Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet 1 Electricity Class X
Worksheet 1 Electricity Class X
Uploaded by
farhaan akhtarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet 1 Electricity Class X
Worksheet 1 Electricity Class X
Uploaded by
farhaan akhtarCopyright:
Available Formats
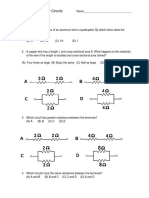
WORKSHEET (ELECTRICITY) CLASS X
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (1 Mark)
1. Define S.I. unit of :
(a) Electric current
(b) Potential difference
(c) Resistance
(d) Electric power
(e) Electrical energy consumed
2. Define the term resistivity.
3. Device used for measuring the current is……………. .
4. Name the element of filament of a bulb.
5. Write two types of resistors combination.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (2 Marks)
6. How the voltmeter and ammeter are connected in a circuit ?
7. Why the filament of bulb has high melting point ?
8. How does fuse wire protect electrical appliances ?
9. Find the number of joules in 1 KWh.
10. Find a relationship between P, I and V.
11. On what factors does resistance of a conductor depend ?
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (3 Marks)
12. State Ohm’s law. Derive relation between I, V and R. Draw the graph between V and I.
13. What is Joule’s heating effect of current P ? Derive its expression.
14. What would be new resistance if length of conductor is doubled and thickness is halved ?
15. Which is the better way to connect lights and other appliances in domestic wiring and why ?
16. Explain the Joule’s law of heating. How and on what factors does the heat produced in a conductor depends ?
17. On what factors, the resistance of a conductor depends ? Give the mathematical expression. Give the SI unit of
resistivity.
18. Find the effective resistance between A and B.
19. CASE STUDY
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v)
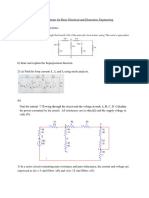
An electric lamp is a device that produces visible light from electric current. It is the most common form of artificial
lighting and is essential to modern society. An electric lamp of resistance 20 Ω and a conductor of resistance 4 Ω are
connected to a 6 V battery as shown in the circuit.
(i) Find the total resistance of the circuit.
(a) 20 Ω (b) 4 Ω (c) 24 Ω (d) 12 Ω
(ii) Find the current through the circuit, is
(a) 0.25 A (b) 0.50 A (c) 1 A (d) 4 A
(iii) Find the potential difference across the electric lamp.
(a) 5 V (b) 10 V (c) 15 V (d) 20 V
(iv) Find the potential difference across conductor.
(a) 0 V (b) 0.25 V (c) 0.5 V (d) 1 V
(v) Calculate power of the lamp.
(a) 2.0 W (b) 1.25 W (c) 0.25 W (d) 6.25 W
You might also like
- 9852 1694 01 Operator's Instructions ROC F7Document160 pages9852 1694 01 Operator's Instructions ROC F7eko sunaryo100% (7)
- 9 Electricity Test - CircuitsDocument5 pages9 Electricity Test - CircuitsRahmonGreen100% (1)
- Electrochem Tutorial SolutionsDocument30 pagesElectrochem Tutorial SolutionsDarren LimNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design Estimation and Costing Unit 2Document10 pagesElectrical Design Estimation and Costing Unit 2srinimeha@gmail.com100% (2)
- X ScienceDocument7 pagesX ScienceSanghamitra ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Physics 3204 Unit 2 Current Electricity - Worksheet 4 Ohms Law 2016-2017Document4 pagesPhysics 3204 Unit 2 Current Electricity - Worksheet 4 Ohms Law 2016-2017ASLAM HANIEFNo ratings yet
- 10th Phys Current ElectrDocument2 pages10th Phys Current ElectrMaryam CHNo ratings yet
- ResistanceDocument16 pagesResistanceDanelNo ratings yet
- Achyuta Public School Electricity-Segment-1 Electric CurrentDocument6 pagesAchyuta Public School Electricity-Segment-1 Electric Currentavp sNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 Class X ElectricityDocument2 pagesWorksheet 2 Class X Electricityfarhaan akhtarNo ratings yet
- Current and Circuits Practice ProblemsDocument15 pagesCurrent and Circuits Practice ProblemsAnthony HuiNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis - I Year ECE - Question BankDocument20 pagesCircuit Analysis - I Year ECE - Question BankPandyselvi Balasubramanian100% (1)
- Physics 40 Marks ch1Document3 pagesPhysics 40 Marks ch1Sanjay NayakNo ratings yet
- Revision Assignment Class 10 PhysicsDocument12 pagesRevision Assignment Class 10 PhysicsKayNo ratings yet
- 2022-23. 12 FinalDocument5 pages2022-23. 12 FinalSrushti ChouguleNo ratings yet
- CH 20Document12 pagesCH 20Sarah Blake100% (3)
- Electricity and Magnetism - QueDocument18 pagesElectricity and Magnetism - QueTxv RushNo ratings yet
- Worksheet X PhysicsDocument31 pagesWorksheet X PhysicsGuru PrasannaNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument2 pagesElectricityyashasviupadhyay19No ratings yet
- 10th ElectricityDocument2 pages10th ElectricityBalmukund KumarNo ratings yet
- CH - 12 - Electricity - Assignment - 2021-22Document3 pagesCH - 12 - Electricity - Assignment - 2021-22Yash DawaniNo ratings yet
- Electricity Book QuestionsDocument6 pagesElectricity Book QuestionsshellyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Krishna School of Emerging Technology and Applied Research (KSET)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank: Krishna School of Emerging Technology and Applied Research (KSET)Vraj PatelNo ratings yet
- Question Bank BeeDocument25 pagesQuestion Bank Beedhruv goraiNo ratings yet
- Ee2i Fee 22212 Ut-1 030323Document4 pagesEe2i Fee 22212 Ut-1 030323ABHI THORATNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 13 FullDocument2 pagesPhysics Chapter 13 FullAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Current ElectricityDocument11 pagesAssignment - Current ElectricityPresident ObamaNo ratings yet
- L36-Worksheet-Resistance, Power, Energy, Voltage EtcDocument6 pagesL36-Worksheet-Resistance, Power, Energy, Voltage EtcjahangirNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity Important Questions 2022-23Document37 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity Important Questions 2022-23Rohan SenapathiNo ratings yet
- Class - 10 - LN - 12 - Class TestDocument8 pagesClass - 10 - LN - 12 - Class TestSrivatsan BalajiNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument8 pagesSample QuestionsSong BrokerNo ratings yet
- ResistanceDocument21 pagesResistanceJustin DawsonNo ratings yet
- Science X Case Study Question 35Document7 pagesScience X Case Study Question 35SHAMBHU DUTTANo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5-Current of ElectricityDocument4 pagesTutorial 5-Current of ElectricityBriana PalmerNo ratings yet
- Resistance: Leaving Cert Physics Long Questions 2018 - 2002Document19 pagesResistance: Leaving Cert Physics Long Questions 2018 - 2002Oheneba Kwadjo Afari DebraNo ratings yet
- Physics For X - CbseDocument9 pagesPhysics For X - Cbsearshad_bahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ElectricityDocument7 pagesTutorial ElectricityKoko Nur IzzatiNo ratings yet
- X - Worksheet 1Document1 pageX - Worksheet 1fs450503333No ratings yet
- X Physics Segment 2 Q-BankDocument7 pagesX Physics Segment 2 Q-Bankavp sNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Electric Circuits: NameDocument7 pagesChapter 19 Electric Circuits: NameTimothy KurbyNo ratings yet
- Chap 12 13 14 15 16 BDocument4 pagesChap 12 13 14 15 16 ByounascheemaNo ratings yet
- Electric Current Circuits Practice ProblemsDocument14 pagesElectric Current Circuits Practice ProblemsSrihith MarakaNo ratings yet
- Easter End of Term 2023 ELE Exam G10Document3 pagesEaster End of Term 2023 ELE Exam G10Shivshankar ChaitramNo ratings yet
- ch11 Sci Practice SheetDocument6 pagesch11 Sci Practice SheetMeetNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- 2019 ME Sample Question PhyDocument4 pages2019 ME Sample Question PhyScorpio AvengerNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Physics .Electricity - Test PaperDocument1 pageClass 10 Physics .Electricity - Test Paperuma100% (1)
- 10th CBSe - CURRENT ELECTRICITY QUESTIONSDocument7 pages10th CBSe - CURRENT ELECTRICITY QUESTIONSmanojboaNo ratings yet
- Series and ParallelDocument7 pagesSeries and ParallelSuryaveer bhatiNo ratings yet
- NUMERICAL - Electricity & Its Effects For (Class X)Document6 pagesNUMERICAL - Electricity & Its Effects For (Class X)Gayathiri SureshNo ratings yet
- Electricity QuestionsDocument11 pagesElectricity QuestionsYuresh YNo ratings yet
- Elec Question Bank EditedDocument125 pagesElec Question Bank EditedWorku BekeleNo ratings yet
- Cbse 10 Electricity Question BankDocument16 pagesCbse 10 Electricity Question BankgpfphysicsNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Degree S1, S2 (S, FE) Examination May 2021 (2015 Scheme)Document3 pagesB.Tech Degree S1, S2 (S, FE) Examination May 2021 (2015 Scheme)Nigil ThomasNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Practice Sheet - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024Document6 pagesElectricity - Practice Sheet - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024jyotikushwahasmart0222No ratings yet
- Worksheet (2) On Current ElectricityDocument7 pagesWorksheet (2) On Current ElectricitySrijit SahaNo ratings yet
- Electricity AssignmentDocument4 pagesElectricity AssignmentAjit Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- 10th Phy T5Document1 page10th Phy T5Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet Class 12Document6 pagesRevision Worksheet Class 12prakyathNo ratings yet
- 658d3a7629127800189fb388 - ## - Electricity - Practice SheetDocument6 pages658d3a7629127800189fb388 - ## - Electricity - Practice SheetGaurav SarohaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Account Paper 1Document23 pagesAccount Paper 1farhaan akhtarNo ratings yet
- Based On Understanding of The E-Lectures-Cum - PPTS, Video Links and Other E - Resources Shared With You, Answer The Following QuestionsDocument2 pagesBased On Understanding of The E-Lectures-Cum - PPTS, Video Links and Other E - Resources Shared With You, Answer The Following Questionsfarhaan akhtarNo ratings yet
- Bases of AccountingDocument5 pagesBases of Accountingfarhaan akhtarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class XDocument2 pagesWorksheet 2 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class Xfarhaan akhtarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Magnetic Effects of Current Class XDocument1 pageWorksheet Magnetic Effects of Current Class Xfarhaan akhtarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 Class X ElectricityDocument2 pagesWorksheet 2 Class X Electricityfarhaan akhtarNo ratings yet
- Xii PB PheDocument1 pageXii PB Phefarhaan akhtarNo ratings yet
- Xii - BDocument2 pagesXii - Bfarhaan akhtarNo ratings yet
- C6.4 Engine Timing CalibrationsDocument4 pagesC6.4 Engine Timing CalibrationsKopyuk Kopyuk Kopyuk KopyukNo ratings yet
- Thermo-Fluid Lab Jimma University JitDocument88 pagesThermo-Fluid Lab Jimma University JitBeki Teka100% (2)
- PowaR Snap ClipsDocument2 pagesPowaR Snap ClipsHiteshChauhanNo ratings yet
- Wärtsilä 32 Engine ManualDocument490 pagesWärtsilä 32 Engine ManualLio Messi100% (1)
- ID (A:40) Descr (A:40 Val (A:40)Document54 pagesID (A:40) Descr (A:40 Val (A:40)shepyNo ratings yet
- Petrophysical Measurements From Drill Cuttings: An Added Value For The Reservoir Characterization ProcessDocument6 pagesPetrophysical Measurements From Drill Cuttings: An Added Value For The Reservoir Characterization ProcessMujtabaNo ratings yet
- Say Bolt ViscometerDocument3 pagesSay Bolt Viscometerghambira75% (4)
- MV Switchgear IEC 62271-200Document14 pagesMV Switchgear IEC 62271-200andhrimnir100% (1)
- Practical Intrinsic Safety For Engineers and TechniciansDocument5 pagesPractical Intrinsic Safety For Engineers and TechniciansFathi MusaNo ratings yet
- Kestrel Static MixersDocument3 pagesKestrel Static MixersGozuengineer GozuNo ratings yet
- DRIESCHER Motordrive UMPlus eDocument4 pagesDRIESCHER Motordrive UMPlus eAbdellah abdouNo ratings yet
- Optics Review AnswersDocument5 pagesOptics Review Answersben0706No ratings yet
- 38LF CatalogDocument2 pages38LF Catalognok.naingooNo ratings yet
- EHS EnglishDocument12 pagesEHS Englishgeraldine.18074No ratings yet
- Amino Acid MetabolismDocument7 pagesAmino Acid MetabolismROHITNo ratings yet
- 1200 Macro ExamplesDocument21 pages1200 Macro ExamplessheetalnathNo ratings yet
- Unforgettable Moment EssayDocument7 pagesUnforgettable Moment Essayafhbfqccp100% (2)
- Ncert Solution Cbse Class 10 Sci Chap 12Document18 pagesNcert Solution Cbse Class 10 Sci Chap 12Kingston JebaraldNo ratings yet
- Abb Rex521 ProteçãoDocument260 pagesAbb Rex521 ProteçãobrunotomeNo ratings yet
- 6035 205 Sample QuestionsDocument3 pages6035 205 Sample QuestionsDavid DaveyNo ratings yet
- Venturi Rev 10Document8 pagesVenturi Rev 10delcololalunaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Names and Formulas of Ionic CompoundsDocument5 pages3.2 Names and Formulas of Ionic CompoundsKen WuNo ratings yet
- Gas Power Plants AlstomDocument28 pagesGas Power Plants AlstomNo Pi100% (2)
- Solar RadiationDocument11 pagesSolar RadiationImaz IswandariNo ratings yet
- Noise Reduction in Gas Turbines Fact SheetDocument12 pagesNoise Reduction in Gas Turbines Fact SheetOM GOYALNo ratings yet
- Biogeometry Newsletter 7 Nov 2013Document3 pagesBiogeometry Newsletter 7 Nov 2013zbhabhaNo ratings yet
- Lec4 BFADocument39 pagesLec4 BFAORK BUNSOKRAKMUNYNo ratings yet