Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Definitions
Definitions
Uploaded by
dianaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sound Class 8Document5 pagesSound Class 8Sanjib MandalNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Sound and HearingDocument12 pagesUnit 4 Sound and Hearingtwy113No ratings yet
- 2017-09-17 Architecture Acoustics (F D Architect's Conflicted Copy)Document69 pages2017-09-17 Architecture Acoustics (F D Architect's Conflicted Copy)HARSHITA JAINNo ratings yet
- Sound NotesDocument5 pagesSound NotesumaNo ratings yet
- SOUND - NotesDocument3 pagesSOUND - Notesnandana jammulaNo ratings yet
- 1 - SoundDocument26 pages1 - SoundOSHIN BALASINGHNo ratings yet
- Sound - EditedDocument2 pagesSound - Edited...No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document38 pagesUnit 2saahasitha 14No ratings yet
- Waves: Wave Is A Disturbance That Travels Through A Medium, and Transports Energy From One Location To AnotherDocument4 pagesWaves: Wave Is A Disturbance That Travels Through A Medium, and Transports Energy From One Location To AnotherOmar TamerNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PDFDocument38 pagesUnit 2 PDFyashaswiniNo ratings yet
- Propagation of SoundDocument3 pagesPropagation of SoundPrajjwal TakNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Sound WavesDocument44 pagesLesson 7 Sound WaveskhiananoribsNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Module 1Document33 pagesAcoustics Module 1mariyaNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument28 pagesSoundKunal100% (1)
- SoundDocument21 pagesSoundNahomy EspinalNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Design 1Document57 pagesAcoustics Design 1Swathika KannanNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Acoustic and Ultrasonic WavesDocument29 pagesUnit-4 Acoustic and Ultrasonic WavesSP.TrushadNo ratings yet
- Properties of SoundDocument23 pagesProperties of Soundmonabeth lumabasNo ratings yet
- Sound & AudioDocument37 pagesSound & Audioapi-27285803No ratings yet
- Lecture-12 Sound Waves, Zaheer Rizvi1Document23 pagesLecture-12 Sound Waves, Zaheer Rizvi1fourtechmediadmeagentsNo ratings yet
- Sound WaveDocument8 pagesSound WaveMalik AyazNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Perception of SoundDocument21 pagesThe Nature and Perception of Soundsheila louiseNo ratings yet
- Amplitude: Loudness Refers To How Loud or Soft A Sound Seems To A ListenerDocument2 pagesAmplitude: Loudness Refers To How Loud or Soft A Sound Seems To A ListenerTatadarz Auxtero LagriaNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument30 pagesSound WavesRidwan Pratama YudhaNo ratings yet
- 2016 SoundDocument69 pages2016 Soundryancasal959No ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument17 pagesAcousticsbhattaraikushal05No ratings yet
- Acoustic Sound and Human EarDocument26 pagesAcoustic Sound and Human EarEmmanuel EhuronNo ratings yet
- Physics of MusicDocument19 pagesPhysics of MusicSiddharta HoangNo ratings yet
- Sound and Its CharacteristicsDocument16 pagesSound and Its CharacteristicsGian Louise BarolaNo ratings yet
- BNCA Architectural AcousticsDocument35 pagesBNCA Architectural AcousticsSakshi DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument5 pagesSoundAvinash MansukNo ratings yet
- Physics Fast Revision NotesDocument8 pagesPhysics Fast Revision NotesdivyanshagrawalbsNo ratings yet
- The Science of SoundDocument23 pagesThe Science of SoundPamela Jiménez RibbaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of A SoundDocument6 pagesPhysical Properties of A Soundsergeyka2004No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Behaviour of Sound: Submitted by Chitra Rana 5 TH SemDocument18 pagesAssignment 1 Behaviour of Sound: Submitted by Chitra Rana 5 TH SemPrateekNo ratings yet
- Traveling Waves and Sound: Physics 11Document7 pagesTraveling Waves and Sound: Physics 11Trishla VermaNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument16 pagesSoundRSNo ratings yet
- The Pitch of A Sound and The Frequency of The Waves of The SoundDocument1 pageThe Pitch of A Sound and The Frequency of The Waves of The SoundAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- SOUNDDocument4 pagesSOUNDHitesh kalraNo ratings yet
- Acoustics: Unit-II Fundamental SDocument38 pagesAcoustics: Unit-II Fundamental SyashaswiniNo ratings yet
- Ear and Properties of SoundDocument15 pagesEar and Properties of SoundAnaliza ToledoNo ratings yet
- BU3 Acoustics PDFDocument257 pagesBU3 Acoustics PDFeyo rimasNo ratings yet
- 2312221519049139Document4 pages2312221519049139Shriya SNo ratings yet
- L6 AcousticDocument24 pagesL6 AcousticghaithNo ratings yet
- Sound IXDocument35 pagesSound IXarpankrishna739No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 (Basic Physics of Sound and The Decibe Scale)Document31 pagesLecture 2 (Basic Physics of Sound and The Decibe Scale)Geoffrey AlleyneNo ratings yet
- Acoustics - Module 1Document40 pagesAcoustics - Module 1Ashna AshrafNo ratings yet
- Is A Sound, Especially One That Is Loud or Unpleasant or That Causes DisturbanceDocument10 pagesIs A Sound, Especially One That Is Loud or Unpleasant or That Causes DisturbanceRajnish AnandNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities 3: Lecture 1 - Waves and Sound WavesDocument120 pagesBuilding Utilities 3: Lecture 1 - Waves and Sound WavesJann BayotNo ratings yet
- Propagation-of-Sound-Waves 2Document4 pagesPropagation-of-Sound-Waves 2Piyush RoyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document38 pagesLecture 1Nisarga JNo ratings yet
- 2021 BUILDING UTILITIES 3 - Module 1 Lecture 1 Waves and Sound Waves (S)Document34 pages2021 BUILDING UTILITIES 3 - Module 1 Lecture 1 Waves and Sound Waves (S)Sophia Manila SillaNo ratings yet
- Sound Chapter of Class-9Document21 pagesSound Chapter of Class-9whitedevilm.k444No ratings yet
- SoundDocument1 pageSoundShōyōHinataNo ratings yet
- SoundsDocument17 pagesSoundsdenden loNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas: SoundDocument1 pagePhysics Formulas: Soundmalanga.bangaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Sound and Classification of SoundDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of Sound and Classification of SoundBRIGHT CHIWEVUNo ratings yet
Definitions
Definitions
Uploaded by
dianaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Definitions
Definitions
Uploaded by
dianaCopyright:
Available Formats
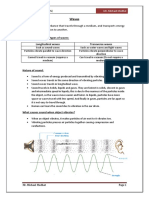
Sound Intensity
Sound intensity, also known as acoustic intensity, is defined as the power carried by sound waves
per unit area in a direction perpendicular to that area.
Resonance
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when the matching vibrations of another object increase
the amplitude of an object’s oscillations.
Interference
Wave interference is the phenomenon that occurs when two waves meet while traveling along
the same medium.
Node
A node is a point along a standing wave where the wave has minimum amplitude.
Antinodes
Antinodes are points on a stationary wave that oscillate with maximum amplitude.
Beats
Beats are the periodic and repeating fluctuations heard in the intensity of a sound when two
sound waves of very similar frequencies interfere with one another.
Timbre
Sound timbre is known as the characteristic waveform of sound that depends on the material
from which it produces.
Pitch
the pitch of a sound is essentially a description of the frequency of the sound. Different pitches
correspond to different frequencies. High pitch means high frequency, and low pitch means low
frequency.
Loudness
Loudness is the human perception of sound intensity. It is frequently measured in dB which is a
scale based on the human threshold of hearing (which is given a measurement of 0 dB on up).
Doppler Effect
Doppler effect, the apparent difference between the frequency at which sound or light waves
leave a source and that at which they reach an observer, caused by relative motion of the observer and
the wave source.
You might also like
- Sound Class 8Document5 pagesSound Class 8Sanjib MandalNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Sound and HearingDocument12 pagesUnit 4 Sound and Hearingtwy113No ratings yet
- 2017-09-17 Architecture Acoustics (F D Architect's Conflicted Copy)Document69 pages2017-09-17 Architecture Acoustics (F D Architect's Conflicted Copy)HARSHITA JAINNo ratings yet
- Sound NotesDocument5 pagesSound NotesumaNo ratings yet
- SOUND - NotesDocument3 pagesSOUND - Notesnandana jammulaNo ratings yet
- 1 - SoundDocument26 pages1 - SoundOSHIN BALASINGHNo ratings yet
- Sound - EditedDocument2 pagesSound - Edited...No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document38 pagesUnit 2saahasitha 14No ratings yet
- Waves: Wave Is A Disturbance That Travels Through A Medium, and Transports Energy From One Location To AnotherDocument4 pagesWaves: Wave Is A Disturbance That Travels Through A Medium, and Transports Energy From One Location To AnotherOmar TamerNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PDFDocument38 pagesUnit 2 PDFyashaswiniNo ratings yet
- Propagation of SoundDocument3 pagesPropagation of SoundPrajjwal TakNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Sound WavesDocument44 pagesLesson 7 Sound WaveskhiananoribsNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Module 1Document33 pagesAcoustics Module 1mariyaNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument28 pagesSoundKunal100% (1)
- SoundDocument21 pagesSoundNahomy EspinalNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Design 1Document57 pagesAcoustics Design 1Swathika KannanNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Acoustic and Ultrasonic WavesDocument29 pagesUnit-4 Acoustic and Ultrasonic WavesSP.TrushadNo ratings yet
- Properties of SoundDocument23 pagesProperties of Soundmonabeth lumabasNo ratings yet
- Sound & AudioDocument37 pagesSound & Audioapi-27285803No ratings yet
- Lecture-12 Sound Waves, Zaheer Rizvi1Document23 pagesLecture-12 Sound Waves, Zaheer Rizvi1fourtechmediadmeagentsNo ratings yet
- Sound WaveDocument8 pagesSound WaveMalik AyazNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Perception of SoundDocument21 pagesThe Nature and Perception of Soundsheila louiseNo ratings yet
- Amplitude: Loudness Refers To How Loud or Soft A Sound Seems To A ListenerDocument2 pagesAmplitude: Loudness Refers To How Loud or Soft A Sound Seems To A ListenerTatadarz Auxtero LagriaNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument30 pagesSound WavesRidwan Pratama YudhaNo ratings yet
- 2016 SoundDocument69 pages2016 Soundryancasal959No ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument17 pagesAcousticsbhattaraikushal05No ratings yet
- Acoustic Sound and Human EarDocument26 pagesAcoustic Sound and Human EarEmmanuel EhuronNo ratings yet
- Physics of MusicDocument19 pagesPhysics of MusicSiddharta HoangNo ratings yet
- Sound and Its CharacteristicsDocument16 pagesSound and Its CharacteristicsGian Louise BarolaNo ratings yet
- BNCA Architectural AcousticsDocument35 pagesBNCA Architectural AcousticsSakshi DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument5 pagesSoundAvinash MansukNo ratings yet
- Physics Fast Revision NotesDocument8 pagesPhysics Fast Revision NotesdivyanshagrawalbsNo ratings yet
- The Science of SoundDocument23 pagesThe Science of SoundPamela Jiménez RibbaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of A SoundDocument6 pagesPhysical Properties of A Soundsergeyka2004No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Behaviour of Sound: Submitted by Chitra Rana 5 TH SemDocument18 pagesAssignment 1 Behaviour of Sound: Submitted by Chitra Rana 5 TH SemPrateekNo ratings yet
- Traveling Waves and Sound: Physics 11Document7 pagesTraveling Waves and Sound: Physics 11Trishla VermaNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument16 pagesSoundRSNo ratings yet
- The Pitch of A Sound and The Frequency of The Waves of The SoundDocument1 pageThe Pitch of A Sound and The Frequency of The Waves of The SoundAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- SOUNDDocument4 pagesSOUNDHitesh kalraNo ratings yet
- Acoustics: Unit-II Fundamental SDocument38 pagesAcoustics: Unit-II Fundamental SyashaswiniNo ratings yet
- Ear and Properties of SoundDocument15 pagesEar and Properties of SoundAnaliza ToledoNo ratings yet
- BU3 Acoustics PDFDocument257 pagesBU3 Acoustics PDFeyo rimasNo ratings yet
- 2312221519049139Document4 pages2312221519049139Shriya SNo ratings yet
- L6 AcousticDocument24 pagesL6 AcousticghaithNo ratings yet
- Sound IXDocument35 pagesSound IXarpankrishna739No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 (Basic Physics of Sound and The Decibe Scale)Document31 pagesLecture 2 (Basic Physics of Sound and The Decibe Scale)Geoffrey AlleyneNo ratings yet
- Acoustics - Module 1Document40 pagesAcoustics - Module 1Ashna AshrafNo ratings yet
- Is A Sound, Especially One That Is Loud or Unpleasant or That Causes DisturbanceDocument10 pagesIs A Sound, Especially One That Is Loud or Unpleasant or That Causes DisturbanceRajnish AnandNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities 3: Lecture 1 - Waves and Sound WavesDocument120 pagesBuilding Utilities 3: Lecture 1 - Waves and Sound WavesJann BayotNo ratings yet
- Propagation-of-Sound-Waves 2Document4 pagesPropagation-of-Sound-Waves 2Piyush RoyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document38 pagesLecture 1Nisarga JNo ratings yet
- 2021 BUILDING UTILITIES 3 - Module 1 Lecture 1 Waves and Sound Waves (S)Document34 pages2021 BUILDING UTILITIES 3 - Module 1 Lecture 1 Waves and Sound Waves (S)Sophia Manila SillaNo ratings yet
- Sound Chapter of Class-9Document21 pagesSound Chapter of Class-9whitedevilm.k444No ratings yet
- SoundDocument1 pageSoundShōyōHinataNo ratings yet
- SoundsDocument17 pagesSoundsdenden loNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas: SoundDocument1 pagePhysics Formulas: Soundmalanga.bangaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Sound and Classification of SoundDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of Sound and Classification of SoundBRIGHT CHIWEVUNo ratings yet