Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsHandout Respiratory and Circdulatory System
Handout Respiratory and Circdulatory System
Uploaded by
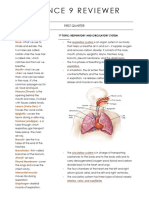
Jerick EpantoThe respiratory system takes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide through breathing. It consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and lungs. Common respiratory diseases include asthma, cystic fibrosis, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, lung cancer and pneumonia.
The circulatory system transports nutrients, oxygen, wastes and protects the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels and blood. The heart pumps blood through two circuits - pulmonary and systemic. Common circulatory diseases are atherosclerosis, stroke, hypertension and heart attack. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce risks of these diseases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Mi Case StudyDocument27 pagesMi Case StudyMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Q1 Module 1 and 2Document3 pagesReviewer - Q1 Module 1 and 2HANNAH MACUDNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Q1 Module 1 and 2Document7 pagesReviewer - Q1 Module 1 and 2HANNAH MACUDNo ratings yet
- BMED 66 Chapter 17 REspiratory SystemDocument7 pagesBMED 66 Chapter 17 REspiratory SystemBSMT 1-1, TAN, NICOLE SELINA L.No ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemElle MateoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument44 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemKlaudette Collin PaynorNo ratings yet
- RESP N Cardio SystemDocument10 pagesRESP N Cardio SystemEmaan AtifNo ratings yet
- Respiratory - Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory - Circulatory SystemClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 First Quarter ALL NotesDocument9 pagesScience 9 First Quarter ALL Notesliannicole884No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument24 pagesRespiratory SystemIan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Human BodyDocument80 pagesLesson 2 The Human BodyJessa May RapadasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Human BodyDocument80 pagesLesson 2 The Human BodyJessa May RapadasNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesParts and Function of Respiratory Systemricky pawigNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory Systemnarichu92No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument53 pagesRespiratory SystemRotan CirebonNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument21 pagesBronchial AsthmaMoonNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 MidtermDocument18 pagesNCM 112 MidtermJULIANNAH ATHENA MERCADONo ratings yet
- Prologue 1.1 BackgroundDocument9 pagesPrologue 1.1 BackgroundWulan Yulia DintasariNo ratings yet
- Apec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesApec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory SystemEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: ASTIKA NUR ROHMAH, S.Kep., NS., M.BiomedDocument43 pagesThe Respiratory System: ASTIKA NUR ROHMAH, S.Kep., NS., M.BiomedAdek KhazeliaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesRespiratory Systemjimboy baddiriNo ratings yet
- Science 1.1Document42 pagesScience 1.1Ina SuzaraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesRespiratory Systemapi-512058127No ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Parts & FuntionsDocument16 pagesRespiratory System: Parts & FuntionsAlthaea LiceraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and RespiratoryDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and RespiratoryAya PalomeraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemAlexi Nicole CastaloneNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesRespiratory SystemDearly Niña OsinsaoNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument14 pagesSciencesheanellerenzsantosNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemKarel Mae SanoriaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory SystemКрістіна БаландаNo ratings yet
- 172 Anatomy Resp SystemDocument29 pages172 Anatomy Resp SystemJerry ZahidNo ratings yet
- Theory of LungDocument7 pagesTheory of LungAndres Dario R LozNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System in Human BeingsDocument11 pagesRespiratory System in Human BeingsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Ventilation Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesRespiratory System: Ventilation Cellular RespirationSoleil MaxwellNo ratings yet
- FSB Physiology 1: Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesFSB Physiology 1: Circulatory SystemSkylar0.comNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2A)Document4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2A)Raiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - NotesDocument4 pagesRespiratory System - NotessNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE BIOLOGY Reviewer: Respiratory System Phases of Respiration Definition of TermsDocument7 pagesSCIENCE BIOLOGY Reviewer: Respiratory System Phases of Respiration Definition of TermsNikki Adolfo MalazoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 1Document21 pagesRespiratory System 1mbouillesissoko55No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument85 pagesRespiratory SystemMiss Glozirie An BacangNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem Pernafasan - Id.enDocument7 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Sistem Pernafasan - Id.enCindy Ari SantiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument15 pagesRespiratory SystemNahid ParveenNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 9..Document4 pagesReviewer in Science 9..nanami's ChildNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Respiratory System (2 Hours Lecture/3 Hours Lab) : at The End of This Unit, Students Will Be Able ToDocument4 pagesUnit 7: Respiratory System (2 Hours Lecture/3 Hours Lab) : at The End of This Unit, Students Will Be Able ToRUSSEL AQUINONo ratings yet
- X Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesX Respiratory SystemHannah DiñosoNo ratings yet
- Lymphatics and Respiratory SystemDocument67 pagesLymphatics and Respiratory Systemnursereview100% (2)
- Respiratory SystemDocument38 pagesRespiratory Systemjhaezhydomafergarcia2020No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Respiratory System PresentationDocument48 pagesChapter 10 Respiratory System PresentationMary Jane LubricoNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument19 pagesScience ReviewerfluyuuyyyNo ratings yet
- 3.lessons 21-22, Respiratory System, PP 446-456Document28 pages3.lessons 21-22, Respiratory System, PP 446-456Lazare ChNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With The Other Organ SystemsDocument60 pagesChapter 1 - Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With The Other Organ SystemsPatricia Sofia DizonNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY DISTURBANCES - HandoutsDocument35 pagesRESPIRATORY DISTURBANCES - Handoutsfebie pachecoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System (Chart)Document4 pagesRespiratory System (Chart)Rommel Urbano YabisNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesFunctional Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemRica Mae TingcoNo ratings yet
- Responses To Altered Respiratory FunctionDocument19 pagesResponses To Altered Respiratory FunctionKoleen KirstenNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working TogetherDocument2 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory Systems Working TogetherPsycho Kpop OtakuNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesRespiratory SystemCHARMAINE ORUGANo ratings yet
- RandomDocument3 pagesRandomBusilaoco, Frances Eve M.No ratings yet
- Science 9 Reviewer First QRTDocument4 pagesScience 9 Reviewer First QRTAshleyNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- The Heart - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pagesThe Heart - Print - Quizizzosama100% (1)
- Heart MurmursDocument7 pagesHeart MurmursOffvb MednuNo ratings yet
- ch.33 Health Assessment-Potter & Perry 7thDocument7 pagesch.33 Health Assessment-Potter & Perry 7thmfw777No ratings yet
- Soalan Pathology 3Document425 pagesSoalan Pathology 3muhammadridhwanNo ratings yet
- (UpToDate) Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis of Tetralogy of FallotDocument27 pages(UpToDate) Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis of Tetralogy of FallotNhựt Ý Nguyễn PhanNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Notes With SpecDocument66 pagesO Level Biology Notes With Specshaayaa71% (7)
- Intro To Patient Care Exam 2 Content QuestionsDocument81 pagesIntro To Patient Care Exam 2 Content QuestionsAlyss Wallschleger50% (2)
- Research Paper On Heart MurmurDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Heart Murmurnodahydomut2100% (1)
- Physician Code ReviewDocument691 pagesPhysician Code ReviewThein Htun Naung100% (2)
- Cardiovascular Physiology: Cardiac Cycle Analysis of Cardiac Activity - PolygramDocument47 pagesCardiovascular Physiology: Cardiac Cycle Analysis of Cardiac Activity - PolygramAndreea ŞtefănescuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyGregg PalabricaNo ratings yet
- Carpentier Classification of Mitral ValveDocument3 pagesCarpentier Classification of Mitral ValveBiswarup PurkayasthaNo ratings yet
- Congestive Cardiac Failure PDFDocument28 pagesCongestive Cardiac Failure PDFNANDHINI S100% (1)
- Cow Dissection DayDocument16 pagesCow Dissection Dayapi-108435797No ratings yet
- Pnle Medical Surgical ReviewDocument17 pagesPnle Medical Surgical ReviewKyla Rose ToledoNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY Cardiovascular SystemPuji PrisylNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثانية عشر - مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولىDocument10 pagesالمحاضرة الثانية عشر - مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولىAbdullah TheNo ratings yet
- Mitral Stenosis and Mitral RegurgitationDocument21 pagesMitral Stenosis and Mitral Regurgitationash_wan88No ratings yet
- Neet Previous Year Question Papers: Pranav PundarikDocument93 pagesNeet Previous Year Question Papers: Pranav Pundarikananyanandurkar10No ratings yet
- Krok 5Document53 pagesKrok 5Wolf WolforNo ratings yet
- Cardio TransDocument7 pagesCardio TransweissNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System (Report)Document2 pagesCardiovascular System (Report)Arlan AbraganNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument63 pagesCase StudyRita PokharelNo ratings yet
- Atrioventricular Canal Defect: Seoul National University Hospital Department of Thoracic & Cardiovascular SurgeryDocument22 pagesAtrioventricular Canal Defect: Seoul National University Hospital Department of Thoracic & Cardiovascular SurgeryMohan MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System QuizDocument18 pagesCirculatory System QuizSreckovic BenjoNo ratings yet
- Best Management in Isolated Right Ventricular Hypoplasia With Septal Defects in AdultsDocument7 pagesBest Management in Isolated Right Ventricular Hypoplasia With Septal Defects in AdultsReinaldi octaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument60 pagesLesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsBeng QuinnNo ratings yet
- Sistem Jantung - SaladinDocument128 pagesSistem Jantung - SaladinJuli Damayanty Harahap100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular System Medical Surgical NursingDocument55 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular System Medical Surgical NursingPrabhjeet Kaur SainiNo ratings yet
Handout Respiratory and Circdulatory System
Handout Respiratory and Circdulatory System
Uploaded by
Jerick Epanto0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesThe respiratory system takes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide through breathing. It consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and lungs. Common respiratory diseases include asthma, cystic fibrosis, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, lung cancer and pneumonia.
The circulatory system transports nutrients, oxygen, wastes and protects the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels and blood. The heart pumps blood through two circuits - pulmonary and systemic. Common circulatory diseases are atherosclerosis, stroke, hypertension and heart attack. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce risks of these diseases.
Original Description:
Original Title
Handout-respiratory-and-circdulatory-system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe respiratory system takes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide through breathing. It consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and lungs. Common respiratory diseases include asthma, cystic fibrosis, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, lung cancer and pneumonia.
The circulatory system transports nutrients, oxygen, wastes and protects the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels and blood. The heart pumps blood through two circuits - pulmonary and systemic. Common circulatory diseases are atherosclerosis, stroke, hypertension and heart attack. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce risks of these diseases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesHandout Respiratory and Circdulatory System
Handout Respiratory and Circdulatory System
Uploaded by
Jerick EpantoThe respiratory system takes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide through breathing. It consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and lungs. Common respiratory diseases include asthma, cystic fibrosis, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, lung cancer and pneumonia.
The circulatory system transports nutrients, oxygen, wastes and protects the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels and blood. The heart pumps blood through two circuits - pulmonary and systemic. Common circulatory diseases are atherosclerosis, stroke, hypertension and heart attack. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce risks of these diseases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
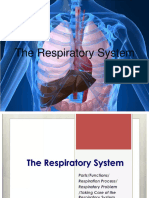
Respiratory/Breathing System
Respiration – process wherein the body takes in O 2 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISEASES
and eliminates gaseous waste products. 1. Asthma is defined as a common, chronic
*The body involved in the process is the respiratory respiratory condition that causes difficulty
tracts breathing due to inflammation of the airways.
THREE DIVISION OF RESPIRATORY TRACTS: 2. Cystic fibrosis is a genetic respiratory disease
1. Upper respiratory tract (nose, nasal passages, caused by a defective gene that creates thick
paranasal sinuses, and pharynx) and sticky mucus that clogs up tubes and
2. Respiratory airways (larynx, trachea, bronchi, passageways.
bronchioles) 3. Chronic bronchitis is a form of COPD
3. Lungs – (respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, emphasized by a chronic cough. Usually
alveolar sacs, and alveoli) people cough up sputum (mucus from the
lungs), especially in the morning.
Parts of respiratory system:
4. Emphysema is a serious respiratory disease,
1. Nose – the organ through which the air enters
which is another form of COPD. The most
and is filtered.
common cause is smoking.
2. Nasal passage – serves as channel for airflow
5. Lung cancer - this cancer develops in the main
through the nose in which the air is warmed,
part of the lungs near the air sacs.
cleaned and moistened.
6. Pneumonia is a common lung disease caused
3. Trachea – also called windpipe; a hollow tube
by an infection in the air sacs in the lungs. The
that serves as the passageway of air into the
infections can be bacterial, viral or fungal.
lungs.
7. Pleural effusion is a collection of fluid between
4. Bronchi – also called bronchial tube; branching
the lung and the chest wall in what’s called the
tube that connects the trachea to the lungs.
pleural space.
5. Bronchioles – the finer subdivisions of the
bronchi; the hairlike tubes that connect to the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
alveoli
6. Alveoli – also called airsacs allow the gas Circulatory system – is also known as internal
exchange in lungs. transport system
- it is also made up of the
EXTERNAL RESPIRATION: cardiovascular system and the
Breathing is a mechanical process of inhaling and lymphatic system
exhaling.
Inhale/inspire FUNCTIONS:
The rib muscle contract and diaphragm contract 1. It transport nutrients an oxygen to various cells
(moves down), the chest cavity expands. The pressure all over the body.
in chest cavity lowers causing the air from the 2. It collects wastes and transports them to
atmosphere to go into the lungs. respective organs where they should be excreted.
Exhale/ expire 3. It helps maintain fluid balance and normal body
The rib muscles relax and the diaphragm relax (moves temp.
down), the chest cavity relaxes. The pressure in the 4. It acts as defense against harmful bacteria that
chest cavity increases causing the air out from the may cause diseases.
lungs. Part of circulatory system:
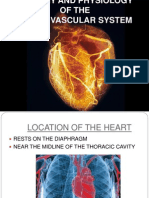
Heart – a muscular organ that pumps blood all
PATHWAY OF AIR INSIDE THE BODY: over the body.
* Nose is the first organ in the respiratory system. - it is a fist size organ that is located between
* Nasal Passage the air is moistened and warmed the lungs behind the breastbone
• Air goes down the Pharynx for filtration. - it is surrounded by a protective membrane
• The filtered air goes down the larynx (voice called Pericardium.
box) that vibrate when the air passes within Major Division:
the cords, creating a sound 1. Left Atrium- receiving chamber
• From the pharynx, air goes to the trachea or 2. Right Atrium – receiving station
windpipe, the tube made up of cartilage which 3. Left ventricle- pumping station
carries the air towards the lungs. 4. Right ventricle – pumping station
• The air descends to the two branches of the
lungs called bronchi to the microscopic tubes Valves inside the heart:
called bronchioles. Semi-lunar valves – prevent backflow of blood from
• The bronchioles branch out into air sacs or arteries to the ventricles.
alveoli, this are the sites of gas exchange. a. Aortic semi-lunar valve – located between the
• Each lung has about 300 million of alveoli. left ventricle and aorta.
b. Pulmonary semi-lunar valve – located 3. systemic Circulation - Movement of blood
between the right ventricle and pulmonary from the heart to the rest of the body,
artery. excluding the lungs.
* Atrioventricular valve – prevent the backflow of
the blood from the atrium to the ventricle, lies
between the atrium and ventricle. Circulatory Diseases:
a. Tricuspid valve – located between the left 1. Atherosclerosis – is a condition that develops
atrium and right ventricle when a substance called builds up in the wall
b. Bicuspid valve – located between left of the arteries making it harder for the blood
atrium and left ventricle. vessel to flow through.
Blood vessels- used to transport blood throughout the 2. Stroke – occurs when it damages the brain
body. when the blood vessels get blocked or leaked
Types of blood vessels: used to transport blood usually from a blood clot.
throughout the body.
3. Hypertension/high blood – it can lead to
1. veins – caries unoxygenated blood towards
severe health complications.
the heart.
4. Heart attack – occurs when the blood to the
- thinner elastic wall
part of the heart is blocked by blood clot, the
2. Capillaries – connect artery to the vein; for
actual site of gas exchange heart muscle supplied by the artery begins ti
- smallest and most numerous found die.
in tissues.
3. Arteries – oxygenated blood away from the Healthy Lifestyle:
heart to the tissues and cells all over the body 1. Exercise regularly.
- thicker and stronger elastic walls 2. Don nor smoke and drink alcohol.
Blood – it transports nutrients and respiratory gases to 3. Eat healthy diet.
all parts of the body. 4. Take time to relax and avoid stress.
- Is a tissue containing of liquid plasma and solid
blood cells.
Types of blood cells:
1. Red blood cells (RBC)
2. White blood cells (WBC)
Plasma – is a yellowish fluid which transports
dissolved substance.
- It contains protein like albumin, globulin,
fibrinogen and antibodies
- It makes about 55% of the total volume of the
blood.
RBC (erythrocytes) – they are red due the
substance (hemoglobin) which is an iron
containing molecule.
- It produces in the bone marrow
(2million/second)
- The life span is approximately 120 days
- It facilitates the diffusion of gasses oxygen and
carbon dioxide
WBC (leukocytes) – lack of hemoglobin they are
produce in the bone marrow
- May live only for few hours some up to a day.
- It plays a major role in protecting the body
from foreign substance which can cause
disease.
Platelets – help blood clot after injury
- It produced in the bone marrow
- It lives for 4-10 days
Types of Circulation
1. Pulmonary circulation – movement of the
blood from the heart to the lung back to the
heart.
2. Coronary circulation – blood circulation in the
heart muscles.
You might also like
- Mi Case StudyDocument27 pagesMi Case StudyMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Q1 Module 1 and 2Document3 pagesReviewer - Q1 Module 1 and 2HANNAH MACUDNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Q1 Module 1 and 2Document7 pagesReviewer - Q1 Module 1 and 2HANNAH MACUDNo ratings yet
- BMED 66 Chapter 17 REspiratory SystemDocument7 pagesBMED 66 Chapter 17 REspiratory SystemBSMT 1-1, TAN, NICOLE SELINA L.No ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemElle MateoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument44 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemKlaudette Collin PaynorNo ratings yet
- RESP N Cardio SystemDocument10 pagesRESP N Cardio SystemEmaan AtifNo ratings yet
- Respiratory - Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory - Circulatory SystemClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 First Quarter ALL NotesDocument9 pagesScience 9 First Quarter ALL Notesliannicole884No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument24 pagesRespiratory SystemIan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Human BodyDocument80 pagesLesson 2 The Human BodyJessa May RapadasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Human BodyDocument80 pagesLesson 2 The Human BodyJessa May RapadasNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesParts and Function of Respiratory Systemricky pawigNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory Systemnarichu92No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument53 pagesRespiratory SystemRotan CirebonNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument21 pagesBronchial AsthmaMoonNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 MidtermDocument18 pagesNCM 112 MidtermJULIANNAH ATHENA MERCADONo ratings yet
- Prologue 1.1 BackgroundDocument9 pagesPrologue 1.1 BackgroundWulan Yulia DintasariNo ratings yet
- Apec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesApec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory SystemEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: ASTIKA NUR ROHMAH, S.Kep., NS., M.BiomedDocument43 pagesThe Respiratory System: ASTIKA NUR ROHMAH, S.Kep., NS., M.BiomedAdek KhazeliaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesRespiratory Systemjimboy baddiriNo ratings yet
- Science 1.1Document42 pagesScience 1.1Ina SuzaraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesRespiratory Systemapi-512058127No ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Parts & FuntionsDocument16 pagesRespiratory System: Parts & FuntionsAlthaea LiceraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and RespiratoryDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and RespiratoryAya PalomeraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemAlexi Nicole CastaloneNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesRespiratory SystemDearly Niña OsinsaoNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument14 pagesSciencesheanellerenzsantosNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemKarel Mae SanoriaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory SystemКрістіна БаландаNo ratings yet
- 172 Anatomy Resp SystemDocument29 pages172 Anatomy Resp SystemJerry ZahidNo ratings yet
- Theory of LungDocument7 pagesTheory of LungAndres Dario R LozNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System in Human BeingsDocument11 pagesRespiratory System in Human BeingsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Ventilation Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesRespiratory System: Ventilation Cellular RespirationSoleil MaxwellNo ratings yet
- FSB Physiology 1: Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesFSB Physiology 1: Circulatory SystemSkylar0.comNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2A)Document4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2A)Raiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - NotesDocument4 pagesRespiratory System - NotessNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE BIOLOGY Reviewer: Respiratory System Phases of Respiration Definition of TermsDocument7 pagesSCIENCE BIOLOGY Reviewer: Respiratory System Phases of Respiration Definition of TermsNikki Adolfo MalazoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 1Document21 pagesRespiratory System 1mbouillesissoko55No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument85 pagesRespiratory SystemMiss Glozirie An BacangNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem Pernafasan - Id.enDocument7 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Sistem Pernafasan - Id.enCindy Ari SantiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument15 pagesRespiratory SystemNahid ParveenNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 9..Document4 pagesReviewer in Science 9..nanami's ChildNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Respiratory System (2 Hours Lecture/3 Hours Lab) : at The End of This Unit, Students Will Be Able ToDocument4 pagesUnit 7: Respiratory System (2 Hours Lecture/3 Hours Lab) : at The End of This Unit, Students Will Be Able ToRUSSEL AQUINONo ratings yet
- X Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesX Respiratory SystemHannah DiñosoNo ratings yet
- Lymphatics and Respiratory SystemDocument67 pagesLymphatics and Respiratory Systemnursereview100% (2)
- Respiratory SystemDocument38 pagesRespiratory Systemjhaezhydomafergarcia2020No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Respiratory System PresentationDocument48 pagesChapter 10 Respiratory System PresentationMary Jane LubricoNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument19 pagesScience ReviewerfluyuuyyyNo ratings yet
- 3.lessons 21-22, Respiratory System, PP 446-456Document28 pages3.lessons 21-22, Respiratory System, PP 446-456Lazare ChNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With The Other Organ SystemsDocument60 pagesChapter 1 - Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With The Other Organ SystemsPatricia Sofia DizonNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY DISTURBANCES - HandoutsDocument35 pagesRESPIRATORY DISTURBANCES - Handoutsfebie pachecoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System (Chart)Document4 pagesRespiratory System (Chart)Rommel Urbano YabisNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesFunctional Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemRica Mae TingcoNo ratings yet
- Responses To Altered Respiratory FunctionDocument19 pagesResponses To Altered Respiratory FunctionKoleen KirstenNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working TogetherDocument2 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory Systems Working TogetherPsycho Kpop OtakuNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesRespiratory SystemCHARMAINE ORUGANo ratings yet
- RandomDocument3 pagesRandomBusilaoco, Frances Eve M.No ratings yet
- Science 9 Reviewer First QRTDocument4 pagesScience 9 Reviewer First QRTAshleyNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- The Heart - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pagesThe Heart - Print - Quizizzosama100% (1)
- Heart MurmursDocument7 pagesHeart MurmursOffvb MednuNo ratings yet
- ch.33 Health Assessment-Potter & Perry 7thDocument7 pagesch.33 Health Assessment-Potter & Perry 7thmfw777No ratings yet
- Soalan Pathology 3Document425 pagesSoalan Pathology 3muhammadridhwanNo ratings yet
- (UpToDate) Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis of Tetralogy of FallotDocument27 pages(UpToDate) Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis of Tetralogy of FallotNhựt Ý Nguyễn PhanNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Notes With SpecDocument66 pagesO Level Biology Notes With Specshaayaa71% (7)
- Intro To Patient Care Exam 2 Content QuestionsDocument81 pagesIntro To Patient Care Exam 2 Content QuestionsAlyss Wallschleger50% (2)
- Research Paper On Heart MurmurDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Heart Murmurnodahydomut2100% (1)
- Physician Code ReviewDocument691 pagesPhysician Code ReviewThein Htun Naung100% (2)
- Cardiovascular Physiology: Cardiac Cycle Analysis of Cardiac Activity - PolygramDocument47 pagesCardiovascular Physiology: Cardiac Cycle Analysis of Cardiac Activity - PolygramAndreea ŞtefănescuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyGregg PalabricaNo ratings yet
- Carpentier Classification of Mitral ValveDocument3 pagesCarpentier Classification of Mitral ValveBiswarup PurkayasthaNo ratings yet
- Congestive Cardiac Failure PDFDocument28 pagesCongestive Cardiac Failure PDFNANDHINI S100% (1)
- Cow Dissection DayDocument16 pagesCow Dissection Dayapi-108435797No ratings yet
- Pnle Medical Surgical ReviewDocument17 pagesPnle Medical Surgical ReviewKyla Rose ToledoNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY Cardiovascular SystemPuji PrisylNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثانية عشر - مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولىDocument10 pagesالمحاضرة الثانية عشر - مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولىAbdullah TheNo ratings yet
- Mitral Stenosis and Mitral RegurgitationDocument21 pagesMitral Stenosis and Mitral Regurgitationash_wan88No ratings yet
- Neet Previous Year Question Papers: Pranav PundarikDocument93 pagesNeet Previous Year Question Papers: Pranav Pundarikananyanandurkar10No ratings yet
- Krok 5Document53 pagesKrok 5Wolf WolforNo ratings yet
- Cardio TransDocument7 pagesCardio TransweissNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System (Report)Document2 pagesCardiovascular System (Report)Arlan AbraganNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument63 pagesCase StudyRita PokharelNo ratings yet
- Atrioventricular Canal Defect: Seoul National University Hospital Department of Thoracic & Cardiovascular SurgeryDocument22 pagesAtrioventricular Canal Defect: Seoul National University Hospital Department of Thoracic & Cardiovascular SurgeryMohan MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System QuizDocument18 pagesCirculatory System QuizSreckovic BenjoNo ratings yet
- Best Management in Isolated Right Ventricular Hypoplasia With Septal Defects in AdultsDocument7 pagesBest Management in Isolated Right Ventricular Hypoplasia With Septal Defects in AdultsReinaldi octaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument60 pagesLesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsBeng QuinnNo ratings yet
- Sistem Jantung - SaladinDocument128 pagesSistem Jantung - SaladinJuli Damayanty Harahap100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular System Medical Surgical NursingDocument55 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular System Medical Surgical NursingPrabhjeet Kaur SainiNo ratings yet