Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Treatment of Hyperkalemia in Adults
Treatment of Hyperkalemia in Adults
Uploaded by
Bharath Kumar ReddyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Treatment of Hyperkalemia in Adults
Treatment of Hyperkalemia in Adults
Uploaded by
Bharath Kumar ReddyCopyright:
Available Formats
Treatment of hyperkalemia in adults
Official reprint from UpToDate® www.uptodate.com
©2023 UpToDate®
Treatment of hyperkalemia in adults
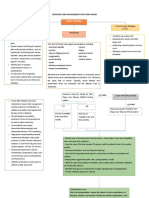
Doesthepatienthave1ormoreclinicalmanifestationsofhvoerkalemia?
Theseinclude:
&duscleweaknessorparalysis
•Cardiacconductionabnormalitiesorarmythmias*
Serumpotassium>6.5mEa/L?
Ne
Areall3ofthefollowinaoresent?
=Serumpotassium>>.>mEarl
=Significantkidneyfunctionimpairment
=Ongoingtissuebreakdown(eg,rhabdomyolysis,crushinjury,
tumorlysissyndrome)orongoingpotassiumabsorption
tea.fromsigninicantgastrointestinalbleedina)
Hyperkalemicemergency
Suchpatientsshouldbetreatedwithraoidlyactingtherabies.
includingIcalaumfirthereareEGGchangesand/ortheserum Istheserumborassium25.3mEal?
potassiumis26.3mEalIandinsulinandalucose.Inaddition.
therapiesthatremovepotassiumfromtheboovshouldbeadministered
(hemodialysis.aastrointestinalcationexchanaers.ordiuretics).
Doesthepatientnavesevere
kidneyfunctionimpairment
(ie,ESKDoroliguria)?
Doesthepatientneed
tobeovumizedforan
impendingsurgerv:
Yes No
Lowerpotassiumpromptly Potassiumcanbeloweredslowly
Althoughtheydonotrequirerapidlyactingtherapies Mostofthesepatientswillhavechronicelevations
le,calcium.insulin.andglucose›.suchbauentsshould inserumpotassiumduetoCKDortheuseof
havetheirpotassiumloweredpromptly(within medicationsthatinhibittheRAS(orboth).
6to12hours).PatientswithESKDoroliguriashouldbe Suchpatientscanoftenbemanagedwithdietary
treatedwithdialvsis,itpossible,oragastrointestinal modification.useofdiuretics(ifaporopriate).
cationexchanger.Otherbauentsshouldbemanaged bicarbonatetherapy(ifmetabolicacidosisispresent).
withreversalofthecauseofhyperkalemia(ifpossible, andreversaloffactorsthatcanproducehyperkalemia
ea.discontinuationofanACEinhibitor.bicarbonate (ea.NSAIDs.hvoovoemial.Lesscommonlv.druas
therapy(ifmetabolicacidosisispresent),diuretics thatinhibittheRasarediscontinued.orgastrointestinal
(ifhypervolemic.thecombinationofsalineinfusionwith cationexchangersareusedonachronicbasis.
diuretics.oragastrointestinalcationexchanger.
ESKD: end-stage kidney disease; ACE: angiotensin-converting enzyme; CKD: chronic kidney disease; RAS: renin-
angiotensin system; NSAIDs: nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs; IV: intravenous; ECG: electrocardiogram.
* Cardiac manifestations of hyperkalemia are discussed in detail in the topic on clinical manifestations of hyperkalemia.
¶ Some experts given IV calcium only to patients with ECG changes. Details are presented in the topic on treatment of
hyperkalemia.
- Page 1 of 2 -
You might also like
- Study Notes Family MedicineDocument49 pagesStudy Notes Family MedicineMedShare85% (27)
- Acute Renal FailureDocument33 pagesAcute Renal FailureAqsa Akbar AliNo ratings yet
- Rent-A-Movie Database Project: YOUR ASSIGNMENT (Deliverables Are Underlined)Document2 pagesRent-A-Movie Database Project: YOUR ASSIGNMENT (Deliverables Are Underlined)Miguel Flores FloresNo ratings yet
- Based On Your Possible Final Diagnosis, What Are The Treatment Plans For Our Patient?Document63 pagesBased On Your Possible Final Diagnosis, What Are The Treatment Plans For Our Patient?Kita kitaNo ratings yet
- Renal EmergenciesDocument93 pagesRenal EmergenciesShubham gaurNo ratings yet
- oPTIMAL MANAGEMENT OF ASCITESDocument8 pagesoPTIMAL MANAGEMENT OF ASCITESRositaMagda MataNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury & Chronic Kidney Disease: Amir Syahmi Derrick Ezra NGDocument45 pagesAcute Kidney Injury & Chronic Kidney Disease: Amir Syahmi Derrick Ezra NGDerrick Ezra NgNo ratings yet
- Biliaryatresia PDFDocument7 pagesBiliaryatresia PDFRendra Perwira AditamaNo ratings yet
- Indications For TransplantDocument4 pagesIndications For TransplantDorina EfrosNo ratings yet
- OLIGURIADocument31 pagesOLIGURIAAnnushika PalanichamyNo ratings yet
- Arritmias X HipercalemiaDocument9 pagesArritmias X Hipercalemiafh2301lrNo ratings yet
- KaliumDocument2 pagesKaliumJustine Kaye Iballa HarligaNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia in Hepatic DiseaseDocument3 pagesAnesthesia in Hepatic DiseaseRoxana SurliuNo ratings yet
- Management of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticleDocument4 pagesManagement of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticlealeNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis Hours: 5. Working Place: Classroom, Hospital Wards. QuestionsDocument5 pagesCirrhosis Hours: 5. Working Place: Classroom, Hospital Wards. QuestionsNahanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Hepatic FailureDocument11 pagesPharmacotherapy of Hepatic FailureMenna ElesawyNo ratings yet
- Reviews: Management of Hyperkalaemia in Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument10 pagesReviews: Management of Hyperkalaemia in Chronic Kidney Diseasebagir_dm10No ratings yet
- Treatment and Prevention of Hyperkalemia in AdultsDocument34 pagesTreatment and Prevention of Hyperkalemia in Adultsr33realNo ratings yet
- 3 and 4 Management of Medically CompromisedDocument63 pages3 and 4 Management of Medically Compromisedranareda499No ratings yet
- Pi Is 0002934308011194Document7 pagesPi Is 0002934308011194Joy SitanggangNo ratings yet
- Done By: Dana Othman: AscitesDocument28 pagesDone By: Dana Othman: Ascitesraed faisalNo ratings yet
- Ascites, SBP, Encephlopathy 2Document78 pagesAscites, SBP, Encephlopathy 2Rida AkramNo ratings yet
- Chandok Et Al, 2010Document8 pagesChandok Et Al, 2010Cika Zahrah DewisoniaNo ratings yet
- Name: Ellaine Jhane T. Domede Bsn1VDocument9 pagesName: Ellaine Jhane T. Domede Bsn1VNeil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Liver Disease Decompensated N PDFDocument6 pagesChronic Liver Disease Decompensated N PDFmzhao230No ratings yet
- OUTPUTDocument3 pagesOUTPUTRoshin Mae E. TejeroNo ratings yet
- Mrcs Upper GitDocument59 pagesMrcs Upper GitAdebisiNo ratings yet
- Treatment and Prevention of Hyperkalemia in Adults - UpToDateDocument24 pagesTreatment and Prevention of Hyperkalemia in Adults - UpToDateJosé Abraham Amaya DuarteNo ratings yet
- Hiperkalemia PDFDocument26 pagesHiperkalemia PDFJesús Arnoldo Vargas OntiverosNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument9 pagesLiver CirrhosismedsmracelisNo ratings yet
- Gi Emergencies SeminarDocument122 pagesGi Emergencies SeminarShubham gaurNo ratings yet
- Aki Inn EmergencyDocument52 pagesAki Inn EmergencyHamza DossaNo ratings yet
- 1. CirrhosisDocument53 pages1. CirrhosisAayush LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury AKIDocument6 pagesAcute Kidney Injury AKIfazeel shah vlogsNo ratings yet
- Adrenalectomia-Open Anterior Left AdrenalectomyDocument8 pagesAdrenalectomia-Open Anterior Left AdrenalectomyLorena AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument6 pagesAplastic AnemiaLargactil CpzNo ratings yet
- Clinical Liver Disease - 2021 - Sharma - Liver Abscess Complications and TreatmentDocument5 pagesClinical Liver Disease - 2021 - Sharma - Liver Abscess Complications and TreatmentNaldo NathanNo ratings yet
- Ascites Hrs B WPDocument101 pagesAscites Hrs B WPGhias Un Nabi TayyabNo ratings yet
- 209 FullDocument5 pages209 FullSamantha DonayreNo ratings yet
- Approach ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesApproach ConsiderationsGunawan SetiawanNo ratings yet
- CK SamplesDocument63 pagesCK SamplesAppu ayyala100% (2)
- 18 - Oncologic - Emergencies (PICU COURSE)Document44 pages18 - Oncologic - Emergencies (PICU COURSE)surasuarezlopezNo ratings yet
- Gout - A Guide For The General and Acute Physicians: Authors: Abhishek AbhishekDocument6 pagesGout - A Guide For The General and Acute Physicians: Authors: Abhishek AbhishekMaretha NazhifahNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi Obat AntikoagulanDocument20 pagesFarmakologi Obat AntikoagulanHenderi SaputraNo ratings yet
- 1800 - Veg - Meal Plan - CompressedDocument55 pages1800 - Veg - Meal Plan - CompressedJilimili EngtipiNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure: Shilpa KathuriaDocument20 pagesAcute Renal Failure: Shilpa Kathuriashrutik91No ratings yet
- Jurnal Reading Management SVTDocument44 pagesJurnal Reading Management SVTsuho exoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name FurosemideDocument1 pageGeneric Name FurosemideChristopher LeeNo ratings yet
- HypercalcemiaDocument50 pagesHypercalcemiaEvelyn EdgarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management: Nursing Management: Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument22 pagesNursing Management: Nursing Management: Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Diseasedian rachmat saputroNo ratings yet
- Clinical Liver Disease - 2012 - Reverter - Management of An Acute Variceal Bleeding EpisodeDocument4 pagesClinical Liver Disease - 2012 - Reverter - Management of An Acute Variceal Bleeding EpisodeEUODIA HANA KRISTINANo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument33 pagesAcute Renal Failureimranqazi11No ratings yet
- Cirrhosis AndrewDocument33 pagesCirrhosis Andrewlionel andreaNo ratings yet
- MX of COVID-19Document49 pagesMX of COVID-19anisNo ratings yet
- ABC of Heart Failure Management Diruretics ACE Inhibitors and NotratesDocument4 pagesABC of Heart Failure Management Diruretics ACE Inhibitors and Notratesgroup38No ratings yet
- Gout and Pseudogout: Prof ZayDocument56 pagesGout and Pseudogout: Prof ZaySindhu BabuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyColleen De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Enalapril, Metropolol, Aspirin, CiticolineDocument8 pagesEnalapril, Metropolol, Aspirin, CiticolineGabriel MatibagNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 AscitesDocument42 pagesLecture 2 AscitesZainab ArshadNo ratings yet
- Book Review (Writing) : Indriyani (1740601042)Document8 pagesBook Review (Writing) : Indriyani (1740601042)Indri YaniNo ratings yet
- Mass SongsDocument20 pagesMass SongsJason LayaNo ratings yet
- A2 - 3 - Mid Course Test With Key - SlideshowDocument24 pagesA2 - 3 - Mid Course Test With Key - SlideshownevenkaNo ratings yet
- NZS 3104 - Specification For Concrete ConstructionDocument43 pagesNZS 3104 - Specification For Concrete ConstructionRihab AbukhdairNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument3 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationkabirNo ratings yet
- A Rite of The WerewolfDocument15 pagesA Rite of The WerewolfRAVINDER BSINGH100% (1)
- Prince Ea-I Just Sued The School SystemDocument3 pagesPrince Ea-I Just Sued The School SystemTizioNo ratings yet
- 4Document6 pages4nikko candaNo ratings yet
- Homework 3 - 2029991 - 01 - Sent (v2)Document4 pagesHomework 3 - 2029991 - 01 - Sent (v2)David E. MuñozNo ratings yet
- Resun Price List Solar Panel-20211227Document1 pageResun Price List Solar Panel-20211227Nemesu LorentNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q4 Intro To KinematicsDocument54 pagesScience 9 Q4 Intro To KinematicsSire WillNo ratings yet
- 51125-07 Vevo LAB User Manual 1.1Document694 pages51125-07 Vevo LAB User Manual 1.1Leon PalomeraNo ratings yet
- Fama FraternitatisDocument10 pagesFama Fraternitatistom watersNo ratings yet
- 1 Apogee General PDFDocument12 pages1 Apogee General PDFJoanNo ratings yet
- Inspection and Test Plan - Steel AssemblyDocument1 pageInspection and Test Plan - Steel AssemblyAvinash LalNo ratings yet
- Bubble Planner Uoi Where We Are in Place and TimeDocument10 pagesBubble Planner Uoi Where We Are in Place and TimeasimaNo ratings yet
- AWS Welding Standard PreviewDocument5 pagesAWS Welding Standard PreviewRavi YadavNo ratings yet
- TW316 PresentationDocument26 pagesTW316 PresentationCherylNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument20 pagesResearch ProposalCharles ChikumbiNo ratings yet
- Herodotus and The Emergence of The DemagDocument15 pagesHerodotus and The Emergence of The DemagKsenija BirmanacNo ratings yet
- Flow Visualization, Edited by Tsuyoshi AsanumaDocument2 pagesFlow Visualization, Edited by Tsuyoshi AsanumaAnonymous A415sJ9No ratings yet
- Zeh-2002-Decoherence - Basic Concepts and Their Interpretation.9506020v3Document42 pagesZeh-2002-Decoherence - Basic Concepts and Their Interpretation.9506020v3sscript14100% (2)
- The Iconic Influence of Queen Elizabeth IIDocument2 pagesThe Iconic Influence of Queen Elizabeth IIpatriciasusckind_574No ratings yet
- NFRCS Therm 5.2-July 06versionDocument302 pagesNFRCS Therm 5.2-July 06versionBojan Bjelajac100% (1)
- Channel Allocation in Cellular SystemDocument40 pagesChannel Allocation in Cellular SystemNishant MittalNo ratings yet
- Hriday Reflections - 02Document170 pagesHriday Reflections - 02Ar Afreen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Study ThisDocument83 pagesStudy Thispavithiran subramaniNo ratings yet
- CPAR Lesson1 Three Major TraditionsDocument28 pagesCPAR Lesson1 Three Major TraditionsShyra Mae PonceNo ratings yet
- Vector Spaces Handwritten Notes WWW - MathcityDocument58 pagesVector Spaces Handwritten Notes WWW - Mathcityatiq4pk89% (9)
- Lesson 1 Social Science and Applied Social ScienceDocument51 pagesLesson 1 Social Science and Applied Social ScienceGERALDINE ROBLESNo ratings yet