Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mech. of Anti - Markonikov Rule
Mech. of Anti - Markonikov Rule
Uploaded by
Dark phantomOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mech. of Anti - Markonikov Rule
Mech. of Anti - Markonikov Rule
Uploaded by
Dark phantomCopyright:
Available Formats
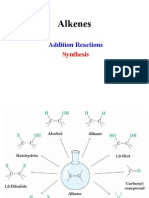
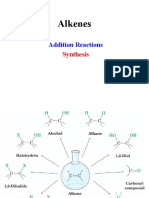
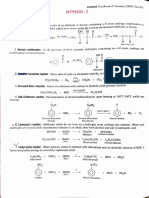
Anti-Markonikov rule Kharasch effect the basis of appropriate mechanism.
on
17. Explain the
or
Kharasch eflect is the addition ofonly HBr to alkenes in the presence of benzoyl peroxide to give
Ans.
the product agaimst the Markownikov rule. For example,
CH,CH = CH, + HBr Benzoyl peroxide - CH,-CH-CH,-Br
P'ropene I-Bronopropane
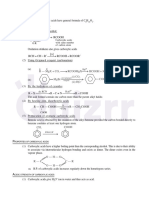
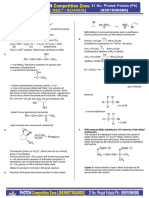
The addition of HBr to unsymmetrical alkene in the presence of benzoyl peroxide occurs by free
radical mechanism. The various steps of this mechanism are
) Benzoyl peroxide undergoes homolytic fission to produce CgH,-CO-0' free radical.
CHCO-0-0-COC, Homolysis - CH,cO-O +0-COC,H,
Benzoyl peroxide Free radical Free radical
i) Free radical CgH,CO-O reacts with HBr to generate free radical Br.
CHCO-0 + H-Br C,H,COOH + Br
Free radical
Free radical Benzoic acid
(ii) Then the free radical Br adds to double bond in such a way to give more stable free radical.
Since 2° free radical is more stable than 1° free radical, it is preferably formed.
Br +CH-CH =
CH, »
CH-CH-CH,Br + CH-CH-CH2
Propenee 2°Free radical
(more stable) Br
1° free radical
(less stable)
(v) The 2° free radical abstracts a Br free radical from HBr resulting in the formation of
anti-Markownikov product.
CH,CH-CH,Br + HBr -CH,CH,-CH,Br +Br
2 free radical 1-Bromopropane
The steps (iü) and (iv) are repeated again and again to form the desired product.
You might also like
- Prices and Taxes of Locally-Manufactured Distilled Spirits 2013Document3 pagesPrices and Taxes of Locally-Manufactured Distilled Spirits 2013Imperator Furiosa100% (2)
- 13 Cationic RearrangementsDocument15 pages13 Cationic RearrangementsaudreyjouotaNo ratings yet
- Sample Study Material: IIT-JAM ChemistryDocument74 pagesSample Study Material: IIT-JAM ChemistryPradeep PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Organic (Nag3)Document25 pagesOrganic (Nag3)riaz.atom4No ratings yet
- 29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument9 pages29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets Quizrrpowerranger34873No ratings yet
- Alkenes ReactionsDocument69 pagesAlkenes Reactionsjazbutuyan1997No ratings yet
- 29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument8 pages29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets QuizrrArjunNo ratings yet
- Adisi Elektrofilik Kimia OrganikDocument25 pagesAdisi Elektrofilik Kimia OrganikAcikaNo ratings yet
- Alkenes ReactionsDocument69 pagesAlkenes ReactionsAhmad SayyedahmadNo ratings yet
- Assignment Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument3 pagesAssignment Haloalkanes and HaloarenesAayush RastogiNo ratings yet
- Alkenes ReactionsDocument69 pagesAlkenes ReactionsHamidatun NisaNo ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument11 pagesIonic EquilibriumAYUSH GOSWAMINo ratings yet
- Haloalkenes and HaloalkensDocument9 pagesHaloalkenes and Haloalkensvinay368kNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Organic Reactions For UG StudentsDocument45 pagesMechanism of Organic Reactions For UG StudentsiycbrthoratNo ratings yet
- Organic Reaction: Addition Substitution Elimination RearrangementDocument39 pagesOrganic Reaction: Addition Substitution Elimination RearrangementJulJayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 (Org) - Part 2Document22 pagesChapter 7 (Org) - Part 2Wacka FlockaNo ratings yet
- Cc2lec - Module 4Document6 pagesCc2lec - Module 4LUKENo ratings yet
- Class 12 Organic SupplementsDocument14 pagesClass 12 Organic Supplementslovishsindhi185No ratings yet
- Carboxlic Acids and Its DerivatiesDocument13 pagesCarboxlic Acids and Its DerivatiesMohammadHussainKhanNo ratings yet
- Aromatic - Aliphatic Compounds (Arenes) : Dr. Ayad MR Raauf 1 Semester College of Pharmacy, Al-Farahidi UniversityDocument8 pagesAromatic - Aliphatic Compounds (Arenes) : Dr. Ayad MR Raauf 1 Semester College of Pharmacy, Al-Farahidi Universityayneeh82489No ratings yet
- Reaction Intermediates: Types of Bond CleavagesDocument31 pagesReaction Intermediates: Types of Bond CleavagesB Sai SidharthNo ratings yet
- 14 Addition To Alkenes 2019Document1 page14 Addition To Alkenes 2019ayushupadhyay548No ratings yet
- Electrophilicadditionfinal 140313091410 Phpapp02Document39 pagesElectrophilicadditionfinal 140313091410 Phpapp02Abdulrahman SaadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document46 pagesChapter 12Eshita SharmaNo ratings yet
- 01-Reaction IntermediatesDocument26 pages01-Reaction IntermediatessavimohanaNo ratings yet
- Reaction of AlkeneDocument55 pagesReaction of Alkenejaydeep TupeNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Alkynes 3Document13 pagesHydrocarbon Alkynes 3Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Pages Containing HWDocument23 pagesHydrocarbon Pages Containing HWashishkumarberia016No ratings yet
- "Master Organic Chemistry": Anti-Markovnikoff BH H Syn AdditionDocument1 page"Master Organic Chemistry": Anti-Markovnikoff BH H Syn AdditionMoncef AbbesNo ratings yet
- Addition To Alkenes CheatsheetDocument1 pageAddition To Alkenes CheatsheetChinmay MhatreNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-9. Hydrocarbons Q & ADocument14 pagesHsslive-Xi-Chem-9. Hydrocarbons Q & AshineNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Reactions With Miscellaneous Reagents: 5.1 N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS)Document47 pagesModule 5 Reactions With Miscellaneous Reagents: 5.1 N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS)Dr Sachin K SinghNo ratings yet
- AlkenesDocument9 pagesAlkenesNIHAAL KANDPALNo ratings yet
- Radical Additions Anti-Markovnikov Product FormationDocument2 pagesRadical Additions Anti-Markovnikov Product Formationmegamon asabeNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and Alkynes2015Document37 pagesAlkenes and Alkynes2015firouzeh68No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lecture Slides PDFDocument179 pagesChapter 8 Lecture Slides PDFjoseph changNo ratings yet
- Halo Alkane Halo AreneDocument16 pagesHalo Alkane Halo Areneujonic13No ratings yet
- 11H Alkene2Document35 pages11H Alkene2henriquejfdsantos4No ratings yet
- Alk Enes Al Kynes ExercisesDocument1 pageAlk Enes Al Kynes ExercisesAR LazagaNo ratings yet
- 12a Alkena Dan Reaksinya Bagian 2Document91 pages12a Alkena Dan Reaksinya Bagian 2ElisNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 29-Jun-2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 29-Jun-2023Sudhir KumarNo ratings yet
- Alkenes: Definition and Structure of AlkenesDocument4 pagesAlkenes: Definition and Structure of AlkenesSekarNo ratings yet
- Homolytic: Click A Box Below To Go To The MechanismDocument29 pagesHomolytic: Click A Box Below To Go To The Mechanismhknhat100% (1)
- Physical Organic Chemistry Chapter ThreeDocument40 pagesPhysical Organic Chemistry Chapter ThreeMULUKEN TILAHUNNo ratings yet
- Many Parameters Influence Nucleophilic SubstitutionDocument29 pagesMany Parameters Influence Nucleophilic SubstitutionImam SyNo ratings yet
- Carboranes AgapinDocument17 pagesCarboranes AgapinJulienne Stephanie Fabie100% (1)
- Dr. R. S. Shinde B.sc. I Sem-I Organic ChemistryDocument36 pagesDr. R. S. Shinde B.sc. I Sem-I Organic ChemistryHaroon Ur RashidNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides - Elimination ReactionsDocument25 pagesAlkyl Halides - Elimination ReactionsWidya FatmawatiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: CollegeDocument34 pagesOrganic Chemistry: CollegeArwa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Alkenes: NomenclatureDocument15 pagesAlkenes: NomenclatureMukesh BishtNo ratings yet
- P-Block I Notes VTCDocument7 pagesP-Block I Notes VTCarunachalam862005No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Alcohol Reactions: I. Reactions of Alcohols With Acids and BasesDocument9 pagesChapter 9 Alcohol Reactions: I. Reactions of Alcohols With Acids and BasesRoberto SIlvaNo ratings yet
- 10 Halogen Derivatives of Alkanes and ArenesDocument3 pages10 Halogen Derivatives of Alkanes and Arenesfedbit2020No ratings yet
- HaloalkanesDocument12 pagesHaloalkanescoding727treeNo ratings yet
- Alkyl and Aryl Halides NEETDocument10 pagesAlkyl and Aryl Halides NEETJagrav GargNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 14-Mar-2021Document12 pagesAdobe Scan 14-Mar-2021Sushrut PujahariNo ratings yet
- Carbocations: Vamsi Rajasekhara Reddy M.Pharmacy 1 Year (Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument15 pagesCarbocations: Vamsi Rajasekhara Reddy M.Pharmacy 1 Year (Pharmaceutical ChemistryRajesh Neppalli100% (1)
- Carbenes 170512195843Document38 pagesCarbenes 170512195843ajayyashpalNo ratings yet
- Name ReactionsDocument6 pagesName Reactionsap39fp3tNo ratings yet
- Worldlink L4u3Document8 pagesWorldlink L4u3Ольга КостюкNo ratings yet
- DRAFT SOAL STS GENAP Kelas XIDocument9 pagesDRAFT SOAL STS GENAP Kelas XIcholisNo ratings yet
- Department of Social Welfare Services: Republic of The Philippines City of CebuDocument2 pagesDepartment of Social Welfare Services: Republic of The Philippines City of CebuadoptifyNo ratings yet
- PDF Ers Handbook of Respiratory Medicine Paolo Palange Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Ers Handbook of Respiratory Medicine Paolo Palange Ebook Full Chapterdoris.stancliff777100% (3)
- Research Article: Labor Induction With Orally Administrated Misoprostol: A Retrospective Cohort StudyDocument10 pagesResearch Article: Labor Induction With Orally Administrated Misoprostol: A Retrospective Cohort StudyLilis RatnawatiNo ratings yet
- Wizard Magazine 019 (1993) c2cDocument198 pagesWizard Magazine 019 (1993) c2cAmirNo ratings yet
- Lean Manufacturing Aplicada A La Industria FarmaceuticaDocument6 pagesLean Manufacturing Aplicada A La Industria FarmaceuticasudermanfitoNo ratings yet
- EMT Refresher FlyerDocument2 pagesEMT Refresher FlyerBillR.YoungNo ratings yet
- 47 XinstDocument2 pages47 XinstA330TurbinexNo ratings yet
- A Hybrid Feature Extraction Method With Regularized Extreme Learning Machine For Brain Tumor ClassificationDocument8 pagesA Hybrid Feature Extraction Method With Regularized Extreme Learning Machine For Brain Tumor ClassificationKhaleda AkhterNo ratings yet
- Ipil Heights Elementary SchoolDocument12 pagesIpil Heights Elementary SchoolAilljim Remolleno ComilleNo ratings yet
- XI-IP-I-Python Fundamentals-Module - I-June-7-2021Document12 pagesXI-IP-I-Python Fundamentals-Module - I-June-7-2021Raju UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Big Data Analytics (2017 Regulation)Document8 pagesBig Data Analytics (2017 Regulation)cskinitNo ratings yet
- AC119 Cashflow StatementDocument82 pagesAC119 Cashflow StatementTINASHENo ratings yet
- Skill 103 Administering A Large-Volume Cleansing EnemaDocument3 pagesSkill 103 Administering A Large-Volume Cleansing EnemaHarley Justiniani Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- OOP SE-203: Submitted By: - ANUJ 2K20/SE/21 - Anurag Munshi 2K20/Se/25Document9 pagesOOP SE-203: Submitted By: - ANUJ 2K20/SE/21 - Anurag Munshi 2K20/Se/25Anurag Munshi 25No ratings yet
- MDO3000 Oscilloscope User Manual 077096801 7Document243 pagesMDO3000 Oscilloscope User Manual 077096801 7karivenNo ratings yet
- Paths To A Green World: The Political Economy of The Global EnvironmentDocument19 pagesPaths To A Green World: The Political Economy of The Global EnvironmentMohammed S M AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- Ultra Mag™ Electromagnetic Flow Meter Submittal PackageDocument19 pagesUltra Mag™ Electromagnetic Flow Meter Submittal PackageSalvador HernándezNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To T-TestsDocument5 pagesAn Introduction To T-Testsbernadith tolinginNo ratings yet
- Spandan HR ManualDocument46 pagesSpandan HR ManualBotanic Hair Oil100% (1)
- Ankle Sprain: Understanding Ankle Sprains The First 48 HoursDocument2 pagesAnkle Sprain: Understanding Ankle Sprains The First 48 HoursDhafin RizkyNo ratings yet
- Guide To Power System Earthing Practice Final (June2009) PDFDocument176 pagesGuide To Power System Earthing Practice Final (June2009) PDFssamonas100% (6)
- Inferno Fury ManualDocument6 pagesInferno Fury ManualJohn BurgerNo ratings yet
- InventoryDocument25 pagesInventoryNeil Joseph AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Sewer Details CVI02720Document19 pagesSewer Details CVI02720Munir Baig100% (1)
- Entities and Their PropertiesDocument9 pagesEntities and Their PropertiesHimadri BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- 4150 Lab 3Document6 pages4150 Lab 3Tan Nguyen VanNo ratings yet
- HardeesDocument24 pagesHardeesformanite33% (3)