Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A3 Inventory Estimation
A3 Inventory Estimation
Uploaded by
KezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A3 Inventory Estimation
A3 Inventory Estimation
Uploaded by
KezCopyright:
Available Formats
INVENTORY ESTIMATION
Immediate information about inventory is sometimes needed where an immediate physical count is
deemed to be impossible due to some circumstances. To estimate inventory value, the entity can either
use:
1. Gross Profit Method or
2. Retail Inventory Method
Use of Inventory Value Estimates
1. Interim Financial Statements
2. Inventory Reasonableness
3. Catastrophe and Other Extraordinary Circumstances
A. Gross Profit Method – allows expressing and using a gross profit percentage based on either
cost of goods sold or net sales to estimate inventory value.
a. Gross Profit Rate Based on Sales
b. Gross Profit Rate Based on Cost
B. Retail Inventory Method – is an inventory estimation method that applies retail (sales price)
information to determine its relationship with costs (cost ratio) and ultimately, the estimated
ending inventory.
The retail inventory method is applicable for industries that has numerous product
offers and variety of goods that monitoring of costs would be burdensome like groceries and
department stores.
Formula:
Beginning Inventory at Retail Price xxx
Add: Net Purchases at Retail Price xxx
Cost of Goods Available for Sale Retail Price xxx
Less: Net Sales (xxx)
Estimated Ending Inventory at Retail Price xxx
Multiply - Cost to Retail Ratio xxx
Estimated Ending Inventory at Cost xxx
Methods of Retail Inventory Estimation
1. Conservative Method – consider all effects of price markups but not consider price
markdowns.
2. Average Method – considers both price markups and price markdowns
3. FIFO Method – cost to retail ratio is only based on current period purchases which excludes
beginning inventory based on the claim that markups and markdowns are applied only to
purchases during the period and not on beginning inventory.
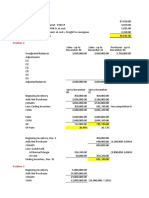
Sample Problem
The following information was made available by Catecoin Company:
Cost Retail
Beginning inventory 965,000 1,227,000
Net purchase 2,598,657 3,300,296
Additional markup 113,5000
Markup cancellation 32,667
Markdown 89,750
Markdown cancellation 13,974
Sales 2,896,745
Sales return 125,697
Sales allowance 33,255
Sale discount 12,576
Conservative
Cost Retail
Beginning inventory 965,000.00 1,227,650.00
Net purchases 2,598,657.00 3,300,296.00
Additional markup 113,500.00
Markup cancellation 32,667.00
Conservative goods available for sale 3,563,657.00 4,608,779.00
Conservative cost-to-retail ratio 77.3232%
Conservative goods available for sale 3,563,657.00 4,608,799.00
Markdown 89,750.00
Markdown cancellation 13,974.00
Goods available for sale for estimation 3,563,657.00 4,533,003.00
Less: Net sales
2,896,745-125,897 2,771,048.00
Ending inventory at retail price 1,761,955.00
Multiply by cost-to-retail ratio 77,332%
Ending inventory at cost 1,362,400.60
Average
Cost Retail
Beginning inventory 965,000.00 1,227,650.00
Net purchases 2,598,657.00 3,300,296.00
Additional markup 113,500.00
Markup cancellation - 32,667.00
Markdown - 89,750.00
Markdown cancellation 13,974.00
Goods available for sale 3,563,657.00 4,553,003.00
Average- cost- to- retail ratio 78.6158%
Goods available for sale 3,563,657.00 4,533,003.00
Less: Net sales
2.896,745-125,697 - 2,711,048.00
Ending inventory at retail price 1,761,955.00
Multiply by cost-to-retail ratio 78.618%
Ending inventory at cost 1,385,175.19
FIF0
Cost Retail
Net purchases 2,598,657.00 3,300,296.00
Additional markup 113,500.00
Markup cancellation - 32,667,00
Markdown - 89,750.00
Markdown cancellation 13,974.00
Purchases during the period 2,598,657.00 3,305,353.00
FIFO cost-to-retail-ratio 78.619%
Purchases during the period 2,598,657.00 3,305,353.00
Beginning inventory 965,000.00 1,227,650.00
Goods available for sale 3,563,657.00 4,533,033.00
Less: Net sales
2,896,745-125,697 - 2,771,048.00
Ending inventory at retail 1,761,955.00
Multiply by cost-to-retail-ratio 78.6197%
Ending inventory at cost 1,385,242.88
You might also like
- Grade 10 Terms and DefinitionsDocument11 pagesGrade 10 Terms and Definitionskhotso86% (7)
- Schaum's Outline of Principles of Accounting I, Fifth EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Outline of Principles of Accounting I, Fifth EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Afar 2 Module CH 7Document12 pagesAfar 2 Module CH 7KezNo ratings yet
- The McGraw-Hill 36-Hour Course: Finance for Non-Financial Managers 3/EFrom EverandThe McGraw-Hill 36-Hour Course: Finance for Non-Financial Managers 3/ERating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- EY Introduction To Financial ModellingDocument8 pagesEY Introduction To Financial ModellingPrashantKNo ratings yet
- Date Received Issued Quantity Unit Cost Amount Quantity Unit CostDocument6 pagesDate Received Issued Quantity Unit Cost Amount Quantity Unit CostLeslyne Love C. NograNo ratings yet
- Inventory - Bio Asset - PPEDocument4 pagesInventory - Bio Asset - PPEPamela Joy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Enterprenuership Project For Garments Sticthing Unit Financail Section - Xls 2012, 13Document20 pagesEnterprenuership Project For Garments Sticthing Unit Financail Section - Xls 2012, 13KabeerMalikNo ratings yet
- Ia 450 455Document6 pagesIa 450 455Christine HingcoNo ratings yet
- Retail Inventory MethodDocument2 pagesRetail Inventory Methodpcdesktop.brarNo ratings yet
- Problems - Inventory Estimation: Retail Inventory MethodDocument13 pagesProblems - Inventory Estimation: Retail Inventory MethodKez MaxNo ratings yet
- IA Chap13-14Document20 pagesIA Chap13-14Patrick Jayson VillademosaNo ratings yet
- AFM-Module 2 IDocument10 pagesAFM-Module 2 IkanikaNo ratings yet
- Inventory EstimationDocument11 pagesInventory EstimationTrace ReyesNo ratings yet
- FDNACCT - Mock Exam - Answer Key - 3 - Fill in The Blank Problems PDFDocument5 pagesFDNACCT - Mock Exam - Answer Key - 3 - Fill in The Blank Problems PDFJames de LeonNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Individual Income Tax Return For Mixed Income EarnerDocument3 pagesPreparation of Individual Income Tax Return For Mixed Income Earnercarl patNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Inventories Exercise 4.0Document1 page1.0 Inventories Exercise 4.0Elmer, Jr. LimbauanNo ratings yet
- Acctg105conjurado AngeliqueDocument18 pagesAcctg105conjurado AngeliquePurpleKyla RosarioNo ratings yet
- Oss Profit Retail Inventory MethodDocument4 pagesOss Profit Retail Inventory MethodLily of the ValleyNo ratings yet
- VALLEJOS-ACCTG 301-Retail Inventoy Method-Hand OutDocument5 pagesVALLEJOS-ACCTG 301-Retail Inventoy Method-Hand OutEllah RahNo ratings yet
- Madamot Company Year 2022 (End) Year 2021 (Beg)Document11 pagesMadamot Company Year 2022 (End) Year 2021 (Beg)VonDrei MedinaNo ratings yet
- ROCO - SCI Unit TestDocument9 pagesROCO - SCI Unit TestRaymond Roco100% (1)
- Proforma Retail Inventory With Solutions To Given Activities and Book Problems Cont..Document6 pagesProforma Retail Inventory With Solutions To Given Activities and Book Problems Cont..Kelsey VersaceNo ratings yet
- Compe SolutionDocument10 pagesCompe SolutionRianell Andrea AsumbradoNo ratings yet
- Addisu Tadesse Adj FSDocument6 pagesAddisu Tadesse Adj FSGali AbamededNo ratings yet
- Seven Heaven Corporation Adjusted Trial Balance For The Year Ended - December 31, 2019Document3 pagesSeven Heaven Corporation Adjusted Trial Balance For The Year Ended - December 31, 2019Judith DurensNo ratings yet
- Q3 AnsDocument2 pagesQ3 AnsKalai ArasanNo ratings yet
- Sol. Man. - Chapter 8 - Inventory Estimation - Ia Part 1aDocument6 pagesSol. Man. - Chapter 8 - Inventory Estimation - Ia Part 1aRezzan Joy Camara MejiaNo ratings yet
- Questions - SeparateDocument3 pagesQuestions - SeparateSANA SAEEDNo ratings yet
- BA 114.1 - Module2 - Inventories - Handout PDFDocument9 pagesBA 114.1 - Module2 - Inventories - Handout PDFKurt OrfanelNo ratings yet
- FS (1) - CFDocument12 pagesFS (1) - CFJessybel BanaganNo ratings yet
- Powerol - Monthly MIS FormatDocument34 pagesPowerol - Monthly MIS Formatdharmender singhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Installment SalesDocument9 pagesLesson 8 Installment SalesheyheyNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument19 pagesProject ReportCA DïvYã PrÁkàsh JäîswãlNo ratings yet
- Break Even Analysis TotalDocument3 pagesBreak Even Analysis Totalm.rahimianNo ratings yet
- ABANILLA, LORRAINE JOY M. - INTACC & 075 - Activity 4 (A04) - Inventory Estimation Methods 3.0Document7 pagesABANILLA, LORRAINE JOY M. - INTACC & 075 - Activity 4 (A04) - Inventory Estimation Methods 3.0Lorraine Joy AbanillaNo ratings yet
- Retail MethodDocument9 pagesRetail MethodToan Nguyen100% (1)
- Chap 4 Activity Answer KeyDocument4 pagesChap 4 Activity Answer KeycykablyatNo ratings yet
- AC - IntAcctg1 Quiz 2 Solution GuideDocument6 pagesAC - IntAcctg1 Quiz 2 Solution Guidejohn hellNo ratings yet
- FS February 2022Document5 pagesFS February 2022Rommel GunioNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument6 pagesAccountingCharisse CruzNo ratings yet
- Projected Income Statement, NURSERY: Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Gross SalesDocument4 pagesProjected Income Statement, NURSERY: Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Gross SalesRhap SodyNo ratings yet
- 18PGP238 Indivisual Assignment Group DDocument4 pages18PGP238 Indivisual Assignment Group DaaidanrathiNo ratings yet
- HW#3Document7 pagesHW#3Ja RedNo ratings yet
- 2020-08 Marginal and Absorption CostingDocument10 pages2020-08 Marginal and Absorption CostingDenis GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Id 2016 Trading AcctDocument1 pageId 2016 Trading AcctMichael FarnellNo ratings yet
- Sol. Man. - Chapter 8 - Inventory Estimation - Ia Part 1a - 2020 EditionDocument14 pagesSol. Man. - Chapter 8 - Inventory Estimation - Ia Part 1a - 2020 EditionJapon, Jenn RossNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1mishal zikriaNo ratings yet
- 5 Year Financial PlanDocument25 pages5 Year Financial Plananwar kadiNo ratings yet
- True or False: Accounting 205 - Quiz 1Document3 pagesTrue or False: Accounting 205 - Quiz 1CHENGNo ratings yet
- Bill FrenchDocument4 pagesBill Frenchabigail franciscoNo ratings yet
- Horizontal AnalysisDocument1 pageHorizontal Analysiswill burrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Solution Exercises Income StatementDocument13 pagesChapter 3. Solution Exercises Income StatementHECTOR ORTEGANo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 AccountingDocument12 pagesChapter 8 AccountingDanica Mae GenaviaNo ratings yet
- 2020-08 Marginal and Absorption CostingDocument6 pages2020-08 Marginal and Absorption CostingDenis GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Merchant Center Income Statement For The Year Ended, DECEMBER 31, 2018Document7 pagesMerchant Center Income Statement For The Year Ended, DECEMBER 31, 2018Melissa RaboNo ratings yet
- Inventory Estimation 1Document6 pagesInventory Estimation 1Kriza CabilloNo ratings yet
- Forda Reviewer IA - PrelimDocument12 pagesForda Reviewer IA - PrelimAltessa Lyn ContigaNo ratings yet
- Activity in Inventory Estimation, Retail InventoryDocument2 pagesActivity in Inventory Estimation, Retail InventoryTrisha VillegasNo ratings yet
- Chapter13 - Gross Profit MethodDocument21 pagesChapter13 - Gross Profit MethodPatrick Jayson VillademosaNo ratings yet
- 8 Inventory EstimationDocument3 pages8 Inventory EstimationJorufel PapasinNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument5 pagesAccountingMarinie CabagbagNo ratings yet
- The Valuation of Digital Intangibles: Technology, Marketing and InternetFrom EverandThe Valuation of Digital Intangibles: Technology, Marketing and InternetNo ratings yet
- Operations Auditing QuizDocument3 pagesOperations Auditing QuizKezNo ratings yet
- Research Capabilityof Teachers Its Correlates Determinantsand Implicationsfor Continuing Professional DevelopmentDocument12 pagesResearch Capabilityof Teachers Its Correlates Determinantsand Implicationsfor Continuing Professional DevelopmentKezNo ratings yet
- Excise TaxDocument7 pagesExcise TaxKezNo ratings yet
- RPT - CollectionDocument3 pagesRPT - CollectionKezNo ratings yet
- Real Property TaxationDocument4 pagesReal Property TaxationKezNo ratings yet
- LGT - CollectionDocument3 pagesLGT - CollectionKezNo ratings yet
- Preferential Taxation - Barangay Micro Business EnterprisesDocument1 pagePreferential Taxation - Barangay Micro Business EnterprisesKezNo ratings yet
- A5 Audit of Ppe Part 1Document10 pagesA5 Audit of Ppe Part 1KezNo ratings yet
- PREFERENTIAL TAXATION - MAGNA CARTA FOR PWDsDocument1 pagePREFERENTIAL TAXATION - MAGNA CARTA FOR PWDsKezNo ratings yet
- Corporate Income TaxationDocument3 pagesCorporate Income TaxationKezNo ratings yet
- Income Payments Subject To CWTDocument1 pageIncome Payments Subject To CWTKezNo ratings yet
- Tax Remedies - Remedies of The GovernmentDocument4 pagesTax Remedies - Remedies of The GovernmentKezNo ratings yet
- Preferential Taxation - Senior Citizens LawDocument2 pagesPreferential Taxation - Senior Citizens LawKezNo ratings yet
- A7 Audit of Intangible AssetsDocument4 pagesA7 Audit of Intangible AssetsKezNo ratings yet
- Deductions From Gross IncomeDocument3 pagesDeductions From Gross IncomeKezNo ratings yet
- Deductions ExamplesDocument25 pagesDeductions ExamplesKezNo ratings yet
- Preferential Taxation - Double Taxation AgreementDocument3 pagesPreferential Taxation - Double Taxation AgreementKezNo ratings yet
- A9 Audit of LiabilitiesDocument7 pagesA9 Audit of LiabilitiesKezNo ratings yet
- A6 Audit of Ppe Part 2Document5 pagesA6 Audit of Ppe Part 2KezNo ratings yet
- A8 Audit of Prepayments, Ip and Other NciDocument7 pagesA8 Audit of Prepayments, Ip and Other NciKezNo ratings yet
- PROBLEMS - Part 2Document16 pagesPROBLEMS - Part 2KezNo ratings yet
- PROBLEMS Part1Document21 pagesPROBLEMS Part1KezNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Midterm FAR 3 Income TaxDocument1 pageMODULE 2 Midterm FAR 3 Income TaxKezNo ratings yet
- MODULE Midterm FAR 3 Share BasedDocument17 pagesMODULE Midterm FAR 3 Share BasedKezNo ratings yet
- Subsequent Events and Cash and Acrrual BasisDocument14 pagesSubsequent Events and Cash and Acrrual BasisKezNo ratings yet
- MODULE Midterm FAR 3 EmpBenefitsDocument15 pagesMODULE Midterm FAR 3 EmpBenefitsKezNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Midterm FAR 3 LeasesDocument31 pagesMODULE 1 Midterm FAR 3 LeasesKezNo ratings yet
- Problems Bonds-PayableDocument8 pagesProblems Bonds-PayableKezNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument5 pagesFormulasKezNo ratings yet
- State Transition Diagram To PLC Ladder Logic Translation WhitepaperDocument15 pagesState Transition Diagram To PLC Ladder Logic Translation WhitepapermhrahbNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3: Solving Linear Systems: Elif TanDocument20 pagesLecture 3: Solving Linear Systems: Elif Tansercan egilmezkolNo ratings yet
- Interpreting PLCDocument30 pagesInterpreting PLCpraveenNo ratings yet
- Brgy. Roblacion 1 Project Proposal PlanDocument10 pagesBrgy. Roblacion 1 Project Proposal PlanKennedy BalmoriNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal Dialysis.Document2 pagesPeritoneal Dialysis.alex_cariñoNo ratings yet
- Charles CarrDocument1 pageCharles CarrCAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Insulating Coatings For Electrical Steels by Composition, Relative Insulating Ability and ApplicationDocument4 pagesInsulating Coatings For Electrical Steels by Composition, Relative Insulating Ability and ApplicationjalilemadiNo ratings yet
- File LayoutDocument8 pagesFile LayoutGrad GuruNo ratings yet
- When Do We Use The Infinitive or - INGDocument2 pagesWhen Do We Use The Infinitive or - INGMarioNo ratings yet
- Integrated InveterDocument24 pagesIntegrated InveterDoan Anh TuanNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers - PMP Exam PrepDocument14 pagesQuestions and Answers - PMP Exam PrepPramod Gupta100% (2)
- Economics Grade 9 & 10 (Quiz 2)Document2 pagesEconomics Grade 9 & 10 (Quiz 2)Nofel AmeenNo ratings yet
- 3 Parks Dubai Glow Garden: FineprintDocument4 pages3 Parks Dubai Glow Garden: Fineprintrichmond_austria7635No ratings yet
- Aircraft Materials, Construction and RepairDocument34 pagesAircraft Materials, Construction and RepairJoshua BarteNo ratings yet
- JR - English Practice - Qps.apDocument20 pagesJR - English Practice - Qps.apnsmviiif08chakravarthyygsNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Convection With AnswersDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Convection With AnswersQueencess Ara TorresNo ratings yet
- Manual Sierra Biro 3334-4003Document47 pagesManual Sierra Biro 3334-4003SEBASTIAN PEREZNo ratings yet
- Cnidaria and CtenophoraDocument53 pagesCnidaria and CtenophorakingbanakonNo ratings yet
- Dr. Jeffrey Kamlet Litigation Documents 10.18Document172 pagesDr. Jeffrey Kamlet Litigation Documents 10.18Phil AmmannNo ratings yet
- Food MovementDocument18 pagesFood MovementSubhadipta BiswasNo ratings yet
- Glorious Innings of Prof.a R RaoDocument24 pagesGlorious Innings of Prof.a R RaoMeghmeghparva100% (1)
- All in Alfloc2Document12 pagesAll in Alfloc2Choice OrganoNo ratings yet
- Electricity Bill Receipt (2674774111)Document1 pageElectricity Bill Receipt (2674774111)Ritesh KatariyaNo ratings yet
- US ARMY - Inventory of Field Manuals As of January 23, 2002Document13 pagesUS ARMY - Inventory of Field Manuals As of January 23, 2002AKsentinelNo ratings yet
- Background Medical CountermeasuresDocument7 pagesBackground Medical Countermeasuresapi-246003035No ratings yet
- BPTP Tera Boq - Split AcDocument36 pagesBPTP Tera Boq - Split AckarunvandnaNo ratings yet
- Ficha Técnica Cable VFD Trex-OnicsDocument1 pageFicha Técnica Cable VFD Trex-OnicsMario Alonso Ruiz CherresNo ratings yet
- Timeline: 2 To 3 Weeks Timeline 4-5 WeeksDocument1 pageTimeline: 2 To 3 Weeks Timeline 4-5 WeeksKester Ray de VeraNo ratings yet