Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 10 Revision Notes Statistics
Class 10 Revision Notes Statistics
Uploaded by
Arzhel BoissinotOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class 10 Revision Notes Statistics
Class 10 Revision Notes Statistics
Uploaded by
Arzhel BoissinotCopyright:
Available Formats
Statistics
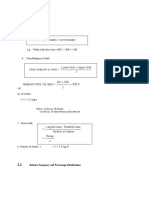
Mean of Grouped Data
Mean is that value of central tendency which is the average of the observations.
There are three methods to find mean for a frequency distribution.
(i) Direct method
where x is the mid-interval
f is the frequency
M is the mean
(ii) (ii) Assumed Mean method
where A = assumed mean
d=x-A
(iii) (iii) Step-deviation method
where i = class size
Mode of Grouped Data
Mode is that value among the observations which has the maximum frequency.
In a grouped frequency distribution, we locate the modal class and find the mode using the
following formula.
f1 f 0
Mode = l h
2 f1 f 0 f 2
l - lower limit of the modal class
h - size of the class interval
f1 - frequency of the modal class
f0 - frequency of the class preceding the modal class
f2 - frequency of the class succeeding the modal class
Median of Grouped Data
Median is a measure of central tendency which gives the value of the middle-most observation in
the data.
In a grouped frequency distribution, we locate the median class and find the median using the
following formula.
N
c
Median = l 2 h
f
l - Lower limit of the median class
c - Cumulative frequency preceding the median class frequency
h - Width of the class interval
N = Sum of the frequencies
Working rule
Step 1: Prepare the table containing less than the cumulative frequency with the help of the given
frequencies.
N
Step 2: Find out the cumulative frequency to which belongs. Class interval of this cumulative
2
frequency is the median class interval.
Step 3: Find out the frequency f and lower limit l of this median class.
Step 4: Find the width 'h' of the median class interval.
Step 5: Find the cumulative frequency c of the class preceding the median class.
Step 6: Apply the formula
N
c
Median = l 2 h , to find the median.
f
Graphs in Statistics
Graphical Representation of Cumulative Frequency Distribution
Cumulative frequency is obtained by adding the frequency of a class interval and the frequencies
of the preceding intervals up to that class interval.
Ogive (Cumulative Frequency Curve)
There are two ways of constructing an Ogive or cumulative frequency curve. (Ogive is pronounced
as O-jive). The curve is usually of 'S' shape.
To Plot an Ogive:
(i) We plot the points with coordinates having abscissae as actual limits and ordinates as the
cumulative frequencies
(ii) Join the plotted points by a smooth curve.
(iii) An Ogive is connected to a point on the X-axis representing the actual lower limit of the first
class.
You might also like
- SS2 Maths Lesson Note PDFDocument104 pagesSS2 Maths Lesson Note PDFdnlbalogun100% (2)
- Class10 Mathematics Chapter 14. StatisticsDocument1 pageClass10 Mathematics Chapter 14. StatisticsBonGXArJoNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Mayank GuptaDocument11 pagesPrepared By: Mayank GuptaSudhanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 14 StatisticsDocument33 pagesChapter - 14 StatisticsYash GoyalNo ratings yet
- Statistics: Measures of Central TendencyDocument1 pageStatistics: Measures of Central TendencyJaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- 02 Data and Preliminary Data Analysis - PrintDocument20 pages02 Data and Preliminary Data Analysis - PrintCahyo Agung SaputraNo ratings yet
- Wikimama Class 11 CH 15 StatisticsDocument8 pagesWikimama Class 11 CH 15 StatisticsWikimamaNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument6 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyCarlo YambaoNo ratings yet
- PAS 111 Week 5Document9 pagesPAS 111 Week 5Franz PampolinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2JAMES AMOSNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 9 Maths Notes For Chapter 14 Statistics PDFDocument4 pagesCbse Class 9 Maths Notes For Chapter 14 Statistics PDFAnkita SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1558589193 SmsDocument18 pagesAssignment 1558589193 Smssukhwant1666No ratings yet
- Median and ModeDocument3 pagesMedian and ModesumNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument4 pagesMeasures of Central Tendencyapi-150547803No ratings yet
- Statistics 10thDocument19 pagesStatistics 10thviswanathbpNo ratings yet
- Statistics Notes by AsDocument4 pagesStatistics Notes by Asrimisadhukhan2008No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Obtaining Data Part 2 PDFDocument71 pagesChapter 2 Obtaining Data Part 2 PDFJulius BoitizonNo ratings yet
- Key Notes: Chapter-14 StatisticsDocument2 pagesKey Notes: Chapter-14 StatisticsManu VermaNo ratings yet
- How To Organize DataDocument4 pagesHow To Organize DataMichael YuNo ratings yet
- Formula and Notes For Class 11 Maths Download PDF Chapter 15. StatisticsDocument16 pagesFormula and Notes For Class 11 Maths Download PDF Chapter 15. StatisticsMohsin Manzoor BhatNo ratings yet
- MCT Grouped DataDocument2 pagesMCT Grouped Datajaredboncales349No ratings yet
- Eda Module 2 Frequency Distribution GraphsDocument24 pagesEda Module 2 Frequency Distribution GraphsLenie BaradasNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument25 pagesStatisticssaurabh singhNo ratings yet
- Statistics Class 11 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 15 (PDF)Document13 pagesStatistics Class 11 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 15 (PDF)Emperor YashNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency - Summary Notes: XX X Be The Given X X X X XDocument2 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency - Summary Notes: XX X Be The Given X X X X XTele SalesNo ratings yet
- What Is Frequency Distribution?Document3 pagesWhat Is Frequency Distribution?ElizabethNo ratings yet
- 4 2.1: Frequency Distributions and Their GraphsDocument2 pages4 2.1: Frequency Distributions and Their GraphsSarah HenryNo ratings yet
- PDF PDFDocument23 pagesPDF PDFKiaraNo ratings yet
- Educ 316 MeasuresofcentraltendencyfinalDocument24 pagesEduc 316 MeasuresofcentraltendencyfinalPaul Carlo GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument13 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyDrAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- ACCTY 312 - Lesson 2Document17 pagesACCTY 312 - Lesson 2shsNo ratings yet
- Eng 2015 Prelims ReviewerDocument11 pagesEng 2015 Prelims ReviewerJERICHO ESTIALBONo ratings yet
- Math7 Q4 Week 6 SSLMDocument4 pagesMath7 Q4 Week 6 SSLMhttps11.the.dynamicsNo ratings yet
- Statistics Chapter-IIDocument66 pagesStatistics Chapter-IIMiley GirmayNo ratings yet
- BYJU'S Learn Portal LoginDocument2 pagesBYJU'S Learn Portal Loginsuganthi sNo ratings yet
- 7 StatisticsDocument62 pages7 StatisticsrahimuddinNo ratings yet
- Frequency DistributionDocument23 pagesFrequency DistributionAngel DeytaNo ratings yet
- Research II Q4 Measures of VariabilityDocument54 pagesResearch II Q4 Measures of Variabilityhrhe heheNo ratings yet
- Measure of Central TendencyDocument2 pagesMeasure of Central TendencykiahjessieNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Basic Statistics DefinitionsDocument4 pagesUnit 6 Basic Statistics DefinitionsAsghar AliNo ratings yet
- JAGUIMIT - Detailed Doc For The PresentationDocument5 pagesJAGUIMIT - Detailed Doc For The PresentationKailah Kristine Congreso JaguimitNo ratings yet
- Practical 2Document5 pagesPractical 2Prajjwal PandeyNo ratings yet
- Central Tendency - Note On Selected TopicsDocument7 pagesCentral Tendency - Note On Selected TopicsTanmay MaityNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Economics Formula Sheet.Document38 pagesStatistics For Economics Formula Sheet.VivekNo ratings yet
- Course Code & Number:FET201Document70 pagesCourse Code & Number:FET201Humam Al-DhubhaniNo ratings yet
- 1 Review of StatisticsDocument24 pages1 Review of StatisticsJay RaelNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1-Math 112EDocument13 pagesAssignment 1-Math 112EAshley DestrizaNo ratings yet
- Lower Limit + Upper Limit Class Midpoint or Mark 2Document8 pagesLower Limit + Upper Limit Class Midpoint or Mark 2Shah AlyahyaNo ratings yet
- ppt3 Descriptive2Document39 pagesppt3 Descriptive2mark perezNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2-Methods of Data PresentationDocument17 pagesChapter-2-Methods of Data PresentationAyu AlemuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document26 pagesChapter 3Shahzaib SalmanNo ratings yet
- Methods of Data PresntationDocument53 pagesMethods of Data PresntationWondmageneUrgessaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Measure of Central TendencyDocument20 pagesLesson 4 Measure of Central Tendencyrahmanzaini100% (1)
- F.Y. B. Sc. Statistics Notes Paper I Unit III Notes Prepared by Prof (MRS) M.J. GholbaDocument39 pagesF.Y. B. Sc. Statistics Notes Paper I Unit III Notes Prepared by Prof (MRS) M.J. GholbaManoj Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Research 3 Quarter 3 - MELC 1 Week 1-2 Inferential StatisticsDocument39 pagesResearch 3 Quarter 3 - MELC 1 Week 1-2 Inferential StatisticsHanna nicole JapsayNo ratings yet
- Learn Statistics Fast: A Simplified Detailed Version for StudentsFrom EverandLearn Statistics Fast: A Simplified Detailed Version for StudentsNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Differential Equations and Stability Theory: An IntroductionFrom EverandOrdinary Differential Equations and Stability Theory: An IntroductionNo ratings yet
- Wonderlic Basic MathDocument1 pageWonderlic Basic MathArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- MITT - CAAT C Math PracticeDocument10 pagesMITT - CAAT C Math PracticeArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Appendix II - PMDDocument6 pagesAppendix II - PMDArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Ecological Characteristics of A Recently Described Critically Endangered Gecko Species Endemic To Central Highland VietnamDocument11 pagesEcological Characteristics of A Recently Described Critically Endangered Gecko Species Endemic To Central Highland VietnamArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning - Nov 2022 Foundation Paper 2 Mark Scheme - EdexcelDocument8 pagesThird Space Learning - Nov 2022 Foundation Paper 2 Mark Scheme - EdexcelArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning - Nov 2022 Higher Paper 2 - EdexcelDocument17 pagesThird Space Learning - Nov 2022 Higher Paper 2 - EdexcelArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Higher Practice Paper IndexDocument4 pagesThird Space Learning Higher Practice Paper IndexArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Revision Notes Some Applications of TrigonometryDocument4 pagesClass 10 Revision Notes Some Applications of TrigonometryArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning - Nov 2022 Higher Paper 2 Mark Scheme - EdexcelDocument9 pagesThird Space Learning - Nov 2022 Higher Paper 2 Mark Scheme - EdexcelArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Revision Notes TrianglesDocument8 pagesClass 10 Revision Notes TrianglesArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Revision Notes Coordinate GeometryDocument7 pagesClass 10 Revision Notes Coordinate GeometryArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes 2022 For CBSE Class 10 Maths Polynomials PDFDocument5 pagesRevision Notes 2022 For CBSE Class 10 Maths Polynomials PDFArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Revision Notes Arithmetic ProgressionsDocument3 pagesClass 10 Revision Notes Arithmetic ProgressionsArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Revision Notes Areas Related To CirclesDocument4 pagesClass 10 Revision Notes Areas Related To CirclesArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Revision Notes ConstructionsDocument3 pagesClass 10 Revision Notes ConstructionsArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Revision Notes CirclesDocument5 pagesClass 10 Revision Notes CirclesArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note On Basic Business Statistics - I Mustafe Jiheeye-1Document81 pagesLecture Note On Basic Business Statistics - I Mustafe Jiheeye-1Nagiib Haibe Ibrahim Awale 6107No ratings yet
- STAT 012 Engineering Data Analysis IMsDocument73 pagesSTAT 012 Engineering Data Analysis IMsaodmarahas56No ratings yet
- Graphical and Tabular Descriptive TechniquesDocument40 pagesGraphical and Tabular Descriptive TechniquesJpagNo ratings yet
- 01 AssignmentDocument5 pages01 AssignmentEmadNo ratings yet
- Stat 4091 Exercise1Document13 pagesStat 4091 Exercise1Random ExistenceNo ratings yet
- Intro StatsDocument109 pagesIntro StatsEshita VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Stat Introduction Units 1& 2Document108 pagesStat Introduction Units 1& 2DaiChi J3SNo ratings yet
- Bbs14e PPT ch02Document71 pagesBbs14e PPT ch02Nguyen Thi Nhung (K16HL)No ratings yet
- Written Report (Group 1) - 2Document21 pagesWritten Report (Group 1) - 2Imanina HanapiNo ratings yet
- Ekstrøm, Claus Thorn - Sørensen, Helle - Introduction To Statistical Data Analysis For The Life Sciences-CRC Press (2014)Document521 pagesEkstrøm, Claus Thorn - Sørensen, Helle - Introduction To Statistical Data Analysis For The Life Sciences-CRC Press (2014)igorsfrNo ratings yet
- Math7 Q4 M5Document15 pagesMath7 Q4 M5AllanEvangelistaNo ratings yet
- TECH RES2 - Lesson 3Document10 pagesTECH RES2 - Lesson 3SER JOEL BREGONDO Jr.No ratings yet
- Research PendingDocument232 pagesResearch PendingAthumaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 STA 201 SolutionDocument8 pagesAssignment 1 STA 201 SolutionMd.borhan UddinNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work: Cambridge O Level Statistics 4040Document46 pagesScheme of Work: Cambridge O Level Statistics 4040Hadia UsmaniNo ratings yet
- 120E1BDocument1 page120E1BSri VarsaNo ratings yet
- Presentation of DataDocument25 pagesPresentation of DataKelliata BenjaminNo ratings yet
- 11 Standard Mathematics Assessment Task 2 2024Document4 pages11 Standard Mathematics Assessment Task 2 2024chanelbeydounNo ratings yet
- Measures of Position (Grouped Data)Document12 pagesMeasures of Position (Grouped Data)Jamaica Rose BalbinNo ratings yet
- Ce 023 Eda Module 4Document5 pagesCe 023 Eda Module 4Roydon Jude SamudioNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics Chapter 2-Part 1Document5 pagesDescriptive Statistics Chapter 2-Part 1aminlaiba2000No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Statistics RefresherDocument32 pagesLesson 2 Statistics RefresherEric PaderNo ratings yet
- Handout 2 Frequency DistributionDocument14 pagesHandout 2 Frequency DistributionRobel Metiku100% (1)
- Elementary Statistics 2nd Edition Navidi Test BankDocument41 pagesElementary Statistics 2nd Edition Navidi Test Bankhanhanselmuv0smNo ratings yet
- 11 StatisticsDocument27 pages11 StatisticsviswanathNo ratings yet
- A Survey About Online and Distance Learning (Odl) On Uitm Tapah StudentsDocument23 pagesA Survey About Online and Distance Learning (Odl) On Uitm Tapah StudentsAzdy HaiqalNo ratings yet
- BARGRAPHPPTDocument46 pagesBARGRAPHPPTtabarotNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Assessment in Learning (Frequency Distribution) - 6Document17 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Assessment in Learning (Frequency Distribution) - 6Katrina QuimnoNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics For BiotechnologyDocument128 pagesBiostatistics For Biotechnologykibiralew DestaNo ratings yet