Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Analysis
Case Analysis
Uploaded by
Cris Anne BautistaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Acute Stroke Management in the Era of ThrombectomyFrom EverandAcute Stroke Management in the Era of ThrombectomyEdgar A. SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Advanced EKG RefresherDocument181 pagesAdvanced EKG RefresherIoana Antonesi100% (3)
- 2011 CardiacSurgery Catalog US 062811Document0 pages2011 CardiacSurgery Catalog US 062811MilagrosCisnerosNo ratings yet
- Brain Aneurysm Thesis StatementDocument7 pagesBrain Aneurysm Thesis Statementchristinewhitebillings100% (2)
- Epidural Hematoma: Continuing Education ActivityDocument16 pagesEpidural Hematoma: Continuing Education ActivityIka AriandanaNo ratings yet
- 4275 15730 1 PBDocument3 pages4275 15730 1 PBNiarsari A. PutriNo ratings yet
- Acv PDFDocument14 pagesAcv PDFFelipe AlcainoNo ratings yet
- Stroke NarrativeDocument10 pagesStroke Narrativecfalcon.medicinaNo ratings yet
- Their Treatments: Brain AneurysmsDocument9 pagesTheir Treatments: Brain AneurysmsArdiansyah P PratamaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral AneurysmDocument6 pagesCerebral AneurysmNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Stroke ThesisDocument7 pagesStroke Thesisnavysavchenkobellevue100% (1)
- Iht Nejm 2014Document10 pagesIht Nejm 2014Ademir Ruiz EcheverríaNo ratings yet
- Imaging of Intracranial Hemorrhage: Jeremy J. Heit, Michael Iv, Max WintermarkDocument21 pagesImaging of Intracranial Hemorrhage: Jeremy J. Heit, Michael Iv, Max WintermarkBrianNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument73 pagesSubarachnoid Hemorrhagederarataye6No ratings yet
- Imaging ICHDocument17 pagesImaging ICHCrhistian GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 2017 HSA Clinical PracticeDocument10 pages2017 HSA Clinical PracticeAndrea MartinezNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument10 pagesSubarachnoid HemorrhageRoberto López Mata100% (1)
- Cerebellopontine Angle TumoursDocument11 pagesCerebellopontine Angle TumoursIsmail Sholeh Bahrun MakkaratteNo ratings yet
- BRAIN AneurysmDocument14 pagesBRAIN AneurysmRikizu HobbiesNo ratings yet
- Hemorragia SubaracnoideaDocument10 pagesHemorragia SubaracnoideaAna TeresaNo ratings yet
- 10.1038@s41572 019 0118 8Document22 pages10.1038@s41572 019 0118 8Anabel AguilarNo ratings yet
- Britz, An Overview of Neurovascular Disease ManagementDocument2 pagesBritz, An Overview of Neurovascular Disease Managementlaila forestaNo ratings yet
- Epidural Hematoma in Emergency Medicine: BackgroundDocument3 pagesEpidural Hematoma in Emergency Medicine: BackgroundMercy HasanNo ratings yet
- Nhjuiy Uyiyui Yuighjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjhg GHJHGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGJ GHJGHJGHJGHJ L MGLFGKJFDGJKJ FGNGKFDGMNN DFJKDGH DJHGJ MNVGMFDXGNMGNFDMGNMDFGDocument16 pagesNhjuiy Uyiyui Yuighjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjhg GHJHGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGJ GHJGHJGHJGHJ L MGLFGKJFDGJKJ FGNGKFDGMNN DFJKDGH DJHGJ MNVGMFDXGNMGNFDMGNMDFGHasan AlkhawaldehNo ratings yet
- Neurovascular Conditions Treated at PennDocument7 pagesNeurovascular Conditions Treated at PennFatrawati BahuaNo ratings yet
- Dust inDocument7 pagesDust inlarkspor31No ratings yet
- Practneurol 2020 002763Document12 pagesPractneurol 2020 002763Fitri ainun MalahayatiNo ratings yet
- Author's Accepted Manuscript: Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRIDocument29 pagesAuthor's Accepted Manuscript: Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRIasfwegereNo ratings yet
- Cerebral AneurysmsDocument12 pagesCerebral AneurysmsDyah Ayu Puspita AnggarsariNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument62 pagesNervous Systemmyat252No ratings yet
- Scientific Report Journal 22 NovDocument6 pagesScientific Report Journal 22 Novnaresh kotraNo ratings yet
- 128 FullDocument12 pages128 FullYovita LimiawanNo ratings yet
- Case Study Cva Gr1Document72 pagesCase Study Cva Gr1Divina Gracia Fabicon Arana100% (1)
- Health Publications: Cerebral Aneurysm Treatment and Perioperative Nursing CareDocument9 pagesHealth Publications: Cerebral Aneurysm Treatment and Perioperative Nursing CareElmer San JoseNo ratings yet
- Acute Intracerebral Haemorrhage - Pract Neurol (2021)Document12 pagesAcute Intracerebral Haemorrhage - Pract Neurol (2021)Billy Priyanto HNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument6 pagesHead InjuryHurrinazilla AwaliaNo ratings yet
- ACV HemorrágicoDocument12 pagesACV HemorrágicoLUIS FELIPE ARTEAGA ARREDONDONo ratings yet
- Daniel D Price, MD Director of International Ultrasound, Department ofDocument3 pagesDaniel D Price, MD Director of International Ultrasound, Department ofPutri Swandayani NofendyNo ratings yet
- Practneurol 2020 002763Document12 pagesPractneurol 2020 002763Edgar MoralesNo ratings yet
- New Options For Neurovascular DiseaseDocument3 pagesNew Options For Neurovascular DiseasecamillarugaNo ratings yet
- Acute Intracerebral HaemorrhageDocument12 pagesAcute Intracerebral HaemorrhageZARF27No ratings yet
- PPTDocument8 pagesPPTArabelle TosocNo ratings yet
- Aneurysm: TypesDocument12 pagesAneurysm: TypesSofia Isabelle GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Neural TourniquetDocument5 pagesThe Neural TourniquetDaniel SherwinNo ratings yet
- Acute Intracerebral Haemorrhage BMJ 2021Document12 pagesAcute Intracerebral Haemorrhage BMJ 2021Jennifer MorenoNo ratings yet
- Interventional NeuroradiologyDocument8 pagesInterventional NeuroradiologyAbhinav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Agarwal 2016Document51 pagesAgarwal 2016Daniel Alfredo Tenorio GonzálezNo ratings yet
- PRADEEP'S - Brain TumorDocument32 pagesPRADEEP'S - Brain TumorPRADEEPNo ratings yet
- Bruce C V Campbell Ischaemic Stroke 2019Document22 pagesBruce C V Campbell Ischaemic Stroke 2019yiyecNo ratings yet
- Hematoma SubduralDocument27 pagesHematoma SubduralRoeder Max Pangramuyen100% (4)
- Jos 15 90Document9 pagesJos 15 90reza ahda kadirNo ratings yet
- What Is An Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) ?Document4 pagesWhat Is An Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) ?Rafika MonalisaNo ratings yet
- Aneurysm BJADocument17 pagesAneurysm BJAParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- Computed TomographyDocument5 pagesComputed TomographyCrisMartAgullanaNo ratings yet
- The Brain: M.K. SastryDocument49 pagesThe Brain: M.K. SastryLupa IngatanNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument17 pagesStrokeJonathan Gutierrez RiosNo ratings yet
- Neurovascular Conditions: Stroke and Transient Ischemic AttackDocument7 pagesNeurovascular Conditions: Stroke and Transient Ischemic AttackGinNo ratings yet
- Farhat Research ArticleDocument1 pageFarhat Research ArticleDr MS HarisNo ratings yet
- Head TraumaDocument15 pagesHead TraumaDede Yusuf FNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument17 pagesStrokeluis sanchezNo ratings yet
- 128 FullDocument12 pages128 FullMarlen Adriana Hilario GómezNo ratings yet
- NEJM - Traumatic Intracraneal Hypertension - 2014Document10 pagesNEJM - Traumatic Intracraneal Hypertension - 2014Christofer George BarreraNo ratings yet
- Prayer PDFDocument2 pagesPrayer PDFCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- RDM Final ExamDocument1 pageRDM Final ExamCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Kuya Tims ExplanationDocument1 pageKuya Tims ExplanationCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Anaysis On Ferdinand Bongbong Marcos Inaugural AddressDocument2 pagesAnaysis On Ferdinand Bongbong Marcos Inaugural AddressCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Kiana FinalDocument1 pageKiana FinalCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Documentation in Disaster Management PDFDocument17 pagesDocumentation in Disaster Management PDFCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Group IIDocument24 pagesDisaster Group IICris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Cassey PDFDocument2 pagesCassey PDFCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - PerdentDocument3 pagesAssignment - PerdentCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Act3 ALBAODocument1 pageAct3 ALBAOCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- AdvertisementDocument1 pageAdvertisementCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Elective 1 Final ExamDocument3 pagesElective 1 Final ExamJonathan Ricarte ArancoNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs - Classification & MechanismDocument1 pageAntihypertensive Drugs - Classification & MechanismAhmed YT100% (1)
- CVA IntroductionDocument12 pagesCVA IntroductionSuzette Rae TateNo ratings yet
- Oriented History TakingDocument77 pagesOriented History Takingali laftaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Patho Exam QDocument17 pages2nd Patho Exam QSaleh RazickNo ratings yet
- Cardialgia. Chronic Coronary DiseaseDocument75 pagesCardialgia. Chronic Coronary DiseaseВиктория ПашаеваNo ratings yet
- Apical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (AHC) : Robert Buttner Mike CadoganDocument36 pagesApical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (AHC) : Robert Buttner Mike CadoganDeliberate self harmNo ratings yet
- (O. Nelson) Small Animal CardiologyDocument208 pages(O. Nelson) Small Animal CardiologyLoredana Gutu100% (1)
- Choledecholithiasis Case StudyDocument8 pagesCholedecholithiasis Case StudyYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- Stones in Galbladder - Pitay Ki Pathri - Homeopathic MedicineDocument4 pagesStones in Galbladder - Pitay Ki Pathri - Homeopathic MedicineParwaz KamalNo ratings yet
- Blood Pharmacology 27-34Document8 pagesBlood Pharmacology 27-34ahmedsalah565vvvNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS) in Anatomy-General Anatomy & Upper LimbDocument10 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQS) in Anatomy-General Anatomy & Upper LimbLoisNo ratings yet
- SPB Physiotherapy College, Surat BPT Question Bank Subject: ACADEMIC YEAR: 2016-17Document6 pagesSPB Physiotherapy College, Surat BPT Question Bank Subject: ACADEMIC YEAR: 2016-1702 Shivani BhagwakarNo ratings yet
- PDF Comprehensive Pediatric Hospital Medicine 2Nd Edition Lisa B Zaoutis Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Comprehensive Pediatric Hospital Medicine 2Nd Edition Lisa B Zaoutis Ebook Full Chaptermike.whitney894100% (4)
- Procedure & Complication of HaemodialysisDocument20 pagesProcedure & Complication of HaemodialysisLintaNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Drugs IDocument3 pagesAdrenergic Drugs IMirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Alcain CPRDocument6 pagesAlcain CPRErika Trina AlcainNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKEDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKEMa. Elaine Carla TatingNo ratings yet
- CPR PowerpointDocument66 pagesCPR Powerpointapi-209542414No ratings yet
- VAD Patient Education ManualDocument12 pagesVAD Patient Education ManualIakovos DanielosNo ratings yet
- AMK DiseasesDocument384 pagesAMK Diseaseshanif ahmadNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 27 Oct 2023Document14 pagesAdobe Scan 27 Oct 2023Adia RiztaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal BisoprololDocument10 pagesJurnal Bisoprololindrias pitalokaNo ratings yet
- Passmedicine MRCP Mcqs-OphthalmologyDocument30 pagesPassmedicine MRCP Mcqs-OphthalmologyMayar Wael100% (3)
- Clinical Enzymology-4th LevelDocument29 pagesClinical Enzymology-4th Leveltony maxxNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorDocument85 pagesDefibrillatorDhruv DesaiNo ratings yet
- Decision Making in Adult Neurology - 2020Document391 pagesDecision Making in Adult Neurology - 2020Ahmad mughalNo ratings yet
- BURNSDocument26 pagesBURNSGaurav pareekNo ratings yet
Case Analysis
Case Analysis
Uploaded by
Cris Anne BautistaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Analysis
Case Analysis
Uploaded by
Cris Anne BautistaCopyright:
Available Formats
When Morton Schimdt came to Portsmouth Regional Hospital for stroke symptoms, it
was discovered that he had brain aneurysm. The team at Portsmouth Stroke and Brain Aneurysm
Clinic was able to build a treatment plan specific to Morton’s condition, who was able to resume
his normal lifestyle right after his procedure. Prevalence ranges from 5-10%, with unruptured
aneurysms accounting for 50% of all aneurysms. Pediatric aneurysms account for only 2% of all
cerebral aneurysms. In the United States, the incidence of ruptured aneurysms is approximately
12 per 100,000 individuals or 30,000 annual cases of aneurysmal SAH.
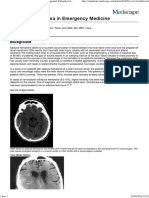
A brain aneurysm (also called a cerebral aneurysm or an intracranial aneurysm) is a
ballooning arising from a weakened area in the wall of a blood vessel in the brain. If the brain
aneurysm expands and the blood vessel wall becomes too thin, the aneurysm will rupture and
bleed into the space around the brain (Hopskin Medicine, 2020). Surgery and/or endovascular
therapy are the treatment for brain aneurysms, whether they are ruptured or unruptured. During
this procedure, your surgeon cuts a small opening in your skull to access the aneurysm.
(Cleveland Clinic, 2020)
1. In patient condition, why do you think the interventional radiology approach will be more
effective rather than invasive surgery?
Interventional radiologists use the least invasive techniques possible, making only small
incisions when necessary. This often results in safer and more effective outcomes than traditional
surgery. Interventional radiology reduces cost, recovery time, pain, and risk to patients who
would otherwise need traditional open surgery. Because of this, IR has become the primary way
to treat many types of conditions. The treatments IR can effectively perform are ever-changing
and expanding.
2. Explain your nursing responsibilities after surgery.
In general, nursing interventions that are required in postoperative care include prompt
pain control, assessment of the surgical site and drainage tubes, monitoring the rate and patency
of IV fluids and IV access, and assessing the patient's level of sensation, circulation, and safety.
3. Explain the complication that may develop in an aneurysm if untreated.
Increased pressure inside the head can cause coma or death. Vasospasm occurs frequently
after subarachnoid hemorrhage when the bleeding causes the arteries in the brain to contract and
limit blood flow to vital areas of the brain.
Cerebral Aneurysm tackles that role of our brain and how it can be damaged. As future
nurses, it is important to be exposed with cases like brain aneurysm in order to be ready for the
future cases we are about to handle in hospitals. Brain aneurysm can be dangerous if left
untreated, and it the responsibility of the nurse to take care of patients before, during, and after
treatment, that’s why nursing interventions should begin as soon as aortic dissection is suspected.
You might also like
- Acute Stroke Management in the Era of ThrombectomyFrom EverandAcute Stroke Management in the Era of ThrombectomyEdgar A. SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Advanced EKG RefresherDocument181 pagesAdvanced EKG RefresherIoana Antonesi100% (3)
- 2011 CardiacSurgery Catalog US 062811Document0 pages2011 CardiacSurgery Catalog US 062811MilagrosCisnerosNo ratings yet
- Brain Aneurysm Thesis StatementDocument7 pagesBrain Aneurysm Thesis Statementchristinewhitebillings100% (2)
- Epidural Hematoma: Continuing Education ActivityDocument16 pagesEpidural Hematoma: Continuing Education ActivityIka AriandanaNo ratings yet
- 4275 15730 1 PBDocument3 pages4275 15730 1 PBNiarsari A. PutriNo ratings yet
- Acv PDFDocument14 pagesAcv PDFFelipe AlcainoNo ratings yet
- Stroke NarrativeDocument10 pagesStroke Narrativecfalcon.medicinaNo ratings yet
- Their Treatments: Brain AneurysmsDocument9 pagesTheir Treatments: Brain AneurysmsArdiansyah P PratamaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral AneurysmDocument6 pagesCerebral AneurysmNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Stroke ThesisDocument7 pagesStroke Thesisnavysavchenkobellevue100% (1)
- Iht Nejm 2014Document10 pagesIht Nejm 2014Ademir Ruiz EcheverríaNo ratings yet
- Imaging of Intracranial Hemorrhage: Jeremy J. Heit, Michael Iv, Max WintermarkDocument21 pagesImaging of Intracranial Hemorrhage: Jeremy J. Heit, Michael Iv, Max WintermarkBrianNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument73 pagesSubarachnoid Hemorrhagederarataye6No ratings yet
- Imaging ICHDocument17 pagesImaging ICHCrhistian GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 2017 HSA Clinical PracticeDocument10 pages2017 HSA Clinical PracticeAndrea MartinezNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument10 pagesSubarachnoid HemorrhageRoberto López Mata100% (1)
- Cerebellopontine Angle TumoursDocument11 pagesCerebellopontine Angle TumoursIsmail Sholeh Bahrun MakkaratteNo ratings yet
- BRAIN AneurysmDocument14 pagesBRAIN AneurysmRikizu HobbiesNo ratings yet
- Hemorragia SubaracnoideaDocument10 pagesHemorragia SubaracnoideaAna TeresaNo ratings yet
- 10.1038@s41572 019 0118 8Document22 pages10.1038@s41572 019 0118 8Anabel AguilarNo ratings yet
- Britz, An Overview of Neurovascular Disease ManagementDocument2 pagesBritz, An Overview of Neurovascular Disease Managementlaila forestaNo ratings yet
- Epidural Hematoma in Emergency Medicine: BackgroundDocument3 pagesEpidural Hematoma in Emergency Medicine: BackgroundMercy HasanNo ratings yet
- Nhjuiy Uyiyui Yuighjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjhg GHJHGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGJ GHJGHJGHJGHJ L MGLFGKJFDGJKJ FGNGKFDGMNN DFJKDGH DJHGJ MNVGMFDXGNMGNFDMGNMDFGDocument16 pagesNhjuiy Uyiyui Yuighjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjhg GHJHGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGJ GHJGHJGHJGHJ L MGLFGKJFDGJKJ FGNGKFDGMNN DFJKDGH DJHGJ MNVGMFDXGNMGNFDMGNMDFGHasan AlkhawaldehNo ratings yet
- Neurovascular Conditions Treated at PennDocument7 pagesNeurovascular Conditions Treated at PennFatrawati BahuaNo ratings yet
- Dust inDocument7 pagesDust inlarkspor31No ratings yet
- Practneurol 2020 002763Document12 pagesPractneurol 2020 002763Fitri ainun MalahayatiNo ratings yet
- Author's Accepted Manuscript: Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRIDocument29 pagesAuthor's Accepted Manuscript: Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRIasfwegereNo ratings yet
- Cerebral AneurysmsDocument12 pagesCerebral AneurysmsDyah Ayu Puspita AnggarsariNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument62 pagesNervous Systemmyat252No ratings yet
- Scientific Report Journal 22 NovDocument6 pagesScientific Report Journal 22 Novnaresh kotraNo ratings yet
- 128 FullDocument12 pages128 FullYovita LimiawanNo ratings yet
- Case Study Cva Gr1Document72 pagesCase Study Cva Gr1Divina Gracia Fabicon Arana100% (1)
- Health Publications: Cerebral Aneurysm Treatment and Perioperative Nursing CareDocument9 pagesHealth Publications: Cerebral Aneurysm Treatment and Perioperative Nursing CareElmer San JoseNo ratings yet
- Acute Intracerebral Haemorrhage - Pract Neurol (2021)Document12 pagesAcute Intracerebral Haemorrhage - Pract Neurol (2021)Billy Priyanto HNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument6 pagesHead InjuryHurrinazilla AwaliaNo ratings yet
- ACV HemorrágicoDocument12 pagesACV HemorrágicoLUIS FELIPE ARTEAGA ARREDONDONo ratings yet
- Daniel D Price, MD Director of International Ultrasound, Department ofDocument3 pagesDaniel D Price, MD Director of International Ultrasound, Department ofPutri Swandayani NofendyNo ratings yet
- Practneurol 2020 002763Document12 pagesPractneurol 2020 002763Edgar MoralesNo ratings yet
- New Options For Neurovascular DiseaseDocument3 pagesNew Options For Neurovascular DiseasecamillarugaNo ratings yet
- Acute Intracerebral HaemorrhageDocument12 pagesAcute Intracerebral HaemorrhageZARF27No ratings yet
- PPTDocument8 pagesPPTArabelle TosocNo ratings yet
- Aneurysm: TypesDocument12 pagesAneurysm: TypesSofia Isabelle GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Neural TourniquetDocument5 pagesThe Neural TourniquetDaniel SherwinNo ratings yet
- Acute Intracerebral Haemorrhage BMJ 2021Document12 pagesAcute Intracerebral Haemorrhage BMJ 2021Jennifer MorenoNo ratings yet
- Interventional NeuroradiologyDocument8 pagesInterventional NeuroradiologyAbhinav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Agarwal 2016Document51 pagesAgarwal 2016Daniel Alfredo Tenorio GonzálezNo ratings yet
- PRADEEP'S - Brain TumorDocument32 pagesPRADEEP'S - Brain TumorPRADEEPNo ratings yet
- Bruce C V Campbell Ischaemic Stroke 2019Document22 pagesBruce C V Campbell Ischaemic Stroke 2019yiyecNo ratings yet
- Hematoma SubduralDocument27 pagesHematoma SubduralRoeder Max Pangramuyen100% (4)
- Jos 15 90Document9 pagesJos 15 90reza ahda kadirNo ratings yet
- What Is An Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) ?Document4 pagesWhat Is An Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) ?Rafika MonalisaNo ratings yet
- Aneurysm BJADocument17 pagesAneurysm BJAParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- Computed TomographyDocument5 pagesComputed TomographyCrisMartAgullanaNo ratings yet
- The Brain: M.K. SastryDocument49 pagesThe Brain: M.K. SastryLupa IngatanNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument17 pagesStrokeJonathan Gutierrez RiosNo ratings yet
- Neurovascular Conditions: Stroke and Transient Ischemic AttackDocument7 pagesNeurovascular Conditions: Stroke and Transient Ischemic AttackGinNo ratings yet
- Farhat Research ArticleDocument1 pageFarhat Research ArticleDr MS HarisNo ratings yet
- Head TraumaDocument15 pagesHead TraumaDede Yusuf FNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument17 pagesStrokeluis sanchezNo ratings yet
- 128 FullDocument12 pages128 FullMarlen Adriana Hilario GómezNo ratings yet
- NEJM - Traumatic Intracraneal Hypertension - 2014Document10 pagesNEJM - Traumatic Intracraneal Hypertension - 2014Christofer George BarreraNo ratings yet
- Prayer PDFDocument2 pagesPrayer PDFCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- RDM Final ExamDocument1 pageRDM Final ExamCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Kuya Tims ExplanationDocument1 pageKuya Tims ExplanationCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Anaysis On Ferdinand Bongbong Marcos Inaugural AddressDocument2 pagesAnaysis On Ferdinand Bongbong Marcos Inaugural AddressCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Kiana FinalDocument1 pageKiana FinalCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Documentation in Disaster Management PDFDocument17 pagesDocumentation in Disaster Management PDFCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Group IIDocument24 pagesDisaster Group IICris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Cassey PDFDocument2 pagesCassey PDFCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - PerdentDocument3 pagesAssignment - PerdentCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Act3 ALBAODocument1 pageAct3 ALBAOCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- AdvertisementDocument1 pageAdvertisementCris Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Elective 1 Final ExamDocument3 pagesElective 1 Final ExamJonathan Ricarte ArancoNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs - Classification & MechanismDocument1 pageAntihypertensive Drugs - Classification & MechanismAhmed YT100% (1)
- CVA IntroductionDocument12 pagesCVA IntroductionSuzette Rae TateNo ratings yet
- Oriented History TakingDocument77 pagesOriented History Takingali laftaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Patho Exam QDocument17 pages2nd Patho Exam QSaleh RazickNo ratings yet
- Cardialgia. Chronic Coronary DiseaseDocument75 pagesCardialgia. Chronic Coronary DiseaseВиктория ПашаеваNo ratings yet
- Apical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (AHC) : Robert Buttner Mike CadoganDocument36 pagesApical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (AHC) : Robert Buttner Mike CadoganDeliberate self harmNo ratings yet
- (O. Nelson) Small Animal CardiologyDocument208 pages(O. Nelson) Small Animal CardiologyLoredana Gutu100% (1)
- Choledecholithiasis Case StudyDocument8 pagesCholedecholithiasis Case StudyYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- Stones in Galbladder - Pitay Ki Pathri - Homeopathic MedicineDocument4 pagesStones in Galbladder - Pitay Ki Pathri - Homeopathic MedicineParwaz KamalNo ratings yet
- Blood Pharmacology 27-34Document8 pagesBlood Pharmacology 27-34ahmedsalah565vvvNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS) in Anatomy-General Anatomy & Upper LimbDocument10 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQS) in Anatomy-General Anatomy & Upper LimbLoisNo ratings yet
- SPB Physiotherapy College, Surat BPT Question Bank Subject: ACADEMIC YEAR: 2016-17Document6 pagesSPB Physiotherapy College, Surat BPT Question Bank Subject: ACADEMIC YEAR: 2016-1702 Shivani BhagwakarNo ratings yet
- PDF Comprehensive Pediatric Hospital Medicine 2Nd Edition Lisa B Zaoutis Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Comprehensive Pediatric Hospital Medicine 2Nd Edition Lisa B Zaoutis Ebook Full Chaptermike.whitney894100% (4)
- Procedure & Complication of HaemodialysisDocument20 pagesProcedure & Complication of HaemodialysisLintaNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Drugs IDocument3 pagesAdrenergic Drugs IMirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Alcain CPRDocument6 pagesAlcain CPRErika Trina AlcainNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKEDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKEMa. Elaine Carla TatingNo ratings yet
- CPR PowerpointDocument66 pagesCPR Powerpointapi-209542414No ratings yet
- VAD Patient Education ManualDocument12 pagesVAD Patient Education ManualIakovos DanielosNo ratings yet
- AMK DiseasesDocument384 pagesAMK Diseaseshanif ahmadNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 27 Oct 2023Document14 pagesAdobe Scan 27 Oct 2023Adia RiztaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal BisoprololDocument10 pagesJurnal Bisoprololindrias pitalokaNo ratings yet
- Passmedicine MRCP Mcqs-OphthalmologyDocument30 pagesPassmedicine MRCP Mcqs-OphthalmologyMayar Wael100% (3)
- Clinical Enzymology-4th LevelDocument29 pagesClinical Enzymology-4th Leveltony maxxNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorDocument85 pagesDefibrillatorDhruv DesaiNo ratings yet
- Decision Making in Adult Neurology - 2020Document391 pagesDecision Making in Adult Neurology - 2020Ahmad mughalNo ratings yet
- BURNSDocument26 pagesBURNSGaurav pareekNo ratings yet