Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 12 - Biology - Human Reproduction
Class 12 - Biology - Human Reproduction
Uploaded by
Astha SaxenaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class 12 - Biology - Human Reproduction
Class 12 - Biology - Human Reproduction
Uploaded by
Astha SaxenaCopyright:
Available Formats
NCERT Solution for Class 12
Biology
Chapter 3 -Human Reproduction
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Humans reproduce. (asexually/sexually)
Ans: Humans reproduce sexually.
(b) Humans are. (oviparous/viviparous/ovoviviparous)
Ans: Humans are viviparous.
(c) Fertilization is in humans. (external/internal)
Ans: Fertilization is internal in humans.
(d) Male and female gametes are. (diploid/haploid)
Ans: Male and female gametes are haploid.
(e) Zygote is. (diploid/haploid)
Ans: Zygote is diploid.
(f) The process of release of the ovum from a mature follicle is called.
Ans: The process of release of the ovum from a mature follicle is called
ovulation.
(g) Ovulation is induced by a hormone called the.
Ans: Ovulation is induced by a hormone called the luteinizing hormone.
(h) The fusion of the male and the female gametes are called.
Ans: The fusion of the male and the female gametes is called fertilization.
(i) Fertilization takes place in the.
Ans: Fertilization takes place in the fallopian tube.
(j) The zygote divides to form, which is implanted in the uterus.
Ans: The zygote divides to form a blastocyst, which is implanted in the uterus.
(k) The structure which provides a vascular connection between the fetus
and uterus is called
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 1
Ans: The structure which provides vascular connection between the foetus
and uterus is called placenta.
2. Draw a labelled diagram of the male reproductive system.
Ans:
3. Draw a labelled diagram of the female reproductive system.
Ans:
4. Write two major functions each of testis and ovary.
Ans:
Functions of the Testis
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 2
➢ Spermatozoa are produced by the process of spermatogenesis.
➢ Male hormone called testosterone is secreted by the Leydig cell of the
seminiferous tubules.
➢ The development of secondary sex characteristics in males is done by a
hormone called Testosterone.
Functions of the ovary
➢ By the process of oogenesis, the ovary produces a female gamete called ova.
➢ A female sex hormone called estrogen is secreted by the mature Graffian
follicle. The development of secondary sex characteristics in females is done
by a hormone called Estrogen.
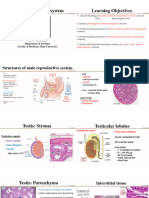
5. Describe the structure of a seminiferous tubule.
Ans: Seminiferous tubules are a highly coiled structure where the production of
sperms in the testes takes place. These tubules are located within the testicular
lobules. The two types of cells namely spermatogonia and Sertoli cells are found
in the germinal epithelial lining of seminiferous tubules. Spermatogonia
produces primary spermatocytes by meiotic divisions which are male germ cells.
Primary spermatocytes undergo further meiotic division to form secondary
spermatocytes and eventually, spermatids. Spermatozoa are produced by the
metamorphosis of the spermatids. Though the Sertoli cells provide nourishment
to the germ cells, they are also referred to as nurse cells. The large polygonal
cells known as interstitial cells or Leydig cells are present between the
seminiferous tubules. Male hormone called testosterone is secreted by these
cells.
6. What is spermatogenesis? Briefly describe the process.
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 3
Ans: The production of sperms from the immature germ cells in males is
referred to as spermatogenesis. It takes place in seminiferous tubules present
inside the testes. During spermatogenesis, a diploid spermatogonium (male
germ cell) increases its size to make a diploid primary spermatocyte. This
diploid primary spermatocyte undergoes first meiotic division (meiosis I),
which is a reductional division to form two equal haploid secondary
spermatocytes. Each secondary spermatocyte then undergoes a second meiotic
division (meiosis II) to form two equal haploid spermatids. Hence, four haploid
spermatids are produced by a diploid spermatogonium. These spermatids by the
process called spermatogenesis are transformed into spermatozoa (sperm).
7. Name the hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis.
Ans: Gonadotropin-releasing hormones secrete Follicle-stimulating hormones
(FSH) and luteinizing hormones (LH) from the hypothalamus. In the process of
spermatogenesis, these hormones are required. FSH acts on Sertoli cells,
whereas LH acts on Leydig cells of the testis and stimulates The method of
spermatogenesis gets stimulated by FSH and LH.
8. Define spermiogenesis and spermiation.
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 4
Ans:
Spermiogenesis
It is the process of changing spermatids into mature spermatozoa or sperms.
Spermiation
The releasing of sperms from the Sertoli cells into the lumen of seminiferous
tubules is called spermiation.
9. Draw a labelled diagram of sperm.
Ans:
10. What are the major components of seminal plasma?
Ans: Semen is the alkaline fluid ejaculated by man. It consists of sperms and
seminal plasma. In the male reproductive system, its major components are
mucus, spermatozoa, and various secretions of accessory glands. For the sperm
to be active, the seminal plasma also contains fructose, calcium, ascorbic acid,
and certain enzymes. Thus, nourishment and protection to sperms are provided.
11. What are the major functions of male accessory ducts and glands?
Ans: Vasa efferentia, Epididymis, Vas deferens, and Rete testis are the male
accessory ducts. A crucial role is played by them in the transport and temporary
storage of sperm. On the contrary, seminal vesicles, prostate glands, and
bulbourethral glands are the male accessory glands. Fluids are secreted by these
glands that help in the lubrication of the reproductive system and sperms.
Dispersion of sperms in the fluid occurs which makes their transportation easier
into the female body. Thus, for the sperms to be active nutrients are also
provided by the fluids.
12. What is oogenesis? Give a brief account of oogenesis.
Ans: The formation of eggs or ova in the ovary is referred to as oogenesis. In
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 5
this process, a diploid oogonium or egg mother cell size increases, and it gets
transformed into a diploid primary oocyte. The diploid primary oocyte after
attaining full growth undergoes first meiotic division i.e., meiosis I or
reductional division to form two unequal haploid daughter cells. A very smaller
cell is known as the first polar body or polocyte, while the larger cell is known
as the secondary oocyte which contains the nucleus and entire cytoplasm with
the yolk. The secondary oocyte undergoes a second meiotic division i.e., meiosis
II or equational division, giving rise to a second polar body and an ovum. Thus,
A single haploid ovum is produced by a diploid oogonium and also two or three
polar bodies are produced in the entire process of Oogenesis.
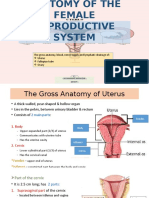
13. Draw a labelled diagram of a section through the ovary.
Ans:
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 6
14. Draw a labelled diagram of a Graafian Follicle?
Ans:
15. Name the functions of the following.
(a) Corpus luteum
Ans: Corpus luteum: The ruptured Grafiaan follicle gives rise to a structure
called the Corpus luteum. A hormone Progesterone hormone during the luteal
phase of the menstrual cycle. The increased amount of progesterone inhibits
the secretions of FSH and LH, thereby preventing ovulation. The proliferation
of the endometrium of the uterus and the process of implantation is also
allowed by the corpus luteum.
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 7
(b) Endometrium
Ans: Endometrium: The innermost lining of the uterus is the endometrium. It
is removed during menstrual discharge each month in the menstrual cycle and
thus it prepares itself for the implantation of the embryo.
(c) Acrosome
Ans: Acrosome: In the sperm, there is a cap-like structure present in the
anterior part called the acrosome. There is a presence of an enzyme called
hyaluronidase enzyme, which hydrolyses the outer membrane of the egg. The
acrosome secretes enzymes that help in the penetration of sperm into the egg
by dissolving the egg membrane during fertilization.
(d) Sperm tail
Ans: Sperm tail: It is the region of the sperm which is several times longer than
the head. The locomotion of the sperm is determined inside the female
reproductive tract by the tail of the sperm.
(e) Fimbriae
Ans: Fimbriae: The finger-like projections at the ovarian end of the fallopian
tube are called fimbriae. After the process of ovulation, they help in the
collection of the ovum which is facilitated by the beating of the cilia.
16. Identify True/False statements. Correct each false statement to make it
true.
(a) Androgens are produced by Sertoli cells. (True/False)
Ans: Androgens are produced by Sertoli cells. (False)
Androgens are produced by Leydig cells found in seminiferous tubules of the
testis.
(b) Spermatozoa get nutrition from Sertoli cells. (True/False)
Ans: Spermatozoa get nutrition from Sertoli cells. (True)
(c) Leydig cells are found in the ovary. (True/False)
Ans: Leydig cells are found in the ovary. (False)
Leydig cells are found in the seminiferous tubules of the testis.
(d) Leydig cells synthesise androgens. (True/False)
Ans: Leydig cells synthesize androgens. (True)
(e) Oogenesis takes place in corpus luteum. (True/False)
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 8
Ans: Oogenesis takes place in corpus luteum. (False)
Oogenesis takes place in the ovary.
(f)Menstrual cycle ceases during pregnancy. (True/False)
Ans: Menstrual cycle ceases during pregnancy. (True)
(g) Presence or absence of hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity
or sexual experience. (True/False)
Ans: Presence or absence of the hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity
or sexual experience. (True)
17. What is the menstrual cycle? Which hormones regulate the menstrual
cycle?
Ans: The menstrual cycle is a rhythmic series of physiological changes in the
sex organs that occur about 28 days throughout a women’s reproductive life.
The end of the cycle is accompanied by the breakdown of the uterine
endothelium, which gets released in the form of blood and mucus through the
vagina. This is known as menses.
The menstrual cycle is regulated by the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH),
luteinizing hormone (LH), estrogen, and progesterone. The anterior pituitary
gland secretes FSH and LH which increase during the follicular phase. A
primary follicle is converted into a Graafian follicle by FSH under the influence
of RH (releasing hormone). The secretion of LH increases gradually which
results in the growth of follicles and secretion of estrogen. The secretion of FSH
is inhibited by Estrogen and it stimulates the secretion of luteinizing hormone.
It also causes the thickening of the uterine endometrium. The increased level of
LH causes the rupturing of the Graafian follicle and releases the ovum into the
fallopian tube. The ruptured Graafian follicle changes to the corpus luteum and
starts secreting progesterone hormone during the luteal phase. Progesterone
hormone helps in the maintenance and preparation of the endometrium for the
implantation of the embryo. High levels of progesterone hormone in the blood
decrease the secretion of LH and FSH, therefore inhibiting further ovulation.
18. What is parturition? Which hormones are involved in induction of
parturition?
Ans: After the complete development of the foetus in the mother’s womb, the
process of giving birth to a newborn baby is called Parturition. Oxytocin and
Relaxin are the two hormones required in this entire process. Oxytocin results
in the contraction of smooth muscles of the myometrium of the uterus, which
pushes the fully formed foetus towards the birth canal. On the opposite hand, the
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 9
relaxin hormone causes there is relaxation of the pelvic ligaments by a hormone
called relaxin and it thus prepares the uterus for childbirth.
19. In our society the women are often blamed for giving birth to daughters.
Can you explain why this is not correct?
Ans: The number of chromosomes present in each individual is 23. 22 pairs of
autosomes in and one or two types of sex chromosomes are present in males.
They may be either X or Y. Whereas, 22 pairs of autosomes and only the X sex
chromosome is found in females. The type of the male gamete (X or Y)during
spermatogenesis A determines the sex of an individual, which further fuses with
the X chromosome containing the female’s egg cell. If the fertilized sperm
contains X, then the baby born will be a girl and if it contains Y, then the baby
born will be a boy.
Thus, for the gender of the child, women should not be blamed.
20. How many eggs are released by a human ovary in a month? How many
eggs do you think would have been released if the mother gave birth to
identical twins? Would your answer change if the twins born were
fraternal?
Ans: Every coming month, a single egg is released by the ovary. Twins are
produced when two babies are in a sequence. Generally, A single egg gives rise
to twins which are produced by the separation of early blastomeres, emerging
from the first zygotic cleavage. Thus, there will be the same genetic make-up in
the developed young ones and so, they are called identical twins.
Sometimes, twins born are fraternal, which means they would have developed
from two separate eggs. This happens when at the same time two eggs (one from
each ovary) are released and fertilization takes place by two separate sperms.
Thus, the developed young ones will have separate genes and are, therefore,
called non-identical or fraternal twins.
21. How many eggs do you think were released by the ovary of a female dog
which gave birth to 6 puppies?
Ans: Dogs and rodents are poly-ovulatory species. More than one ovum is
released from the ovary in these species at the time of ovulation. Therefore,
Ovary released six eggs from a female dog to produce six puppies.
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 10
You might also like
- H-Mole Chapter I-VDocument103 pagesH-Mole Chapter I-VJoevence Gazo CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class-12 Biology Chapter-3 Human ReproductionDocument12 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class-12 Biology Chapter-3 Human ReproductionAnonymous tmX4vzlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDocument10 pagesChapter 3 Human ReproductionRameshwer KambleNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document13 pagesChap 3Sabah SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Biology Class-12 Chapter-3Document9 pagesBiology Class-12 Chapter-3mokanrajan141106No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 3 Human ReproductionTheLost GuyNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproductionjiya jainNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology NcertSolutions Chapter 3Document11 pages12 Biology NcertSolutions Chapter 3vijayan vijayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Human Reproductionlavishbhati691No ratings yet
- CH - 3 - Ncert SolutionsDocument6 pagesCH - 3 - Ncert SolutionsJanani VijayarajNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 Human ReproductionDocument16 pagesCh-2 Human ReproductionShivam Kumar100% (1)
- tJISjCwWKppIrfVbBOdL PDFDocument31 pagestJISjCwWKppIrfVbBOdL PDFBharati GulajkarNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions-Human ReproductionDocument14 pagesNcert Solutions-Human ReproductionSHAIKH YUNUS ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Human ReproductionDocument8 pagesChapter-3 Human ReproductionbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 - Human ReproductionDocument17 pagesImportant Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 - Human ReproductionYuvraj MehtaNo ratings yet
- Q & A Notebook Chap 03Document13 pagesQ & A Notebook Chap 03umamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- 12th Bio - Zoology Previous Year Public Exam Question & Answer EMDocument28 pages12th Bio - Zoology Previous Year Public Exam Question & Answer EMabdullad27107No ratings yet
- LN 3 - Human ReproductionDocument14 pagesLN 3 - Human ReproductionZara KNo ratings yet
- Marks Wise Questions CH-2Document22 pagesMarks Wise Questions CH-2lakshshah5116No ratings yet
- Bio Investment BankingDocument10 pagesBio Investment BankingGoutham shetty MNo ratings yet
- XII Bio Chp-3 Ques-AnsDocument7 pagesXII Bio Chp-3 Ques-Ans3humika24No ratings yet
- Why Are Human Testes Located Outside The Abdominal CavityDocument3 pagesWhy Are Human Testes Located Outside The Abdominal Cavityrethishsugu28No ratings yet
- Gametogenesis Process in HumanDocument10 pagesGametogenesis Process in HumanFerhaeeza KalayakanNo ratings yet
- ch-8 - TERM 2 - REVISION NOTES - 2021-22Document15 pagesch-8 - TERM 2 - REVISION NOTES - 2021-22Turani SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Practice 1Document19 pagesChapter 3 Practice 1Kim VnehaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: 3.1 T M R SDocument15 pagesHuman Reproduction: 3.1 T M R SSrajanNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Male Reproduction SystemDocument9 pagesBiology Notes Male Reproduction SystemSunderNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Human Reproduction - Grade 12Document27 pagesWorksheet On Human Reproduction - Grade 12Palani G Pazhani GNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Animals - TB QuestionsDocument7 pagesReproduction in Animals - TB Questionshafsatabarak.rNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3Document27 pagesNCERT Exemplar For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3Me RahaviNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Life Science Human Reproduction NotesDocument138 pagesGrade 12 Life Science Human Reproduction NotesLulo NnenaNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction For Grade 11 Worksheet 2Document8 pagesPlant Reproduction For Grade 11 Worksheet 2KISHANo ratings yet
- Gametogenesis Process in HumanDocument13 pagesGametogenesis Process in HumanRiski UntariNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction-IiDocument11 pagesHuman Reproduction-IiSuryansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System - MaleDocument38 pagesReproductive System - MaleBenilda Mae TandocNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Human ReproductionDocument8 pagesRevision Notes On Human ReproductionTeodor TelemanNo ratings yet
- PP5. Human ReproductionDocument138 pagesPP5. Human ReproductionSamalaniNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction NotesDocument5 pagesHuman Reproduction NotesRaniaNo ratings yet
- Army Public School Gopalpur: Class-Xii Science Subject - Biology Chapter-3 Human Reproduction NotesDocument7 pagesArmy Public School Gopalpur: Class-Xii Science Subject - Biology Chapter-3 Human Reproduction NotesAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Biology 12 - The Reproductive System!: Name: Block: DateDocument4 pagesBiology 12 - The Reproductive System!: Name: Block: DateLerr Real Relle100% (1)
- New DOC DocumentDocument10 pagesNew DOC Documentponragavan2k07No ratings yet
- Daug - Activity No.1 - Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesDaug - Activity No.1 - Reproductive SystemFRANCINE JULIA DAUGNo ratings yet
- Biology - Human ReproductionDocument21 pagesBiology - Human Reproductionsgw67No ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis: Four Haploid CellsDocument10 pagesSexual Reproduction and Meiosis: Four Haploid CellsJohnieer Bassem MoferdNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction-1Document21 pagesHuman Reproduction-1Coni Espinoza YupanquiNo ratings yet
- Gametes, Gametogenesis Usually Starts With GametogoniaDocument9 pagesGametes, Gametogenesis Usually Starts With GametogoniaDAGUIBIG, Patricia S.No ratings yet
- Gametogenesis and FertilizationDocument10 pagesGametogenesis and FertilizationJustus MutuaNo ratings yet
- HumanDocument18 pagesHumanDavidson VishalNo ratings yet
- OgenisisDocument52 pagesOgenisisBharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Biology Folio: Name: Amir Afiq Bin AzlanDocument26 pagesBiology Folio: Name: Amir Afiq Bin AzlanAmir AfiqNo ratings yet
- Define The FollowingDocument19 pagesDefine The FollowingAbhinav AtrayNo ratings yet
- Bio CH2 Q-A WriteDocument3 pagesBio CH2 Q-A Writerswatti234No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Module - 3 - Male Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesLecture Notes Module - 3 - Male Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyMariaImranNo ratings yet
- PP5. Human ReproductionDocument100 pagesPP5. Human ReproductionhellohlayisoNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From SUPERCOPDocument10 pagesMaterial Downloaded From SUPERCOPkritika0% (1)
- Temporary Module1 Science5Document10 pagesTemporary Module1 Science5Lena Beth Tapawan YapNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in HumansDocument11 pagesSexual Reproduction in HumansAkash RamroopNo ratings yet
- XII - 3. Human ReprodutionDocument5 pagesXII - 3. Human Reprodutionkaustavdas3235No ratings yet
- Exp 6 (Reproductive System)Document7 pagesExp 6 (Reproductive System)divendran raveintharanNo ratings yet
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction PyqsDocument7 pagesHuman Reproduction PyqsMrityunjay PandeyNo ratings yet
- The Female Prostate Revisited: Perineal Ultrasound and Biochemical Studies of Female EjaculateDocument6 pagesThe Female Prostate Revisited: Perineal Ultrasound and Biochemical Studies of Female EjaculatephampullovNo ratings yet
- The Beauty of Female Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesThe Beauty of Female Reproductive SystemKlarenz RomNo ratings yet
- 51 Lecture The Gynecological ExamDocument69 pages51 Lecture The Gynecological ExamTarek TarekNo ratings yet
- Applied Veterinary Gynaecology and Obste1 PDFDocument377 pagesApplied Veterinary Gynaecology and Obste1 PDFHamza AlviNo ratings yet
- Answer Page 47Document1 pageAnswer Page 47Shavonne LaiNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet in Science 5 Second Quarter Activity Sheet 1Document4 pagesActivity Sheet in Science 5 Second Quarter Activity Sheet 1dinnes masubay100% (3)
- Q1 &Q2 1st Summative Test Science 5 EDITEDDocument14 pagesQ1 &Q2 1st Summative Test Science 5 EDITEDTrishaAnnSantiagoFidel100% (2)
- Chapter 8: Nursing Care of The Subfertile CoupleDocument10 pagesChapter 8: Nursing Care of The Subfertile CoupleAlyssaGrandeMontimorNo ratings yet
- Zucchi 2010Document5 pagesZucchi 2010Ghani Ikhsan MajidNo ratings yet
- Histology Male Reproductive 2023Document17 pagesHistology Male Reproductive 2023VARITPOL CHAROENYINGPAISALNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesAnatomy of Female Reproductive SystemLenovo Legion Y520No ratings yet
- Animal Reproduction - Class PresentationDocument120 pagesAnimal Reproduction - Class PresentationRenz Dela Cruz ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Cell, Organ, CycleDocument56 pagesReproductive Cell, Organ, CycleAjay MeghanathiNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Gametogenesis 1 2021Document9 pagesPraktikum Gametogenesis 1 2021Cici LestariNo ratings yet
- What Are The Parts of The Male External Sexual Anatomy?Document3 pagesWhat Are The Parts of The Male External Sexual Anatomy?bla blaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Reproductive - Glands FinalDocument32 pagesLecture Reproductive - Glands FinalerikaquitaraaaNo ratings yet
- Histology Male ReproductiveDocument31 pagesHistology Male Reproductivekhiks34No ratings yet
- Reading: Reviewer in Science 5Document2 pagesReading: Reviewer in Science 5Joice Ann PolinarNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Human (Chapter 3) Teaching Notes - (Module 1)Document2 pagesReproduction in Human (Chapter 3) Teaching Notes - (Module 1)succiniNo ratings yet
- Physiology of MenstruationDocument11 pagesPhysiology of MenstruationDavid CalaloNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Female Genitalia and RectumDocument2 pagesAssessment of The Female Genitalia and RectumLi mNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Daily Lesson Log: Joel F. GautDocument4 pagesGrade 5 Daily Lesson Log: Joel F. GautJoel GautNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy of Female Reproductive SystemseongeokNo ratings yet
- CP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Document11 pagesCP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing ReviewerDocument119 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewerasdf100% (1)
- A&P 2402 Male Reproductive Review Questions With AnswersDocument6 pagesA&P 2402 Male Reproductive Review Questions With AnswersHanna Belle GoreNo ratings yet
- RP2Document2 pagesRP2moorditya moordiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Human Reproduction - Grade 12Document27 pagesWorksheet On Human Reproduction - Grade 12Palani G Pazhani GNo ratings yet