Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Production Part Approval Process PPAP
Production Part Approval Process PPAP
Uploaded by
Jinhua NiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Production Part Approval Process PPAP
Production Part Approval Process PPAP
Uploaded by
Jinhua NiCopyright:
Available Formats
Production Part Approval Process (PPAP)
1. Production part approval process (PPAP) [1] is used in 6. Process Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
the automotive supply chain for establishing confidence in (PFMEA)
component suppliers and their production processes, by 7. Control Plan
means of demonstrating that "All customer engineering 8. Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA)
design record and specification requirements are properly 9. Dimensional Results
understood by the supplier and that the process has the 10. Records of Material / Performance Test Results
potential to produce product consistently meeting these 11. Initial Process Studies
requirements during an actual production run at the 12. Qualified Laboratory Documentation
quoted production rate." 13. Appearance Approval Report (AAR)
14. Sample Production Parts
15. Master Sample
Although individual manufacturers have their own
16. Checking Aids
particular requirements, the Automotive Industry Action
17. Customer-Specific Requirements
Group (AIAG) has developed a common PPAP standard as
18. Part Submission Warrant (PSW)
part of the advanced product quality planning (APQP) – and
encouraging the use of common terminology and standard 5. PPAP Examples
forms to document project status. The result of this process
is a series of documents gather ed in one specific location (a 5.1.1 Process Flow Example
binder or electronically) called the "PPAP Package". The
PPAP package is a series of documents which need a formal
approval by the supplier and customer. The for m that
summarizes this package is called PSW (part submission
warrant). The approval of the PSW indicates that the
supplier responsible person (usually the Quality Engineer)
has reviewed this package and that the customer has not
identified any issues that would prevent its approbation.
2. Applicability of PPAP [2]
Whenever Customer or Supplier under following
manufacturing phase, PPAP is required.
(1) New Part (2) Engineering Change (3) Tooling: Transfer, Figure 1 PPAP Process Flow Example [3]
Replacement, Refurbishment (4) Correction of Discrepancy
5.1.2. PPAP documentation example
(5) Tooling Inactive > 1 Year (6) Change to optional
construction or material (7) Sub-supplier or material source From following PPAP template, it is understood that how
change (8) Change in part-processing (9) Parts produced at NCR r equires to maintain PPAP from part supplier at
new or additional location. different level.
3. Benefits of PPAP [2]
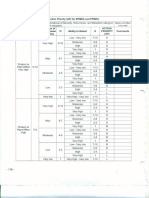
PPAP Levels for Submission & Retention
(1) Helps to maintain design integrity (2) Identifies issues Requirement Level 1 Level 2
Submission Level
Level 3 Level 4 Level 5
early for resolution (3) Reduces warranty changes and cost 1. Design Records of Saleable Product R R R * R
of poor quality (4) Assist with managing supplier changes a. For proprietary components/details
b. For all other components/details
R
R
R
R
R
R
*
*
R
R
(5) Prevents use of unapproved and uncomfortming parts 2. Engineering Change Documents, if any
3. Customer Engineering approval, if required
R
R
S
S
S
S
*
*
S
S
(6) Identifies suppliers that need more improvement (7) 4. Design FMEA
5. Process Flow Diagrams
R
R
R
R
R
S
*
*
R
S
Improves overall quality of the product and customer 6. Process FMEA
7. Dimensional Results
R
S
R
S
S
S
*
*
S
S
8. Material, Performance, Test Results R S S * S
satisfaction. 9. Initial Process Study R R R * R
10. Measurement System Analysis Studies R R S * S
11. Qualified Laboratory Documentation R R S * S
4. Official PPAP Requirements [2] 12. Control Plan
13. Part Submission Warrant (PSW)
R
S
R
S
S
S
*
*
S
S
14. Appearance Approval Report, (AAR) if applicable S S S * S
15. Bulk Material Requirements Checklist (for bulk
Following documents should be submitted or retained by material only)
16. Sample Product
R
R
R
S
R
S
*
*
R
S
organization to customer at different levels of PPAP. 17. Master Sample
18. Checking Aids
R
R
R
R
R
R
*
*
R
R
Organization’s quality level and Customer’s requirement 19. Records of compliance with Customer-Specific
Requirements (DVP&R) R R R * R
will define the requirement of level. S = The supplier shall submit to NCR and retain a copy of records or documentation items at appropriate locations.
R = The supplier shall retain at appropriate locations and make readily available to NCR upon request.
1. Design Records * = The supplier shall retain at appropriate locations, and submit to NCR upon request. NCR will identify what is
needed for submission.
2. Authorized Engineering Change Documents
3. Customer Engineering Approval, if required PLEASE CONTACT YOUR SUPPLIER QUALITY ENGINEER WITH ANY QUESTIONS .
4. Design Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
(DFMEA) applied in special situations
Figure 2 PPAP Levels for Submission/Retention [2]
5. Process Flow Diagram
6. Chrysler Case Study [4] 6.2. Mopar – Quality Part Management
By this case study it is understood that how Chrysler LLC is Mopar is the parts, service and customer care organiza tion
using PPAP for quality supply chain management. Chrysler within Chrysler Group LLC. Mopar also designs and builds a
requires Organizations to submit production and/or service small number of customized vehicles.
part approvals in accordance with PPAP guidelines.
Following table illustrates under certain manufacturing
6.1 Chrysler’s Requirement in accordance with PPAP phases Mopar’s PPAP requirements to be followed by
supplier organization.
6.1.1. Submission Levels
Organizations providing parts to a Chrysler Assembly plant
follows the guidelines for Submission Level 4.
Organizations providing certain designated parts to a
Chrysler Component or Powertrain plant follow the
guidelines for Submission Level 2, or as otherwise specified
by the rec eiving plant.
In cases where Chrysler requires a bulk material
submission, the organization takes reference from the bulk
material section in the PPAP manual.
6.1.2. Submission to Customer (Chrysler)
Organizations preparing a PPAP submission for
PRODUCTION PARTS designated for use at any Chrysler 7. Conclusion
production facility completes and retain a PSW in
a o da e with Ch ysle ’s e ui e e ts.
The auto industry giants like Ford, Chrysler, GM and their
6.1.3. Che cking Aids vast network of suppliers strictly adhere to the
PPAP. Initially developed by AIAG (Auto Industry Action
Checking aids shall be submitted when required to perform Group), PPAP has now spread to just about every other
dimensional inspection of the part being submitted. industry. PPAP is used to formally reduce risks prior to
product or service release, in a team oriented manner using
6.1.4. Appe arance and Approval Report well established tools and techniques. Both product launch
and any part revision (with a change in the manufacturing
Organizations are required to complete a Chrysler process) require PPAP submission. In addition, each part
Appearance Approval Report if the design records include must be annually recertified. Of course, this means up-front
any appearance features (e.g. Colour, Grain, Finish, supplier training and developmental costs as well as small
Appearance Standards, or Mastering Standards). Prior to on-going maintenance costs associated with PPAP.
completion of the PSW, organizations shall obtain a
Chrysler Product Design Office approval signature on the
References
AAR.
[1] Citations from www.wikipedia.com
6.1.5. Interim Approval Authorization
[2] PPAP Training Presentation of NCR
[3] PPAP 4th Edition – March 2006 – AIAG
The Interim Approval Authorization (IAA) is an official
[4] Chrysler Group LLC Customer Specific Requirements for
document approved by Chrysler to allow interim approval
and shipment of parts which do not fully meet all PPAP use with PPAP.
requirements. In cases where interim approval is granted,
the organization will receive an approved IAA from Chrysler
authorizing shipment for a limited time or a specified
quantity of parts.
6.1.6. Third Party Laboratory
O ga izatio s ot desig ated y Ch ysle as PPAP “elf –
Ce tified a e e ui ed to use a I“O/IEC 7 5 a edited
third party laboratory to verify dimensional and
material/functional tests prior to completion of a PSW.
You might also like
- Ipc Whma a 620e En英文识别版 2022线缆及线束组件的要求与验收Document17 pagesIpc Whma a 620e En英文识别版 2022线缆及线束组件的要求与验收cdmingNo ratings yet
- Fluonox KB2455LDocument3 pagesFluonox KB2455LAtham MuhajirNo ratings yet
- FORD - Label Standards - 24062020Document43 pagesFORD - Label Standards - 24062020csabaNo ratings yet
- Debit Policy - SupplierDocument1 pageDebit Policy - SupplierSAKTHIVEL ANo ratings yet
- GQADocument26 pagesGQARaduz HaduzNo ratings yet
- SEQI - IATF16949 - Internal Auditor - Training - Evaluation - QuestionnaireDocument11 pagesSEQI - IATF16949 - Internal Auditor - Training - Evaluation - QuestionnaireR.BALASUBRAMANINo ratings yet
- John Deere Standard: Approved For Supplier DistributionDocument48 pagesJohn Deere Standard: Approved For Supplier DistributionRicardo VitorianoNo ratings yet
- Canada Student Visa - Importance of SOPDocument15 pagesCanada Student Visa - Importance of SOPOluwadamilola Shitta-beyNo ratings yet
- Bizagi Modeler User GuideDocument391 pagesBizagi Modeler User GuideGas69_1No ratings yet
- PEAR 4 Manufacturing - 20calibration TestDocument3 pagesPEAR 4 Manufacturing - 20calibration TestDay CruzNo ratings yet
- Sae J121M-2013Document5 pagesSae J121M-2013phan hoai nam PhanNo ratings yet
- Powder Coat Performance Spec WSS M70J5 C1Document9 pagesPowder Coat Performance Spec WSS M70J5 C1Michal BílekNo ratings yet
- Plating Abbreviations GeneralDocument4 pagesPlating Abbreviations GeneralMustafa EyisoyNo ratings yet
- PSWDocument2 pagesPSWLinda G. CordovaNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Materials PropertiesDocument1 pageCeramic Materials PropertiesIntanasa NurdentiNo ratings yet
- Castrol Rustilo DW 902Document2 pagesCastrol Rustilo DW 902vivekpattni0% (1)
- Supply Specification DBL 5555: General ConditionsDocument17 pagesSupply Specification DBL 5555: General ConditionsMateo BanzanNo ratings yet
- Control Plan H.TDocument1 pageControl Plan H.TABHISHEK PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Cast Iron by Spark Atomic Emission Spectrometry: Standard Test Method ForDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Cast Iron by Spark Atomic Emission Spectrometry: Standard Test Method ForcommandoNo ratings yet
- ATE N 553 81.09 (En)Document11 pagesATE N 553 81.09 (En)Miguel QueirosNo ratings yet
- Gauges and InstrumentsDocument14 pagesGauges and InstrumentsRatan Misra100% (1)
- CSR MATRIX ISO TS GM FORD FCA-Regulations-CQI-111516Document46 pagesCSR MATRIX ISO TS GM FORD FCA-Regulations-CQI-111516PaulaMagalhães100% (1)
- QMS - CA Exercise ISODocument3 pagesQMS - CA Exercise ISOBharat DigheNo ratings yet
- SCM-FR-5-G Supplier Re-Evaluation FormDocument4 pagesSCM-FR-5-G Supplier Re-Evaluation Formrichard nagassarNo ratings yet
- PSWDocument1 pagePSWKunal KarmakarNo ratings yet
- PPAP Workbook 20220215Document43 pagesPPAP Workbook 20220215FRANCISCO JAVIER MALDONADONo ratings yet
- PFMEA and CP Training MaterialDocument38 pagesPFMEA and CP Training Materialshariq warsi100% (1)
- D0031 (2012-N) NES: Marking of Polymeric PartsDocument16 pagesD0031 (2012-N) NES: Marking of Polymeric PartsDiego CamargoNo ratings yet
- QAP - Rubber liningBORLDocument1 pageQAP - Rubber liningBORLdada shaikNo ratings yet
- WI-PUR-02 Criteria - Supplier Audit Frequency EvaluationDocument1 pageWI-PUR-02 Criteria - Supplier Audit Frequency EvaluationRakesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ph-Ec InfoDocument4 pagesPh-Ec InfoNick ChooNo ratings yet
- Oxsilan Presentation PDFDocument41 pagesOxsilan Presentation PDFHưng TrầnNo ratings yet
- Part Sample WarrantDocument1 pagePart Sample WarrantmageroteNo ratings yet
- An Brief Overview On Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument8 pagesAn Brief Overview On Corporate Social ResponsibilityMansangat Singh KohliNo ratings yet
- FAF03-111-2-Externally Supplied ContentDocument6 pagesFAF03-111-2-Externally Supplied ContentKinga EnNo ratings yet
- RRP 58005 REV E - UnlockedDocument8 pagesRRP 58005 REV E - UnlockedEmanuel MarkmanNo ratings yet
- Manualul Calitatii Aviatie PDFDocument15 pagesManualul Calitatii Aviatie PDFStefan GrozaNo ratings yet
- Ts 11879Document9 pagesTs 11879Prabhat MishraNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Practices & Manual For POH of Schaku Couplers: 2019-20 8/1.0 October 2019Document55 pagesMaintenance Practices & Manual For POH of Schaku Couplers: 2019-20 8/1.0 October 2019carriage drawingNo ratings yet
- Delforno Takeaway MenuDocument2 pagesDelforno Takeaway MenuSirkd ShumbaNo ratings yet
- Name Engineering Standard Number: Cummins ConfidentialDocument18 pagesName Engineering Standard Number: Cummins ConfidentialshankarNo ratings yet
- Technical Specfication - en 1563 - SGDocument4 pagesTechnical Specfication - en 1563 - SGstores svaplNo ratings yet
- Hard Anodizing of Aluminum and Its AlloysDocument3 pagesHard Anodizing of Aluminum and Its Alloysgray-watts-4023No ratings yet
- The 3DayCar Programme - The Environmental Impact of The 3DayCarDocument44 pagesThe 3DayCar Programme - The Environmental Impact of The 3DayCarYan1203No ratings yet
- 2.FCA US LLC Customer-Specific Requirements IATF 16949 - Apr 12, 2018Document48 pages2.FCA US LLC Customer-Specific Requirements IATF 16949 - Apr 12, 2018Jose Cepeda0% (1)
- VDA - Band - 16 - 3. Ausgabe 2016 - EnglischDocument83 pagesVDA - Band - 16 - 3. Ausgabe 2016 - EnglischManuel NevarezNo ratings yet
- MOM - Control PlanDocument17 pagesMOM - Control PlanraghulramasamyNo ratings yet
- RedBus Ticket - TR6S26340861Document4 pagesRedBus Ticket - TR6S26340861tushar trivediNo ratings yet
- Sample Ppap DocumentDocument132 pagesSample Ppap Documentఆనంద్ అవధానులNo ratings yet
- Autoliv Material Specification: Flat Hot Rolled Steel For Safety Products - E116088Document4 pagesAutoliv Material Specification: Flat Hot Rolled Steel For Safety Products - E116088krishnamartial8269No ratings yet
- En 14399 & en 15048 FPC Points To Be CoveredDocument8 pagesEn 14399 & en 15048 FPC Points To Be Coveredsks27974No ratings yet
- Report of Activity - DTD 27.09.2022Document4 pagesReport of Activity - DTD 27.09.2022Dilip PatilNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment Process AuditDocument2 pagesHeat Treatment Process AuditVishram VaidyaNo ratings yet
- FMEA TablesDocument7 pagesFMEA TablesMohamedNo ratings yet
- 2019 - KIA US Supplier Quality Manual KR GA PD SQD S 0001 - 02!19!2019Document32 pages2019 - KIA US Supplier Quality Manual KR GA PD SQD S 0001 - 02!19!2019rekik99266No ratings yet
- SPC V V IyerDocument85 pagesSPC V V IyerAravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Defect History: Sr. No Typeof Defect Action StatusDocument22 pagesDefect History: Sr. No Typeof Defect Action StatusSameer SaxenaNo ratings yet
- International StandardDocument7 pagesInternational StandardManasa SgrNo ratings yet
- Jis D0201 1995Document23 pagesJis D0201 1995Mahardika Kurnia DewantaraNo ratings yet
- Gage R&R Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesGage R&R Cheat SheetMario RojasNo ratings yet
- Gas NitridingDocument64 pagesGas NitridingSRIGUSTI REGA MUGIANo ratings yet
- PPAP TrainingDocument127 pagesPPAP TrainingAbhilash AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Action Construction Equipment LTD.: Ra DH Oad, Dudh La, D STT A - 121102, A A 1 RDocument192 pagesAction Construction Equipment LTD.: Ra DH Oad, Dudh La, D STT A - 121102, A A 1 RRishab WahalNo ratings yet
- CLI PT Daun Biru EngineeringDocument4 pagesCLI PT Daun Biru EngineeringKhoir HarahapNo ratings yet
- Chap 04 Customer Perceptions of ServiceDocument26 pagesChap 04 Customer Perceptions of Servicelann.yenNo ratings yet
- DSV BIM Bill of Lading - SHA71300926Document2 pagesDSV BIM Bill of Lading - SHA71300926luisinaNo ratings yet
- 1 Siraj Biodiversity Professional AgreementDocument2 pages1 Siraj Biodiversity Professional Agreementsiraj bekelieNo ratings yet
- Deepanshu CV October 2021 - 1655808176031 - Deepanshu KatariaDocument3 pagesDeepanshu CV October 2021 - 1655808176031 - Deepanshu KatariaSatish SinghNo ratings yet
- Coa Gar 42-40Document1 pageCoa Gar 42-40UMKM OKENo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 and 18 - Investment in Associates What Is An Associate? Accounting Procedures of Investment in AssociateDocument2 pagesChapter 17 and 18 - Investment in Associates What Is An Associate? Accounting Procedures of Investment in AssociateRanee DeeNo ratings yet
- money: Revealed: Gupta's Circular Money TrailDocument14 pagesmoney: Revealed: Gupta's Circular Money TrailAna LourençoNo ratings yet
- Customer Grievance Redressal Policy - 2018Document14 pagesCustomer Grievance Redressal Policy - 2018oliver senNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Canadian 4th Edition Steen Test BankDocument18 pagesHuman Resource Management Canadian 4th Edition Steen Test Banklegacycuttinglkhd100% (25)
- The Barefoot Investor 2Document3 pagesThe Barefoot Investor 2noxaga3615No ratings yet
- ADCPL - Healthcare Hospitality & Institutional Projects.Document177 pagesADCPL - Healthcare Hospitality & Institutional Projects.Aashray Design Consultants Pvt LtdNo ratings yet
- Course Notes Handbook RSGDocument26 pagesCourse Notes Handbook RSGjaeNo ratings yet
- Inp 2205 - Advance Accounting - Question PaperDocument10 pagesInp 2205 - Advance Accounting - Question PaperAnshit BahediaNo ratings yet
- Exercises Chapter 04Document23 pagesExercises Chapter 04vintcs181892No ratings yet
- Sr. No Bank Name Bank Official Name Contact Number E-Mail IDDocument2 pagesSr. No Bank Name Bank Official Name Contact Number E-Mail IDSrijan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Location Selection & Layout Planning For A New College BuildingDocument7 pagesLocation Selection & Layout Planning For A New College BuildingSwostik RoutNo ratings yet
- Iapm NotesDocument45 pagesIapm NotesBhai ho to dodoNo ratings yet
- Diageo PLC Fundamental Company Report Including Financial, SWOT, Competitors and Industry AnalysisDocument15 pagesDiageo PLC Fundamental Company Report Including Financial, SWOT, Competitors and Industry Analysisvicky thapliyalNo ratings yet
- Grab100k Com NewDocument20 pagesGrab100k Com NewDigital TrixNo ratings yet
- Installment Promissory Note 1Document1 pageInstallment Promissory Note 1api-385482345No ratings yet
- A New Day For SustainabilityDocument9 pagesA New Day For SustainabilityswaraNo ratings yet
- S4F72 EN Col23 CO A4Document19 pagesS4F72 EN Col23 CO A4Asif Ali MughalNo ratings yet
- (Adaolisa Read Ahead) Differetnt Departments in An OrgansiationDocument4 pages(Adaolisa Read Ahead) Differetnt Departments in An OrgansiationNatus PaulusNo ratings yet
- Jose Miguel Vienes Mr. Pascual Abrazaldo BSBA-311 09 Activity 2 (3) Case Study: Which Approach Is Best?Document2 pagesJose Miguel Vienes Mr. Pascual Abrazaldo BSBA-311 09 Activity 2 (3) Case Study: Which Approach Is Best?Miguel VienesNo ratings yet
- 2023 Paper SB10Document8 pages2023 Paper SB10MattNo ratings yet
- Table of Conent of SOPDocument16 pagesTable of Conent of SOPFaysalNo ratings yet