Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Climatic Architecture
Bio Climatic Architecture
Uploaded by
Clara AbrahamOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Climatic Architecture
Bio Climatic Architecture
Uploaded by
Clara AbrahamCopyright:
Available Formats
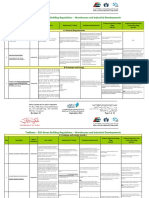
WHAT IS BIOCLIMATIC ARCHITETURE?
• Bioclimatic design of a building is the design which govern the climate of each
region, aims to ensure the necessary conditions with minimal energy
consumption, utilizing available environmental sources.
• Main aim is to help save energy for lighting as well as heating and cooling of
buildings and adapt buildings to local climate.
• Various techniques used include thermal protection shell, passive solar systems
techniques and natural cooling and natural lighting techniques.
• In final effect safe and comfortable building which is created does not harm
the environment but contributes to its health and enriched biodiversity.
Landscaping and vegetation Openings, semi openings, Ventilation
PRINCIPLES OF BIOCLIMATIC pattern fenestrations
ARCHITETURE
Bioclimatic design takes into
account the local climate and
includes the following principles:
• Heat protection of the buildings in
winter as well as in summer, using
appropriate techniques which are
applied to the external envelope
of the building.
• Appropriate orientation of the
buildings and especially their
openings (preferably towards the Location of water bodies and
south), by the layout of interior evaporative cooling
spaces according to their heating
requirements, and by passive
solar systems which collect solar
radiation and act as “natural”
heating as well as lighting systems.
• Protection of the buildings from
the summer sun, by shading but
also by the appropriate treatment
of the building envelope (i.e. use Building form and Orientation
of reflective colors and surfaces).
• Removal of the heat which
accumulates in summer in the
building to the surrounding
environment using by natural Building Envelope & Materials
means (passive cooling systems
and techniques)
• Improvement – adjustment of
environmental conditions in the
interiors of buildings so that their
inhabitants find them comfortable
and pleasant (i.e. increasing the
air movement inside spaces, heat
storage, or cool storage in walls).
• Ensuring insolation combined with
solar control for daylighting of
buildings, in order to provide Shading Devices
sufficient and evenly distributed
light in interior spaces.
• Improvement of the microclimate
around buildings, through the
bioclimatic design of exterior
spaces and in general, of the built
environment, adhering to all of
the above principles.
EXAMPLES
- Solaris, Singapore
- Sino-Italian Ecological and Energy
Efficient Building, Beijing, China
- East Gate Center, Zimbabwe
BIOCLIMATIC ARCHITECTURE
ANPHY ABRAHAM
ROLL NO 13
S6 B. ARCH
You might also like
- Ebook PDF Understanding Construction Drawings For Housing and Small Business Canadian Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Understanding Construction Drawings For Housing and Small Business Canadian Edition PDFcharles.hensley246100% (38)
- Govt of Dubai (U-Factor)Document23 pagesGovt of Dubai (U-Factor)Faizul Zainudin100% (2)
- A Guide to Natural Ventilation Design: A Component in Creating Leed ApplicationFrom EverandA Guide to Natural Ventilation Design: A Component in Creating Leed ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Literature Case Study On Design CollegeDocument21 pagesLiterature Case Study On Design CollegeSophia Chin100% (1)
- Astm c1060Document6 pagesAstm c1060jorgeNo ratings yet
- HMDA Building GuidelinesDocument88 pagesHMDA Building GuidelinesMaitreyi Yellapragada100% (1)
- Cold-Climate Buildings Design GuideDocument20 pagesCold-Climate Buildings Design Guideaftab ali AnsariNo ratings yet
- Bio Climatic Design Principles and Design TechniquesDocument14 pagesBio Climatic Design Principles and Design TechniquesYeng TarucNo ratings yet
- Bioclimatic StructuresDocument2 pagesBioclimatic StructuresVernelle Marie P. Ilagan0% (1)
- Cib22300 PDFDocument8 pagesCib22300 PDFGregorio Jimenez GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Bioclimatic Design at The Site Planning Scale: By: Donald Watson & Kenneth LabsDocument47 pagesBioclimatic Design at The Site Planning Scale: By: Donald Watson & Kenneth Labskiran tatipudiNo ratings yet
- ERD Home Assignment-Group 3 (Passive Energy Systems)Document58 pagesERD Home Assignment-Group 3 (Passive Energy Systems)Bharani Madamanchi100% (1)
- Energy Efficiency PEDADocument26 pagesEnergy Efficiency PEDAAnime SketcherNo ratings yet
- Bio-Climatic Commercial ComplexDocument6 pagesBio-Climatic Commercial ComplexSunny SharmaNo ratings yet
- Al Bahr Tower - Case Study: Abu Dhabi Experiences Hot and Humid ClimateDocument3 pagesAl Bahr Tower - Case Study: Abu Dhabi Experiences Hot and Humid ClimatepoojaNo ratings yet
- 010 An Ultra Energy Efficient Building in Palestine PDFDocument6 pages010 An Ultra Energy Efficient Building in Palestine PDFGhennadii TăutulNo ratings yet
- Energy Management in Building2Document23 pagesEnergy Management in Building2Anonymous QVy30sJhNo ratings yet
- Tropical Design 1Document34 pagesTropical Design 1Arki MarkNo ratings yet
- Tropical Architecture: Shelves, Overhangs, Roof and Wall Insulation and Considerably The Shading From TheDocument5 pagesTropical Architecture: Shelves, Overhangs, Roof and Wall Insulation and Considerably The Shading From TheMic sanNo ratings yet
- Passive Heating Design StrategiesDocument23 pagesPassive Heating Design StrategiesRoopendraKumarNo ratings yet
- Sino-Italian EcologicalDocument9 pagesSino-Italian EcologicalHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Lecture 2 - Environmental Control Systems (3681)Document21 pagesLecture 1 - Lecture 2 - Environmental Control Systems (3681)M Hammad Manzoor100% (1)
- Buildng ScienceDocument13 pagesBuildng ScienceDenzel NgNo ratings yet
- 2 Ars Sosio Ekologi-Arsitektur Berkelanjutan 2014Document37 pages2 Ars Sosio Ekologi-Arsitektur Berkelanjutan 2014onyvjNo ratings yet
- Building Envelope Design Possive Cooling TechniqueDocument8 pagesBuilding Envelope Design Possive Cooling TechniqueMarie Cris Gajete MadridNo ratings yet
- Passive StrategiesDocument41 pagesPassive Strategiesᴘʀᴀᴊᴡᴀʟ ɢᴏᴡᴅᴀNo ratings yet
- Passive HeatingDocument38 pagesPassive Heatingyusuf stephenNo ratings yet
- Passive Design Strategies For Building: in A Hot and Dry ClimateDocument22 pagesPassive Design Strategies For Building: in A Hot and Dry ClimateMishika Mehta 21No ratings yet
- Solar Passive ArchitectureDocument28 pagesSolar Passive ArchitectureAnu Alreja100% (6)
- Bioclimatic Architecture: Chapter 1: IntroductionDocument4 pagesBioclimatic Architecture: Chapter 1: IntroductionVanshika DograNo ratings yet
- Slide Presentation Passive DesignDocument24 pagesSlide Presentation Passive DesignNuratiqah Sharifah100% (1)
- Presentation 3Document31 pagesPresentation 3infantshethekNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document17 pagesLecture 8qtyzyvx7znNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Bioclimatic ArchitectureDocument4 pagesThe Concept of Bioclimatic Architectureomarshamia404No ratings yet
- Building Envelope Reading Response 5 Ishika Sarawagi: TH THDocument2 pagesBuilding Envelope Reading Response 5 Ishika Sarawagi: TH THIshika SarawagiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Energy Conscious Design: Proc. of Int. Conf. On Emerging Trends in Engineering and TechnologyDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Energy Conscious Design: Proc. of Int. Conf. On Emerging Trends in Engineering and TechnologyNayaabNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1 Strategies and Technologies 11.08.2021Document50 pagesLecture-1 Strategies and Technologies 11.08.2021SIMRAN KAURNo ratings yet
- Passive Solar BuildingDocument21 pagesPassive Solar BuildingAjay kumar DasariNo ratings yet
- Poorva Dudhalkar (CP - Assi.3)Document10 pagesPoorva Dudhalkar (CP - Assi.3)mrunmayee pandeNo ratings yet
- Teori Arsitektur Ii: Environmental Bioclimatic DesignDocument15 pagesTeori Arsitektur Ii: Environmental Bioclimatic DesignEsher Tanga TodingNo ratings yet
- Sangath HotdryDocument5 pagesSangath HotdrySagar AroraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Energy Transfer in BuildingsDocument74 pagesUnit 1 Energy Transfer in BuildingsmithileshwarreddymithileshNo ratings yet
- Low Cost Construction TechnologiesDocument4 pagesLow Cost Construction TechnologiesSunil BeheraNo ratings yet
- Figure 1: Active Building ModelDocument7 pagesFigure 1: Active Building Modeladeel raziNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Thermal InsulationDocument21 pagesWeek 1 Thermal InsulationMelody PanghulanNo ratings yet
- Passive Building DesignDocument7 pagesPassive Building DesignM.i.SimonNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Deign StrategiesDocument6 pagesActive and Passive Deign Strategiesrishav rajNo ratings yet
- Residential Building For Sustainability Analysis With Reference ToDocument15 pagesResidential Building For Sustainability Analysis With Reference Toayeshazahid546No ratings yet
- Passive Cooling 2Document9 pagesPassive Cooling 2TUYIZERE EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- High-Performance Building Envelopes: Design Methods For Energy Efficient FacadesDocument15 pagesHigh-Performance Building Envelopes: Design Methods For Energy Efficient FacadesHiddenKoalaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document12 pagesLecture 5abdufatahNo ratings yet
- Thermal Insulation in Building PDFDocument31 pagesThermal Insulation in Building PDFAkirasNo ratings yet
- Theme Green ArchitectureDocument37 pagesTheme Green Architecturehakimoo reghaiNo ratings yet
- Solar Passive ArchitectureDocument10 pagesSolar Passive ArchitectureNeha BangerNo ratings yet
- Eea PresentationDocument20 pagesEea PresentationKirthika AnandharajNo ratings yet
- Industrial Case StudyDocument70 pagesIndustrial Case StudyShivani KothawadeNo ratings yet
- Passivedesign 190510095141Document56 pagesPassivedesign 190510095141AKASHIC WORLDNo ratings yet
- Principles of Energy Concious DesignDocument65 pagesPrinciples of Energy Concious DesignRitika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document23 pagesLecture 4zienabNo ratings yet
- PedaDocument9 pagesPedavishalakshiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 l1.4 Checklist of Relevant Design ConceptsDocument2 pages1.1 l1.4 Checklist of Relevant Design ConceptsGeorge GartzounisNo ratings yet
- Heritage Buildings and SustainabilityDocument6 pagesHeritage Buildings and SustainabilityAJAYI ADEMOLANo ratings yet
- Energy-Efficient Building Envelope, Sciencedirect OverviewDocument30 pagesEnergy-Efficient Building Envelope, Sciencedirect OverviewsuranjanacNo ratings yet
- Slide Passive Design BuildingDocument18 pagesSlide Passive Design BuildingNuratiqah Sharifah100% (1)
- Sustainable Renovation: Strategies for Commercial Building Systems and EnvelopeFrom EverandSustainable Renovation: Strategies for Commercial Building Systems and EnvelopeNo ratings yet
- What Are Heritage Interpretation CentresDocument4 pagesWhat Are Heritage Interpretation CentresClara AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Thesis Preparatory Booklet - Contemporary Design and HistoricalDocument16 pagesThesis Preparatory Booklet - Contemporary Design and HistoricalClara AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Documentation of PuducherryDocument57 pagesDocumentation of PuducherryClara AbrahamNo ratings yet
- District Hall BostonDocument5 pagesDistrict Hall BostonClara AbrahamNo ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument14 pagesAcousticsClara AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Student Friendly Spaces StudyDocument2 pagesStudent Friendly Spaces StudyClara AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Gautam Buddha University Case StudyDocument34 pagesGautam Buddha University Case StudyClara AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Tribhuvan University Institute of EngineeringDocument14 pagesTribhuvan University Institute of EngineeringROHIT SHRESTHANo ratings yet
- Solar Passive Design Features For Hot & Dry ClimateDocument73 pagesSolar Passive Design Features For Hot & Dry ClimateSUHANI VERMANo ratings yet
- Assessment of Waterproofing Failures in Concrete Buildings and StructuresDocument15 pagesAssessment of Waterproofing Failures in Concrete Buildings and StructuresRahul JangirNo ratings yet
- Build A Better Home - WallsDocument12 pagesBuild A Better Home - WallsCeyanezNo ratings yet
- Tce Dsign Guidepdf PDFDocument327 pagesTce Dsign Guidepdf PDFzaheeruddin_mohdNo ratings yet
- 2017 Book - Energy Efficieny LSF Buildings PDFDocument26 pages2017 Book - Energy Efficieny LSF Buildings PDFmabuhamdNo ratings yet
- Optimising Energy Through Kinetic FacadesDocument117 pagesOptimising Energy Through Kinetic FacadesHasiba BarisaNo ratings yet
- Passive Cooling Techniques ARCHITECUREDocument8 pagesPassive Cooling Techniques ARCHITECURERHYME KIDSNo ratings yet
- Alucobond ProductDocument27 pagesAlucobond ProductYus wantoNo ratings yet
- HVAC Enclosure DesignDocument2 pagesHVAC Enclosure DesignJohn ANo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Building EA PRS SRSDocument120 pagesChapter 6 Building EA PRS SRSsugamNo ratings yet
- Dawn of Green ArchitectureDocument25 pagesDawn of Green ArchitectureDr Hector C Sikazwe100% (1)
- Case Study 15.12.2016 PDFDocument20 pagesCase Study 15.12.2016 PDFHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Energy Audit Energy Conservation Basics - ORIGINALDocument70 pagesEnergy Audit Energy Conservation Basics - ORIGINALAhmed Sherif100% (1)
- Cool and Green Roofs An Energy and Comfort Comparison PDFDocument11 pagesCool and Green Roofs An Energy and Comfort Comparison PDFLarissa de FreitasNo ratings yet
- Bioclimatic Design Principles and PractiDocument30 pagesBioclimatic Design Principles and PractiSana ShamimNo ratings yet
- Corus Building Systems - ProfileDocument13 pagesCorus Building Systems - ProfileClef GonadanNo ratings yet
- Day 1-Wind Loading NSCP 2015Document77 pagesDay 1-Wind Loading NSCP 2015Nick OperarioNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Building PhysicsDocument52 pagesFundamental of Building PhysicssyafixNo ratings yet
- ASCE 7-22 CH 26 - For PC - SouDocument68 pagesASCE 7-22 CH 26 - For PC - SousharethefilesNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Site Responsive ArchitectureDocument19 pagesSustainable Site Responsive ArchitectureGowri ShankariNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam - IngcongDocument15 pagesMidterm Exam - IngcongI's ShopNo ratings yet
- sans10400-XA DraftDocument16 pagessans10400-XA DraftAndreas KamwankaNo ratings yet
- Hvac ProjectDocument95 pagesHvac ProjectSTAD87100% (3)
- SBC - Code - 602 Energy Low RiseDocument194 pagesSBC - Code - 602 Energy Low RiseMohamed AmrNo ratings yet