Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Visual Impairment Simplified
Visual Impairment Simplified
Uploaded by
Justine Joy Sabalboro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesPhysical disability refers to conditions affecting physical abilities like mobility or strength. There are two categories - hereditary/congenital disabilities present at birth and acquired disabilities caused by accidents or medical conditions. Examples include cerebral palsy, arthritis, and muscular dystrophy. Visual impairments range from partial to complete vision loss and can be caused by diseases, injuries, or refractive errors like nearsightedness treatable with lenses. An ophthalmologist examines the eye structure and may perform tests of vision, visual fields, and eye pressure.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPhysical disability refers to conditions affecting physical abilities like mobility or strength. There are two categories - hereditary/congenital disabilities present at birth and acquired disabilities caused by accidents or medical conditions. Examples include cerebral palsy, arthritis, and muscular dystrophy. Visual impairments range from partial to complete vision loss and can be caused by diseases, injuries, or refractive errors like nearsightedness treatable with lenses. An ophthalmologist examines the eye structure and may perform tests of vision, visual fields, and eye pressure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesVisual Impairment Simplified
Visual Impairment Simplified
Uploaded by
Justine Joy SabalboroPhysical disability refers to conditions affecting physical abilities like mobility or strength. There are two categories - hereditary/congenital disabilities present at birth and acquired disabilities caused by accidents or medical conditions. Examples include cerebral palsy, arthritis, and muscular dystrophy. Visual impairments range from partial to complete vision loss and can be caused by diseases, injuries, or refractive errors like nearsightedness treatable with lenses. An ophthalmologist examines the eye structure and may perform tests of vision, visual fields, and eye pressure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
• Physical disability refers to a condition that affects a person's physical abilities, such as mobility,
strength, and coordination.
• There are two main categories of physical disability: hereditary/congenital (present at birth or due
to inherited genetic issues) and acquired (resulting from an accident, infection, or medical
condition).
• Examples of physical disabilities include cerebral palsy, arthritis, muscular dystrophy, multiple
sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, and repetitive strain injury.
• Physical disabilities can affect mobility, coordination, balance, and manipulation of equipment,
and may also impact speech, vision, and energy levels.
• Some physical disabilities are temporary or have periods of remission, while others are
permanent.
• Accommodations for students with physical disabilities should be tailored to their individual needs
and may include the use of assistive devices such as wheelchairs or walking aids.
• Visual impairment refers to any kind of vision loss, including complete blindness or partial vision
loss.
• Visual impairment can be caused by diseases or injuries that affect the eye or brain.
• Some visual impairments can be treated with eyeglasses or contact lenses, but others cannot
be fully restored with medical treatment or corrective lenses.
• People with legal blindness have vision that is significantly weaker than someone with perfect
vision. They can see an object from 20 feet away as well as someone with perfect vision can
from 200 feet away.
• Visual impairment is rare in teenagers and is usually caused by injuries such as sports accidents
or car accidents.
• Amblyopia is a condition where a child's eye doesn't see as well as the other eye. It is also called
a "lazy eye." It can happen when the eyes are misaligned or crossed. The brain might ignore the
messages from one of the misaligned eyes and the vision in that eye doesn't develop normally.
• Cataracts are cloudy spots in the lens of the eye. The lens is a clear part of the eye that helps
light pass through and focus on the retina. When cataracts are present, the light cannot pass
through easily and it causes vision problems. Symptoms of cataracts include double vision, blurry
vision, trouble seeing in the dark, and colors that look faded.
• Diabetic retinopathy is a condition where the blood vessels in the back of the eye become
damaged because of diabetes. People with this condition might not have any problems seeing
at first, but if it gets worse, they can become blind. Teens with diabetes should get regular eye
exams to check for this condition. To prevent diabetic retinopathy, people with diabetes should
not smoke, keep their blood pressure and blood sugar under control, and take good care of their
health.
• Glaucoma is a condition where the pressure inside the eye gets too high. This pressure can
damage the nerves in the eye and cause vision loss. Sometimes, glaucoma can be caused by
other health problems, but sometimes it happens for no known reason. It is more common in
older people, but it can also happen to babies and children. People with glaucoma may not notice
any problems with their vision at first, but as the condition gets worse, they may start to lose their
sight. If it is not treated, people with glaucoma can become blind.
• Macular degeneration is a condition where the macula, a sensitive part of the retina, gets worse
over time. The retina is the part of the eye that helps us see. Macular degeneration can make it
hard to see fine details and can cause vision loss. It is more common in older people, but it can
also happen to younger people. Too much sunlight and smoking can increase the risk for this
condition. Symptoms of macular degeneration may include trouble reading or watching TV, and
distorted vision where lines look wavy or objects look bigger or smaller than they should.
• Trachoma is an infection in the eye caused by a germ called Chlamydia trachomatis. It is very
contagious and is more common in poor rural areas where people live close together and don't
have clean water and good sanitation. Trachoma can cause inflammation in the eye.
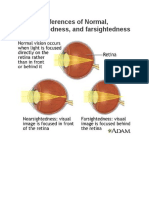
• Near-sightedness (also called short-sightedness or myopia) is a condition where light focuses
in front of the retina, causing distant objects to appear blurry.
• Far-sightedness (also called long-sightedness, hypermetropia, or hyperopia) is a condition
where close objects appear blurry but distant objects are clear.
• Presbyopia is a condition that affects people as they get older and makes it harder to see close
objects clearly.
• Astigmatism is a condition where the eye's refractive power is not symmetrical, causing
distorted or blurry vision. It can cause eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at night.
• Near-sightedness, far-sightedness, presbyopia, and astigmatism are all types of refractive
errors. They can be treated with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery.
• An ophthalmologist is a doctor who specializes in examining, diagnosing, and treating eyes and
eye diseases.
• When someone goes to see an ophthalmologist, the doctor will look at the structure of the eye.
• The ophthalmologist may also do some simple tests like a visual acuity test (reading an eye
chart to measure distance vision), a visual field test (measuring side vision), and a tonometry
test (checking fluid pressure in the eye for glaucoma).
You might also like
- Profed07-Foundation of Special and Inclusive Education-Chapter 2Document9 pagesProfed07-Foundation of Special and Inclusive Education-Chapter 2Ken100% (1)
- Management of Refractive Errors PDFDocument168 pagesManagement of Refractive Errors PDFJorge Flores100% (3)
- Visual ImpairmentDocument9 pagesVisual ImpairmentMeti Guda100% (1)
- Prof Ed 7 Difficulties in SeeingDocument4 pagesProf Ed 7 Difficulties in Seeingyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Aging SensoryDocument8 pagesAging SensoryTjut Intan Permata SariNo ratings yet
- Eye Diseases Ppt. 2024Document43 pagesEye Diseases Ppt. 2024Sri Ram 07No ratings yet
- Ochiul Si Bolile SaleDocument7 pagesOchiul Si Bolile SaleRares PopeiaNo ratings yet
- HyperopiaDocument6 pagesHyperopiageeneevzzNo ratings yet
- VI Psa Pres Common Eye Conditions2Document58 pagesVI Psa Pres Common Eye Conditions2PopeyeNo ratings yet
- What Causes BlindnessDocument3 pagesWhat Causes Blindnessskyblueangel15No ratings yet
- Lay Forum NotesDocument7 pagesLay Forum NotesCleoGomezNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument11 pagesCataractFSO MedicNo ratings yet
- Impaired VisionDocument3 pagesImpaired VisionJannelle Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Vi Psa Pres Common Eye Conditions Aug10 3.08.29 PMDocument58 pagesVi Psa Pres Common Eye Conditions Aug10 3.08.29 PMSarthak KabiNo ratings yet
- Age-Related Cataract & GlaucomaDocument26 pagesAge-Related Cataract & Glaucomasweetyeyal2002No ratings yet
- 2018.12.eye Conditions in Adults - Final 5th December 2018Document18 pages2018.12.eye Conditions in Adults - Final 5th December 2018KOMATSU SHOVELNo ratings yet
- Blindness Removed MergedDocument16 pagesBlindness Removed Mergedsanju tiwariNo ratings yet
- Myopia CausesDocument6 pagesMyopia Causeseekshu559812No ratings yet
- Eye Health From A - ZDocument10 pagesEye Health From A - ZRiyaz RiyazNo ratings yet
- Visually Impaired: Photophobia DiplopiaDocument9 pagesVisually Impaired: Photophobia DiplopiaGinalen MartelNo ratings yet
- Bio Khushil 12Document23 pagesBio Khushil 12khushilgajpal2007No ratings yet
- Sight SavingDocument3 pagesSight SavingenelrahNo ratings yet
- Name - Krishna Chouhan CLASS - 12th B: Kendriya Vidyalaya No.2 IndoreDocument11 pagesName - Krishna Chouhan CLASS - 12th B: Kendriya Vidyalaya No.2 IndoreKrishna ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument19 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectGopikrishna united67% (3)
- Blackboard1 150313105122 Conversion Gate01Document45 pagesBlackboard1 150313105122 Conversion Gate01jessajoy deslateNo ratings yet
- Vision Loss (Blindness), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVision Loss (Blindness), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Classification: Associated ProblemsDocument13 pagesClassification: Associated ProblemsYrraFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Cataract: What You Should KnowDocument24 pagesCataract: What You Should KnowshinhyejjNo ratings yet
- Eye Variations - Docx 5.2Document15 pagesEye Variations - Docx 5.2cryptojanus25No ratings yet
- Desry Sevti Eka Putri 1410070100105Document11 pagesDesry Sevti Eka Putri 1410070100105Diah FebruarieNo ratings yet
- Eye Overview: Anatomy, Health and Disease States: Not Illustrated in Chart AboveDocument4 pagesEye Overview: Anatomy, Health and Disease States: Not Illustrated in Chart AboveSarly Puspita AriesaNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument6 pagesCataractKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Eye Problems in ChildrenDocument6 pagesEye Problems in ChildrenSachin CharodiNo ratings yet
- AgingDocument7 pagesAgingElienai de LeonNo ratings yet
- Visual Impaired: Ang Wee Shin Nur Athirah Binti Zaidon Anis AdibahDocument29 pagesVisual Impaired: Ang Wee Shin Nur Athirah Binti Zaidon Anis AdibahShahirah Zafirah100% (2)
- Visual ImpairmentDocument11 pagesVisual ImpairmentnunutsehaynuNo ratings yet
- Project 220209165249Document32 pagesProject 220209165249Lakshmanan RNo ratings yet
- Group 9 Mathematics Year Today School YearDocument44 pagesGroup 9 Mathematics Year Today School YearElsie GumocNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY - Docx2.oDocument27 pagesBIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY - Docx2.oK GhatageNo ratings yet
- Visual ImpairmentDocument7 pagesVisual ImpairmentShirley Briagas50% (2)
- Vision ImpairmentDocument7 pagesVision ImpairmentAmarie HarrisNo ratings yet
- The Most Common Causes of Eye Problems1Document4 pagesThe Most Common Causes of Eye Problems1shree ganeshNo ratings yet
- What Causes Cataract?Document3 pagesWhat Causes Cataract?Eye spacialistNo ratings yet
- Cataracts Diabetes Diuretics EyeDocument4 pagesCataracts Diabetes Diuretics Eyevandana singhNo ratings yet
- Eye Disorder:: Refractive ErrorsDocument13 pagesEye Disorder:: Refractive Errorsতৌহিদুল ইসলামNo ratings yet
- 9 Visually-ImpairedDocument10 pages9 Visually-ImpairedJunadrian GenitoNo ratings yet
- Common Retinal Diseases: FloatersDocument7 pagesCommon Retinal Diseases: FloatersDan-Dan Irika CentinoNo ratings yet
- Myopia (Nearsightedness) Notes by - JUSTIN SIRDocument9 pagesMyopia (Nearsightedness) Notes by - JUSTIN SIRgeorgejhon1949No ratings yet
- Name: Shumaila Azam Reg No: 70098213 Section: B Topic: Causes of Blindness Mam: Tahira Kalsoom Subject: Optometric ProceduresDocument8 pagesName: Shumaila Azam Reg No: 70098213 Section: B Topic: Causes of Blindness Mam: Tahira Kalsoom Subject: Optometric Proceduresshumaila khanNo ratings yet
- Cataracts: A Leading Cause of Preventable Blindness: Neda Karimi, M.D. Represented by Dr.R.Handoko Pratomo, SPMDocument71 pagesCataracts: A Leading Cause of Preventable Blindness: Neda Karimi, M.D. Represented by Dr.R.Handoko Pratomo, SPMNefri TiawarmanNo ratings yet
- VISUAL AND HEARING PROBLEMS SDocument6 pagesVISUAL AND HEARING PROBLEMS SMegan Rose MontillaNo ratings yet
- Normal ChangesDocument26 pagesNormal ChangesGlizzle MacaraegNo ratings yet
- MyopiaDocument3 pagesMyopiaAbu RidhuwanNo ratings yet
- Causes of HandicapsDocument14 pagesCauses of HandicapsKim HuitNo ratings yet
- EyeDocument115 pagesEyemalathiNo ratings yet
- Health 1 17Document3 pagesHealth 1 17Rosie SaquinNo ratings yet
- GLAUCOMa Edited2Document8 pagesGLAUCOMa Edited2Maki CabuenaNo ratings yet
- Written Report in LEARNERS WITH PHYSICAL DISABILITIES 1-2Document5 pagesWritten Report in LEARNERS WITH PHYSICAL DISABILITIES 1-2Kyla CabullosNo ratings yet
- Investrigatory Project (Term I) : Subject - BIOLOGYDocument20 pagesInvestrigatory Project (Term I) : Subject - BIOLOGYRehan RazaNo ratings yet
- Kimberly Cruz - OphthalmologyDocument5 pagesKimberly Cruz - OphthalmologyKimberly CruzNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Identifying ShapesDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Identifying ShapesJustine Joy Sabalboro100% (1)
- Summarized Version of The Remaining Topics For Lesson 3 SG 3Document2 pagesSummarized Version of The Remaining Topics For Lesson 3 SG 3Justine Joy SabalboroNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document14 pagesModule 5Justine Joy SabalboroNo ratings yet
- Summarized Version For Lesson 4 SG 3Document3 pagesSummarized Version For Lesson 4 SG 3Justine Joy SabalboroNo ratings yet
- Module Overview: Unit 4 - Teacher As A Person in SocietyDocument10 pagesModule Overview: Unit 4 - Teacher As A Person in SocietyJaafar SorianoNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document27 pagesModule 4Justine Joy SabalboroNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument2 pagesThe Human Eye and The Colourful WorldXxxxxxNo ratings yet
- Health and HygieneDocument14 pagesHealth and HygieneGautam NigamNo ratings yet
- Human Eye (Prashant Kirad)Document15 pagesHuman Eye (Prashant Kirad)shrikantmisal17100% (6)
- Refraction and AccommodationDocument80 pagesRefraction and Accommodationapi-19916399100% (2)
- Notes of 10th Cbse Human EyeDocument7 pagesNotes of 10th Cbse Human EyeAvichal TatuNo ratings yet
- Fact SheetDocument3 pagesFact SheetSoraya Al-obinayNo ratings yet
- Optometric Case AnalysisDocument93 pagesOptometric Case AnalysisJoseph Israel100% (1)
- Class 10 Science (Physics) MCQs Chapter 11 QuestionsDocument28 pagesClass 10 Science (Physics) MCQs Chapter 11 QuestionsKSA TEXTILENo ratings yet
- Accommodation in The EyesDocument2 pagesAccommodation in The EyesCresanelle PoloNo ratings yet
- Myopia, Hyperopia and Astigmatism: A Complete Review With View of DifferentiationDocument5 pagesMyopia, Hyperopia and Astigmatism: A Complete Review With View of DifferentiationlaksonoNo ratings yet
- LASIK Eye SurgeryDocument3 pagesLASIK Eye SurgeryplaksharNo ratings yet
- Vision DX Code - Crosswalk For ICDDocument1 pageVision DX Code - Crosswalk For ICDFaisal AhammedNo ratings yet
- Trisha Mae B. Somintac WEEK 4 Physics 2Document6 pagesTrisha Mae B. Somintac WEEK 4 Physics 2Darlene Dacanay DavidNo ratings yet
- Refractive ErrorsDocument7 pagesRefractive ErrorsJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- IS Case Study DisabilitiesDocument5 pagesIS Case Study DisabilitiesRuchiNo ratings yet
- Pinhole NDocument4 pagesPinhole NNizam MohamedNo ratings yet
- Nearsighted and Farsighted InformationsDocument6 pagesNearsighted and Farsighted InformationsPia LomagdongNo ratings yet
- Science Class 10 Sample PaperDocument12 pagesScience Class 10 Sample Papervishwath donepudiNo ratings yet
- On Light: Science Holiday Homework Made By-Aish Mishra Class-8 Diamond Roll No.-6Document9 pagesOn Light: Science Holiday Homework Made By-Aish Mishra Class-8 Diamond Roll No.-6Ansh MishraNo ratings yet
- Lenses and RefractionDocument140 pagesLenses and RefractionElla Julienne EralinoNo ratings yet
- 09 EmmetropizationDocument18 pages09 EmmetropizationMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- Adis Pasalic - Doktorat-EngDocument91 pagesAdis Pasalic - Doktorat-EngHariom ShuklaNo ratings yet
- HiperopiaDocument29 pagesHiperopiaJoice Sari TampubolonNo ratings yet
- LIGHT CLASS 8 Module CompleteDocument23 pagesLIGHT CLASS 8 Module CompleteAshish SundaNo ratings yet
- NCM IO3 Eye ExaminationDocument50 pagesNCM IO3 Eye ExaminationNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7 EMDocument13 pagesChapter-7 EMsrisatwikneyyalaNo ratings yet
- Lasik: Eyeglasses Contact LensesDocument3 pagesLasik: Eyeglasses Contact Lensesvandana singhNo ratings yet
- Hyper Metro PiaDocument2 pagesHyper Metro PiaNathan ManiamNo ratings yet
- Health6 q1 Mod1 Personalhealthissuesandconcern v1Document23 pagesHealth6 q1 Mod1 Personalhealthissuesandconcern v1Lhen YanzonNo ratings yet