Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Econ Seatwork
Econ Seatwork
Uploaded by
Aila BascoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Econ Seatwork
Econ Seatwork
Uploaded by
Aila BascoCopyright:
Available Formats
1. Create your own example of Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility and explain comprehensively.
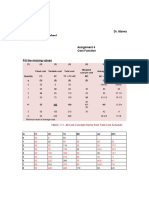
Let us first understand utility, which is Here we can picture that each additional
defined as the satisfaction that a customer consumption of chocolate from 10 it decreases in
receives from a product. Marginal is the 3 and so on due to the decreasing of satisfaction
additional, and Marginal Utility is the increase in of consumers that tends to decrease
utility or satisfaction after purchasing one or more continuously
Consumption Total Utility Marginal Utility
products. For example, when we crave 1st 10 10
something, let's say a chocolate bar, the first 2nd 17 7
consumption of the chocolate bar we bought 3rd 21 4
gave us the most satisfaction, but when we buy it 4 th
22 1
again, although
somehow it can somehow
still satisfy us not as much as the 5 th
20 -2
first one our enjoyment was decreasing overtime
after consuming another chocolate and makes us
consume lesser and lesser.
2. Why should a firm continue to operate under short-run period when TR is greater than VC but
less than TC?
A firm should continue to exist as long as Total Revenue exceeds Variable Costs, but when variable
costs exceed total revenue, it is time to shut down. Because stopping production will cost more than
continuing production without profit. As fixed costs have already been paid, the expense on fixed costs
would be wasted if production were to be stopped, so it's more advisable that the business continue to
operate under short-run period as it can still generate a profit.
3. Differentiate the external economies of scale and internal economies of scale.
External economies of scale refer to circumstances that are external to the business but contribute
to its efficiency in terms of increased output and lower unit cost of production. For example, when there is
smooth transportation, a company can reduce transportation costs and avoid supply delays. Another
example is when the government implements a policy regarding the requirements of hiring an employee, it
can be a big help to the business to ensure the quality of the performance of an employee that can greatly
impact their production, aside from that as we know that the suppliers pertain as external, external
economies of scale can produce various of suppliers and it’s beneficial to the businesses. On the other
hand, the internal economies of scale are more on the inside of a business, it focuses on the workforce of
the whole business and its production efficiency, from the division of labor, modern techniques of
production, and human resources development that can raise the productivity and cost efficient.
4. Why should the rich countries use capital-intensive technology?
Given that they can afford to acquire fixed capital assets such as land, machines, capital, and plant
for manufacturing, they can utilize these to expand their businesses even further by investing more in
machineries and technologies, with this their production will be faster and more efficient and with the fact
that the labor is expensive in rich countries and so it’s wise to make use of their capital in modern
technology.
5. Why should the poor countries use labor-intensive technology?
Because poor countries typically lack in source of capital, it is advantageous to maximize on what
they do have, which is labor. They have the advantage of having a large employment potential because
many people are looking for work to support their families. Consider this a chance to increase the scale of
its output with the same amount of capital but more labor.
You might also like
- Business Plan On BagasseDocument64 pagesBusiness Plan On BagasseAbid Ahasan100% (8)
- BASCO, Aila O. - Assignment 1 - OAMT 40033 MEDICAL TRANSCRIPTIONDocument4 pagesBASCO, Aila O. - Assignment 1 - OAMT 40033 MEDICAL TRANSCRIPTIONAila BascoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - 7 Discussion Question Jay - Heizer - Barry - Render - Chuck - Munson - Operation Operation Management 12th EditionDocument37 pagesChapter 1 - 7 Discussion Question Jay - Heizer - Barry - Render - Chuck - Munson - Operation Operation Management 12th EditionJeannete MeliianaNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Goal: by Eliyahu M. Goldratt and Jeff Cox | Includes AnalysisFrom EverandSummary of The Goal: by Eliyahu M. Goldratt and Jeff Cox | Includes AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Suppose Widgets Are Made Using Staplers (K) and Labor (L) - The Production Function For A Widget Manufacturer Is Given byDocument6 pagesSuppose Widgets Are Made Using Staplers (K) and Labor (L) - The Production Function For A Widget Manufacturer Is Given byAhmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- ECON 210 Homework 2Document3 pagesECON 210 Homework 2Nas DNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - EconomicsDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 - EconomicsChelsea ProtheroNo ratings yet
- 9 Theories - Research ActivityDocument143 pages9 Theories - Research Activityapi-2978344330% (1)
- Project Report Six SigmaDocument71 pagesProject Report Six SigmaBishwajeet Jha100% (4)
- Quality and Performance Excellence 8E Chapter 3Document33 pagesQuality and Performance Excellence 8E Chapter 3Aisah ReemNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Consumer BehaviorDocument41 pagesWeek 5 - Consumer BehaviorAdruffNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - Behaviour of A Firm and Short Run ProductionDocument62 pagesWeek 6 - Behaviour of A Firm and Short Run ProductionAdruffNo ratings yet
- Common Sense InvestingDocument20 pagesCommon Sense InvestingAman TiwariNo ratings yet
- AP9-AA4-Ev2-Resumen Del Proyecto en InglésDocument3 pagesAP9-AA4-Ev2-Resumen Del Proyecto en InglésOswaldo ChávezNo ratings yet
- ECO151 Ch8 NotesDocument10 pagesECO151 Ch8 NotesZimkhitha XhonteloNo ratings yet
- Case Studies Unit 4Document7 pagesCase Studies Unit 4Rebma AsaunNo ratings yet
- Gcse Business Topic 1.1 Part 1 Entreprise and EntrepreneurshipDocument10 pagesGcse Business Topic 1.1 Part 1 Entreprise and EntrepreneurshipBH 7moodNo ratings yet
- Homework On EconomicsDocument2 pagesHomework On EconomicsDennica TanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Consumer and Financial DecisionsDocument65 pagesTopic 1 - Consumer and Financial DecisionsDK01No ratings yet
- Aec 001-Bacc 001 (Econ) - Week 9 Module-1Document5 pagesAec 001-Bacc 001 (Econ) - Week 9 Module-1Nicole ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BusinessDocument8 pagesIntroduction To BusinessMaruf AhmedNo ratings yet
- Activity 7.1 Read The Case Study Below and Then Answer The Questions That Follow. Operating at Full CapacityDocument7 pagesActivity 7.1 Read The Case Study Below and Then Answer The Questions That Follow. Operating at Full CapacityMariuxi Guarnizo GuarnizoNo ratings yet
- Operations ResearchDocument3 pagesOperations ResearchSWATI KUMARI SHARMANo ratings yet
- ACCA Inventories ChapterDocument55 pagesACCA Inventories ChapterRich KishNo ratings yet
- Mission Visson SimplifiedDocument4 pagesMission Visson SimplifiedAdnan AshrafNo ratings yet
- Either Ethics or Profit Is Necessary For A Business To Survive One or The Other Is More ImportantDocument4 pagesEither Ethics or Profit Is Necessary For A Business To Survive One or The Other Is More ImportantTomaNo ratings yet
- T2 FinalDocument6 pagesT2 FinalWassim AlwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Application - Costs and ProductionDocument2 pagesChapter 9 Application - Costs and ProductionNathalia Giselle BetancourtNo ratings yet
- ADL 04 Managerial Economics V3Document23 pagesADL 04 Managerial Economics V3Amit100% (8)
- YED Business RelevanceDocument6 pagesYED Business RelevanceAnusree SivasamyNo ratings yet
- Respostas e Aplicações em InglêsDocument193 pagesRespostas e Aplicações em InglêsRPDPNo ratings yet
- Business Plan To Be SubmittedDocument36 pagesBusiness Plan To Be SubmittedbuenafefloresNo ratings yet
- Real World Examples of Price Discrimination:: 2. Age DiscountsDocument3 pagesReal World Examples of Price Discrimination:: 2. Age DiscountsMarie Sheryl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics: Assignment#1Document10 pagesManagerial Economics: Assignment#1Akshat BansalNo ratings yet
- Module 2 General Functions of CreditDocument41 pagesModule 2 General Functions of CreditCaroline Grace Enteria MellaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 8 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 8 PDFhannah100% (1)
- Full Microeconomics Canadian 14Th Edition Mcconnell Solutions Manual Online PDF All ChapterDocument38 pagesFull Microeconomics Canadian 14Th Edition Mcconnell Solutions Manual Online PDF All Chapterbrianlenz430286100% (7)
- ChotuKool Group 6 Div 3Document11 pagesChotuKool Group 6 Div 3Prakher SinghNo ratings yet
- Seminar, Week Commencing 19 October 2020: Key Concepts This WeekDocument3 pagesSeminar, Week Commencing 19 October 2020: Key Concepts This WeekYago GrandesNo ratings yet
- Business Studies Book AnswersDocument10 pagesBusiness Studies Book AnswersTooba SohailNo ratings yet
- Benefits To Society From Perfect CompetitionDocument5 pagesBenefits To Society From Perfect Competitionmia cadenNo ratings yet
- Coca-Cola (2) Advertising&Promotional StrtegyDocument104 pagesCoca-Cola (2) Advertising&Promotional StrtegyAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- National Cranberry Cooperative 1981Document10 pagesNational Cranberry Cooperative 1981Nicole Dorado0% (1)
- XII Business Studies Worksheet Chapter 3Document6 pagesXII Business Studies Worksheet Chapter 3Shaveta DhandNo ratings yet
- Module 10Document21 pagesModule 10Tin ZamudioNo ratings yet
- Xii Bs - CH 3 Case StudyDocument19 pagesXii Bs - CH 3 Case StudyMOHAMMED IZAAN IQBAL IQBAL MOHAMMED MANGALORENo ratings yet
- BTVN Chap 1 2 MacroDocument4 pagesBTVN Chap 1 2 MacroÉc ÉcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3Anushka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Microeconomics 20th Edition McConnell Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument38 pagesInstant Download PDF Microeconomics 20th Edition McConnell Solutions Manual Full Chapterhankisukuta100% (6)
- It's Cookie TimeDocument12 pagesIt's Cookie TimeAngelica AcostaNo ratings yet
- Basic Micro Econ - Semi Final ModuleDocument11 pagesBasic Micro Econ - Semi Final ModuleCristy RamboyongNo ratings yet
- Economics Chapter 7 ReviewDocument2 pagesEconomics Chapter 7 ReviewAnaNo ratings yet
- Customer and Sales Module in Eresource ERPDocument94 pagesCustomer and Sales Module in Eresource ERPeresourceerpNo ratings yet
- Theory of Cost and ProfitsDocument17 pagesTheory of Cost and ProfitsLyn Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Electricity Buying For DummiesDocument52 pagesElectricity Buying For DummiesWan Zorah Othman100% (1)
- Business Environment - Case Studies QuesDocument13 pagesBusiness Environment - Case Studies QuesKing KongNo ratings yet
- LongTermCapitalBudgeting WenceslaoWilliamDocument2 pagesLongTermCapitalBudgeting WenceslaoWilliamWiLliamLoquiroWencesLaoNo ratings yet
- MANAGERDocument8 pagesMANAGERzealousNo ratings yet
- MSC301: Production Operations Management Long Take-Home AssignmentDocument6 pagesMSC301: Production Operations Management Long Take-Home AssignmentZerin Tasnim AnannaNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument3 pagesEconomicsMaxine Lois PagaraganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Practice - SolutionDocument18 pagesChapter 1-Practice - SolutionXpertZ Pro 1No ratings yet
- Cost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsFrom EverandCost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- StramaDocument2 pagesStramaAila BascoNo ratings yet
- LEGAAAALDocument3 pagesLEGAAAALAila BascoNo ratings yet
- NORMALIZATIONDocument1 pageNORMALIZATIONAila BascoNo ratings yet
- STRATDocument4 pagesSTRATAila BascoNo ratings yet
- DBMS AssDocument2 pagesDBMS AssAila BascoNo ratings yet
- To Write EconDocument1 pageTo Write EconAila BascoNo ratings yet
- Strama Case StudyDocument4 pagesStrama Case StudyAila BascoNo ratings yet
- Customer AnalyticsDocument3 pagesCustomer AnalyticsAila BascoNo ratings yet
- Stra MaaaaDocument2 pagesStra MaaaaAila BascoNo ratings yet
- Econ AssDocument1 pageEcon AssAila BascoNo ratings yet
- BASCO, Aila O. - Assignment 3 - OAMT 40033 MEDICAL TRANSCRIPTIONDocument2 pagesBASCO, Aila O. - Assignment 3 - OAMT 40033 MEDICAL TRANSCRIPTIONAila BascoNo ratings yet
- BASCO, Aila O. - Assignment 2 - OAMT 40033 MEDICAL TRANSCRIPTIONDocument3 pagesBASCO, Aila O. - Assignment 2 - OAMT 40033 MEDICAL TRANSCRIPTIONAila BascoNo ratings yet
- TQM 2 MARKSDocument12 pagesTQM 2 MARKSMARIYAPPANNo ratings yet
- Capital Projects Cost EstimationDocument87 pagesCapital Projects Cost EstimationRapee PuaksungnoenNo ratings yet
- BS 4660 PDFDocument43 pagesBS 4660 PDFhessian123No ratings yet
- Chap013 Target Costing Cost MNGTDocument49 pagesChap013 Target Costing Cost MNGTramaNo ratings yet
- Resumen de Metodología de Software FactoryDocument13 pagesResumen de Metodología de Software FactoryrigohowardNo ratings yet
- ManfDocument34 pagesManfAnantha NarayananNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4-1Document2 pagesAssignment 4-1Fady AttefNo ratings yet
- Marginal AnalysisDocument6 pagesMarginal AnalysisSha MatNo ratings yet
- Danone Case StudyDocument14 pagesDanone Case Studypustyu_nice50% (2)
- Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase StudyShashin VyasNo ratings yet
- Lean Six Sigma: R. MuraliDocument236 pagesLean Six Sigma: R. MuraliBlueboy •100% (1)
- Does CPFR Mitigate The Costs of SKU Proliferation PDFDocument5 pagesDoes CPFR Mitigate The Costs of SKU Proliferation PDFNikhilNo ratings yet
- Certified Lean Practitioner Day 2Document218 pagesCertified Lean Practitioner Day 2Basu ShaivaNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument7 pagesProduct Life CycleKinich AhauNo ratings yet
- Principle MaterialDocument35 pagesPrinciple MaterialHay JirenyaaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Introduction To Materials Management 6th Edition Arnold Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Introduction To Materials Management 6th Edition Arnold Test Bank PDFflotegiantizelpjwy100% (18)
- Chanel Mobile Art Case StudyDocument8 pagesChanel Mobile Art Case StudyArchitecture Parametric100% (1)
- Civil Engineering Department: Project Management CC603Document12 pagesCivil Engineering Department: Project Management CC603shahrolhazrienNo ratings yet
- Oee PDFDocument5 pagesOee PDFsdvikkiNo ratings yet
- 01 - Materials Management Slide 01 To 13 PDFDocument428 pages01 - Materials Management Slide 01 To 13 PDFSanjay ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- User Manual Whirlpool Awt 5100 eDocument2 pagesUser Manual Whirlpool Awt 5100 eCiprian Ionuț Bongeag0% (1)
- Jidoka SampleDocument8 pagesJidoka SampleHai Dai Nguyen MinhNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Nature of Cost, Cost Pools, Cost Objects, and Cost DriversDocument6 pages3.1 Nature of Cost, Cost Pools, Cost Objects, and Cost Driverslang droidNo ratings yet
- 20123400024Document7 pages20123400024Phạm Công KiênNo ratings yet
- Total Productive Maintenance: The Evolution in Maintenance and EfficiencyDocument7 pagesTotal Productive Maintenance: The Evolution in Maintenance and Efficiencylaukik_rautNo ratings yet
- Gemba Kaizen: by Ismail ClementDocument30 pagesGemba Kaizen: by Ismail ClementArvind SinghNo ratings yet
- GPPM 22 PDFDocument64 pagesGPPM 22 PDFKirti Ambastha100% (1)