Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L1 - Pangea, Oceans, Lines of Earth, GMT, IDL, ITZ, Solstice, Equinox
L1 - Pangea, Oceans, Lines of Earth, GMT, IDL, ITZ, Solstice, Equinox
Uploaded by
lizyl5ruoisze5dalida0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views45 pagesThe document discusses Pangea drift theory, which proposed that the Earth's continents were once joined together in a supercontinent called Pangea before drifting apart. It also describes the five major oceans - Arctic, Antarctic, Indian, Atlantic, and Pacific. Additionally, it provides information about lines of longitude and latitude that divide the globe, including the prime meridian, tropics, seasons, international date line, and time zones.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses Pangea drift theory, which proposed that the Earth's continents were once joined together in a supercontinent called Pangea before drifting apart. It also describes the five major oceans - Arctic, Antarctic, Indian, Atlantic, and Pacific. Additionally, it provides information about lines of longitude and latitude that divide the globe, including the prime meridian, tropics, seasons, international date line, and time zones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views45 pagesL1 - Pangea, Oceans, Lines of Earth, GMT, IDL, ITZ, Solstice, Equinox
L1 - Pangea, Oceans, Lines of Earth, GMT, IDL, ITZ, Solstice, Equinox
Uploaded by
lizyl5ruoisze5dalidaThe document discusses Pangea drift theory, which proposed that the Earth's continents were once joined together in a supercontinent called Pangea before drifting apart. It also describes the five major oceans - Arctic, Antarctic, Indian, Atlantic, and Pacific. Additionally, it provides information about lines of longitude and latitude that divide the globe, including the prime meridian, tropics, seasons, international date line, and time zones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 45
• Pangea Drift Theory
• Oceans of the world
• Lines of Globe
•The theory was proposed by geophysicist and meteorologist
Alfred Wegener in 1912
•Continental drift was a revolutionary theory explaining that
continents shift position on Earth's surface
•Earth’s continents were once part of an enormous, single
landmass called Pangea
•Idea of continental drift were based on several lines of evidence:
fit of continent, paleoclimate indicators, truncated geologic
features, and fossils
• Arctic Ocean
• Antarctic / Southern Ocean
• Indian Ocean
• Atlantic Ocean
• Pacific Ocean
•Smallest of the world’s oceans, centering
approximately on the North Pole.
•Earth's northernmost body of water.
•It encircles the Arctic, and flows beneath it. Most
of the Arctic Ocean is covered by ice throughout
the year—although that is starting to change as
temperatures climb.
• The word “Arctic” comes from the Greek word
“Arktikos”, meaning “near the Bear”.
• Covers approximately one-sixteenth of Earth’s total
ocean area.
• Has a crucial impact on Earth’s climate.
• It pulls in waters from the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian
Oceans, helping drive a global circulation system
known as the conveyor belt, which transports heat
around the planet.
• Cold, dense water that sinks to the ocean floor off
Antarctica also helps store carbon in the deep ocean.
• Was named Southern Ocean because of its current.
• Covers approximately one-fifth of the total
ocean area of the world.
• Forty per cent of the world’s offshore oil
production takes place in the Indian Ocean
basin.
• Named after the country India
• Covers approximately one-fifth of Earth’s surface
• Separate the continents of Europe and Africa to the
east from those of North and South America to the
west.
• The ocean’s name, derived from Greek mythology,
means the “Sea of Atlas.”
• It is second in size to the Pacific Ocean.
• 60° S parallel in the south to the Arctic in the north
and lying between the continents of Asia and
Australia on the west and North America and South
America on the east.
• Largest, occupying about one-third of the surface of
the globe.
• Mariana Trench—also the greatest depth found in
any ocean.
• Called “Pacifico” by Ferdinand Magellan which
means “peaceful”.
• Meridians
• Parallel
• Longitude
• Latitude
• The prime meridian is the line of 0° longitude,
the starting point for measuring distance both
east and west around Earth.
• The 0° longitude that passes through Greenwich,
near London is considered a standard, and all
the time of all other zones are calculated
accordingly.
The Tropic of Cancer was named because at
the time of its naming, the sun was
positioned in the Cancer constellation
during the June solstice. Likewise, the Tropic
of Capricorn was named because the sun
was in the constellation Capricorn during the
December solstice.
• GMT
• International Date Line
• Seasons of Solstice and Equinox
• International Time Zones
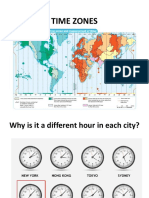
What is GMT?
What is GMT?
The "Greenwich Mean Time"
refers to the time zone at the zero
degree of longitude that runs
through the London suburb of
Greenwich and takes its name from
it. It is also called the zero meridian.
Every 15° longitude represents one
hour's difference in time: (24 x 15 =
360, the degrees of a circle).
International Date Line
The International Date Line (IDL)
is an imaginary line on Earth's surface defining the boundary
between one day and the next.
The International Date Line is the boundary where each
calendar day starts and is also known as the
“Line of Demarcation” because it separates
two calendar dates:
When you cross the date line traveling east, you subtract a day,
and if you cross the line traveling west, you add a day.
International Time Zones
We have 24 different time zones in the world. Because
the Earth rotates 360° every 24 hours, each time zone
is 15° longitude apart from the other. (360÷24=15)
Gaining and losing time
When you move to the right, you gain time.
In other words, for every time zone that you move towards
the right, you add one hour.
But when you head toward the left, you lose an hour.
Why Are Some Time Zone Lines Not Straight?
Time zone lines are not always straight in order to accommodate the
desires of nations within the boundaries of the zone.
The irregularity is mainly due to political factors and has nothing to
do with geography or any other natural cause.
Many countries in South America deflect time zone lines around their
boundaries so that the entire nation is within the same time zone.
Some nations not only deflect the lines around their borders but ignore any
lines passing within their borders entirely.
For example, China, which is about as wide as the continental United States,
only has one time zone. Countries to the north and south of China follow the
regular 15-degree-wide time zone lines, with some deflection.
Top five countries with most
number of time zones:
• France - 12
• United States of America - 11
• Russia - 11
• United Kingdom - 9
• Australia - 8
You might also like
- Starfinder AP #37 - Fly Free or Die - Part 4 of 6 - The White Glove Affair - Interactive Maps (PZO7237)Document3 pagesStarfinder AP #37 - Fly Free or Die - Part 4 of 6 - The White Glove Affair - Interactive Maps (PZO7237)Olivier Renaud0% (1)
- Nga - Sig.0012 2.0.0 UtmupsDocument86 pagesNga - Sig.0012 2.0.0 UtmupsMohammad Ibna AnwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2Vasundhara SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Lec.3-Globe & Geologic TimeDocument27 pagesLec.3-Globe & Geologic TimeSaira IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Imaginary Lines Narrative ReportDocument3 pagesImaginary Lines Narrative ReportRolly Jan AntivoNo ratings yet
- 2 Principles of Geography and Basic TermsDocument25 pages2 Principles of Geography and Basic TermsJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Latitudes and LongitudesDocument13 pagesLatitudes and LongitudesLovekiran KaurNo ratings yet
- Globe Latitudes and LongitudesDocument20 pagesGlobe Latitudes and LongitudesKalai Selvi MohanNo ratings yet
- World Geography Sumit Sir EnglishDocument63 pagesWorld Geography Sumit Sir EnglishRavindra Rajput100% (1)
- Basic Geography: The Globe and Its FeaturesDocument7 pagesBasic Geography: The Globe and Its FeaturesJerel John Calanao100% (1)
- Climatology 1 LatLongDocument14 pagesClimatology 1 LatLongVikram DasNo ratings yet
- The Earth and The Universe IIDocument35 pagesThe Earth and The Universe IIlucia.benito.sanz12No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Globe Latitudes and Longitudes WatermarkDocument15 pagesChapter 2 Globe Latitudes and Longitudes WatermarkVarsha SharmaNo ratings yet
- THE IDL NotesDocument3 pagesTHE IDL Notesgraff9752No ratings yet
- T G 1653646560 Time Zones Powerpoint Ver 1Document8 pagesT G 1653646560 Time Zones Powerpoint Ver 1Malvika BalchandaniNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Environment: Fourth QuarterDocument25 pagesThe Philippine Environment: Fourth Quartercjoy omaoengNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument17 pagesGeographyGracia OmariNo ratings yet
- EnvironmentalDocument4 pagesEnvironmentalSirupyEwe GamerNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial Navigation Module 1Document17 pagesTerrestrial Navigation Module 1subashrincy5No ratings yet
- Earth Geometry.Document69 pagesEarth Geometry.Kennedy Mwenya75% (4)
- There Are Many Imaginary Lines That Go Around The Earth One Way or AnotherDocument2 pagesThere Are Many Imaginary Lines That Go Around The Earth One Way or AnotherShahzad ImamNo ratings yet
- World Geography - Time & Climate Zones - Latitude, Longitude, Tropics, Meridian and More | Geography for Kids | 5th Grade Social StudiesFrom EverandWorld Geography - Time & Climate Zones - Latitude, Longitude, Tropics, Meridian and More | Geography for Kids | 5th Grade Social StudiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Time ZoneDocument16 pagesTime ZoneJobins KjNo ratings yet
- Different Lines On MapDocument25 pagesDifferent Lines On MapJohn Lord LillesNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Science: Jhune Dominique P. Galang VII-James Mrs. Riza Fontelera Science TeacherDocument2 pagesAssignment in Science: Jhune Dominique P. Galang VII-James Mrs. Riza Fontelera Science TeacherJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Geographic Gird Latitudes and Longitudes Question and AnswersDocument3 pagesGeographic Gird Latitudes and Longitudes Question and AnswersAll GamerNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bokaro Steel City Class - 6 Sub: GeographyDocument8 pagesDelhi Public School Bokaro Steel City Class - 6 Sub: GeographyPriyanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- What Are Time Zones?: by Cindy GriggDocument4 pagesWhat Are Time Zones?: by Cindy GriggArias LinaNo ratings yet
- Latitudes and Longitudes: Geography UPSCDocument9 pagesLatitudes and Longitudes: Geography UPSCSoumen DharNo ratings yet
- Geog Ch. 1 SummaryDocument7 pagesGeog Ch. 1 SummaryScion McKinleyNo ratings yet
- Latitude and LongitudeDocument18 pagesLatitude and Longitudemelgazar tanjayNo ratings yet
- Geography and GlobeDocument2 pagesGeography and GlobeJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Geography Revision: Siyamthanda DhladhlaDocument11 pagesGeography Revision: Siyamthanda Dhladhladhladhlasiyamthanda99No ratings yet
- Parallels and MeridiansDocument25 pagesParallels and MeridiansRIA SEKHRINo ratings yet
- Review Notes 3 1Document6 pagesReview Notes 3 1Johnner BelaongNo ratings yet
- Earth – Basics ,Latitudes and LongitudesDocument42 pagesEarth – Basics ,Latitudes and Longitudesishanime77No ratings yet
- Latitude and LongitudeDocument25 pagesLatitude and Longitudeshalini singhNo ratings yet
- Time CalculationDocument9 pagesTime CalculationmothusiamosselloNo ratings yet
- Legacy College of Compostela Dagohoy ST., Pob. Compostela, Davao de Oro Province Modified CourseworkDocument8 pagesLegacy College of Compostela Dagohoy ST., Pob. Compostela, Davao de Oro Province Modified CourseworkMerlita BoyoseNo ratings yet
- Prelim Notes For Tour 2aDocument46 pagesPrelim Notes For Tour 2aNette de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Latitude Lines: Important Parallels of Latitudes IncludeDocument6 pagesLatitude Lines: Important Parallels of Latitudes Includetriyambakyadav04No ratings yet
- Latitudes and Longitudes Geography Notes For UPSCDocument2 pagesLatitudes and Longitudes Geography Notes For UPSCBhupender GhosliyaNo ratings yet
- Latitudes and Longitudes Geography Notes For UPSCDocument2 pagesLatitudes and Longitudes Geography Notes For UPSCSuvashreePradhan100% (1)
- Lecture 6 Geodesy and Coordinate SystemsDocument20 pagesLecture 6 Geodesy and Coordinate SystemskhakhamasetiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 GlobeDocument26 pagesLesson 4 Globevonangel.doradoNo ratings yet
- Globe: A Planet's Meridian Adopted As The Zero of LongitudeDocument2 pagesGlobe: A Planet's Meridian Adopted As The Zero of LongitudeMark Jess HuabNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Geography Module 02Document12 pagesClass 9 Geography Module 02sanjaikumarmishra24No ratings yet
- Class 6-10th Geography Ncert Concise SummaryDocument175 pagesClass 6-10th Geography Ncert Concise Summaryfocac81660No ratings yet
- Longnitude LatitudeDocument6 pagesLongnitude Latitudemohanr786No ratings yet
- Meridian (Geography)Document5 pagesMeridian (Geography)Dimitrios Christos SarvanisNo ratings yet
- 101 Lec03Document53 pages101 Lec03yasiv29532No ratings yet
- Ga Power Capsule For Geography For Defence Exams 2018-19Document18 pagesGa Power Capsule For Geography For Defence Exams 2018-19Ahmad Zia AliNo ratings yet
- GeografiaDocument24 pagesGeografiathaislipsNo ratings yet
- Imaginery Lines On EarthDocument1 pageImaginery Lines On Earthveerbc2020No ratings yet
- What Are Longitudes and LatitudesDocument2 pagesWhat Are Longitudes and LatitudesClaudene GellaNo ratings yet
- Latitudes and Longitudes PDFDocument8 pagesLatitudes and Longitudes PDFvivan874164No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Geography Notes Chapter 2 - Globe Latitudes and LongitudesDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 6 Geography Notes Chapter 2 - Globe Latitudes and Longitudesdhivya sankarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Planet EarthDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Planet EarthamsterdamjaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument4 pagesDocumentShubham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ographic Grid-Latitudes & Longitudes PDFDocument36 pagesOgraphic Grid-Latitudes & Longitudes PDFAadya Singh100% (1)
- Different Parts of The GlobeDocument3 pagesDifferent Parts of The GlobeCharina Morales33% (6)
- Geography 1 - Maps, Globes & Atlases | Maps for Kids - Latitudes, Longitudes & Tropics | 4th Grade Children's Science Education booksFrom EverandGeography 1 - Maps, Globes & Atlases | Maps for Kids - Latitudes, Longitudes & Tropics | 4th Grade Children's Science Education booksNo ratings yet
- Revisiting The Guidelines in Assessment of LearningDocument31 pagesRevisiting The Guidelines in Assessment of Learninglizyl5ruoisze5dalidaNo ratings yet
- Constructing Traditional Forms of AssessmentDocument40 pagesConstructing Traditional Forms of Assessmentlizyl5ruoisze5dalidaNo ratings yet
- Proposed General Guidelines in Designing or Revisiting Syllabi in The New NormalDocument9 pagesProposed General Guidelines in Designing or Revisiting Syllabi in The New Normallizyl5ruoisze5dalidaNo ratings yet
- Revisiting The Guidelines in Reviewing SyllabiDocument17 pagesRevisiting The Guidelines in Reviewing Syllabilizyl5ruoisze5dalidaNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Sharing Session - 07132022 - AVIS ToolDocument25 pagesKnowledge Sharing Session - 07132022 - AVIS ToolJigar KotadiyaNo ratings yet
- TSSR Zsmg-2529 Kandidat A Gajah DemakDocument12 pagesTSSR Zsmg-2529 Kandidat A Gajah DemakBambang Ritno SNo ratings yet
- ACP 32 Volume 1 - Map ReadingDocument66 pagesACP 32 Volume 1 - Map Readingcockybundoo100% (1)
- Comparing Types of Maps WorksheetDocument4 pagesComparing Types of Maps WorksheetRahab ParkNo ratings yet
- Latitude / Longitude To VOR Conversion Greg Clark 8/31/2004Document4 pagesLatitude / Longitude To VOR Conversion Greg Clark 8/31/2004Rose AriantiNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of PoolvilleDocument1 pageTopographic Map of PoolvilleHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- DAO 2007-29 by Engr. Broddett B. AbatayoDocument21 pagesDAO 2007-29 by Engr. Broddett B. AbatayoBroddett Bello AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Student World Atlas Malestrom PDFDocument115 pagesStudent World Atlas Malestrom PDFMeisterKurosawa100% (1)
- Topographic Map of Pearsall NorthDocument1 pageTopographic Map of Pearsall NorthHistoricalMaps100% (1)
- Mapa Catastral Dass-10-12-2019Document1 pageMapa Catastral Dass-10-12-2019Carlos Manuel Xar Simón ManoloNo ratings yet
- Surveying 3Document2 pagesSurveying 3Sam MorettiNo ratings yet
- Jessie Kasynski Resume 2010Document1 pageJessie Kasynski Resume 2010travelmanNo ratings yet
- Buy Flat Earth MapDocument5 pagesBuy Flat Earth MapBrian Hara0% (1)
- 2.1 General Navigation 143 Vol 2Document143 pages2.1 General Navigation 143 Vol 2Salman Siddiqui67% (3)
- Different Parts of The GlobeDocument3 pagesDifferent Parts of The GlobeCharina Morales33% (6)
- Ref: SP 8-032 Map Reading and Land NavigationDocument29 pagesRef: SP 8-032 Map Reading and Land NavigationJovie Masongsong50% (2)
- Modern ChartworkDocument207 pagesModern ChartworkBisrat100% (2)
- Grids and CoordinatesDocument27 pagesGrids and Coordinatesapi-247725573No ratings yet
- New General Mathematics For Secondary Schools 3 TG Chapter 7Document2 pagesNew General Mathematics For Secondary Schools 3 TG Chapter 7Adeniyi100% (1)
- Design Theory For Web MapsDocument18 pagesDesign Theory For Web MapsJazib ImranNo ratings yet
- B Task 2nd AssignmentDocument6 pagesB Task 2nd Assignmentomezing purplingNo ratings yet
- Peta Topografi: Desa Citatah Kecamatan Cipatat Kabupaten Bandung Barat Provinsi Jawa BaratDocument1 pagePeta Topografi: Desa Citatah Kecamatan Cipatat Kabupaten Bandung Barat Provinsi Jawa BaratAli TamrinNo ratings yet
- STM Blast NotificationDocument1 pageSTM Blast NotificationMiftakhul UlumuddinNo ratings yet
- LatitudesDocument10 pagesLatitudesMITALI PARIRANo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of Spring BranchDocument1 pageTopographic Map of Spring BranchHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Introduction To Geospatial Technologies 2nd EditionDocument4 pagesTest Bank For Introduction To Geospatial Technologies 2nd Editionvineryfinesse0yn7e4No ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document93 pagesLecture 1Art CaubaNo ratings yet
- Stardust and Secrets A Short Talk About Maps and Their UsesDocument4 pagesStardust and Secrets A Short Talk About Maps and Their Usesamandes00No ratings yet