Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guía Primer Parcial - Psychogerontology
Guía Primer Parcial - Psychogerontology
Uploaded by
Alejandro Sanchez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views4 pages1. The document discusses key terms related to aging such as life expectancy, longevity, and life cycle. It also covers various biological theories of aging including programmed senescence, endocrine, immunological, and free radicals theories.
2. Physical changes that occur with aging are discussed for various organs and systems like skin, bones, brain, and sexuality. Sensory and psychomotor functioning like hearing, vision, strength, and balance also diminish with age.
3. Cognitive functioning in older adults is examined including intelligence, problem solving, processing speeds, attention switching, memory, and wisdom. Various brain structures are also implicated in age-related cognitive changes.
Original Description:
Guía psicogerontologia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document discusses key terms related to aging such as life expectancy, longevity, and life cycle. It also covers various biological theories of aging including programmed senescence, endocrine, immunological, and free radicals theories.
2. Physical changes that occur with aging are discussed for various organs and systems like skin, bones, brain, and sexuality. Sensory and psychomotor functioning like hearing, vision, strength, and balance also diminish with age.
3. Cognitive functioning in older adults is examined including intelligence, problem solving, processing speeds, attention switching, memory, and wisdom. Various brain structures are also implicated in age-related cognitive changes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views4 pagesGuía Primer Parcial - Psychogerontology
Guía Primer Parcial - Psychogerontology
Uploaded by
Alejandro Sanchez1. The document discusses key terms related to aging such as life expectancy, longevity, and life cycle. It also covers various biological theories of aging including programmed senescence, endocrine, immunological, and free radicals theories.
2. Physical changes that occur with aging are discussed for various organs and systems like skin, bones, brain, and sexuality. Sensory and psychomotor functioning like hearing, vision, strength, and balance also diminish with age.
3. Cognitive functioning in older adults is examined including intelligence, problem solving, processing speeds, attention switching, memory, and wisdom. Various brain structures are also implicated in age-related cognitive changes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
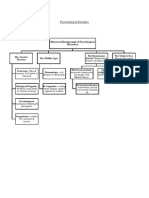
GUÍA PRIMER PARCIAL Basic terms
• Life expectancy: stadistic, statistical probable time on
PSYCHOGERANTOLOGY organism can live according to age and other circumstances
• Longevity: descriptive and observable, life durability, life
expectancy in based on this term
UNIT 1: Psychical functioning on older adults • Life circle: longest period the members of a specie can live
Professional and occupational cycle Changes during senescence’s
• After their 65 years old they like their jobs, it’s not stressful Biological aging theories
• More product than younger ones
Generic programming
• Work that requires precision, at constant rhythm and Programmed senescence theory:
theories genes
mature judgement
Retirement Endocrine theory: hormones
Immunological theory: failures
• First stablished in many industrial countries, end of lath
century and beginning of the 20th Evolutionary theory: reproduce
• Obligatory retirement at 65 years old Variable rate theories Wear theory: wear out (desgaste)
• Obligatory retirement declared illegal in some countries
Free radicals’ theory: accumulated
Gender damage
Life rate theory: metabolism
• Men: “honeymoon”, then continues retirement (+metabolismo-mueres)
• Women: retirement with a lesser influence, mood affected
Autoimmune theory: attack itself
• In both, self-control was the key to predict their mood = specific conditions (cancer)
Styles Pshysical changes
• Focus on family lifestyle: daily activities | non cognitive Skin • Wrinkles
• Balance investment: there are balance between work, • Moles
family and… • Liver spots
• UV rays
• Serious recreation: they learn cognitive activities
Organic systemic • Chronical stress
(recreation, carpentry
• Depress the immune functioning
• Voluntary work: activities that bring personal satisfaction
• Which makes elder
• People susceptible to infections
Height and bones • Kyphosis • Chronic insomnia (not good)
• Osteoporosis • Depression or drugs (med drugs)
Brian • Decrease on the capacity to inhibit • Easily wake up
irrelevant or non-wanted thoughts
• Gets smalls Sexuality later life
• Cognitive functions decrease Men • Keep any active sexual expression 70-80
• Main thing a higher sexual activity than
Social and cognitive consequences due to brain changes women
• More time have erection y ejaculate
• Cognitive functions decreases: decrease on the capacity to Women • Have psychical ability all life
inhibit or non-wanted thoughts • Excitation signals are less intense (ex:
• The amygdala shows a lesser response towards negative breast engorgement)
events, but not towards positive (las respuestas hacia lo Important factor: good sexual functioning = continuous sexual
negative se polarizan) activity
Sensory and psychomotor functioning UNIT 2: Cognitive functioning in older adults
• Hearing: hearing loss Intelligence
• Vision:
Classic aging patter / Weschler Scale
o More light required
o Problems to perceive depth and color • Decrease of performance scale– new information
o Accidents as consequences • Maintain of verbal scale– same information
o Cataracts and muscular degeneration
Seattle’s study
o Glaucoma
Strength, resistance, balance, and reaction time • Perceptual speed declines
• The long they live, the most decline of performance
• Usually, adults lose from 10% to 20% of their strength at 70 • Variation among individuals
years old • Training helps
• Resistance also diminishes among women
• The strength and muscle power decrease because is a result Primary mental • perceptual speed
of natural aging activity decrease and illness habilities • inductive reasoning
• space orientation
Sleep • number / calculation
• fluency
• Sleep and dream less • verbal meaning
• Deep sleep hours restricted
Problem solving • Semantic: a lesser deterioration after 60´s, general
knowledge
• Efficient / flexible way
• Procedural: relatively little affected, steps
• Age differences reduced
• Solving problems: don’t diminish, there had been progress Brian structures
at them
• Quality has a modest relation with tases performance not
with age
Changes on processing capacities
• Processing speed – first to deteriorate
• Switch attention – tends to become slower
• Knowledge and ingrained habits – better performance
• Training – increase speed to process information Wisdom
Cognitive capacities and mortality • Jung and Erickson talked about as end of personal growth
• Has been studs as cognitive ability
• Implies insight and paradoxical awareness of reality
Reaction
IQ • Paul Baltes and Cols: research
time
Categories wisdoms • Life context in social changes
as expert knowledge • Life uncertainties
• Study 15 points below = 75% die before 70´s • Factual (pragmatism)
• Reaction Time = proves efficiency at information processing • Procedural
• Relativism on ethical valves and life
Memory
Short term memory • Meaning of life and human condition
• Sensory memory (+): it remains, what it captures now • Levels od knowledge, reason and advice
• Working memory (-): más difícil acomodar nueva • Associated with depth and balance (concrete situations)
información • Combines mind and virtue (character)
Wellness: personal / humanity
Long term memory • Not easy to get, but to recognitive
• Episodic: highest probability of deterioration, original
memory
Unit 3: psychosocial functioning in older people
Integrity of self us hopelessness
8th stage
• Integrity
• Acceptance
• Wisdom
• No regress
• Hopelessness inevitable
Paternity
• Bonds with keep strongers
• Differences between traditional and Scandinavian European
countries
• Bond between mother and daughter tends to be really close
• Offspring provide help
• Some elder parents continue with economical help and
worry very much if their offsprings have a mental or physical
illness
• Senior people that had to take care of children feel pressure
Grandchildren
• Satisfying (comrade)
• Pamper the grandchildren
Friends
• Healthier
• Happier
• Hanlie change
• Intimacy
• Fun and pleasure
• Immediate
• Joyful pressure
You might also like
- Leadership Academy - AnthonyRobbinsDocument1 pageLeadership Academy - AnthonyRobbinsBordeanu Alina86% (22)
- Transactional-Analysis-Case PresentationDocument23 pagesTransactional-Analysis-Case PresentationKrizzia Louise B. Cabrera100% (1)
- Basic 2 Work in Team EnvironmentDocument38 pagesBasic 2 Work in Team EnvironmentCarole Amorado GomezNo ratings yet
- Zerzan - Age of GriefDocument4 pagesZerzan - Age of GriefNicolas JuarezNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior 12 2016Document15 pagesHuman Behavior 12 2016aalijahabbasNo ratings yet
- Geria Prelims 1Document4 pagesGeria Prelims 1kurtsalvadorbsnNo ratings yet
- 3 4 Rle Care of Older PersonDocument6 pages3 4 Rle Care of Older Personjjmaxh20No ratings yet
- Reaserch MethodsDocument16 pagesReaserch Methodsapi-716949398No ratings yet
- Module 4 Rev For RecitDocument5 pagesModule 4 Rev For RecitAdrian PrinceNo ratings yet
- 04.psychiatry SamplesDocument50 pages04.psychiatry SamplesCherinet KibruNo ratings yet
- Abnormal PsychologyDocument4 pagesAbnormal PsychologySazia BegumNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Introduction of Abnormal PsychologyPDF - 240220 - 220006Document24 pagesLecture 1-Introduction of Abnormal PsychologyPDF - 240220 - 220006hui xin ngNo ratings yet
- Exercicios para o CérebroDocument60 pagesExercicios para o CérebroMarco Aurélio de MeloNo ratings yet
- Individualistic Theories of CrimeDocument1 pageIndividualistic Theories of Crimemah1kh4tunNo ratings yet
- Ek Nai Subha V2.0: Aga Khan Health Board of IndiaDocument16 pagesEk Nai Subha V2.0: Aga Khan Health Board of IndiaMeenakshi ananthkrishnanNo ratings yet
- AdultHip AbstractsDocument60 pagesAdultHip AbstractsJafild Fild riverNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document78 pagesLecture 2Sema HazemNo ratings yet
- PSY 1204 Chapter 1. Notes AY. 2022 2023Document3 pagesPSY 1204 Chapter 1. Notes AY. 2022 2023drownpour.hc25No ratings yet
- New Views of Mind/Brain Aging: Darlene V. Howard, PH.DDocument39 pagesNew Views of Mind/Brain Aging: Darlene V. Howard, PH.DNational Press FoundationNo ratings yet
- Psychology Chapter 1Document6 pagesPsychology Chapter 1Charmander LynNo ratings yet
- chp13 Psychological DisordersDocument83 pageschp13 Psychological DisordersMichelleNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Disease and DisordersDocument28 pagesMental Health Disease and DisordersCharleson OtubuNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Models of PsychopathologyDocument5 pagesTheoretical Models of PsychopathologyAnshika ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Psych DisordersDocument44 pagesPsych DisordersKhadeeja hannaNo ratings yet
- ( ) 2 ., - (2022.09.14)Document68 pages( ) 2 ., - (2022.09.14)QubricNo ratings yet
- Abnormal PsychologyDocument5 pagesAbnormal PsychologyShyNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorders Overview Depression: Psychology 311 Abnormal PsychologyDocument4 pagesMood Disorders Overview Depression: Psychology 311 Abnormal PsychologyPat PiamphongsantNo ratings yet
- Geriatric NursingDocument3 pagesGeriatric NursingggukNo ratings yet
- Part 3 - Mental Illness - Psychological Health and WellbeingDocument24 pagesPart 3 - Mental Illness - Psychological Health and Wellbeingapi-642709499No ratings yet
- Disorders and ModelsDocument7 pagesDisorders and ModelsVasvi VermaNo ratings yet
- Psy 301 Itp All LecturesDocument17 pagesPsy 301 Itp All LecturesJANICAH JOY REYESNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To PsychologyDocument34 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To PsychologySheniqua GreavesNo ratings yet
- PERSONALITYDocument4 pagesPERSONALITYJustine BayabosNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 ReviewerDocument12 pagesNCM 114 ReviewerEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Theories of Aging: Akshata Hinge Akshata AradhyeDocument15 pagesTheories of Aging: Akshata Hinge Akshata AradhyeAditi ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- EmotionDocument42 pagesEmotiondemet ulkuNo ratings yet
- Cluster BDocument132 pagesCluster BShella Thea WibawaNo ratings yet
- Deviance and Social ControlDocument22 pagesDeviance and Social ControlJui ProvidoNo ratings yet
- HomeopathyDocument46 pagesHomeopathyamitjain2892100% (3)
- Medical Treatment of Persistent Post Concussive Symptoms - Kuemmerle Neuro Boston Childrens Hospital HarvardDocument27 pagesMedical Treatment of Persistent Post Concussive Symptoms - Kuemmerle Neuro Boston Childrens Hospital HarvardRexDavidGidoNo ratings yet
- Theories of Personality Prelim ReviewerDocument8 pagesTheories of Personality Prelim ReviewerKiana De UngriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Evolution of Psychology1Document33 pagesChapter 1 - Evolution of Psychology1Hoàng Ngọc PhúcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PRT 2Document9 pagesChapter 5 PRT 2nayaddouaihyNo ratings yet
- EmotionsDocument58 pagesEmotionsthivyaashini SellaNo ratings yet
- The Middle and Old AgeDocument38 pagesThe Middle and Old Agenkivc100% (2)
- Clinical Psych Summary QsDocument6 pagesClinical Psych Summary Qssathmijayasinghe2007No ratings yet
- CH4 PsychoanalysisDocument16 pagesCH4 PsychoanalysisCarlos Del GiudiceNo ratings yet
- BPY1033 Theories of Counseling: Week 2: Psychoanalytic TherapyDocument28 pagesBPY1033 Theories of Counseling: Week 2: Psychoanalytic TherapynayanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Body RythymsDocument13 pagesChapter 5 Body RythymsHaider EjazNo ratings yet
- Psychodynamic Approach.Document65 pagesPsychodynamic Approach.bevorsiNo ratings yet
- PsychoanalysisDocument70 pagesPsychoanalysisaz.rah.e.khudiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To PsychologyDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To PsychologyassmmNo ratings yet
- FUNDADocument33 pagesFUNDALea Mee CastroverdeNo ratings yet
- Top Reviewer 1ST SemDocument4 pagesTop Reviewer 1ST SemFlorie Mae GutezaNo ratings yet
- 1 Looking at AbnormalityDocument27 pages1 Looking at AbnormalityShara Valleser100% (1)
- S207 LP01 Week3 NotesDocument50 pagesS207 LP01 Week3 NoteseloithatNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Clinical PsychologyDocument89 pagesWeek 5 - Clinical PsychologyDora SimunovicNo ratings yet
- PSY1011 - Psychological Disorders LectureDocument61 pagesPSY1011 - Psychological Disorders LectureeeNo ratings yet
- Untreated Trauma: The Signs, Sources, and Science: Video 2 WorksheetDocument5 pagesUntreated Trauma: The Signs, Sources, and Science: Video 2 Worksheethorses and stuffNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior 6 2016Document12 pagesHuman Behavior 6 2016Aazmeer RahmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Abnormal PsychologyDocument44 pagesUnit 1 Abnormal PsychologyMohammed SaniNo ratings yet
- Etiology - Psychopathology 2Document138 pagesEtiology - Psychopathology 2poojabarua219No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan PP and CsDocument36 pagesLesson Plan PP and CsMamta SinghNo ratings yet
- Implications of Personality DevelopmentDocument3 pagesImplications of Personality DevelopmentAlbert Chew0% (1)
- Therapy Blank Critical Appraisal WorksheetDocument3 pagesTherapy Blank Critical Appraisal WorksheetRebecca WongNo ratings yet
- PERDEV - Midterm 2019 2020 Answer Key 1Document5 pagesPERDEV - Midterm 2019 2020 Answer Key 1Margie SanduanNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis Topics in Psychology in IndiaDocument7 pagesPHD Thesis Topics in Psychology in Indialanasorrelstulsa100% (4)
- E4 - Inveja (Inglês)Document231 pagesE4 - Inveja (Inglês)foxc675No ratings yet
- The Effect of Emotion Regulation Strategies On AngerDocument6 pagesThe Effect of Emotion Regulation Strategies On AngerDavidLeucasNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Psychology in Modules 10th Edition David G MyersDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Psychology in Modules 10th Edition David G MyersElizabethMitchelliapn100% (47)
- Mygov 999999999915134583Document1 pageMygov 999999999915134583r61751543No ratings yet
- FT Geriatri - Balance On Elderly-1Document45 pagesFT Geriatri - Balance On Elderly-1Ncuhi DonggoNo ratings yet
- Family TherapyDocument34 pagesFamily TherapyJoan SinghNo ratings yet
- Lo Et Al 2017 The Effects of Family-Based MindfulnessDocument14 pagesLo Et Al 2017 The Effects of Family-Based MindfulnessDavid ZNo ratings yet
- Being Seen or Being Watched A Psychoanalytic Perspective On Body DysmorphiaDocument20 pagesBeing Seen or Being Watched A Psychoanalytic Perspective On Body DysmorphiaChloe VellaNo ratings yet
- PDHM I Module 1Document6 pagesPDHM I Module 1Kate Francine RebutazoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture Society and Politics Quarter 1Document11 pagesUnderstanding Culture Society and Politics Quarter 1Edrelle Borac100% (1)
- SCL Worksheet Week 11 Components of A Concluding Paragraph - Author's OpinionDocument5 pagesSCL Worksheet Week 11 Components of A Concluding Paragraph - Author's OpinionFARAH HIDAYAHNo ratings yet
- Final Capstone Reflection Journal EntryDocument4 pagesFinal Capstone Reflection Journal Entryapi-652926802No ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PSYCHOLOGY 9990/21Document12 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PSYCHOLOGY 9990/21Andy KoeNo ratings yet
- Teresa Pham Final Proposal OutlineDocument11 pagesTeresa Pham Final Proposal Outlineapi-642824502No ratings yet
- MODULE 7 Mental Health and Well Being in Middle and Late AdolescenceDocument33 pagesMODULE 7 Mental Health and Well Being in Middle and Late Adolescenceace fuentesNo ratings yet
- Karen Horney Abduls PDFDocument31 pagesKaren Horney Abduls PDFlala123No ratings yet
- MPOB-Unit 3 and Unit 4Document29 pagesMPOB-Unit 3 and Unit 4Vaibhav guptaNo ratings yet
- SPG Election: Hagbay Elementary SchoolDocument8 pagesSPG Election: Hagbay Elementary SchoolShalee Carpio BalanquitNo ratings yet
- Situation Reasons Effect Reaction AdviceDocument11 pagesSituation Reasons Effect Reaction AdviceMariel Samonte VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Rws 33Document4 pagesRws 33Chawie CjNo ratings yet
- The Work-Life Conflict and Satisfaction With LifeDocument9 pagesThe Work-Life Conflict and Satisfaction With LifeGabriela-Cristina MocanuNo ratings yet
- Section 4 The Ta 101 Introductory CourseDocument11 pagesSection 4 The Ta 101 Introductory CourseDubravka PešordaNo ratings yet