Formulas For 2D Shapes - VPkrisretro1No ratings yet
- Angle: Units of Measure For AnglesDocument6 pagesAngle: Units of Measure For AnglesashokNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument2 pagesTrigonometrydummkopfworkNo ratings yet
- Transformations: Reflection: RDocument6 pagesTransformations: Reflection: RTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- MTC 121Document7 pagesMTC 121Rica AlhambraNo ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry: Trigonometry Angle Unit ConversionDocument5 pagesPlane Trigonometry: Trigonometry Angle Unit ConversionZairah Ann BorjaNo ratings yet
- (ENM012 AY22-23) W2 - Trigonometric Functions - D - 1Document10 pages(ENM012 AY22-23) W2 - Trigonometric Functions - D - 1Johnny SiasonNo ratings yet
- Mensuration PDFDocument33 pagesMensuration PDFSudhanshu Kumar100% (1)
- Chapter 5 TransformationsDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Transformationsdenis kipkiruiNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument101 pagesTrigonometryMarilyn LiconoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.5: Measurements of Directions and Angles: Unit IDocument12 pagesLesson 1.5: Measurements of Directions and Angles: Unit ICarlo CabanusNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions 2Document34 pagesTrigonometric Functions 2Sahil JindalNo ratings yet
- Module I TrigoDocument6 pagesModule I TrigoAteng FordNo ratings yet
- Day-4-UPCAMP-2018Document40 pagesDay-4-UPCAMP-2018afunabermudezNo ratings yet
- Angle Investigation Math JosueDocument5 pagesAngle Investigation Math JosueJohanna MartinezNo ratings yet
- (ENM012 AY22-23) W2 - Trigonometric Functions - D - 1Document9 pages(ENM012 AY22-23) W2 - Trigonometric Functions - D - 1Jaxon RiegoNo ratings yet
- Coterminal Angle and Reference AngleDocument23 pagesCoterminal Angle and Reference Anglekaredad57No ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration ReviewerDocument9 pagesSolid Mensuration ReviewerAlice AsmodeusNo ratings yet
- 3.1 2D-TransformatonDocument7 pages3.1 2D-TransformatonnisamNo ratings yet
- Basic GeometryDocument24 pagesBasic GeometryEtha Cantik100% (1)
- Cartesian PlaneDocument39 pagesCartesian PlaneBol Mën NhialNo ratings yet
- Curvilinear Perspective: Exploring Depth Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandCurvilinear Perspective: Exploring Depth Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Geology Weak 3 and 4Document2 pagesGeology Weak 3 and 4Ana May BanielNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Surveying Module 1 and 2Document2 pagesFundamentals of Surveying Module 1 and 2Ana May BanielNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITYDocument6 pagesACTIVITYAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics Operations OnDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics Operations OnAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- FIDP Revised Output - Business and Consumer LoansDocument4 pagesFIDP Revised Output - Business and Consumer LoansAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Teaching Guide (ATG) Revised OutputDocument4 pagesAdaptive Teaching Guide (ATG) Revised OutputAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- New Document300 20 Nov 2021 09 58 23Document1 pageNew Document300 20 Nov 2021 09 58 23Ana May BanielNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Teaching Guide (ATG) OutputDocument4 pagesAdaptive Teaching Guide (ATG) OutputAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- Conic-Parabola 101Document27 pagesConic-Parabola 101Ana May BanielNo ratings yet
- Lesson-1 in ARTSDocument30 pagesLesson-1 in ARTSAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- Mus Ic of Min Doro: Yvhan Gabriel T. Fernando and Krentz ToleteDocument7 pagesMus Ic of Min Doro: Yvhan Gabriel T. Fernando and Krentz ToleteAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- TG 17 Nov 2021 10 25 17Document5 pagesTG 17 Nov 2021 10 25 17Ana May BanielNo ratings yet
Reference Angle
Reference Angle
Uploaded by
Ana May Baniel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesA reference angle is the acute angle formed between a reflex angle's terminal side and the x-axis when drawn on a coordinate plane, allowing trigonometric functions to be simplified for angles of any value. Reference angles are always between 0 and 90 degrees, using the x-axis as a frame of reference. While an angle and its reference angle give the same value for trig functions, the sign may differ depending on the angle's quadrant.
Original Description:
reference angle
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA reference angle is the acute angle formed between a reflex angle's terminal side and the x-axis when drawn on a coordinate plane, allowing trigonometric functions to be simplified for angles of any value. Reference angles are always between 0 and 90 degrees, using the x-axis as a frame of reference. While an angle and its reference angle give the same value for trig functions, the sign may differ depending on the angle's quadrant.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesReference Angle
Reference Angle
Uploaded by
Ana May BanielA reference angle is the acute angle formed between a reflex angle's terminal side and the x-axis when drawn on a coordinate plane, allowing trigonometric functions to be simplified for angles of any value. Reference angles are always between 0 and 90 degrees, using the x-axis as a frame of reference. While an angle and its reference angle give the same value for trig functions, the sign may differ depending on the angle's quadrant.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Reference Angle
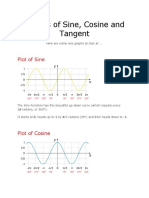
What is a Reference Angle
A reflex angle is the smallest acute angle that the terminal arm of the angle
makes with the x-axis when drawn on a coordinate plane. Regardless of the
location of the terminal side, the reference angle measures the closest distance of
that side from the x-axis.
Reference Angle
The reference angle is used for simplifying the calculations related to
trigonometric functions with different angles. Their value is always between 0
and 90° when measured in degrees or 0 and π/2 when measured in radians. A
reference angle always uses an x-axis as its frame of reference.
Looking at the picture above, every angle is measured from the positive part of
the x-axis to its terminal side by traveling in a counterclockwise direction.
Reference Angles and Trigonometric Functions
The two axes, x, and y divide the plane into four quadrants, named I, II, III, and IV.
The numbering starts from the upper right one, the first quadrant, where both
coordinates are positive as we continue to move in the anticlockwise direction.
Normally, the four trigonometric functions: sine, cosine, tangent, and cotangent
give the same value for an angle and its reference angle. The only thing that
varies is the sign.
You might also like
- Module in Techno Week 3 4Document8 pagesModule in Techno Week 3 4Ana May BanielNo ratings yet
- The Use of Trigonometry in NavigationDocument5 pagesThe Use of Trigonometry in NavigationJanPoulPoscabol100% (2)
- Analytic Geometry MATH 004 (TIP Reviewer)Document9 pagesAnalytic Geometry MATH 004 (TIP Reviewer)James Lindo100% (1)
- Reference Angle (Trigo)Document2 pagesReference Angle (Trigo)Nadine Clare FloresNo ratings yet
- Pelham Trigonometry Vocabulary (Article) Author Pelham School DistrictDocument2 pagesPelham Trigonometry Vocabulary (Article) Author Pelham School DistrictCarl YapNo ratings yet
- EngrdrawDocument2 pagesEngrdrawriegonationNo ratings yet
- Math 12-1 NotesDocument12 pagesMath 12-1 NotesJulliene Angela CarpioNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Notes and VideosDocument31 pagesTrigonometry Notes and VideosAnibor EzekielNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Imp QuesDocument23 pagesComputer Graphics Imp QuesDr. MANU SINGH KEC (CSE)No ratings yet
- Angles in Standard Position: Mathematics Iv Mr. Carlo R. Dela CruzDocument23 pagesAngles in Standard Position: Mathematics Iv Mr. Carlo R. Dela CruzPaolo DavidNo ratings yet
- The Unit CircleDocument4 pagesThe Unit CircleNuur AiisyaahNo ratings yet
- MATHS ProjectDocument40 pagesMATHS ProjectShrija Padhi100% (1)
- Experiment No.3: "To Calculate Area of Irregular Shapes by Using Planimeter." ObjectiveDocument10 pagesExperiment No.3: "To Calculate Area of Irregular Shapes by Using Planimeter." ObjectiveMahrukh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Cris PPT 3Document16 pagesCris PPT 3JUDE BALDOVISONo ratings yet
- MAJ 3 - Handout 2Document12 pagesMAJ 3 - Handout 2Annalie LobianoNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument65 pagesTrigonometryChristine BalladNo ratings yet
- Maths PresentationDocument19 pagesMaths PresentationAbha BansalNo ratings yet
- If You Know The Coordinates of A Group of Points You CanDocument16 pagesIf You Know The Coordinates of A Group of Points You CanSanaka LogesNo ratings yet
- Angles LM'SDocument2 pagesAngles LM'S22-70282No ratings yet
- Interactive Unit Circle ActivityDocument10 pagesInteractive Unit Circle Activityapi-260038645No ratings yet
- Basic Functions and The Right TriangleDocument15 pagesBasic Functions and The Right TriangleChetan Tolia100% (1)
- Geometry Reference: Points, Lines and Planes CirclesDocument2 pagesGeometry Reference: Points, Lines and Planes Circlesmarko1234No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions - WikipediaDocument14 pagesTrigonometric Functions - WikipediaAlone EulerNo ratings yet
- Dictionary PDFDocument95 pagesDictionary PDFFaiza Faizan100% (1)
- Graphs of SineDocument6 pagesGraphs of SineMary Jasmine AzulNo ratings yet
- Shear MappingDocument2 pagesShear MappingTheLuckS; ラッキー矢印No ratings yet
- Principal Moments of InertiaDocument13 pagesPrincipal Moments of Inertiabruno_matos7No ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration: Mr. Mark Jave C. Gualberto, RME Lecturer IDocument12 pagesSolid Mensuration: Mr. Mark Jave C. Gualberto, RME Lecturer IAzha Clarice VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Engineering BertolineDocument49 pagesEngineering BertolineKami BabaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 (8) .PDF YilaDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 3 (8) .PDF YilaFasiko AsmaroNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 DLS 26-27Document6 pagesMathematics 10 DLS 26-27Ivan Miguel MariNo ratings yet
- Module 5 TrigonometryDocument0 pagesModule 5 TrigonometryManish MishraNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions Topic SummaryDocument13 pagesTrigonometric Functions Topic SummaryPerson GainableNo ratings yet
- Angles and Circles: Drawing Angles in Standard PositionDocument4 pagesAngles and Circles: Drawing Angles in Standard PositionFrancesca RicafortNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument13 pagesEngineering DrawingVIVEK V SNo ratings yet
- KKKDocument6 pagesKKKKavi MukilanNo ratings yet
- Angle Measurement: Instruments Used For Angular MeasurementDocument8 pagesAngle Measurement: Instruments Used For Angular MeasurementSayanSanyalNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument12 pagesTrigonometryGwyneth Lei T. ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Formulas For 2D Shapes - VPDocument21 pagesMensuration Formulas For 2D Shapes - VPkrisretro1No ratings yet
- Angle: Units of Measure For AnglesDocument6 pagesAngle: Units of Measure For AnglesashokNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument2 pagesTrigonometrydummkopfworkNo ratings yet
- Transformations: Reflection: RDocument6 pagesTransformations: Reflection: RTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- MTC 121Document7 pagesMTC 121Rica AlhambraNo ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry: Trigonometry Angle Unit ConversionDocument5 pagesPlane Trigonometry: Trigonometry Angle Unit ConversionZairah Ann BorjaNo ratings yet
- (ENM012 AY22-23) W2 - Trigonometric Functions - D - 1Document10 pages(ENM012 AY22-23) W2 - Trigonometric Functions - D - 1Johnny SiasonNo ratings yet
- Mensuration PDFDocument33 pagesMensuration PDFSudhanshu Kumar100% (1)
- Chapter 5 TransformationsDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Transformationsdenis kipkiruiNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument101 pagesTrigonometryMarilyn LiconoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.5: Measurements of Directions and Angles: Unit IDocument12 pagesLesson 1.5: Measurements of Directions and Angles: Unit ICarlo CabanusNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions 2Document34 pagesTrigonometric Functions 2Sahil JindalNo ratings yet
- Module I TrigoDocument6 pagesModule I TrigoAteng FordNo ratings yet
- Day-4-UPCAMP-2018Document40 pagesDay-4-UPCAMP-2018afunabermudezNo ratings yet
- Angle Investigation Math JosueDocument5 pagesAngle Investigation Math JosueJohanna MartinezNo ratings yet
- (ENM012 AY22-23) W2 - Trigonometric Functions - D - 1Document9 pages(ENM012 AY22-23) W2 - Trigonometric Functions - D - 1Jaxon RiegoNo ratings yet
- Coterminal Angle and Reference AngleDocument23 pagesCoterminal Angle and Reference Anglekaredad57No ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration ReviewerDocument9 pagesSolid Mensuration ReviewerAlice AsmodeusNo ratings yet
- 3.1 2D-TransformatonDocument7 pages3.1 2D-TransformatonnisamNo ratings yet
- Basic GeometryDocument24 pagesBasic GeometryEtha Cantik100% (1)
- Cartesian PlaneDocument39 pagesCartesian PlaneBol Mën NhialNo ratings yet
- Curvilinear Perspective: Exploring Depth Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandCurvilinear Perspective: Exploring Depth Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Geology Weak 3 and 4Document2 pagesGeology Weak 3 and 4Ana May BanielNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Surveying Module 1 and 2Document2 pagesFundamentals of Surveying Module 1 and 2Ana May BanielNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITYDocument6 pagesACTIVITYAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics Operations OnDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics Operations OnAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- FIDP Revised Output - Business and Consumer LoansDocument4 pagesFIDP Revised Output - Business and Consumer LoansAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Teaching Guide (ATG) Revised OutputDocument4 pagesAdaptive Teaching Guide (ATG) Revised OutputAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- New Document300 20 Nov 2021 09 58 23Document1 pageNew Document300 20 Nov 2021 09 58 23Ana May BanielNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Teaching Guide (ATG) OutputDocument4 pagesAdaptive Teaching Guide (ATG) OutputAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- Conic-Parabola 101Document27 pagesConic-Parabola 101Ana May BanielNo ratings yet
- Lesson-1 in ARTSDocument30 pagesLesson-1 in ARTSAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- Mus Ic of Min Doro: Yvhan Gabriel T. Fernando and Krentz ToleteDocument7 pagesMus Ic of Min Doro: Yvhan Gabriel T. Fernando and Krentz ToleteAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- TG 17 Nov 2021 10 25 17Document5 pagesTG 17 Nov 2021 10 25 17Ana May BanielNo ratings yet