Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - UTI NCP - NCM 112 Lec
Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - UTI NCP - NCM 112 Lec
Uploaded by
Gen Paulo Estoya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - UTI NCP - NCM 112 Lec
Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - UTI NCP - NCM 112 Lec
Uploaded by
Gen Paulo EstoyaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
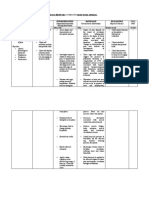
SAN PABLO COLLEGE
COLLEGE OF NURSING
NURSING CARE PLAN
Patient’s Name:
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired urinary elimination r/t frequent urination evidence by dysuria.
ASSESSMENT PLANNING/GOAL IMPLEMENTATION RATIONALE EVALUATION GOAL MET
Desired Outcome Independent/dependent Reason for the intervention Expected Outcome
Nursing intervention
Pertinent Data: Patient will: Nurse will: Why: Positive result Yes No
Subjective: • Client will achieve • Assess the patient’s • Can help determine • Patient achieved ✓
• Lower back pain normal urinary pattern of the factors that may normal urinary
• Dysuria elimination pattern, elimination. predispose the elimination pattern,
• Frequent urination as evidenced by patient to UTI and as evidenced by
• Urethral discharge absence sign of serves as a basis for absence sign of
(primarily in men) urinary disorders determining urinary disorders
(urgency, oliguria, appropriate (urgency, oliguria,
Objective: dysuria). interventions. dysuria).
• Fever / chills • Client will • Note the client’s age • UTI is more • Patient
• Foul-smelling urine demonstrate and gender. prevalent in women demonstrates
behavioral than in men at behavioral
techniques to younger ages, techniques to
prevent urinary although the gap prevent urinary
infection. narrows in later life. infection.
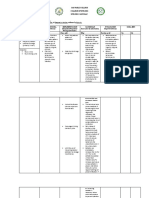
About one out of
every five women
will develop a UTI
during their lifetime.
Older adults are also
prone to developing
UTI caused by
incomplete bladder
emptying due to
structural
abnormalities and
decreased bladder
tone.
• Instruct the female • This technique helps
client to wipe from prevent bacteria in
front to back. the anal region from
spreading to the
vagina and,
ultimately, the
urethra. Proper
perineal care helps in
minimizing the risk of
contamination and
reinfection.
• Encourage drinking • Daily intake of
cranberry juice. cranberry juice
(about 8 to 10 oz)
helps prevent and
control symptoms of
UTI. It has been
shown to reduce
adherence of
bacteria to the
uroepithelial cells in
the urinary tract.
• Limit the use of • Catheter use
indwelling bladder dramatically
catheters to manage increases the risk for
incontinence. UTI. The risk for
catheter-associated
urinary tract
infection (CAUTI)
increases each day a
urinary catheter is
placed. Alternative
measures such as
regular toileting can
prevent infection. If
an indwelling
catheter is
necessary, follow
strict interventions
to prevent infection
and urosepsis.
If the client goal was not met, briefly describe why and what step would be taken next:
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Submitted by: Estoya, Gen Paulo C.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - Deep Vein Thrombosis NCP - NCM 112 LecDocument2 pagesEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - Deep Vein Thrombosis NCP - NCM 112 LecGen Paulo EstoyaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - UTI NCP - NCM 112 Lec PDFDocument3 pagesEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - UTI NCP - NCM 112 Lec PDFGen Paulo EstoyaNo ratings yet
- Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - HTN NCP - NCM 112 LecDocument2 pagesEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - HTN NCP - NCM 112 LecGen Paulo EstoyaNo ratings yet
- Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - Heart Failure NCP - NCM 112 LecDocument4 pagesEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - Heart Failure NCP - NCM 112 LecGen Paulo EstoyaNo ratings yet
- Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - BPH NCP - NCM 112 LecDocument3 pagesEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - BPH NCP - NCM 112 LecGen Paulo EstoyaNo ratings yet
- Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - Anemia NCP - NCM 112 LecDocument5 pagesEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - Anemia NCP - NCM 112 LecGen Paulo EstoyaNo ratings yet