Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ortho Classifications
Ortho Classifications
Uploaded by
zakariaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ortho Classifications
Ortho Classifications
Uploaded by
zakariaCopyright:
Available Formats
Ortho Classifications
14 classifications
Humerus (2 classifications)
1. Classification of proximal humerus fracture
Name: Neer’s classification (based on fracture segments(
Classes:
• Type I – Articular segment
• Type II – Greater tuberosity
• Type III – Lessor tuberosity
• Type IV – Humeral shaft
2. Supracondyler fracture of the humerus
Name: Gartland classification
Classes:
• Type I – Non-displaced
• Type II – Displaced fracture with intact posterior cortex
• Type III – Complete displace
Radius (1 Classification)
3. Head of radius fracture
Name: Manson Classification
Classes:
• Type I - Undisplaced radial head or neck
• Type II - Displaced radial head or neck
• Type III - Severely comminuted radial head or neck
• Type IV - Radial fracture with dislocation
Ulna (1 Classification)
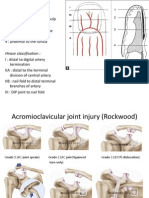
4. Monteggia Fracture Dislocation
Name: Bado Classification
Classes:
• Type I – Anterior dislocation
• Type II – Posterior dislocation
• Type III – Lateral dislocation
• Type IV – Anterior dislocation with radial shaft fracture
Femur (5 Classifications)
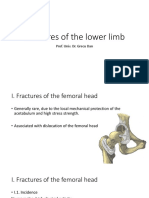
5. Femoral head fracture
Name: Pipkin Classification
Classes:
Type I - Fracture inferior to fovea
Type II - Fracture superior to fovea
Type III - Femoral head + acetabulum fracture
Type IV - Femoral head + femoral neck fracture
6. Femoral neck fracture
Name: Garden Classification
Classes:
Type I – Incomplete fracture
Type II – Completed fracture + non-displaced
Type III – Complete fracture + partially displaced
Type IV - Femoral head + fully displaced
7. Intertrochanteric fracture
Name: Evan’s Classification
Classes:
Type I – two part undisplaced
Type 2 – two part displaced
Type 3 – three fragments without posteriolateral support
Type – 4 three fragments without medial supprt
Type 5 – four fragments without posteri-lateral and posterior-medial support
Type 6 – Reverse oblique fracture
8. Femoral shaft fracture
Name: Winquist and Hansen classification
Classes:
• Type 0 - No comminution
• Type 1 - Insignificant butterfly fragment with transverse or short oblique fracture
• Type 2 - Large butterfly of less than 50% of the bony width, > 50% of cortex intact
• Type 3 - Larger butterfly leaving less than 50% of the cortex in contact
• Type 4 - Segmental comminution
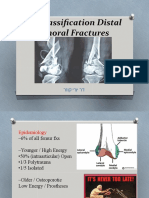
9. Distal femoral fracture
Name: Muller
Classes:
• Type A – Extra-articular (supracondylar)
• Type B - Inta-articular (unicondyler)
• Type B – Inta-articular (Bicondyler)
Tibia (3 Classifications)
10. Tibial Palateu fracture
Name: Schatzker’s Classification
Classes:
• Type I – Split
• Type II – Split depression
• Type III – Central depression
• Type IV – Split fracture (Medial)
• Type V – Bicondyler fracture
• Type VI – Dislocation of metaphysis and diaphysis
11. Tibial shaft fracture
Name: Tscherne and Goetzen closed fracture classification
Classes:
• Grade 0 – minimal soft tissue injury, simple pattern fracture
• Grade 1 – Superficial abrasion, mild-to-moderate pattern fracture
• Grade 2 – Deep abrasion, impending compartmental syndrome, severe pattern
fracture
• Grade 3 – Extended crush, Severe pattern, neurovascular injury
12. Tibial pilon fracture
Name: Ruedi and Allgower
Classes:
• Type I – non-displaced cleavage of the ankle joint
• Type II – Displaced fracture with minimal impaction or comminution
• Type III – Displaced fracture with minimal impaction or comminution and articular
impaction
Ankle (1 Classification)
13. Ankle joint fracture
Name: Weber Danis Classification
Classes:
Type A - Fibula Fracture distal to mortise
Type B - Fibula Fracture at the level of the mortise
Type C - Fibula Fracture proximal to mortise
You might also like
- Radiographic Pathology For Technologists 6th Edition Kowalczyk Test BankDocument8 pagesRadiographic Pathology For Technologists 6th Edition Kowalczyk Test Bankbridgetmercersftzmojgre100% (14)
- Shoulder ExamDocument3 pagesShoulder ExamAdriana Valadares TalonNo ratings yet
- Trauma Manual (Podiatry)Document403 pagesTrauma Manual (Podiatry)QuantumjanitorNo ratings yet
- Class II MalocclusionDocument67 pagesClass II Malocclusionsonal agarwal100% (1)
- Periarticular Fracture ClassificationDocument55 pagesPeriarticular Fracture ClassificationAdithya Stephana MahendraNo ratings yet
- PR OrtoDocument6 pagesPR OrtoJunaidi SalamNo ratings yet
- Facial Fractures ClassificationDocument72 pagesFacial Fractures ClassificationAmar Mahesh KalluNo ratings yet
- Hip Dislocation LengkapDocument30 pagesHip Dislocation Lengkapmuhammad mikoNo ratings yet
- Fracture Classification in AdultsDocument38 pagesFracture Classification in AdultsammarNo ratings yet
- Ankle and FootDocument76 pagesAnkle and FootAaliyah ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:: Dr. Ranjeet Kumar ChaudharyDocument22 pagesPrepared By:: Dr. Ranjeet Kumar ChaudharyDrRanjeet Kumar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Malocclusion 160605101556Document34 pagesMalocclusion 160605101556sabihuddinNo ratings yet
- Fractures of The Lower Limb: Prof. Univ. Dr. Grecu DanDocument126 pagesFractures of The Lower Limb: Prof. Univ. Dr. Grecu DanSorin BarbuNo ratings yet
- Distal Radial Fractures NNNNNDocument24 pagesDistal Radial Fractures NNNNNDrnasser NasNo ratings yet
- 16th TIBIAL FracturesDocument51 pages16th TIBIAL FracturesMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Fracture EponymsDocument43 pagesFracture EponymsSarah Sy-SantosNo ratings yet
- Classification of Fractures - BasicDocument19 pagesClassification of Fractures - BasicAdeel HashmiNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Fracture: Dr. Ashok Kumar K.RDocument32 pagesMandibular Fracture: Dr. Ashok Kumar K.RAditya Samantaray100% (2)
- Fracture Classification and Eponym Fractures: Supervisor: DR SyarifahDocument56 pagesFracture Classification and Eponym Fractures: Supervisor: DR SyarifahNurul AshikinNo ratings yet
- Classification of Mandibular Condylar Fractures: David B. Powers, MD, DMD, FRCS (Ed)Document10 pagesClassification of Mandibular Condylar Fractures: David B. Powers, MD, DMD, FRCS (Ed)Mashood AhmedNo ratings yet
- Classification of MalocclusionDocument30 pagesClassification of MalocclusionFazeela JamalNo ratings yet
- AO Classification Distal Femoral FracturesDocument13 pagesAO Classification Distal Femoral FracturesЮрий КозарNo ratings yet
- Fraktur FemurDocument20 pagesFraktur FemurFajar Tea JieNo ratings yet
- Fracture Classifications in OrthopaedicsDocument33 pagesFracture Classifications in Orthopaedicsmario100% (2)
- Physeal Injuries FinalDocument49 pagesPhyseal Injuries FinalAnkit KarkiNo ratings yet
- A Strategy To Prevent Complications of Hyperextension TypeDocument11 pagesA Strategy To Prevent Complications of Hyperextension TypeYovita GotamaNo ratings yet
- Salter HarrisDocument21 pagesSalter HarrisAmy KochNo ratings yet
- "Must Know" Classifications: Gustillo Salter-HarrisDocument4 pages"Must Know" Classifications: Gustillo Salter-HarrisHo Yong WaiNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Jasjus MSCDocument10 pagesPresentasi Jasjus MSCsteven hkNo ratings yet
- Fracturas de Muñeca: Said Plazola Mercado R1 TyoDocument13 pagesFracturas de Muñeca: Said Plazola Mercado R1 TyoSaid Plazola MercadoNo ratings yet
- Hospital Presentation TellaDocument27 pagesHospital Presentation TellaOlalekan TellaNo ratings yet
- OSTEOLOGY Lower Limb 3 and 4Document5 pagesOSTEOLOGY Lower Limb 3 and 4Famela Anne GOmez MadambaNo ratings yet
- Final UPMC Pocket BookDocument28 pagesFinal UPMC Pocket Bookkarate.b97No ratings yet
- Ortho EssentialsDocument8 pagesOrtho EssentialsShoban RajNo ratings yet
- Study Cast Analysis Module 2 Lesson 1Document37 pagesStudy Cast Analysis Module 2 Lesson 1Jurgen CapellanNo ratings yet
- Classification SystemsDocument11 pagesClassification SystemsKelli StevensNo ratings yet
- Class Iii Malocclusion: Presented By: Dr. Shreya SinghDocument110 pagesClass Iii Malocclusion: Presented By: Dr. Shreya SinghRohini TondaNo ratings yet
- Mid Face Fracture JSMUDocument145 pagesMid Face Fracture JSMUdaneshkumarytcNo ratings yet
- Fracture ManagementDocument19 pagesFracture ManagementManaha Sekonyela TjamelaNo ratings yet
- Shaft of Tibia FracturesDocument38 pagesShaft of Tibia FracturesSahithya MNo ratings yet
- Clay Shoveler's FractureDocument26 pagesClay Shoveler's FracturerineeshNo ratings yet
- Le Fort I, Ii, IiiDocument51 pagesLe Fort I, Ii, IiiEticha EmbaboNo ratings yet
- Classification of Malocclusion: Dr.K.Preethi Post GradúateDocument45 pagesClassification of Malocclusion: Dr.K.Preethi Post GradúatenivethaseshaNo ratings yet
- Reporters: NG, Hanna Ong, Sharmaine Panol, Mytz Peredo, Alyssa Rigon, SeanDocument20 pagesReporters: NG, Hanna Ong, Sharmaine Panol, Mytz Peredo, Alyssa Rigon, SeanLena EmataNo ratings yet
- Upper Extremity Fracture (Minus Distal Radius and Hand)Document16 pagesUpper Extremity Fracture (Minus Distal Radius and Hand)TB DOTS RS CAROLUS SALEMBANo ratings yet
- Lateral Condylar FracturesDocument14 pagesLateral Condylar FracturesYousra ShaikhNo ratings yet
- G.V. Black Caries Classification (Class I To VI)Document2 pagesG.V. Black Caries Classification (Class I To VI)Madhusmita SahuNo ratings yet
- CondyleBookChapter3 PDFDocument6 pagesCondyleBookChapter3 PDFShkelzen KomoniNo ratings yet
- 1 FructureDocument23 pages1 FructureGizachew AsimareNo ratings yet
- SipDocument12 pagesSipadi3636No ratings yet
- Elbow FracturesDocument21 pagesElbow Fracturesnovitafitri123No ratings yet
- Fractureppt 220926101711 044bb831Document61 pagesFractureppt 220926101711 044bb831Felix SabuNo ratings yet
- To TraumatoDocument3 pagesTo TraumatoRebel ElNo ratings yet
- Classification of MalocclusionDocument51 pagesClassification of MalocclusionYuvashreeNo ratings yet
- Classification of FractureDocument4 pagesClassification of FractureSaran Zaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Classification of FractureDocument4 pagesClassification of FractureSaran Zaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Condylar FracturesDocument91 pagesCondylar FracturesSaranya MohanNo ratings yet
- Salter Harris FractureDocument24 pagesSalter Harris FractureFredy GunawanNo ratings yet
- Reduction, Relocation and Splinting in Emergency Room (RASER)From EverandReduction, Relocation and Splinting in Emergency Room (RASER)No ratings yet
- Metacarpal FractureDocument45 pagesMetacarpal FractureJinnasit TeeNo ratings yet
- DislocationDocument46 pagesDislocationShaa ShawalishaNo ratings yet
- First Aid For FracturesDocument34 pagesFirst Aid For FracturesRhy Enne CelestialNo ratings yet
- 04 - Femur Neck and HeadDocument28 pages04 - Femur Neck and HeadammarNo ratings yet
- Sprains and StrainsDocument23 pagesSprains and StrainsokaciaNo ratings yet
- First Aid GuideDocument1 pageFirst Aid GuideStyx XieNo ratings yet
- Medical Language Accelerated 2Nd Edition Full ChapterDocument36 pagesMedical Language Accelerated 2Nd Edition Full Chapteredward.weisner630100% (23)
- Perbandingan Kompres Air Hangat Dengan Rendam Air Garam Terhadap Penurunan Skala Nyeri PenderitaDocument9 pagesPerbandingan Kompres Air Hangat Dengan Rendam Air Garam Terhadap Penurunan Skala Nyeri PenderitaLuluk Novaliadin AzaleaNo ratings yet
- Fracture Lower Limb 2Document21 pagesFracture Lower Limb 2Ahmed MostafaNo ratings yet
- PE 112 Pathfit Movement Competency Training Lessons 2 and 3 (Injuries and First Aid)Document15 pagesPE 112 Pathfit Movement Competency Training Lessons 2 and 3 (Injuries and First Aid)Markjan S. AlmoginoNo ratings yet
- Fracturas RXDocument53 pagesFracturas RXLindsay Kelly Vega MezaNo ratings yet
- Treatment and Rehabilitation of Fractures (Stanley Hoppenfeld)Document1 pageTreatment and Rehabilitation of Fractures (Stanley Hoppenfeld)小蓮花No ratings yet
- Shoulder PathologiesDocument33 pagesShoulder PathologiesjermaineNo ratings yet
- MSK Congenital DisordersDocument49 pagesMSK Congenital DisordersFarah Balqis BaragbahNo ratings yet
- PHT 482 Musculoskeletal Diseases and DisordersDocument12 pagesPHT 482 Musculoskeletal Diseases and DisordersMonica StephenieNo ratings yet
- Diaphyseal Fractures in Children Final - 2Document62 pagesDiaphyseal Fractures in Children Final - 2Arlina Wiyata GamaNo ratings yet
- PTS BAHASA INDONESIA KLS X (Asria, S.PD.) (Respons)Document29 pagesPTS BAHASA INDONESIA KLS X (Asria, S.PD.) (Respons)sabiqNo ratings yet
- To Slip Inferior The Result Is A Spondylolisthesis: The Four Grades of Spondylolisthesisare As Follows: °°Document2 pagesTo Slip Inferior The Result Is A Spondylolisthesis: The Four Grades of Spondylolisthesisare As Follows: °°Katrina Vea CalaroNo ratings yet
- Radiology: Joint Knee Without ContrastDocument1 pageRadiology: Joint Knee Without ContrastAli BrexetNo ratings yet
- Unicorns, Dragons, PolymyositisDocument3 pagesUnicorns, Dragons, PolymyositisMusleh AlgarniNo ratings yet
- Ijcmsr 312 v1Document7 pagesIjcmsr 312 v1AshliiqueNo ratings yet
- MyopathyDocument31 pagesMyopathyNur LailaturrizaNo ratings yet
- Arthritis: Dr.A.Prakash M.S. Orthopedics Fellow in Trauma and Arthroplasty. Ortho Life Hospital, ErodeDocument36 pagesArthritis: Dr.A.Prakash M.S. Orthopedics Fellow in Trauma and Arthroplasty. Ortho Life Hospital, ErodemrkasprakashNo ratings yet
- The Failed Hallux ValgusDocument127 pagesThe Failed Hallux ValgusFlorin MacarieNo ratings yet
- Osteogénesis ImperfectaDocument13 pagesOsteogénesis ImperfectaCheby MorenoNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Vs OsteoarthritisDocument10 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis Vs OsteoarthritisPratyusha100% (1)
- Scaohoid Fracture 4Document34 pagesScaohoid Fracture 4Noor Al Zahraa Ali100% (1)
- Pe AproapeDocument1 pagePe AproapeRoxa777No ratings yet