Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comparing Two or More Independent Groups
Comparing Two or More Independent Groups
Uploaded by
Cassy Andrea PadillaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Comparing Two or More Independent Groups
Comparing Two or More Independent Groups
Uploaded by
Cassy Andrea PadillaCopyright:
Available Formats
ACTIVITY 2
Comparing Two or More Independent Groups
NAME: SCORE:
SECTION: DATE:
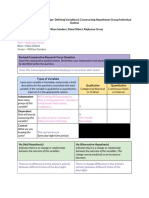
I. Direction: Complete the table below according to the assumption needs to consider in the following
statistical test of difference.
STATISTICAL TEST ASSUMPTION
COMPARING TWO OR A. One-Way Analysis Dependent Variable 1. Continuous scale -
MORE INDEPENDENT of Variance (ANOVA) Interval or Ratio.
GROUPS 2. Approximately
normally distributed
for each group of
independent variable.
Independent Variable 3. Two or more
categorical
independent groups.
Observation 4. Independence of
observation.
Variance 5. Homogenous.
B. Kruskal-Wallis Test Dependent Variable 6. Ordinal Level
7. Continuous Level
Independent Variable 8. Two or more
categorical,
independent groups.
Observation 9. Independence of
observation.
Variance 10. Kruskal-Wallis Test
can be used to
compare the median
in dependent variable
if distribution have
same shape. If the
shape is different,
mean ranks is may be
used to compare the
test.
II. Direction: Discuss the difference of One-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and Kruskal-Wallis Test.
Cite at least one example.
One-Way Analysis of Variance is testing the null hypothesis if its “Ho: All group means are equal.” and
“Ha: Not all groups are equal.” To know if the null hypothesis should reject or not, the p-value of
significant difference exist among groups is less than 0.05. For example, the mother who has
experience of premature and those who not are being compared. In data given, p-value is less than to
0.05, therefore the babies birthweight differs across mother history of premature labor.
Kruskal-Wallis Test shows ranks and test statistic table to show if the shape same or not by mean
ranks or median. For example, mothers who has experience of premature labor is lower than the
mothers who has no experience. The results are grouped according to the data.
You might also like
- Test Bank For Statistics For Business and Economics 7th Edition by NewboldDocument54 pagesTest Bank For Statistics For Business and Economics 7th Edition by Newbolda161855766100% (4)
- MASH WhatStatisticalTestHandout PDFDocument2 pagesMASH WhatStatisticalTestHandout PDFMatteoParolloNo ratings yet
- Practical Research MODULE 2Document8 pagesPractical Research MODULE 2Hannah Bianca Regullano100% (5)
- Anderson-Darling Normality Test CalculatorDocument4 pagesAnderson-Darling Normality Test CalculatorMansoor Ali0% (3)
- To Show Whether or Not Colours Are Evenly Distributed in A Bag of Gummi BearsDocument6 pagesTo Show Whether or Not Colours Are Evenly Distributed in A Bag of Gummi BearsRahul MistryNo ratings yet
- Module Exercises in Master StatisticsDocument6 pagesModule Exercises in Master StatisticsMARIA THERESA M. HERBOLINGO0% (5)
- Activity 1 ResearchDocument2 pagesActivity 1 ResearchCassy Andrea PadillaNo ratings yet
- Analisis Data InferensiDocument17 pagesAnalisis Data InferensiFARHANA MUBINNo ratings yet
- Giped OutlineDocument3 pagesGiped Outlineapi-525576012No ratings yet
- Quizlet PDFDocument1 pageQuizlet PDFgulzira3amirovnaNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Writing Thesis and Dissertation 1Document72 pagesA Guide To Writing Thesis and Dissertation 1louella repolloNo ratings yet
- Assumptions: Pitfalls of Regression AnalysisDocument9 pagesAssumptions: Pitfalls of Regression AnalysisJohn Aaron MirabelNo ratings yet
- AnovaDocument17 pagesAnovaAndrea LeonorNo ratings yet
- Activity 3-Table Completion On Parametric Test-Hazel P. PatalotDocument2 pagesActivity 3-Table Completion On Parametric Test-Hazel P. PatalothazelppatalotNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Variance (Anova)Document17 pagesAnalysis of Variance (Anova)Andrea LeonorNo ratings yet
- Basic Between Subject and Between-Subjects Factorial DesignDocument3 pagesBasic Between Subject and Between-Subjects Factorial DesignReagine ArciagaNo ratings yet
- What Is This Test (One-Way ANOVA) For?Document7 pagesWhat Is This Test (One-Way ANOVA) For?Zaheen00 FatimaNo ratings yet
- MANOVA - Multivariate Analysis of Variance: Why Do You Need MANOVA?Document2 pagesMANOVA - Multivariate Analysis of Variance: Why Do You Need MANOVA?Vijay SeelanNo ratings yet
- 14 Experimental Psych SummaryDocument3 pages14 Experimental Psych SummaryYvonne SipalayNo ratings yet
- Two Way Anova: Welly Ernando Septian Rezy Nurul NatasaDocument19 pagesTwo Way Anova: Welly Ernando Septian Rezy Nurul Natasaheri wahyudiNo ratings yet
- Name: Muhammad Siddique Class: B.Ed. Semester: Fifth Subject: Inferential Statistics Submitted To: Sir Sajid AliDocument5 pagesName: Muhammad Siddique Class: B.Ed. Semester: Fifth Subject: Inferential Statistics Submitted To: Sir Sajid Aliusama aliNo ratings yet
- DLP Week 3 PR2Document5 pagesDLP Week 3 PR2stephanie maloloyonNo ratings yet
- AnovaDocument26 pagesAnovaRadhel Faith ToloNo ratings yet
- Anova1 2101Document36 pagesAnova1 2101Vaishali ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Chap 1-4 Reviewer Psych StatsDocument3 pagesChap 1-4 Reviewer Psych StatsLuisa EsplanadaNo ratings yet
- Multivariate Analysis of VarianceDocument29 pagesMultivariate Analysis of VarianceAC BalioNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Essentials of Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 2nd Edition Nolan Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Essentials of Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 2nd Edition Nolan Solutions Manual PDFmortgagechoric3yh7100% (13)
- Full Download Essentials of Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 2nd Edition Nolan Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Essentials of Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 2nd Edition Nolan Solutions Manualonerarysavable.waw8100% (42)
- How To Interpret and Report The Results From Multi Variable AnalysisDocument6 pagesHow To Interpret and Report The Results From Multi Variable AnalysisSofia Batalha0% (1)
- Essentials of Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 2nd Edition Nolan Solutions ManualDocument14 pagesEssentials of Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 2nd Edition Nolan Solutions ManualDebraFloresotzax100% (18)
- Statistical Tests For Comparative StudiesDocument7 pagesStatistical Tests For Comparative StudiesalohaNo ratings yet
- Yr 10 Sci Method Booklet W Questions W AnswersDocument25 pagesYr 10 Sci Method Booklet W Questions W Answersbk3pgxrthpNo ratings yet
- Advanced ANOVA - MANOVA - WikiversityDocument7 pagesAdvanced ANOVA - MANOVA - WikiversityDivya pathakNo ratings yet
- Assumption 1Document1 pageAssumption 1مركز ريلاكس للعلاج الطبيعيNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research Lecture Notes # 4Document1 pageNursing Research Lecture Notes # 4Jesamin PacquiaoNo ratings yet
- Anastat ReportingDocument31 pagesAnastat ReportingElsie DomeNo ratings yet
- Ocampo Research Enrichment 3Document2 pagesOcampo Research Enrichment 3ELISHA OCAMPONo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics: Paper #6Document11 pagesAdvanced Statistics: Paper #6Precious NosaNo ratings yet
- Types of Anova Tests - Methods of Criminologial ResearchDocument3 pagesTypes of Anova Tests - Methods of Criminologial Research9b8448srqnNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: Grade Level: Grade 12Document5 pagesPractical Research 2: Grade Level: Grade 12Diane SagunNo ratings yet
- Math 1F - 4 StatisticsDocument8 pagesMath 1F - 4 StatisticsJay-pNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Variables and Their UsesDocument18 pagesKinds of Variables and Their UsesMatthew ItingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Discriminant AnalysisDocument20 pagesChapter 25 - Discriminant AnalysisUmar Farooq AttariNo ratings yet
- Anova AncovaDocument10 pagesAnova AncovaYus100% (2)
- Unit 3-Anova - Ancova Manova-MancovaDocument11 pagesUnit 3-Anova - Ancova Manova-MancovaRuchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Group 5-Comprehensive OutlineDocument15 pagesGroup 5-Comprehensive OutlineNEIL MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Statistical Tools For Data AnalysisDocument4 pagesStatistical Tools For Data AnalysisGrace AtrazoNo ratings yet
- Manova: Presented ByDocument13 pagesManova: Presented ByAmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- ANOVAWelchcorrection Satterthwaitecorrectionand Kruskal Wallistestcomparisonoftype IerrorrateandpowerDocument23 pagesANOVAWelchcorrection Satterthwaitecorrectionand Kruskal Wallistestcomparisonoftype IerrorrateandpowerevelynNo ratings yet
- STEM PR2 Osorio Week-3-4Document16 pagesSTEM PR2 Osorio Week-3-4ganda dyosaNo ratings yet
- M2 - Two-Way Factorial ANOVAsDocument26 pagesM2 - Two-Way Factorial ANOVAsJunjie GohNo ratings yet
- Variables and HypothesisDocument2 pagesVariables and HypothesisMercedes CandelonNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics: Descriptive Analysis and Differences Between GroupsDocument17 pagesBiostatistics: Descriptive Analysis and Differences Between GroupsOneng IfayaniNo ratings yet
- Manova One Powerpoint 1 STATDocument35 pagesManova One Powerpoint 1 STATCherrie Almonte CasumpangNo ratings yet
- Last Meeting IncompleteDocument6 pagesLast Meeting IncompleteJerene Denzil NacarNo ratings yet
- Understanding The One-Way ANOVADocument13 pagesUnderstanding The One-Way ANOVAxxkooonxxNo ratings yet
- More Than Two Groups: ANOVA and Chi-SquareDocument67 pagesMore Than Two Groups: ANOVA and Chi-SquarearjunNo ratings yet
- SPSS Lab Session 3Document10 pagesSPSS Lab Session 3Aimen NaeemNo ratings yet
- Table Stat Test Example SPSSDocument42 pagesTable Stat Test Example SPSSAlton JurahNo ratings yet
- Repeated Anova Factorial AnovaDocument1 pageRepeated Anova Factorial AnovaharrisonwhiteNo ratings yet
- QUIZ Income TaxDocument1 pageQUIZ Income TaxCassy Andrea PadillaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 ResearchDocument2 pagesActivity 1 ResearchCassy Andrea PadillaNo ratings yet
- Taxation ReviewerDocument6 pagesTaxation ReviewerCassy Andrea PadillaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Research StatsDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 Research StatsCassy Andrea PadillaNo ratings yet
- Chanski and Ellis - Peer FeedbackDocument7 pagesChanski and Ellis - Peer Feedbacktjohns56No ratings yet
- Research Methods and Statistics Full NotesDocument68 pagesResearch Methods and Statistics Full NotesDipti PandeyNo ratings yet
- Statistical Tests For Comparative StudiesDocument7 pagesStatistical Tests For Comparative StudiesalohaNo ratings yet
- Modules in Stat101Document133 pagesModules in Stat101Lope BautistaNo ratings yet
- JOralMaxillofacPathol 2013 17-1-65 110733Document8 pagesJOralMaxillofacPathol 2013 17-1-65 110733sonata333No ratings yet
- Engineering Statistics Handbook 7. Product and Process ComparisonsDocument144 pagesEngineering Statistics Handbook 7. Product and Process Comparisonsagbas20026896No ratings yet
- IB IA HL Levels of ProcessingDocument23 pagesIB IA HL Levels of ProcessingMrGreenankle25% (4)
- Fourth Quarter ExaminationDocument7 pagesFourth Quarter ExaminationWilliam SorianoNo ratings yet
- Minitab Project ReportDocument3 pagesMinitab Project Reportramonfer79No ratings yet
- A Guide To Doing Statistics in Second Language Research Using RDocument320 pagesA Guide To Doing Statistics in Second Language Research Using Rcowpea2009No ratings yet
- Research Methods: 1. Course DescriptionDocument4 pagesResearch Methods: 1. Course DescriptionIves LeeNo ratings yet
- Statistical InferenceDocument29 pagesStatistical InferencemegldNo ratings yet
- 28 The Impact of Incentive Mechanisms On Project PerformanceDocument11 pages28 The Impact of Incentive Mechanisms On Project PerformanceSérgio PaiáguaNo ratings yet
- 2-Way Analysis of VarianceDocument34 pages2-Way Analysis of VarianceREY ANTHONY MIGUELNo ratings yet
- ITEF102 - Probability and StatisticsDocument3 pagesITEF102 - Probability and StatisticsHarold LuceroNo ratings yet
- NPCR and UACI Randomness Tests For Image EncryptionDocument8 pagesNPCR and UACI Randomness Tests For Image EncryptionCyberJournals MultidisciplinaryNo ratings yet
- Statistics Q4-SummativeDocument7 pagesStatistics Q4-Summativeneil ponoyNo ratings yet
- Independent and Paired Sample T-Test 2Document11 pagesIndependent and Paired Sample T-Test 2Putri KaryadwiNo ratings yet
- Anova: Two-Factor With ReplicationDocument3 pagesAnova: Two-Factor With Replicationracnal ulinnuhaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) : Empowering Program For Farmers' WelfareDocument14 pagesCorporate Social Responsibility (CSR) : Empowering Program For Farmers' WelfareMalcolm ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Stat and Prob - Q4 - Week 3 - Module 3 - Identifying The Appropriate Rejection Region For A Given Level of SignificanceDocument25 pagesStat and Prob - Q4 - Week 3 - Module 3 - Identifying The Appropriate Rejection Region For A Given Level of Significanceryan nableNo ratings yet
- Unit One Sampling and Sampling DistributionDocument41 pagesUnit One Sampling and Sampling DistributionEbsa AdemeNo ratings yet
- PRPY 121A Psychological Statistics - 7Document12 pagesPRPY 121A Psychological Statistics - 7Lea Sapphira SuronNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 TestDocument35 pagesLecture 7 Test21142467No ratings yet
- Mann Whitney U Test: ENS 185 - Data AnalysisDocument100 pagesMann Whitney U Test: ENS 185 - Data AnalysisClarkNo ratings yet
- Statistical Application Da 2 SrishtiDocument7 pagesStatistical Application Da 2 SrishtiSimran MannNo ratings yet