Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uts Midterm Reviewer
Uts Midterm Reviewer
Uploaded by
Lee TziCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Bjørn Bandlien - Strategies of Passion Love and Marriage in Old Norse Society - Brepols (2005) PDFDocument364 pagesBjørn Bandlien - Strategies of Passion Love and Marriage in Old Norse Society - Brepols (2005) PDFAli Kılıç100% (2)
- Budgeting and Spending Behaviors of AccountancyDocument9 pagesBudgeting and Spending Behaviors of AccountancyLyan0% (1)
- Deconstructing The Representations of Black Womanhood and White Female Sexuality in Contemporary Hip-Hop MusicDocument53 pagesDeconstructing The Representations of Black Womanhood and White Female Sexuality in Contemporary Hip-Hop Musicjulian_obubo5915No ratings yet
- Sexual and Material Self Reiewer UtsDocument3 pagesSexual and Material Self Reiewer UtsYanela YishaNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMUnderstanding The SelfDocument4 pagesMIDTERMUnderstanding The SelfAngelita CayabyabNo ratings yet
- SSP 111 ReviewerDocument3 pagesSSP 111 Reviewernaih marchessaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Lessons 4-5 Understanding The SelfDocument4 pagesReviewer Lessons 4-5 Understanding The SelfNikka VelascoNo ratings yet
- The Sexual Self - Sex and GenderDocument5 pagesThe Sexual Self - Sex and GenderKlo MonNo ratings yet
- Uts MidtermDocument7 pagesUts MidtermGewel Bardaje AmboyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Self ReviewerDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Self Reviewerblinknation08No ratings yet
- Chapter Ii-Unpacking The SelfDocument4 pagesChapter Ii-Unpacking The SelfMariz EreseNo ratings yet
- UTS MidtermDocument6 pagesUTS MidtermJustin Paul GallanoNo ratings yet
- F2F Synch Discussion NotesDocument7 pagesF2F Synch Discussion NotesmiatrishaponceNo ratings yet
- Procreation:: 1. Theory of EvolutionDocument3 pagesProcreation:: 1. Theory of EvolutionSophia RoseNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument5 pagesUnderstanding The Selfhazel.gutierrezNo ratings yet
- UTS Ulol Taena SyetDocument5 pagesUTS Ulol Taena SyetAnnyeongNo ratings yet
- Physical Self Self-Understanding Tips To Have A Good Physical Self ImageDocument12 pagesPhysical Self Self-Understanding Tips To Have A Good Physical Self ImageSamantha AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Gender and SocietyDocument11 pagesGender and SocietyJUDY ANN DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- Rev Uts MidtermsDocument2 pagesRev Uts MidtermsBhebz Erin MaeNo ratings yet
- Rev Uts Midterms.2Document3 pagesRev Uts Midterms.2Bhebz Erin MaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Human Sexuality: Biological Differences Expression of The SexDocument2 pagesChapter 4: Human Sexuality: Biological Differences Expression of The SexMacchi MagsNo ratings yet
- Gensoc Prelims To FinalsDocument27 pagesGensoc Prelims To FinalsTrexy NorialNo ratings yet
- Midterm UndsDocument5 pagesMidterm UndsAries GanotNo ratings yet
- Gned08 Lesson6-11Document17 pagesGned08 Lesson6-11Ragel RamosNo ratings yet
- Gender & SocietyDocument2 pagesGender & Society2078230No ratings yet
- Gender and Society 1,2,3Document7 pagesGender and Society 1,2,3Alysson CincoNo ratings yet
- GEC 2 Chapter 2 Lesson 1Document42 pagesGEC 2 Chapter 2 Lesson 1rodel d. brionesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer UtsDocument4 pagesReviewer UtsJannie LeilaNo ratings yet
- Cymon Uts ReviewerDocument5 pagesCymon Uts Reviewerdannahkayeamancio0No ratings yet
- 6-9 Uts ReviewerDocument11 pages6-9 Uts ReviewerAngeline VegaNo ratings yet
- Cmca Prelim TermDocument14 pagesCmca Prelim TermLj Marie GallaNo ratings yet
- Uts 2ND ExamDocument2 pagesUts 2ND ExamJunzen Ralph YapNo ratings yet
- Uts ReviewerDocument7 pagesUts Reviewerfritzcastillo026No ratings yet
- I. Eastern VS Western: Undself Reviewer: SemisDocument6 pagesI. Eastern VS Western: Undself Reviewer: Semislala gasNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument4 pagesUnderstanding The SelfIce IsidroNo ratings yet
- Gned 10-ReviewerDocument4 pagesGned 10-ReviewerTyrelNo ratings yet
- Man - Has Always Been A Fascinating Organism.: CharityDocument4 pagesMan - Has Always Been A Fascinating Organism.: CharityPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- UTS SexDocument21 pagesUTS Sexden mNo ratings yet
- Uts Midterms AdDocument12 pagesUts Midterms AdAngel DimapelisNo ratings yet
- The Physical Self: The Self As Impacted by The Body: Erik EriksonDocument4 pagesThe Physical Self: The Self As Impacted by The Body: Erik Eriksonsecret poNo ratings yet
- Understanding SelfDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Selfheatherhdez8No ratings yet
- Uts ReviewerDocument10 pagesUts ReviewerJUSTINE MARRA RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument42 pagesUnderstanding The SelfGlyza Marie Sederio ButronNo ratings yet
- Midterm UtsDocument3 pagesMidterm UtsLina ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Uts Unit Test IiDocument7 pagesReviewer Uts Unit Test IistupidbrowneyesNo ratings yet
- Midterms Reviewer For UtsDocument8 pagesMidterms Reviewer For UtsRieghn Rommel DagohoyNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument9 pagesEnergyJunry MingoNo ratings yet
- Ardsabiera: Forgot Password?Document16 pagesArdsabiera: Forgot Password?Xael XaelNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument8 pagesUnderstanding The SelfMelanie DadiosNo ratings yet
- Uts ReviewerDocument11 pagesUts ReviewertristhantangonanNo ratings yet
- Justine Mae Vergara P-104Document13 pagesJustine Mae Vergara P-104Gaile YabutNo ratings yet
- GENSOC ReviewerDocument3 pagesGENSOC ReviewerPatricia San GasparNo ratings yet
- GAS PrelimDocument8 pagesGAS PrelimJustin Paul GallanoNo ratings yet
- Gender, Sex and SexualityDocument22 pagesGender, Sex and SexualitySoorya SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- UndSelf ReviewerDocument7 pagesUndSelf ReviewerFranklinowen EscalaNo ratings yet
- Uts - FinalsDocument7 pagesUts - FinalsLEGASPI, Nefertiri Dominique N.No ratings yet
- Finals Reviewer STSDocument9 pagesFinals Reviewer STSJerle Mae ParondoNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument5 pagesREVIEWERRELADOR KATHLEENNo ratings yet
- S3 - Lesson 2Document2 pagesS3 - Lesson 2Joyle Ann BorrerosNo ratings yet
- Uts-Reviewwer MidtermDocument6 pagesUts-Reviewwer MidtermElvira MirajulNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesUnderstanding The Self Midterm ReviewerbiancaNo ratings yet
- UTS - Midterm Notes (Unit 2 - Lessons 1 To 4)Document13 pagesUTS - Midterm Notes (Unit 2 - Lessons 1 To 4)Dhon Aldrin CastroNo ratings yet
- Harding 1987Document18 pagesHarding 1987Alex SousaNo ratings yet
- Women Access To Justice PDFDocument163 pagesWomen Access To Justice PDFdogarsahabNo ratings yet
- J. Lorber - Believing Is Seeing - Biology As IdeologyDocument15 pagesJ. Lorber - Believing Is Seeing - Biology As IdeologyantonioNo ratings yet
- Lesson-3 4Document37 pagesLesson-3 4Kath MercadejasNo ratings yet
- SOGIE Bill: Gender Equality or Revenge of The LGBTDocument15 pagesSOGIE Bill: Gender Equality or Revenge of The LGBTDavid SanianaNo ratings yet
- 02-Gender Differences in Hong Kong Adolescent CONS GREEN PURCHS BEHAVIORDocument15 pages02-Gender Differences in Hong Kong Adolescent CONS GREEN PURCHS BEHAVIORkhoiruman muhammadNo ratings yet
- HRD 829 Course Outline 21Document4 pagesHRD 829 Course Outline 21Losh Min RyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Developmental Stages of LifeDocument31 pagesChapter 3 - Developmental Stages of LifeKean LeeNo ratings yet
- Op Ed Charlotte FoulonDocument2 pagesOp Ed Charlotte FoulonMOHAMMAD DATUGANNo ratings yet
- The Journey Back To Eden: Restoring The Creator's Design For Women and Men by Glen G. ScorgieDocument33 pagesThe Journey Back To Eden: Restoring The Creator's Design For Women and Men by Glen G. ScorgieZondervanNo ratings yet
- Writing Scope and Delimitation and Significance of The StudyDocument2 pagesWriting Scope and Delimitation and Significance of The StudyGian Nikolai Menia50% (2)
- Educ 112 - List of Topics For PresentationDocument2 pagesEduc 112 - List of Topics For PresentationKaichou Giselle LAng-ayNo ratings yet
- Gned10 L3Document3 pagesGned10 L3jovannadalaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument21 pagesUntitledapi-242071517No ratings yet
- Women Scientists ProjectDocument81 pagesWomen Scientists ProjectReema NegiNo ratings yet
- The Dialectic of SexDocument3 pagesThe Dialectic of SexdnegrutNo ratings yet
- CHI Chinese Culture and Language: College of Arts and SciencesDocument3 pagesCHI Chinese Culture and Language: College of Arts and SciencesHS ComputersNo ratings yet
- Love As Rebellion and ShameDocument7 pagesLove As Rebellion and ShameslipgunNo ratings yet
- Sutton. Law - Society - Origins, Interactions, and ChangeDocument322 pagesSutton. Law - Society - Origins, Interactions, and ChangeJuan Camilo Portela GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 100 Million Women Are Missing Amartya SenDocument15 pages100 Million Women Are Missing Amartya SenAdrPVNo ratings yet
- Claudia de Lima COsta - Equivocation, Translation, and Performative Interseccionality Notes On Decolonial Feminist Practices and Ethics in Latin America.Document27 pagesClaudia de Lima COsta - Equivocation, Translation, and Performative Interseccionality Notes On Decolonial Feminist Practices and Ethics in Latin America.Marcelo SpitznerNo ratings yet
- Fem PedagogyDocument13 pagesFem Pedagogyfem_com_pedNo ratings yet
- Baluan Nhs Gad Accoplishment Report 2022Document3 pagesBaluan Nhs Gad Accoplishment Report 2022Kim Hyun SunNo ratings yet
- The Status of Women in Indigenous African SocietiesDocument14 pagesThe Status of Women in Indigenous African SocietiesBatista.No ratings yet
- Subversive Beauty - Victorian Bodies of ExpressionDocument159 pagesSubversive Beauty - Victorian Bodies of ExpressionAswathy P JNo ratings yet
- Sociology Unit-Third Year: Semester-1 Course Duration: 45 HoursDocument4 pagesSociology Unit-Third Year: Semester-1 Course Duration: 45 HoursShiblyNo ratings yet
- Orange Knowledge Programme Country FocusDocument8 pagesOrange Knowledge Programme Country FocusJill DagreatNo ratings yet
Uts Midterm Reviewer
Uts Midterm Reviewer
Uploaded by
Lee TziOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Uts Midterm Reviewer
Uts Midterm Reviewer
Uploaded by
Lee TziCopyright:
Available Formats
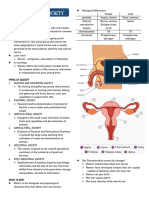
LESSON 1: WESTERN & EASTERN CULTURE
TOTAL SELF PHYSICAL SELF CARE
CONFUCIANISM – a code of ethical conduct of a. Academic Self - Good nutrition
how one should act according to their b. Non-Academic Self - Sufficient amount of recovery time
relationship with other people. - Social Self - Necessary exercise
SELF CULTIVATION – is seen as the ultimate - Emotional Self MENTAL SELF CARE – is a two-fold process
purpose of life - Physical Self EMOTIONAL SELF CARE
CHUN TZU – its characteristics is still embedded - All emotions are essentially energy in
in his or her social relationships. PHYSICAL SELF ESTEEM motion. (The Presence Process, Michael
SUBDUED SELF – personal needs are repressed - Sport Competence Brown)
for the good of many. - Attractive Body
TAOISM – living in the way of Tao or universe. - Physical Power LESSON 3: THE SEXUAL SELF
The ideal self is selflessness, but this is not - Physical Condition
forgetting about the self, it is living a Sexual Self – defined as an individual’s
balanced life with society and nature. SIGMUND FREUD – physical body is the core of evaluation of his or her own sexual feelings and
BUDDHISM – the self is seen as an illusion human experience actions.
NIRVANA – the highest state that someone can WILHELM REICH – the body is central to all Behavior – the way a person or thing acts or
attain dynamic psychological functioning reacts
ERIK ERIKSON – experience is firmly associated Sex – refers to the physical physiological
WESTERN: on the ground plan of the body differences between males and females
Individualistic ABRAHAN MASLOW – once the psychological - Defined by the reproductive organs
Straightforward needs are met, the person becomes dedicated to
Forceful in their communication and attaining the higher-order needs THREE SEX VARIATIONS:
decision-making Self-actualization - Male
Values equality Esteem - Female
Love and belonging - Intersex
EASTERN: Safety needs
Collective Psychological needs Male – a person with penis or male reproductive
organ
Looks after the welfare of their group
RELIGION - XY chromosomes
Values cooperation
Indian Tradition – appraised growth and - Produces high levels of testosterone
More compromising
enlightenment as the whole-body event Female – a person with vagina or female
Puts more emphasis on hierarchy reproductive organ
Buddhist Tradition – the body deserves love and
respect - XX chromosomes
LESSON 2: THE PHYSICAL SELF
- Releases high levels of estrogen Pansexual – attracted to multiple genders 4. Budget, budget, budget
Intersex – a person born with sexual anatomy or 5. Save in order to be safe
chromosomes that do not fit the traditional THREE ASPECTS TO DESCRIBE SEXUALITY: 6. Keep your spending habits in check
definition 1) Feelings/Fantasies 7. Increase income flow
Diamond (2002) – “Gender refers to social or 2) Behaviors 8. Good debt vs. bad debt
cultural roles played by male or female in the 3) Identity 9. Make your money grow
society.” 10. Protect the future
Gender Expression – describes how someone QUEER THEORY – a perspective that questions 11. Your greatest investment is still yourself
prefers to express his/her gender to the world the manner in which we have been taught to 12. Enjoy life no matter what.
think about sexual orientation.
THREE GENDER VARIATIONS: EVE KOSOFSKY SEDGWICK – even identical
- Cisgender genital acts mean very different things to people.
- Transgender
- Gender Fluid LESSON 4: THE MATERIAL SELF
Cisgender – a person identifying with the sex William James – one of the first to value things
assigned at birth - The self is the totality of everything
Transgender – gender identity does not match Jean-Paul Sartre & Russel Berk – theorized how
the sex assigned at birth objects become extensions of ourselves or our
Gender Fluid – refers to a person whose gender identities
identity is not fixed
THREE WAYS WE CONNECT W/ OBJECTS:
SEXUALITY – part of a person expressed 1. Controlling an object
through sexual activities & relationships 2. Connection with an object
Sexual Identity – how a person chooses to 3. Knowing about something
describe or label his/her sexuality
Heterosexual – a person who is attracted Materialism – belief of a person on the
to the opposite sex. importance of material objects to the happiness
Homosexual – attracted to people of the or success
same sex
Bisexual – attracted to both male and IDEAS ON MANAGING RESOURCES
female 1. Keep your perspective in check
Asexual – they never desire sex but in a 2. Have money, do not just pretend
romantic relationship 3. Have your own goal, take your time
You might also like
- Bjørn Bandlien - Strategies of Passion Love and Marriage in Old Norse Society - Brepols (2005) PDFDocument364 pagesBjørn Bandlien - Strategies of Passion Love and Marriage in Old Norse Society - Brepols (2005) PDFAli Kılıç100% (2)
- Budgeting and Spending Behaviors of AccountancyDocument9 pagesBudgeting and Spending Behaviors of AccountancyLyan0% (1)
- Deconstructing The Representations of Black Womanhood and White Female Sexuality in Contemporary Hip-Hop MusicDocument53 pagesDeconstructing The Representations of Black Womanhood and White Female Sexuality in Contemporary Hip-Hop Musicjulian_obubo5915No ratings yet
- Sexual and Material Self Reiewer UtsDocument3 pagesSexual and Material Self Reiewer UtsYanela YishaNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMUnderstanding The SelfDocument4 pagesMIDTERMUnderstanding The SelfAngelita CayabyabNo ratings yet
- SSP 111 ReviewerDocument3 pagesSSP 111 Reviewernaih marchessaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Lessons 4-5 Understanding The SelfDocument4 pagesReviewer Lessons 4-5 Understanding The SelfNikka VelascoNo ratings yet
- The Sexual Self - Sex and GenderDocument5 pagesThe Sexual Self - Sex and GenderKlo MonNo ratings yet
- Uts MidtermDocument7 pagesUts MidtermGewel Bardaje AmboyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Self ReviewerDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Self Reviewerblinknation08No ratings yet
- Chapter Ii-Unpacking The SelfDocument4 pagesChapter Ii-Unpacking The SelfMariz EreseNo ratings yet
- UTS MidtermDocument6 pagesUTS MidtermJustin Paul GallanoNo ratings yet
- F2F Synch Discussion NotesDocument7 pagesF2F Synch Discussion NotesmiatrishaponceNo ratings yet
- Procreation:: 1. Theory of EvolutionDocument3 pagesProcreation:: 1. Theory of EvolutionSophia RoseNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument5 pagesUnderstanding The Selfhazel.gutierrezNo ratings yet
- UTS Ulol Taena SyetDocument5 pagesUTS Ulol Taena SyetAnnyeongNo ratings yet
- Physical Self Self-Understanding Tips To Have A Good Physical Self ImageDocument12 pagesPhysical Self Self-Understanding Tips To Have A Good Physical Self ImageSamantha AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Gender and SocietyDocument11 pagesGender and SocietyJUDY ANN DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- Rev Uts MidtermsDocument2 pagesRev Uts MidtermsBhebz Erin MaeNo ratings yet
- Rev Uts Midterms.2Document3 pagesRev Uts Midterms.2Bhebz Erin MaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Human Sexuality: Biological Differences Expression of The SexDocument2 pagesChapter 4: Human Sexuality: Biological Differences Expression of The SexMacchi MagsNo ratings yet
- Gensoc Prelims To FinalsDocument27 pagesGensoc Prelims To FinalsTrexy NorialNo ratings yet
- Midterm UndsDocument5 pagesMidterm UndsAries GanotNo ratings yet
- Gned08 Lesson6-11Document17 pagesGned08 Lesson6-11Ragel RamosNo ratings yet
- Gender & SocietyDocument2 pagesGender & Society2078230No ratings yet
- Gender and Society 1,2,3Document7 pagesGender and Society 1,2,3Alysson CincoNo ratings yet
- GEC 2 Chapter 2 Lesson 1Document42 pagesGEC 2 Chapter 2 Lesson 1rodel d. brionesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer UtsDocument4 pagesReviewer UtsJannie LeilaNo ratings yet
- Cymon Uts ReviewerDocument5 pagesCymon Uts Reviewerdannahkayeamancio0No ratings yet
- 6-9 Uts ReviewerDocument11 pages6-9 Uts ReviewerAngeline VegaNo ratings yet
- Cmca Prelim TermDocument14 pagesCmca Prelim TermLj Marie GallaNo ratings yet
- Uts 2ND ExamDocument2 pagesUts 2ND ExamJunzen Ralph YapNo ratings yet
- Uts ReviewerDocument7 pagesUts Reviewerfritzcastillo026No ratings yet
- I. Eastern VS Western: Undself Reviewer: SemisDocument6 pagesI. Eastern VS Western: Undself Reviewer: Semislala gasNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument4 pagesUnderstanding The SelfIce IsidroNo ratings yet
- Gned 10-ReviewerDocument4 pagesGned 10-ReviewerTyrelNo ratings yet
- Man - Has Always Been A Fascinating Organism.: CharityDocument4 pagesMan - Has Always Been A Fascinating Organism.: CharityPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- UTS SexDocument21 pagesUTS Sexden mNo ratings yet
- Uts Midterms AdDocument12 pagesUts Midterms AdAngel DimapelisNo ratings yet
- The Physical Self: The Self As Impacted by The Body: Erik EriksonDocument4 pagesThe Physical Self: The Self As Impacted by The Body: Erik Eriksonsecret poNo ratings yet
- Understanding SelfDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Selfheatherhdez8No ratings yet
- Uts ReviewerDocument10 pagesUts ReviewerJUSTINE MARRA RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument42 pagesUnderstanding The SelfGlyza Marie Sederio ButronNo ratings yet
- Midterm UtsDocument3 pagesMidterm UtsLina ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Uts Unit Test IiDocument7 pagesReviewer Uts Unit Test IistupidbrowneyesNo ratings yet
- Midterms Reviewer For UtsDocument8 pagesMidterms Reviewer For UtsRieghn Rommel DagohoyNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument9 pagesEnergyJunry MingoNo ratings yet
- Ardsabiera: Forgot Password?Document16 pagesArdsabiera: Forgot Password?Xael XaelNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument8 pagesUnderstanding The SelfMelanie DadiosNo ratings yet
- Uts ReviewerDocument11 pagesUts ReviewertristhantangonanNo ratings yet
- Justine Mae Vergara P-104Document13 pagesJustine Mae Vergara P-104Gaile YabutNo ratings yet
- GENSOC ReviewerDocument3 pagesGENSOC ReviewerPatricia San GasparNo ratings yet
- GAS PrelimDocument8 pagesGAS PrelimJustin Paul GallanoNo ratings yet
- Gender, Sex and SexualityDocument22 pagesGender, Sex and SexualitySoorya SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- UndSelf ReviewerDocument7 pagesUndSelf ReviewerFranklinowen EscalaNo ratings yet
- Uts - FinalsDocument7 pagesUts - FinalsLEGASPI, Nefertiri Dominique N.No ratings yet
- Finals Reviewer STSDocument9 pagesFinals Reviewer STSJerle Mae ParondoNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument5 pagesREVIEWERRELADOR KATHLEENNo ratings yet
- S3 - Lesson 2Document2 pagesS3 - Lesson 2Joyle Ann BorrerosNo ratings yet
- Uts-Reviewwer MidtermDocument6 pagesUts-Reviewwer MidtermElvira MirajulNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesUnderstanding The Self Midterm ReviewerbiancaNo ratings yet
- UTS - Midterm Notes (Unit 2 - Lessons 1 To 4)Document13 pagesUTS - Midterm Notes (Unit 2 - Lessons 1 To 4)Dhon Aldrin CastroNo ratings yet
- Harding 1987Document18 pagesHarding 1987Alex SousaNo ratings yet
- Women Access To Justice PDFDocument163 pagesWomen Access To Justice PDFdogarsahabNo ratings yet
- J. Lorber - Believing Is Seeing - Biology As IdeologyDocument15 pagesJ. Lorber - Believing Is Seeing - Biology As IdeologyantonioNo ratings yet
- Lesson-3 4Document37 pagesLesson-3 4Kath MercadejasNo ratings yet
- SOGIE Bill: Gender Equality or Revenge of The LGBTDocument15 pagesSOGIE Bill: Gender Equality or Revenge of The LGBTDavid SanianaNo ratings yet
- 02-Gender Differences in Hong Kong Adolescent CONS GREEN PURCHS BEHAVIORDocument15 pages02-Gender Differences in Hong Kong Adolescent CONS GREEN PURCHS BEHAVIORkhoiruman muhammadNo ratings yet
- HRD 829 Course Outline 21Document4 pagesHRD 829 Course Outline 21Losh Min RyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Developmental Stages of LifeDocument31 pagesChapter 3 - Developmental Stages of LifeKean LeeNo ratings yet
- Op Ed Charlotte FoulonDocument2 pagesOp Ed Charlotte FoulonMOHAMMAD DATUGANNo ratings yet
- The Journey Back To Eden: Restoring The Creator's Design For Women and Men by Glen G. ScorgieDocument33 pagesThe Journey Back To Eden: Restoring The Creator's Design For Women and Men by Glen G. ScorgieZondervanNo ratings yet
- Writing Scope and Delimitation and Significance of The StudyDocument2 pagesWriting Scope and Delimitation and Significance of The StudyGian Nikolai Menia50% (2)
- Educ 112 - List of Topics For PresentationDocument2 pagesEduc 112 - List of Topics For PresentationKaichou Giselle LAng-ayNo ratings yet
- Gned10 L3Document3 pagesGned10 L3jovannadalaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument21 pagesUntitledapi-242071517No ratings yet
- Women Scientists ProjectDocument81 pagesWomen Scientists ProjectReema NegiNo ratings yet
- The Dialectic of SexDocument3 pagesThe Dialectic of SexdnegrutNo ratings yet
- CHI Chinese Culture and Language: College of Arts and SciencesDocument3 pagesCHI Chinese Culture and Language: College of Arts and SciencesHS ComputersNo ratings yet
- Love As Rebellion and ShameDocument7 pagesLove As Rebellion and ShameslipgunNo ratings yet
- Sutton. Law - Society - Origins, Interactions, and ChangeDocument322 pagesSutton. Law - Society - Origins, Interactions, and ChangeJuan Camilo Portela GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 100 Million Women Are Missing Amartya SenDocument15 pages100 Million Women Are Missing Amartya SenAdrPVNo ratings yet
- Claudia de Lima COsta - Equivocation, Translation, and Performative Interseccionality Notes On Decolonial Feminist Practices and Ethics in Latin America.Document27 pagesClaudia de Lima COsta - Equivocation, Translation, and Performative Interseccionality Notes On Decolonial Feminist Practices and Ethics in Latin America.Marcelo SpitznerNo ratings yet
- Fem PedagogyDocument13 pagesFem Pedagogyfem_com_pedNo ratings yet
- Baluan Nhs Gad Accoplishment Report 2022Document3 pagesBaluan Nhs Gad Accoplishment Report 2022Kim Hyun SunNo ratings yet
- The Status of Women in Indigenous African SocietiesDocument14 pagesThe Status of Women in Indigenous African SocietiesBatista.No ratings yet
- Subversive Beauty - Victorian Bodies of ExpressionDocument159 pagesSubversive Beauty - Victorian Bodies of ExpressionAswathy P JNo ratings yet
- Sociology Unit-Third Year: Semester-1 Course Duration: 45 HoursDocument4 pagesSociology Unit-Third Year: Semester-1 Course Duration: 45 HoursShiblyNo ratings yet
- Orange Knowledge Programme Country FocusDocument8 pagesOrange Knowledge Programme Country FocusJill DagreatNo ratings yet