Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sci-8 SSLM Q2 W6
Sci-8 SSLM Q2 W6
Uploaded by
QUEENIE JAM ABENOJAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sci-8 SSLM Q2 W6
Sci-8 SSLM Q2 W6
Uploaded by
QUEENIE JAM ABENOJACopyright:
Available Formats
SCIENCE – GRADE 8
Name: ______________________________________ Date: ____________________
Grade: ______________________________________ Section: ___________________
Quarter: 2 Week: 6 MELC(s): trace the path of typhoons that enter
the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR) using a map and tracking data
(S8ES-IIf-21).
Title of Textbook/LM to Study: Science 8 Learner’s Module
Chapter: 5 Pages: 139-141 Topic: The Philippine Area of Responsibility
Objectives:
● explain what is meant when a typhoon has entered the Philippine Area of
Responsibility.
● plot the Philippine Area of Responsibility given the latitude and longitude;
● track the location of tropical cyclone or typhoon as it moves from day to day;
● determine the path of a tropical cyclone, given the latitude and longitude position; and
● explain why PAGASA regularly monitors when a tropical cyclone is within the
Philippine Area of Responsibility.
Let Us Discover
In this Learning Activity Sheet presents weather disturbances that take place in the
Philippines every year. When a weather disturbance enters the Philippine Area of
Responsibility (PAR), the weather bureau begins to monitor it.
What is PAGASA?
PAGASA (Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Administration) is a
Philippine government agency created on December 8, 1972 by virtue of Presidential Decree
No. 78 reorganizing the Philippines Weather Bureau into PAGASA. It uses three domains
where they monitor, analyze and forecast tropical cyclones:
Tropical Cyclone Information Domains, Tropical Cyclone Advisory
Domain and the Philippines Area of Responsibility. If a tropical
cyclone is present inside these domains, PAGASA is tasked to do
the following: monitor the weather and climate of the country;
provide information to the public about typhoon and flood warnings; deliver weather forecasts
and advisories; and provide facts related to climatology, meteorology, and astronomy. This
government agency functions to serve the Filipinos, protect them and their properties, and to
support the economy, productivity, and sustainable development of the country.
GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, v.r. 02.00, Effective April 21, 2021
In the Philippines, we use the same word for all categories of tropical cyclones. We call it
Bagyo whether it is a tropical cyclone, tropical storm or a typhoon. It is accompanied with very
strong winds, heavy rains and very large ocean waves. According to PAGASA, there are about
20 tropical cyclones that enter PAR. Where is the Philippine Area of Responsibility?
How big is the Philippine Area of Responsibility?
The exact dimensions of this domain are the area of the Western North Pacific
bounded by imaginary lines connecting the coordinates:
50N 1150E, 150N 1150E, 210N 1200E, 250N 1350E, 50N 1350E
Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR) is an area of the Earth’s surface enclosing the
Philippines, Palau, Taiwan and the northern tip of Borneo.
Once a tropical cyclone enters Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR), it is
automatically given a local name so Filipinos can easily remember it. One must
remember that the Philippine Area of Responsibility is different from the country
itself. When we say a tropical cyclone is entering the PAR, it doesn’t mean that
it will hit the Philippine landmasses. It may still change its course or re-curve
away from the country. Its path follows three general directions: (a) Northward
from point of origin, the storms follow a northerly direction, only affecting small
islands. ; (b) Straight. A general westward path affects the Philippines, Southern China, Taiwan
and Vietnam; (c) Re-curving. Storm re-curving affects eastern China, Korea and Japan.
Let Us Try
On the Philippine map next page, the numbers running left side are latitude values and
the numbers along the bottom are longitude numbers. See if you can determine Philippine
Area of Responsibility using the latitude and longitude coordinate lines.
Activity 1:
Plotting the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR)
Objectives:
After performing this activity, you should be able to:
1. read map,
2. given the latitude and longitude of a tropical cyclone, tell if it has entered the Philippine Area
of Responsibility, and
3. explain what is meant when a typhoon has entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility.
Materials:
map of the Philippines and vicinity pencil
Procedures:
1. Locate the given latitude and longitude on the map. Latitude measures how far for
north or south is and longitude how far for east or west from the prime meridian. Plot the
following points on the map below (Figure3).
GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, v.r. 02.00, Effective April 21, 2021
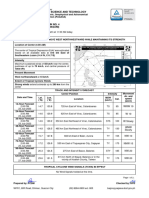
Table 2: Coordinates of the Philippine Area of Responsibility
Points Latitude Longitude
A 5°N 115°E
B 15°N 115°E
C 21°N 120°E
D 25°N 120°E
E 25°N 135°E
F 5°N 135°E
2. Connect the plotted points. The region within is the Philippine Area of Responsibility or
PAR. It is the job of PAGASA to monitor all tropical cyclones that enter this area.
Guide Questions:
1. If a typhoon is located at 15°N, 138°E, is it within the PAR?__________________
2. How about if the typhoon is at 14°N, 117°E, is it inside the PAR?______________
3. What does Philippine Area of Responsibility mean?________________________
4. What is meant when a typhoon entered the Philippines Area of Responsibility?
______________________________________________________________
5. Is Taiwan part of Philippine Area of Responsibility? Why?____________________
Figure 4 : Map of the Philippines and vicinity
Reference: K-12 Module for Science 8 pages 140-141 (Modified)
Let Us Do
In the following activity, you will be tracking a tropical cyclone as it enters and exits
the PAR.
Activity 2: Where is it Going?
Objectives:
In this activity, you should be able to
1. To track the location of tropical cyclone or typhoon as it moves from day to day;
2. Determine the path of a tropical cyclone, given the latitude and longitude position.
GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, v.r. 02.00, Effective April 21, 2021
3. Explain why PAGASA regularly monitors when a tropical cyclone is within the
Philippine Area of Responsibility.
Materials:
Map of Philippine Area of Responsibility Tracking data Pen Ruler
Procedures:
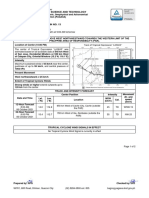
1. Using the data in Table 2, plot the day-to-day location of the tropical cyclone Yolanda on
the map showing the Philippine Area of Responsibility.
2. Mark each location with a dot. You may use colored pencils/pens to emphasize the dots.
3. Connect the dot to track the cyclone from November 6, 2013 to November 9, 2013
Table 2: Location of Super Typhoon Yolanda (International name HAIYAN)
Location of Eye of Location of Eye of
Tropical Cyclone Tropical Cyclone
Date Time Date Time
Latitud Longitud Longitud
Latitude
e e e
11/5/201 11/7/201
9:00:00 PM 7.225 140.509 3:00:00 PM 10.433 128.011
3 3
11/6/201 11/7/201
12:00:00 AM 7.325 139.7 6:00:00 PM 10.6 126.925
3 3
11/6/201 11/7/201
3:00:00 AM 7.455 138.838 9:00:00 PM 10.814 125.856
3 3
11/6/201 11/8/201
6:00:00 AM 7.6 137.95 12:00:00 AM 11.025 124.775
3 3
11/6/201 11/8/201
9:00:00 AM 7.748 137.068 3:00:00 AM 11.21 123.655
3 3
11/6/201 11/8/201
12:00:00 PM 7.9 136.175 6:00:00 AM 11.4 122.55
3 3
11/6/201 11/8/201
3:00:00 PM 8.035 135.247 9:00:00 AM 11.617 121.545
3 3
11/6/201 11/8/201
6:00:00 PM 8.2 134.35 12:00:00 PM 11.85 120.5
3 3
11/6/201 11/8/201
9:00:00 PM 8.425 133.553 3:00:00 PM 12.113 119.211
3 3
11/7/201 11/8/201
12:00:00 AM 8.7 132.775 6:00:00 PM 12.325 118
3 3
11/7/201 11/8/201
3:00:00 AM 8.984 131.957 9:00:00 PM 12.347 117.18
3 3
11/7/201 11/9/201
6:00:00 AM 9.325 131.075 12:00:00 AM 12.45 116.475
3 3
11/7/201 11/9/201
9:00:00 AM 9.779 130.109 3:00:00 AM 12.884 115.612
3 3
11/7/201
12:00:00 PM 10.2 129.075
3
GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, v.r. 02.00, Effective April 21, 2021
(Illustrator: ALONA ROSE L. JIMENEA, GSCNHS)
Figure 3: The Philippine Area of Responsibility
Guide Questions:
1. What is the local name of the Super Typhoon recorded and monitored by
PAGASA?___________________________________________________________
2. From what body of water did Super Typhoon Yolanda originate?
___________________________________________________________________
3. What direction did Super Typhoon Yolanda take as it crossed the
Philippines?__________________________________________________________
4. On what day did Super Typhoon Yolanda hit land?
____________________________________________________________________
5. When did Yolanda enter the Philippine Area of Responsibility?
____________________________________________________________________
6. When did Yolanda leave the Philippine Area of Responsibility?
____________________________________________________________________
7. In what path did Yolanda move? __________________________________________
8. Which provinces were hit directly by the eye of the super typhoon?
____________________________________________________________________
9. Why is Yolanda categorized as a super Typhoon? ____________________________
10. Explain why PAGASA regularly monitors a tropical cyclone when it is within the
Philippine Area of Responsibility. _________________________________________
GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, v.r. 02.00, Effective April 21, 2021
Let Us Apply
Activity 3: Learn Tracking Me...
Read the scenario on the right side and answer the questions.
Read this!
Grace goes to her school early in the morning. The
security guard informs her that their classes are suspended
because of a coming tropical cyclone in Mindanao.
Answer this!
What will Grace do to know if the tropical cyclone is already
in the country?
What Philippine agency monitors and observes typhoons
via radio satellite?
How do Grace prepare herself for tropical cyclone?
JGBPeñas
References
● Campo, Pia C.,et. al (2013). Science 8 Learner’s Module pp. 139-141.
● Science Links Grade 8 Edited Edition , Madriaga,E., et al., pages 199-201
● SCI-Bytes Grade 8, Fernandez, P., et al., pages 270-271
● Project EASE Science 1 Module14, pages 4-5
● http://bagong.pagasa.dost.gov.ph/climate/tropical-cyclone-associated-rainfall
● https://www.wunderground.com/hurricane/archive/WP/2013
● http://bagong.pagasa.dost.gov.ph/learning-tools/philippine-area-of-responsibility
● https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Typhoon
SSLM Development Team
Writer: Jeanaline Grace B. Peñas
Evaluator: Marlene C. Gevero
Illustrator: Alona Rose L. Jimenea, Jeanaline Grace B. Peñas
Creative Arts Designer: Reggie D. Galindez
Education Program Supervisor: Edilbert A. Reyes
Education Program Supervisor – Learning Resources: Sally A. Palomo
Curriculum Implementation Division Chief: Juliet F. Lastimosa
Asst. Schools Division Superintendent: Carlos G. Susarno, Ph. D.
Schools Division Superintendent: Romelito G. Flores, CESO V
GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, v.r. 02.00, Effective April 21, 2021
You might also like
- Understanding TyphoonDocument43 pagesUnderstanding TyphoonJosene Mae Banang Maghari89% (9)
- Activity Sheet Hit The Mark: Plotting The Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR)Document2 pagesActivity Sheet Hit The Mark: Plotting The Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR)shellehhh maeee63% (8)
- Reading Test 2: Section 1Document4 pagesReading Test 2: Section 1Quang Nguyen0% (2)
- Earthquake Case Study 4 - Chile 1960Document23 pagesEarthquake Case Study 4 - Chile 1960Carlos Andrés ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Science - 8 - q2 - wk5 - Trace The Path of Typhoons That Enters The Par Using Map and Tracking DataDocument9 pagesScience - 8 - q2 - wk5 - Trace The Path of Typhoons That Enters The Par Using Map and Tracking DataAileen Ocampo50% (2)
- SLP - Science - Grade 8 - Q2 - LP 8Document16 pagesSLP - Science - Grade 8 - Q2 - LP 8Robelyn ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Science - 8 - q2 - wk5 - Trace The Path of Typhoons That Enters The Par Using Map and Tracking DataDocument11 pagesScience - 8 - q2 - wk5 - Trace The Path of Typhoons That Enters The Par Using Map and Tracking DataAileen Ocampo100% (4)
- Science Q2 Weeks5to8Document34 pagesScience Q2 Weeks5to8maeyonnaise127No ratings yet
- Q1-Week 3-Trenches and Active Volcanoes BerganciaDocument5 pagesQ1-Week 3-Trenches and Active Volcanoes BerganciakumiNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Q1 Week 5Document10 pagesScience 8 Q1 Week 5Jerikho De JesusNo ratings yet
- Demo Lesson Plan - SecondgradingDocument6 pagesDemo Lesson Plan - Secondgradingmary grace100% (1)
- Module 2 - TyphoonDocument24 pagesModule 2 - Typhoonlil pony ssiNo ratings yet
- ACTUAL LESSON PLAN in DEPEDDocument4 pagesACTUAL LESSON PLAN in DEPEDNo one KnowsNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q2 Module5 TrackingATyphoon V4Document13 pagesScience8 Q2 Module5 TrackingATyphoon V4Salve Gregorio AguirreNo ratings yet
- Science-8: National Christian Life CollegeDocument6 pagesScience-8: National Christian Life CollegeLannayah coNo ratings yet
- g8 Earth Science q2 Module 4 Philippine Area of ResponsibilityDocument8 pagesg8 Earth Science q2 Module 4 Philippine Area of Responsibilityajilianzyre100% (2)
- Science8 q2 Mod5of6 Thephilippineareaofresponsibility v2Document26 pagesScience8 q2 Mod5of6 Thephilippineareaofresponsibility v2Bainalyn BaludiNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 TyphoonDocument4 pagesActivity 1 TyphoonMarian SilvaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 TyphoonDocument4 pagesActivity 1 TyphoonBing Sepe Culajao100% (2)
- 8 Sci LM U2 - M2Document17 pages8 Sci LM U2 - M2Jboy Mnl67% (6)
- Science: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument34 pagesScience: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDainielle Marie PascualNo ratings yet
- Adm Q2W 5 6 G8Document32 pagesAdm Q2W 5 6 G8mallarimelanie59No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Philippine Area of ResponsibilityDocument5 pagesLesson 1: The Philippine Area of ResponsibilityMaria Cristina DelmoNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration, PAGASA, Monitors Its Activities. PAGASADocument3 pagesAtmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration, PAGASA, Monitors Its Activities. PAGASAMaria Cristina Delmo100% (1)
- Department of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesDarius MaestroNo ratings yet
- TD 2 - Cebu City and Province Geophysical ProfileDocument40 pagesTD 2 - Cebu City and Province Geophysical ProfileChan VillaflorNo ratings yet
- CredentialsDocument25 pagesCredentialsAna Altavano DukaNo ratings yet
- Science7 Lasq4 Week-1Document7 pagesScience7 Lasq4 Week-1Jinky AydallaNo ratings yet
- Tracing The Location of A TyphoonDocument27 pagesTracing The Location of A TyphoonJoh A NnaNo ratings yet
- Department of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesAllen Timtiman BisqueraNo ratings yet
- Q2 Science8 Las W5Document19 pagesQ2 Science8 Las W5Ronna Jean SambitanNo ratings yet
- TcadvisoryDocument2 pagesTcadvisoryAna BruNo ratings yet
- Q2 Science8 Las W4Document24 pagesQ2 Science8 Las W4Ronna Jean Sambitan100% (1)
- The 05 March 2017 Ms5.9 Surigao Earthquake AftershockDocument5 pagesThe 05 March 2017 Ms5.9 Surigao Earthquake AftershockColin Kay R. CajoteNo ratings yet
- Sci8 - Q2 - M5 - Tracking The Path of TyphoonDocument24 pagesSci8 - Q2 - M5 - Tracking The Path of TyphoonMai Mai100% (2)
- Activity Sheet - Tracking Typhoon PARDocument4 pagesActivity Sheet - Tracking Typhoon PARoganayenshiNo ratings yet
- December 1-2-2022Document9 pagesDecember 1-2-2022Cecille PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Co1 2021 2022 - GutierrezDocument6 pagesCo1 2021 2022 - GutierrezARCELIE NARCANo ratings yet
- Science 8 q2 WK 5slht 6Document5 pagesScience 8 q2 WK 5slht 6zabala.vanessa.sixdaffodil100% (1)
- ADVANCE COPY 20231001 MEMO ACTIVATION For Regions I and CAR EOC and DORMS For TS JENNYDocument5 pagesADVANCE COPY 20231001 MEMO ACTIVATION For Regions I and CAR EOC and DORMS For TS JENNYMary TenorioNo ratings yet
- Earthquake ActivityDocument2 pagesEarthquake ActivityShania Mary BaluranNo ratings yet
- 02 Science10 - Q1 - Wk2 - LASDocument14 pages02 Science10 - Q1 - Wk2 - LASHen RyNo ratings yet
- Content of Site-Specific Hazard Report For PEZADocument7 pagesContent of Site-Specific Hazard Report For PEZAmark_torreonNo ratings yet
- Department of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Science and Technology: Republic of The Philippinesshao butongNo ratings yet
- TcadvisoryDocument2 pagesTcadvisoryDennmark Duran IgutNo ratings yet
- Science 7 4Q ModuleDocument49 pagesScience 7 4Q ModuleAlex CabalfinNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q1 - DW4Document4 pagesScience 10 - Q1 - DW4Des AbrasiaNo ratings yet
- SSI WorksheetDocument3 pagesSSI Worksheetarvie.adrianoNo ratings yet
- PAGASA 23-TC05 Egay TCB#04Document2 pagesPAGASA 23-TC05 Egay TCB#04Grace Mecate VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3. Tracking A Tropical Cyclone - MAMURIDocument4 pagesActivity 3. Tracking A Tropical Cyclone - MAMURIEirik Nathan MamuriNo ratings yet
- Q2 Sci8 w1L2 Pre-ActivityDocument6 pagesQ2 Sci8 w1L2 Pre-Activitydianarose anasarioNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Tracking A TyphoonDocument38 pagesQuarter 2 Tracking A Typhoonnutssdeez944No ratings yet
- Department of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Science and Technology: Republic of The Philippinesdeejay_263No ratings yet
- Activity 3. Tracking A Tropical Cyclone - MAMURIDocument4 pagesActivity 3. Tracking A Tropical Cyclone - MAMURIEirik Nathan MamuriNo ratings yet
- PAGASA 23-TC05 Egay TCB#05Document2 pagesPAGASA 23-TC05 Egay TCB#05Grace Mecate VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- QUARTER 2 LESSON 5 Pathway of TyphoonDocument17 pagesQUARTER 2 LESSON 5 Pathway of TyphoonJose BundalianNo ratings yet
- Finding Faults - AsyncDocument4 pagesFinding Faults - AsyncchristinalaxaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE - Q1 - W7 - Mod16 - Earth and Life Science (Geologic Hazards)Document11 pagesSCIENCE - Q1 - W7 - Mod16 - Earth and Life Science (Geologic Hazards)Liesel0% (1)
- DRRR11 Q2 Mod8Document8 pagesDRRR11 Q2 Mod8Rommel HapitaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 ScienceDocument21 pagesQuarter 3 SciencevinleonardbNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 8 - TyphoonDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in Science 8 - TyphoonEpoy86% (7)
- Science8 q2 Earthquakeswaves v2Document25 pagesScience8 q2 Earthquakeswaves v2QUEENIE JAM ABENOJANo ratings yet
- Science - Grade 7: Let Us DiscoverDocument7 pagesScience - Grade 7: Let Us DiscoverQUEENIE JAM ABENOJANo ratings yet
- Science8 - Q2 - EarthquakesAnd Faults - V1Document19 pagesScience8 - Q2 - EarthquakesAnd Faults - V1QUEENIE JAM ABENOJANo ratings yet
- Sci-8 SSLM Q2 W4Document5 pagesSci-8 SSLM Q2 W4QUEENIE JAM ABENOJANo ratings yet
- Sci-8 SSLM Q2 W7Document7 pagesSci-8 SSLM Q2 W7QUEENIE JAM ABENOJANo ratings yet
- Sci-8 SSLM Q2 W5 DiazmDocument6 pagesSci-8 SSLM Q2 W5 DiazmQUEENIE JAM ABENOJANo ratings yet
- Sci-8 SSLM Q2 W3Document5 pagesSci-8 SSLM Q2 W3QUEENIE JAM ABENOJANo ratings yet
- Sci-8 SSLM Q2 W2 VillanuevaDocument5 pagesSci-8 SSLM Q2 W2 VillanuevaQUEENIE JAM ABENOJANo ratings yet
- Sci-8 SSLM q2 w1 Saldivia-wo-AkDocument5 pagesSci-8 SSLM q2 w1 Saldivia-wo-AkQUEENIE JAM ABENOJANo ratings yet
- PROJECT: Janathon Bonik, Dhaka Savar: by Engr. Ali AsgorDocument9 pagesPROJECT: Janathon Bonik, Dhaka Savar: by Engr. Ali AsgorMehedi H. RanaNo ratings yet
- Abbreviation List PDFDocument1 pageAbbreviation List PDFSachin BarotNo ratings yet
- Natural Disasters Vocabulary Cards Classroom Posters Flashcards Fun Activities Games - 72195Document1 pageNatural Disasters Vocabulary Cards Classroom Posters Flashcards Fun Activities Games - 72195Natalia Soledad RojasNo ratings yet
- Earthquake 2005 in PakistanDocument3 pagesEarthquake 2005 in PakistanAnoo 123No ratings yet
- Causes of LandslidesDocument9 pagesCauses of LandslidesSauRabh BaRmanNo ratings yet
- 1991 PinatuboDocument1 page1991 PinatuboClaudetteNo ratings yet
- Oxnard: Tsunami Evacuation MapsDocument2 pagesOxnard: Tsunami Evacuation MapsVentura County Star100% (1)
- Dalupaon National High School: Department of EducationDocument3 pagesDalupaon National High School: Department of Educationjeanette PradesNo ratings yet
- Revised-Radar-Form-1-2-Template - EditedDocument2 pagesRevised-Radar-Form-1-2-Template - EditedRON DANIEL EDOLOVERIONo ratings yet
- Hurricane BrochureDocument2 pagesHurricane Brochurewa1abiNo ratings yet
- Science: The Effects of Earthquakes and Volcanic Eruptions - Quarter 4Document12 pagesScience: The Effects of Earthquakes and Volcanic Eruptions - Quarter 4Haycel FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Types of EmergenciesDocument12 pagesTypes of EmergenciesAfzaalUmairNo ratings yet
- Historical Disaster Events For Month of DecemberDocument1 pageHistorical Disaster Events For Month of DecemberSampath KukulavithanaNo ratings yet
- EssayDocument2 pagesEssayMaria Lourdes Donadillo VelardeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science VDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in Science VKemela Joy Biñas - RadadonNo ratings yet
- Movie The ImpossibleDocument4 pagesMovie The ImpossibleJoyce Reinat Ortiz100% (1)
- Emdat Public 2020 09 08 Query Uid-Tmmal2Document1,514 pagesEmdat Public 2020 09 08 Query Uid-Tmmal2Karun BamanuNo ratings yet
- Hurricane Sandy Thesis StatementDocument4 pagesHurricane Sandy Thesis StatementStacy Vasquez100% (2)
- Barangay Contingency PlanDocument2 pagesBarangay Contingency PlanChristopher Montebon100% (1)
- Earthquake ScienceDocument2 pagesEarthquake ScienceSarilyn SimonNo ratings yet
- Eva Project ReportDocument6 pagesEva Project ReportHarsh BhallaNo ratings yet
- 2ND Quarer Exam Science 8Document3 pages2ND Quarer Exam Science 8Markjay LegoNo ratings yet
- NAS2 Liquefaction SPT 1998NCEER N SPTDocument1 pageNAS2 Liquefaction SPT 1998NCEER N SPTHanafiahHamzahNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument3 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-264090670No ratings yet
- Cyclone Amphan-Page 2Document2 pagesCyclone Amphan-Page 2Rajib LoharNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary: Natural: Man-MadeDocument3 pagesVocabulary: Natural: Man-MadeFabrizio SulcaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Engineering Course OutlineDocument2 pagesEarthquake Engineering Course OutlineMISKIR TADESSENo ratings yet
- Earthquakes, Forces of NatureDocument36 pagesEarthquakes, Forces of Natureevoid100% (1)